Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
O
Yoshii, Kenji; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Hiroyuki; Kambe, Takashi*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Muraoka, Yuji*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Mori, Shigeo*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(6), p.063708_1 - 063708_4, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report the change of magnetic properties of multiferroic YbFe O
O , caused by cooling in the presence of an electrical current. The magnetization measured after the cooling becomes smaller by about 10-20% than that after cooling without a current. The current also affects the magnetic anisotropy below about 100 K; the magnetic coercivity is increased by about 10-20%. These phenomena may arise from a coexistence of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic domains, or a disturbance in the formation of charge-ordered domains. From the applied viewpoint, the enhancement of anisotropy by an electrical current offers a method for stabilizing magnetization other than the well-known method, i.e., exchange bias.
, caused by cooling in the presence of an electrical current. The magnetization measured after the cooling becomes smaller by about 10-20% than that after cooling without a current. The current also affects the magnetic anisotropy below about 100 K; the magnetic coercivity is increased by about 10-20%. These phenomena may arise from a coexistence of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic domains, or a disturbance in the formation of charge-ordered domains. From the applied viewpoint, the enhancement of anisotropy by an electrical current offers a method for stabilizing magnetization other than the well-known method, i.e., exchange bias.
 O
O
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Sakamoto, Yuma*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Noda, Yukio*; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
Physical Review B, 88(14), p.140403_1 - 140403_5, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:63.20(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) O
O (
( = Ho, Er)
= Ho, Er)Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Nishihata, Keisuke*; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Noda, Yukio*; Tokura, Yoshinori*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(17), p.2513 - 2516, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:24.63(Physics, Condensed Matter) O
O
Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Sakamoto, Yuma*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Noda, Yukio*; Abe, Nobuyuki*; Taniguchi, Koji*; Arima, Takahisa*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(7), p.077204_1 - 077204_4, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:86.26(Physics, Multidisciplinary) O
O
Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Noda, Yukio*; Kaneko, Koji; Metoki, Naoto; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Kay, Kohn*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(3), p.034718_1 - 034718_5, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.47(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Fukunaga, Sakae*; Nakayama, Mamoru*; Jintoku, Takashi*; ; Kudo, Akira*
JNC TJ8400 2002-037, 68 Pages, 2002/02
We conducted the following four investigations concerned with microbial influence in geological disposal facilities. (1)Improvement of the FEP dictionary and investigation on chemical evolution of nitrate by microbes. (2)Experimental estimation of microbial mobility in compacted Na bentonite saturated by synthetic seawater with 30wt% silica sand and Ca bentonite with 30wt% silica sand. (Both dry densities are 1.6 g/cm .) (3)Habitation of microbes in Na rich bentonite deposit and Ca rich one. (4)Interaction between SRB (sulfate reducing bacteria) and Np in a reducing environment at Eh=-85mV. As the result, it was revealed that (1)microbial activity in near field rock and microbial denitrification of nitrate under the existence of electron donor are important, (2)microbes didn't move in Na bentonite in 3 weeks and moved to the distance of 20mm in Ca bentonite, and (3)microoragnisms existed at the inside of the deposits. (4) The difference between distribution coefficient of Eh=-85mV and Eh=-500mV was evaluated.
.) (3)Habitation of microbes in Na rich bentonite deposit and Ca rich one. (4)Interaction between SRB (sulfate reducing bacteria) and Np in a reducing environment at Eh=-85mV. As the result, it was revealed that (1)microbial activity in near field rock and microbial denitrification of nitrate under the existence of electron donor are important, (2)microbes didn't move in Na bentonite in 3 weeks and moved to the distance of 20mm in Ca bentonite, and (3)microoragnisms existed at the inside of the deposits. (4) The difference between distribution coefficient of Eh=-85mV and Eh=-500mV was evaluated.
Fukunaga, Sakae*; Nakayama, Mamoru*; Jintoku, Takashi*; ; Kudo, Akira*
JNC TJ8400 2002-036, 186 Pages, 2002/02
We conducted the following four investigations concerned with microbial influence in geological disposal facilities. (1)Improvement of the FEP dictionary and investigation on chemical evolution of nitrate by microbes. (2)Experimental estimation of microbial mobility in compacted Na bentonite saturated by synthetic seawater with 30wt% silica sand and Ca bentonite with 30wt% silica sand. (Both dry densities are 1.6 g/cm .) (3)Habitation of microbes in Na rich bentonite deposit and Ca rich one. (4)Interaction between SRB (sulfate reducing bacteria) and Np in a reducing environment at Eh=-85mV. As the result, it was revealed that (1)microbial activity in near field rock and microbial denitrification of nitrate under the existence of electron donor are important, (2)microbes didn't move in Na bentonite in 3 weeks and moved to the distance of 20mm in Ca bentonite, and (3)microoragnisms existed at the inside of the deposits. (4)The difference between distribution coefficient of Eh=-85mV and Eh=-500mV was evaluated.
.) (3)Habitation of microbes in Na rich bentonite deposit and Ca rich one. (4)Interaction between SRB (sulfate reducing bacteria) and Np in a reducing environment at Eh=-85mV. As the result, it was revealed that (1)microbial activity in near field rock and microbial denitrification of nitrate under the existence of electron donor are important, (2)microbes didn't move in Na bentonite in 3 weeks and moved to the distance of 20mm in Ca bentonite, and (3)microoragnisms existed at the inside of the deposits. (4)The difference between distribution coefficient of Eh=-85mV and Eh=-500mV was evaluated.
 Mn
Mn O
O (
(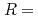 Ho, Er)
Ho, Er)Wakimoto, Shuichi; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Nishihata, Keisuke*; Noda, Yukio*; Tokura, Yoshinori*
no journal, ,
Polarized neutron diffraction experiments have been performed on multiferroic materials  Mn
Mn O
O (
(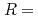 Ho, Er) under electric fields in the ferroelectric commensurate (CM) and the low-temperature incommensurate (LT-ICM) phases. It is found that the magnetic chirality is proportional to the electric polarization and magnetic chirality can be switched by the polarity of the electric polarization in both the CM and LT-ICM phases. However, upon the transition from the CM to LT-ICM phase, the reduction of the electric polarization is not accompanied by any reduction of the magnetic chirality, implying that the CM and LT-ICM phases contain different mechanisms of the magnetoelectric coupling.
Ho, Er) under electric fields in the ferroelectric commensurate (CM) and the low-temperature incommensurate (LT-ICM) phases. It is found that the magnetic chirality is proportional to the electric polarization and magnetic chirality can be switched by the polarity of the electric polarization in both the CM and LT-ICM phases. However, upon the transition from the CM to LT-ICM phase, the reduction of the electric polarization is not accompanied by any reduction of the magnetic chirality, implying that the CM and LT-ICM phases contain different mechanisms of the magnetoelectric coupling.
 Mn
Mn O
O
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Nishihata, Keisuke*; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Noda, Yukio*; Tokura, Yoshinori*
no journal, ,
Polarized neutron diffraction experiments have been performed on multiferroic materials  Mn
Mn O
O (
(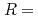 Ho, Er) under electric fields in the ferroelectric commensurate (CM) and the low-temperature incommensurate (LT-ICM) phases. It is found that the magnetic chirality is proportional to the electric polarization and magnetic chirality can be switched by the polarity of the electric polarization in both the CM and LT-ICM phases. However, upon the transition from the CM to LT-ICM phase, the reduction of the electric polarization is not accompanied by any reduction of the magnetic chirality, implying that the CM and LT-ICM phases contain different mechanisms of the magnetoelectric coupling.
Ho, Er) under electric fields in the ferroelectric commensurate (CM) and the low-temperature incommensurate (LT-ICM) phases. It is found that the magnetic chirality is proportional to the electric polarization and magnetic chirality can be switched by the polarity of the electric polarization in both the CM and LT-ICM phases. However, upon the transition from the CM to LT-ICM phase, the reduction of the electric polarization is not accompanied by any reduction of the magnetic chirality, implying that the CM and LT-ICM phases contain different mechanisms of the magnetoelectric coupling.
 Mn
Mn O
O (
(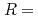 Ho, Er)
Ho, Er)Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Nishihata, Keisuke*; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Noda, Yukio*; Tokura, Yoshinori*
no journal, ,
Polarized neutron scattering experiments have been performed on multiferroic materials  Mn
Mn O
O (
(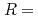 Ho, Er) under electric fields to study the direct relation between the electric polarization and the magnetic chiral structure of Mn spins. It is found that, after cooling in electric fields down to temperatures where the system has both commensurate magnetic order and ferroelectricity, the magnetic chiral order parameter is proportional to the polarization.
Ho, Er) under electric fields to study the direct relation between the electric polarization and the magnetic chiral structure of Mn spins. It is found that, after cooling in electric fields down to temperatures where the system has both commensurate magnetic order and ferroelectricity, the magnetic chiral order parameter is proportional to the polarization.
 O
O
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Sakamoto, Yuma*; Noda, Yukio*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
no journal, ,
 (Mn
(Mn Ga
Ga )
) O
O
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Sakamoto, Yuma*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Noda, Yukio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Mn
Mn O
O (
( =Ho, Er)
=Ho, Er)Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Nishihata, Keisuke*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Noda, Yukio*; Tokura, Yoshinori*
no journal, ,
Polarized neutron scattering experiments have been performed on multiferroic materials  Mn
Mn O
O (
(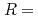 Ho, Er) under electric fields to study the direct relation between the electric polarization and the magnetic chiral structure of Mn spins. It is found that the magnetic chirality is proportional to the polarization, consisntent with the inverse-DM model.
Ho, Er) under electric fields to study the direct relation between the electric polarization and the magnetic chiral structure of Mn spins. It is found that the magnetic chirality is proportional to the polarization, consisntent with the inverse-DM model.
 O
O
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Noda, Yukio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Mn
Mn O
O
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Sakamoto, Yuma*; Noda, Yukio*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
no journal, ,
 O
O
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Sakamoto, Yuma*; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Noda, Yukio*
no journal, ,
 (Mn
(Mn Ga
Ga )
) O
O
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Sakamoto, Yuma*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Noda, Yukio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English