Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 C alloy measured in the electrostatic levitation furnace onboard the international space station
C alloy measured in the electrostatic levitation furnace onboard the international space stationIshikawa, Takehiko*; Oda, Hirohisa*; Koyama, Chihiro*; Shimonishi, Rina*; Ikeuchi, Rumiko*; Paradis, P.-F.*; Okada, Jumpei*; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Yamano, Hidemasa
International Journal of Microgravity Science and Application, 42(2), p.420202_1 - 420202_10, 2025/04
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Emura, Yuki; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Morita, Koji*; Nakamura, Kinya*; Ahmed, Z.*; Pellegrini, M.*
Proceedings of 14th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation, and Safety (NTHOS-14) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2024/08
This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2022. A specific result in this paper is to obtain first experimental data of B C-SS eutectic freezing.
C-SS eutectic freezing.
Tanaka, Kazuya; Yamaji, Keiko*; Masuya, Hayato*; Tomita, Jumpei; Ozawa, Mayumi*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Tokunaga, Kohei; Fukuyama, Kenjin*; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Maamoun, I.*; et al.
Chemosphere, 355, p.141837_1 - 141837_11, 2024/05
In this study, biogenic Mn(IV) oxide was applied to remove Ra from mine water collected from a U mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge center. Just 7.6 mg of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide removed more than 98% of the  Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10
Ra from 3 L of mine water, corresponding to a distribution coefficient of 10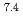 mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
mL/g for Ra at pH 7. The obtained value was convincingly high for practical application of biogenic Mn(IV) oxide in water treatment.
 solution in the gigapascal pressure range
solution in the gigapascal pressure rangeYamaguchi, Toshio*; Fukuyama, Nami*; Yoshida, Koji*; Katayama, Yoshinori*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori
Liquids (Internet), 3(3), p.288 - 302, 2023/09
We report the structure of an aqueous 2 mol/kg MgCl solution at pressures from 0.1 MPa to 4 GPa and temperatures from 300 to 500 K revealed by X-ray and neutron scattering measurements. The scattering data are analyzed by empirical potential structure refinement (EPSR) modeling to derive the pair distribution functions, coordination number distributions, angle distributions, and spatial density functions as a function of pressure and temperature. Mg
solution at pressures from 0.1 MPa to 4 GPa and temperatures from 300 to 500 K revealed by X-ray and neutron scattering measurements. The scattering data are analyzed by empirical potential structure refinement (EPSR) modeling to derive the pair distribution functions, coordination number distributions, angle distributions, and spatial density functions as a function of pressure and temperature. Mg forms rigid solvation shells extended to the third shell; the first solvation shell of six-fold octahedral coordination with about six water molecules at 0 GPa transforms into about five water molecules and one Cl
forms rigid solvation shells extended to the third shell; the first solvation shell of six-fold octahedral coordination with about six water molecules at 0 GPa transforms into about five water molecules and one Cl due to the formation of the contact ion pairs in the GPa pressure range. The Cl
due to the formation of the contact ion pairs in the GPa pressure range. The Cl solvation shows a substantial pressure dependence; the coordination number of a water oxygen atom around Cl
solvation shows a substantial pressure dependence; the coordination number of a water oxygen atom around Cl increases from 8 at 0.1 MPa/300 K to 10 at 4 GPa/500 K. The solvent water transforms the tetrahedral network structure at 0.1 MPa/300 K to a densely packed structure in the GPa pressure range; the number of water oxygen atoms around a central water molecule gradually increases from 4.6 at 0.1 MPa/298 K to 8.4 at 4 GPa/500 K.
increases from 8 at 0.1 MPa/300 K to 10 at 4 GPa/500 K. The solvent water transforms the tetrahedral network structure at 0.1 MPa/300 K to a densely packed structure in the GPa pressure range; the number of water oxygen atoms around a central water molecule gradually increases from 4.6 at 0.1 MPa/298 K to 8.4 at 4 GPa/500 K.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Emura, Yuki; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Morita, Koji*; Nakamura, Kinya*; Pellegrini, M.*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai 2023-Nendo Nenji Taikai Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/09
A research project has been conducting thermophysical property measurement of a eutectic melt, eutectic melting reaction and relocation experiments, eutectic reaction mechanism investigation, and physical model development on the eutectic melting reaction for reactor application analysis in order to simulate the eutectic melting reaction and relocation behavior of boron carbide as a control rod material and stainless steel during a core disruptive accident in an advanced sodium-cooled fast reactor designed in Japan. This paper describes the project overview and progress until JFY2022.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Emura, Yuki; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; Morita, Koji*; Nakamura, Kinya*; Fukai, Hirofumi*; et al.
Proceedings of 13th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-13) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2022/09
This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2020. Specific results in this paper are the measurement of the eutectic reaction rates and the validation of physical model describing the eutectic reaction in the analysis code through the numerical analysis of the B C-SS eutectic reaction rate experiments in which a B
C-SS eutectic reaction rate experiments in which a B C pellet was placed in a SS crucible.
C pellet was placed in a SS crucible.
 U accumulations in
U accumulations in 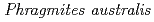 naturally growing at the mill tailings pond; Iron plaque formation possibly related to root-endophytic bacteria producing siderophores
naturally growing at the mill tailings pond; Iron plaque formation possibly related to root-endophytic bacteria producing siderophoresNakamoto, Yukihiro*; Doyama, Kohei*; Haruma, Toshikatsu*; Lu, X.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Fukuyama, Kenjin; Fukushima, Shigeru; Ohara, Yoshiyuki; Yamaji, Keiko*
Minerals (Internet), 11(12), p.1337_1 - 1337_17, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.78(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Mine drainage is a vital water problem in the mining industry worldwide because of the heavy metal elements and low pH. Rhizofiltration using wetland plants is an appropriate method to remove heavy metals from the water via accumulation in the rhizosphere. 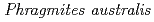 is one of the candidate plants for this method because of metal accumulation, forming iron plaque around the roots. At the study site, which was the mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge uranium mine,
is one of the candidate plants for this method because of metal accumulation, forming iron plaque around the roots. At the study site, which was the mill tailings pond in the Ningyo-toge uranium mine,  has been naturally growing since 1998. The results showed that
has been naturally growing since 1998. The results showed that  accumulated Fe, Mn, and
accumulated Fe, Mn, and  U in the nodal roots without/with iron plaque compared with other plant tissues. Among the 837 bacterial colonies isolated from nodal roots, 88.6% showed siderophore production activities. Considering iron plaque formation around
U in the nodal roots without/with iron plaque compared with other plant tissues. Among the 837 bacterial colonies isolated from nodal roots, 88.6% showed siderophore production activities. Considering iron plaque formation around  roots, we hypothesized that microbial siderophores might influence iron plaque formation because bacterial siderophores have catechol-like functional groups. The complex of catechol or other phenolics with Fe was precipitated due to the networks between Fe and phenolic derivatives. The experiment using bacterial products of root endophytes, such as
roots, we hypothesized that microbial siderophores might influence iron plaque formation because bacterial siderophores have catechol-like functional groups. The complex of catechol or other phenolics with Fe was precipitated due to the networks between Fe and phenolic derivatives. The experiment using bacterial products of root endophytes, such as 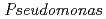 spp. and
spp. and 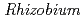 spp., showed precipitation with Fe ions, and we confirmed that several
spp., showed precipitation with Fe ions, and we confirmed that several 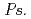 spp. and
spp. and 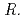 spp. produced unidentified phenolic compounds. In conclusion, root-endophytic bacteria such as
spp. produced unidentified phenolic compounds. In conclusion, root-endophytic bacteria such as 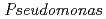 spp. and
spp. and 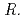 spp., isolated from metal-accumulating roots of
spp., isolated from metal-accumulating roots of  , might influence iron plaque formation as the metal accumulation site. Iron plaque formation is related to tolerance in
, might influence iron plaque formation as the metal accumulation site. Iron plaque formation is related to tolerance in  , and
, and 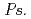 spp. and
spp. and 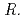 spp. might indirectly contribute to tolerance.
spp. might indirectly contribute to tolerance.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Emura, Yuki; Kamiyama, Kenji; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 28) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2021/08
One of the key issues in a core disruptive accident (CDA) evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors is eutectic reactions between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation. Such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses in the past, therefore it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study focuses on B
C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation. Such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses in the past, therefore it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study focuses on B C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in a range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a CDA computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2019. Specific results in this paper are the validation of physical model describing B
C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in a range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a CDA computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2019. Specific results in this paper are the validation of physical model describing B C-SS eutectic reaction in the CDA analysis code, SIMMER-III, through the numerical analysis of the B
C-SS eutectic reaction in the CDA analysis code, SIMMER-III, through the numerical analysis of the B C-SS eutectic melting experiments in which a B
C-SS eutectic melting experiments in which a B C block was placed in a SS pool.
C block was placed in a SS pool.
Iizuka, Riko*; Goto, Hirotada*; Shito, Chikara*; Fukuyama, Ko*; Mori, Yuichiro*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.12632_1 - 12632_10, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.44(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The Earth's core consist of Fe-Ni alloy with some light elements (H, C, O, Si, S etc.). Hydrogen (H) is the most abundant element in the universe and one of the promising candidates. In this study, we have investigated the effects of sulfur(S) on hydrogenation of iron-hydrous silicate system containing saturated water in the ideal composition of the primitive Earth. We observed a series of phase transitions of Fe, dehydration of the hydrous mineral, and formation of olivine and enstatite with increasing temperature. The FeS formed as the coexisting phase of Fe under high-pressure and temperature condition, but its unit cell volume did not increase, suggesting that FeS is hardly hydrogenated. Recovered samples exhibited that H and S can be incorporated into solid Fe, which lowers the melting temperature as Fe(H )-FeS system. No detection of other light elements (C, O, Si) in solid Fe suggests that they dissolve into molten iron hydride and/or FeS in the later process of Earth's core-mantle differentiation.
)-FeS system. No detection of other light elements (C, O, Si) in solid Fe suggests that they dissolve into molten iron hydride and/or FeS in the later process of Earth's core-mantle differentiation.
 Fe
Fe O
O with distributed equivalent circuit model
with distributed equivalent circuit modelFukada, Yukimasa*; Fukuyama, Ryota*; Fujiwara, Kosuke*; Yoshii, Kenji; Shigematsu, Kei*; Azuma, Masaki*; Ikeda, Naoshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(2), p.024710_1 - 024710_6, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.70(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report an analysis of the dielectric glasslike state of the spin- and charge-ordered system Lu Fe
Fe O
O , which has structural and physical properties analogous to those of the electronic ferroelectrics
, which has structural and physical properties analogous to those of the electronic ferroelectrics  Fe
Fe O
O (
( : rare earth). Aging and memory effects of resistivity were found in the electric impedance response. We performed a numerical analysis with equivalent electric circuits that have a logarithmic Gaussian distribution of resistance and capacitance. The distribution parameters well explained the glassy nature of the electric and dielectric properties between 100 and 200 K and the distribution variations of charge- and magnetic-ordered domains underlying the glass nature.
: rare earth). Aging and memory effects of resistivity were found in the electric impedance response. We performed a numerical analysis with equivalent electric circuits that have a logarithmic Gaussian distribution of resistance and capacitance. The distribution parameters well explained the glassy nature of the electric and dielectric properties between 100 and 200 K and the distribution variations of charge- and magnetic-ordered domains underlying the glass nature.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Emura, Yuki; Kamiyama, Kenji; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; et al.
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2020/08
One of the key issues in a core disruptive accident (CDA) evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors is eutectic reactions between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation. Such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses in the past, therefore it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study focuses on B
C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation. Such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses in the past, therefore it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study focuses on B C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in a range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2018. Specific results in this paper are boron concentration distributions of solidified B
C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in a range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2018. Specific results in this paper are boron concentration distributions of solidified B C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Emura, Yuki; Kamiyama, Kenji; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; et al.
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.418 - 427, 2019/09
Eutectic reactions between boron carbide (B C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation are one of the key issues in a core disruptive accident (CDA) evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors. Since such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses, it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study is focusing on B
C) and stainless steel (SS) as well as its relocation are one of the key issues in a core disruptive accident (CDA) evaluation in sodium-cooled fast reactors. Since such behaviors have never been simulated in CDA numerical analyses, it is necessary to develop a physical model and incorporate the model into the CDA analysis code. This study is focusing on B C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in the range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies by 2017. Specific results in this paper is boron concentration distributions of solidified B
C-SS eutectic melting experiments, thermophysical property measurement of the eutectic melt, and physical model development for the eutectic melting reaction. The eutectic experiments involve the visualization experiments, eutectic reaction rate experiments and material analyses. The thermophysical properties are measured in the range from solid to liquid state. The physical model is developed for a severe accident computer code based on the measured data of the eutectic reaction rate and the physical properties. This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies by 2017. Specific results in this paper is boron concentration distributions of solidified B C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
C-SS eutectic sample in the eutectic melting experiments, which would be used for the validation of the eutectic physical model implemented into the computer code.
Abe, Mitsushi*; Bae, S.*; Beer, G.*; Bunce, G.*; Choi, H.*; Choi, S.*; Chung, M.*; da Silva, W.*; Eidelman, S.*; Finger, M.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(5), p.053C02_1 - 053C02_22, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:161 Percentile:99.30(Physics, Multidisciplinary)This paper introduces a new approach to measure the muon magnetic moment anomaly  and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)
and the muon electric dipole moment (EDM)  at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure
at the J-PARC muon facility. The goal of our experiment is to measure  and
and  using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for
using an independent method with a factor of 10 lower muon momentum, and a factor of 20 smaller diameter storage-ring solenoid compared with previous and ongoing muon g-2 experiments with unprecedented quality of the storage magnetic field. Additional significant differences from the present experimental method include a factor of 1000 smaller transverse emittance of the muon beam (reaccelerated thermal muon beam), its efficient vertical injection into the solenoid, and tracking each decay positron from muon decay to obtain its momentum vector. The precision goal for  is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of
is a statistical uncertainty of 450 parts per billion (ppb), similar to the present experimental uncertainty, and a systematic uncertainty less than 70 ppb. The goal for EDM is a sensitivity of  e
e cm.
cm.
Ishizawa, Akihiro*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Imadera, Kenji*; Kasuya, Naohiro*; Kanno, Ryutaro*; Satake, Shinsuke*; Tatsuno, Tomoya*; Nakata, Motoki*; Nunami, Masanori*; Maeyama, Shinya*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 92(3), p.157 - 210, 2016/03
The high-performance computer system Helios which is located at The Computational Simulation Centre (CSC) in The International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) started its operation in January 2012 under the Broader Approach (BA) agreement between Japan and the EU. The Helios system has been used for magnetised fusion related simulation studies in the EU and Japan and has kept high average usage rate. As a result, the Helios system has contributed to many research products in a wide range of research areas from core plasma physics to reactor material and reactor engineering. This project review gives a short catalogue of domestic simulation research projects. First, we outline the IFERC-CSC project. After that, shown are objectives of the research projects, numerical schemes used in simulation codes, obtained results and necessary computations in future.
Unno, Masayoshi*; Ishikawa, Kumiko*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Tamada, Taro; Hagiwara, Yoshinori*; Sugishima, Masakazu*; Wada, Kei*; Yamada, Taro*; Tomoyori, Katsuaki; Hosoya, Takaaki*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 137(16), p.5452 - 5460, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:62.63(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Phycocyanobilin, a light-harvesting and photoreceptor pigment in higher plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, is synthesized from biliverdin IX (BV) by phycocyanobilin:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PcyA) via two steps of two-proton-coupled two-electron reduction. We determined the neutron structure of PcyA from cyanobacteria complexed with BV, revealing the exact location of the hydrogen atoms involved in catalysis. Notably, approximately half of the BV bound to PcyA was BVH
(BV) by phycocyanobilin:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PcyA) via two steps of two-proton-coupled two-electron reduction. We determined the neutron structure of PcyA from cyanobacteria complexed with BV, revealing the exact location of the hydrogen atoms involved in catalysis. Notably, approximately half of the BV bound to PcyA was BVH , a state in which all four pyrrole nitrogen atoms were protonated. The protonation states of BV complemented the protonation of adjacent Asp105. The "axial "water molecule that interacts with the neutral pyrrole nitrogen of the A-ring was identified. His88 N
, a state in which all four pyrrole nitrogen atoms were protonated. The protonation states of BV complemented the protonation of adjacent Asp105. The "axial "water molecule that interacts with the neutral pyrrole nitrogen of the A-ring was identified. His88 N was protonated to form a hydrogen bond with the lactam O atom of the BV A-ring. His88 and His74 were linked by hydrogen bonds via H
was protonated to form a hydrogen bond with the lactam O atom of the BV A-ring. His88 and His74 were linked by hydrogen bonds via H O
O . These results imply that Asp105, His88, and the axial water molecule contribute to proton transfer during PcyA catalysis.
. These results imply that Asp105, His88, and the axial water molecule contribute to proton transfer during PcyA catalysis.
 Fe
Fe O
O (R=Yb and Lu)
(R=Yb and Lu)Yoshii, Kenji; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Fukuyama, Ryota*; Nagata, Tomoko*; Kambe, Takashi*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Mori, Shigeo*
Solid State Communications, 173, p.34 - 37, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.06(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have investigated the magnetic properties of R Fe
Fe O
O (R=Yb and Lu), which belongs to the homologous family of electronic ferroelectric RFe
(R=Yb and Lu), which belongs to the homologous family of electronic ferroelectric RFe O
O . Magnetization measurements show ferrimagnetic ordering at the Neel temperature (T
. Magnetization measurements show ferrimagnetic ordering at the Neel temperature (T ) of about 270 K, which is slightly higher than that of RFe
) of about 270 K, which is slightly higher than that of RFe O
O (T
(T about 230-250 K). Observation of spin glass and exchange bias shows a coexistence of ferromagnetic and antiferromagneticinteractions, similarly to RFe
about 230-250 K). Observation of spin glass and exchange bias shows a coexistence of ferromagnetic and antiferromagneticinteractions, similarly to RFe O
O . This situation gives rise to a complex magnetic change and a broad peak of magnetic entropy change. Some characteristics, such as refrigeration temperatures higher than in RFe
. This situation gives rise to a complex magnetic change and a broad peak of magnetic entropy change. Some characteristics, such as refrigeration temperatures higher than in RFe O
O , seem to offer a possibility of this system to applications.
, seem to offer a possibility of this system to applications.
Giruzzi, G.*; Garcia, J.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Schneider, M.*; Artaud, J. F.*; Baruzzo, M.*; Bolzonella, T.*; Farina, D.*; Figini, L.*; Fujita, Takaaki; et al.
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
Okuda, Shin*; Miyamoto, Kenji*; Fukuyama, Toshishige*; Nishioka, Shu*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Fukano, Azusa*; Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi
AIP Conference Proceedings 1515, p.107 - 113, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:93.28(Physics, Applied)A meniscus of plasma-beam boundary in H ion sources largely affects the extracted H
ion sources largely affects the extracted H ion beam optics. Recently it is shown that the beam halo is mainly caused by the meniscus, i.e. ion emissive surface, close to the plasma grid (PG) where its curvature is large. The purpose of this study is to clarify the effect of H
ion beam optics. Recently it is shown that the beam halo is mainly caused by the meniscus, i.e. ion emissive surface, close to the plasma grid (PG) where its curvature is large. The purpose of this study is to clarify the effect of H surface production rate on plasma meniscus and beam halo formation with PIC (particle-in-cell) modeling. It is shown that the plasma meniscus and beam halo formation is strongly dependent on the amount of surface produced H
surface production rate on plasma meniscus and beam halo formation with PIC (particle-in-cell) modeling. It is shown that the plasma meniscus and beam halo formation is strongly dependent on the amount of surface produced H ions.
ions.
Odaka, Hirokazu*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; Takeda, Shinichiro*; Fukuyama, Taro*; Hagino, Koichi*; Saito, Shinya*; Sato, Tamotsu*; Sato, Goro*; Watanabe, Shin*; Kokubun, Motohide*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 695, p.179 - 183, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:82.98(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have developed a new Si/CdTe semiconductor double-sided strip detector (DSD) Compton camera. The camera consists of a 500- m-thick Si-DSD and four layers of 750-
m-thick Si-DSD and four layers of 750- m-thick CdTe-DSDs all of which have common electrode configuration segmented into 128 strips on each side with pitches of 250
m-thick CdTe-DSDs all of which have common electrode configuration segmented into 128 strips on each side with pitches of 250 m. In order to realize high angular resolution and to reduce size of the detector system, a stack of DSDs with short stack pitches of 4 mm is utilized to make the camera. Taking advantage of the excellent energy and position resolutions of the semiconductor devices, the camera achieves high angular resolutions of 4.5 degrees at 356 keV and 3.5 degrees at 662 keV. To obtain such high resolutions together with an acceptable detection efficiency, we demonstrate data reduction methods including energy calibration using Compton scattering continuum and depth sensing in the CdTe-DSD. We also discuss imaging capability of the camera and show simultaneous multi-energy imaging.
m. In order to realize high angular resolution and to reduce size of the detector system, a stack of DSDs with short stack pitches of 4 mm is utilized to make the camera. Taking advantage of the excellent energy and position resolutions of the semiconductor devices, the camera achieves high angular resolutions of 4.5 degrees at 356 keV and 3.5 degrees at 662 keV. To obtain such high resolutions together with an acceptable detection efficiency, we demonstrate data reduction methods including energy calibration using Compton scattering continuum and depth sensing in the CdTe-DSD. We also discuss imaging capability of the camera and show simultaneous multi-energy imaging.
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Fukuyama, Atsushi*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 88(11), p.678 - 680, 2012/11
no abstracts in English