Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
O by
by  inelastic neutron scattering and their reactivity with ethylene
inelastic neutron scattering and their reactivity with ethyleneYamazoe, Seiji*; Yamamoto, Akira*; Hosokawa, Saburo*; Fukuda, Ryoichi*; Hara, Kenji*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Kamazawa, Kazuya*; Tsukuda, Tatsuya*; Yoshida, Hisao*; Tanaka, Tsunehiro*
Catalysis Science & Technology, 11(1), p.116 - 123, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:21.89(Chemistry, Physical)Kunimaru, Takanori; Mikake, Shinichiro; Nishio, Kazuhisa; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; Hikima, Ryoichi; Tanno, Takeo; Sanada, Hiroyuki; et al.
JAEA-Review 2013-018, 169 Pages, 2013/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) at Tono Geoscience Center (TGC) is pursuing a geoscientific research and development project namely the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project in crystalline rock environment in order to construct scientific and technological basis for geological disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste (HLW). The MIU Project has three overlapping phases: Surface-based Investigation phase (Phase I), Construction phase (Phase II), and Operation phase (Phase III). The MIU Project has been ongoing the Phase II and the Phase III in 2011 fiscal year. This report shows the results of the investigation, construction and collaboration studies in fiscal year 2011, as a part of the Phase II and Phase III based on the MIU Master Plan updated in 2010.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sakaki, Hironao; Ogura, Koichi; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Tanimoto, Tsuyoshi; Kanasaki, Masato; Yogo, Akifumi; Hori, Toshihiko; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 19(3), p.030706_1 - 030706_4, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:24.31(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A 7 MeV proton beam collimated to 16 mrad containing more than 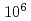 particles is experimentally demonstrated by focusing a 2J, 60 fs pulse of a Ti:sapphire laser onto targets of different materials and thicknesses placed in a millimeter scale conical holder. The electric potential induced on the target holder by laser-driven electrons accelerates and dynamically controls a portion of a divergent quasi-thermal proton beam originated from the target, producing a quasi-monoenergetic "pencil" beam.
particles is experimentally demonstrated by focusing a 2J, 60 fs pulse of a Ti:sapphire laser onto targets of different materials and thicknesses placed in a millimeter scale conical holder. The electric potential induced on the target holder by laser-driven electrons accelerates and dynamically controls a portion of a divergent quasi-thermal proton beam originated from the target, producing a quasi-monoenergetic "pencil" beam.
Sakanaka, Shogo*; Akemoto, Mitsuo*; Aoto, Tomohiro*; Arakawa, Dai*; Asaoka, Seiji*; Enomoto, Atsushi*; Fukuda, Shigeki*; Furukawa, Kazuro*; Furuya, Takaaki*; Haga, Kaiichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.2338 - 2340, 2010/05
Future synchrotron light source using a 5-GeV energy recovery linac (ERL) is under proposal by our Japanese collaboration team, and we are conducting R&D efforts for that. We are developing high-brightness DC photocathode guns, two types of cryomodules for both injector and main superconducting (SC) linacs, and 1.3 GHz high CW-power RF sources. We are also constructing the Compact ERL (cERL) for demonstrating the recirculation of low-emittance, high-current beams using above-mentioned critical technologies.
Fukuda, Seiji; Kondo, Hitoshi; Okubo, Toshiyuki
JNC TN9410 2004-010, 56 Pages, 2004/03
The Old Waste Treatment Facility of JOYO(0ld JWTF), operation of which stopped in 1995, is scheduled to be dismantled starting in 2010. In order to reduce worker's radiation exposure, it is necessary to reduce radiation dose rate of the main equipments by system chemical decontamination before dismantling. In thjs research, the decontamination solutions were selected in view of reduction of consequential waste amount and expense of treatment of decontamination waste. We evaluated decontamination factor (DF) in test with contaminated samples (Hot test). Moreover we performed a conceptual design of the decontamination system using the decontamination solution that obtained the highest DF in hot test. The solution selected in hot test did not achieve the target DF to all equipments. For some equipment more aggressive solutions, which dissolve contaminants and base metal, would be needed, however using these solutions would tend to increase consequential waste amount and expense of treatment of decontamination waste. Therefore, we evaluated the dissolution rate of these solutions for stainless steels in test with non-contaminated samples (Cold test). The main result of obtaining through the hot test and the cold test is shown below.(1)By alternating immersions in sodium hydroxide solution and nitric acid, the highest DF was obtained. (Maximum of DF=10.7, 80 deg-C). (2)The decontamination system is composed of two decontamination solution tanks, a washing water tank, a pump that supplies decontamination solutions and washing water, and filters for removing contaminants. (3)The test samples were immersed in various solutions (HN03 + HF, HCl, H2S04) for 24 hours at room temperature. As a result, it was confirmed that the dissolution rate of HN03 + HF is remarkably large compared with other solutions (7.43 micro-m/day).
Kondo, Hitoshi; Fukuda, Seiji; Okubo, Toshiyuki
JNC TN9410 2004-007, 48 Pages, 2004/03
When the plan of decommissioning such as nuclear fuel cycle facilities and small-scale research reactors is examined, It is necessary to select the technology and the process of the work procedure, and to optimize the index (such as the radiation dose, the cost, amount of the waste, the number of workers, and the term of works, etc.) concerning dismantling the facility. In our waste management section, Development of the decommissioning management system, which is called "DECMAN", for the support of making the decommissioning plan ls advanced. DECMAN automatically calculates the index by using the facility data and dismantling method. This paper describes the remodeling of program to the personal computer and the system verification by evaluation of real work (Dismantling of the liquor dissolver in the old Joyo Waste Treatment Facility (the old JWTF), the glove boxes in Deuterium Critical Assembly (DCA), and the incinerator in Waste Dismantling Facility (WDF)). The outline of remodeling and verification is as follows. (1)Additional function. 1)Equipment arrangement mapping, 2)Evaluation of the radiation dose by using the air dose rate, 3)I/O of data that uses EXCEL (software) (2)Comparison of work amount between calculation value and results value: The calculation value is 222.67 man-hour against the result value 249.40 man- hour in the old JWTF evaluation. (3)Forecast of accompanying work is predictable to multiply a certain coeffient by the calculation value. (4)A new idea that expected the amount of the work was constructed by using the calculation value of DECMAN.
Konno, Shotaro; Fukuda, Seiji; ; Hazama, Taira; ; Hashimoto, Makoto
JNC TN9410 2002-015, 59 Pages, 2002/10
Deuterium critical assembly (DCA) is a critical facility with 1 kW maximum thermal output reached its initial criticality in 1969. DCA operations were stopped on 26 September 2001, then it has been planed to submit a legal application for decommissioning of DCA to MEXT and to shift to decommissioning phase. In this work, we have evaluated the calculation value of neutron flux by comparison with an actual measurement in biological shield and the amount of contaminated radioactive materials etc. to make a document on estimation of the inventories and the wastes quantity etc. in the legal application. Results are as follows. (1)Fast, epithermal and thermal neutron flux calculated have exceeded the measurement data at almost all location. Therefore concentration of activated materials calculated by neutron flux calculation value is estimated higher than actual that. (2)The amount of radioactive materials that contaminated by nuclides other than tritium is estimated about 3.0
September 2001, then it has been planed to submit a legal application for decommissioning of DCA to MEXT and to shift to decommissioning phase. In this work, we have evaluated the calculation value of neutron flux by comparison with an actual measurement in biological shield and the amount of contaminated radioactive materials etc. to make a document on estimation of the inventories and the wastes quantity etc. in the legal application. Results are as follows. (1)Fast, epithermal and thermal neutron flux calculated have exceeded the measurement data at almost all location. Therefore concentration of activated materials calculated by neutron flux calculation value is estimated higher than actual that. (2)The amount of radioactive materials that contaminated by nuclides other than tritium is estimated about 3.0 10
10 Bq. The concentration of tritium-contaminated radioactive materials is estimated about 4.1
Bq. The concentration of tritium-contaminated radioactive materials is estimated about 4.1 10
10 Bq/g at the maximum in concrete, about 7.6
Bq/g at the maximum in concrete, about 7.6  10
10 Bq/g in the surface of aluminum plumbing. (3)Consequential waste quantity (solid waste) to radioactive waste generated in total process of dismantling is estimated about 30ton. As for Radioactive liquid waste quantity, moderator for specimen is estimated about 1.4m
Bq/g in the surface of aluminum plumbing. (3)Consequential waste quantity (solid waste) to radioactive waste generated in total process of dismantling is estimated about 30ton. As for Radioactive liquid waste quantity, moderator for specimen is estimated about 1.4m , consequential liquid wastes is estimated about 300m
, consequential liquid wastes is estimated about 300m . (4)The amount of Tritium generated in dismantling (radioactive gas waste) is estimated about 7.25
. (4)The amount of Tritium generated in dismantling (radioactive gas waste) is estimated about 7.25 10
10 Bq in dismantling of heavy water system facility, measurement control system facility and neutron reactor.
Bq in dismantling of heavy water system facility, measurement control system facility and neutron reactor.
Nakamura, Hiroo; Tsuji, Shunji; ; Ozeki, Takahisa; Ishida, Shinichi; Azumi, Masafumi; Akiba, Masato; Ando, Toshiro; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fukuda, Takeshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 30(2), p.235 - 250, 1990/02
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:52.09(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hiroo; Tsuji, Shunji; ; Ozeki, Takahisa; Ishida, Shinichi; Azumi, Masafumi; Akiba, Masato; Ando, Toshiro; Fujii, Tsuneyuki; Fukuda, Takeshi; et al.
JAERI-M 89-106, 52 Pages, 1989/08
no abstracts in English
 Pu Based on ICRP Publication 30
Pu Based on ICRP Publication 30Koizumi, Katsuzo; Ishiguro, Hideharu; Fukuda, Seiji
Hoken Butsuri, 16(1), p.51 - 59, 1981/00
Fukuda, Seiji; Kato, Jinzo; Onishi, Takeshi; Watanabe, Kozo; Okubo, Katsuichi; Ouchi, Masafusa; Isozaki, Hiroshi; Seki, Mamoru; Mito, Norio; Tsuruo, Akira; et al.
JAERI 1028, 55 Pages, 1962/10
no abstracts in English
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Sagisaka, Akito; Maeda, Shota; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Ogura, Koichi; Fukuda, Yuji; Matsukawa, Kenya*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Maeda, Shota; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Sakaki, Hironao; Sagisaka, Akito; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Ogura, Koichi; Fukuda, Yuji; Matsukawa, Kenya*; et al.
no journal, ,
In JAEA, the high energy ions generated by the interaction between Ultra-intense Ultra-Short pulse laser and thin-foil target is being studied. Irradiating condition must be optimized to generate higher energy ions while suppress the becoming gigantic of laser. It is necessary to know the physical phenomenon in plasma to determine the parameter to optimize from the information on the electron and neutron, X-rays, which are generated simultaneously with ion. In this study, in order to measure electron temperature accurately, an electron spectrometer was developed which have broad range (1-200 MeV). The detector is comprised of permanent magnets and a fluorescent plate, CCD camera. In the presentation, the result of the calibration experiment carried out using 4, 9, 12, 15 MeV quasi-monoenergetic electron beam in HIBMC will be reported. Moreover, response analysis method was inspected using PHITS which is particle transporting Monte Carlo simulation code, and will also report the result.
Sagisaka, Akito; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Ogura, Koichi; Sakaki, Hironao; Maeda, Shota; Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Yogo, Akifumi; et al.
no journal, ,
High-intensity laser and thin-foil interactions produce high-energy particles, hard X-ray, high-order harmonics, and terahertz radiation. A proton beam driven by a high-intensity laser has received attention as a compact ion source for medical and other applications. We have performed several high intensity laser-matter interaction experiments using a thin-foil target irradiated by Ti:sapphire laser (J-KAREN) at JAEA. The pulse duration was typically  40 fs (FWHM). The electron density profiles of the preformed plasma were observed with the interferometer. The high temporal contrast laser system could reduce the preformed plasma. The maximum proton energy gradually increased as the laser performance improved and finally protons of
40 fs (FWHM). The electron density profiles of the preformed plasma were observed with the interferometer. The high temporal contrast laser system could reduce the preformed plasma. The maximum proton energy gradually increased as the laser performance improved and finally protons of  40 MeV energy were observed at the peak laser intensity of
40 MeV energy were observed at the peak laser intensity of  1
1  10
10 W/cm
W/cm .
.
Sagisaka, Akito; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Ogura, Koichi; Sakaki, Hironao; Maeda, Shota; Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A. Y.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Kanasaki, Masato; et al.
no journal, ,
High-intensity laser and thin-foil interactions produce high-energy particles, hard X-ray, high-order harmonics, and terahertz radiation. A proton beam driven by a high-intensity laser has received attention as a compact ion source for medical and other applications. We have performed several high intensity laser-matter interaction experiments using a thin-foil target irradiated by Ti:sapphire laser (J-KAREN) at JAEA. The pulse duration was typically  40 fs (FWHM). The high-order harmonics (2nd
40 fs (FWHM). The high-order harmonics (2nd 4th) were observed with the spectrometer in the reflected direction. The maximum proton energy of
4th) were observed with the spectrometer in the reflected direction. The maximum proton energy of  40 MeV energy were observed at the peak laser intensity of
40 MeV energy were observed at the peak laser intensity of  1
1 10
10 W/cm
W/cm .
.
Sagisaka, Akito; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Ogura, Koichi; Sakaki, Hironao; Maeda, Shota*; Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Fukuda, Yuji; Kanasaki, Masato*; et al.
no journal, ,
High-intensity laser and thin-foil interactions produce high-energy particles, hard X-ray, high-order harmonics, and terahertz radiation. A proton beam driven by a high-intensity laser has received attention as a compact ion source for medical and other applications. We have performed several high intensity laser-matter interaction experiments using a thin-foil target irradiated by Ti:sapphire laser (J-KAREN) at JAEA. The pulse duration was typically  40 fs (FWHM). The high-order harmonics (2nd
40 fs (FWHM). The high-order harmonics (2nd  4th) were observed with the spectrometer in the reflected direction. The maximum proton energy of
4th) were observed with the spectrometer in the reflected direction. The maximum proton energy of  40 MeV energy were observed at the peak laser intensity of
40 MeV energy were observed at the peak laser intensity of  1
1 10
10 W/cm
W/cm .
.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sakaki, Hironao; Ogura, Koichi; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Tanimoto, Tsuyoshi; Yogo, Akifumi; Hori, Toshihiko; Sagisaka, Akito; Fukuda, Yuji; et al.
no journal, ,
We have successfully accelerate quasi-mono-energetic collimated 7MeV proton beam bt the interaction between the 2J 60fs Ti Sappire laser pulses with the thin-foil target on the target holder with conical cavity. The focusing and energy selection is by the E-field induced along the surface of the conical cavity by the point charge brought away by the escape electrons.
Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ogura, Koichi; Tanimoto, Tsuyoshi*; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sakaki, Hironao; Fukuda, Yuji; Kanasaki, Masato; Kando, Masaki; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Sagisaka, Akito*; et al.
no journal, ,
We present the extension of the maximum energy of protons from the interaction between the short-pulse compact laser system and solid thin-foil target. The laser pulses with parameters of 800 nm in wavelength, 40 fs of pulse width, 7 J of energy, 10 contrast are focused onto the target with the peak intensity of more than 10
contrast are focused onto the target with the peak intensity of more than 10 Wcm
Wcm , which is also well confirmed by the measured electron temperature of 16 MeV. We report about the acceleration mechanism as well as future prospect on the proton acceleration experiment at JAEA.
, which is also well confirmed by the measured electron temperature of 16 MeV. We report about the acceleration mechanism as well as future prospect on the proton acceleration experiment at JAEA.