Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Fe
Fe O
O with distributed equivalent circuit model
with distributed equivalent circuit modelFukada, Yukimasa*; Fukuyama, Ryota*; Fujiwara, Kosuke*; Yoshii, Kenji; Shigematsu, Kei*; Azuma, Masaki*; Ikeda, Naoshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 90(2), p.024710_1 - 024710_6, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:22.16(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report an analysis of the dielectric glasslike state of the spin- and charge-ordered system Lu Fe
Fe O
O , which has structural and physical properties analogous to those of the electronic ferroelectrics
, which has structural and physical properties analogous to those of the electronic ferroelectrics  Fe
Fe O
O (
( : rare earth). Aging and memory effects of resistivity were found in the electric impedance response. We performed a numerical analysis with equivalent electric circuits that have a logarithmic Gaussian distribution of resistance and capacitance. The distribution parameters well explained the glassy nature of the electric and dielectric properties between 100 and 200 K and the distribution variations of charge- and magnetic-ordered domains underlying the glass nature.
: rare earth). Aging and memory effects of resistivity were found in the electric impedance response. We performed a numerical analysis with equivalent electric circuits that have a logarithmic Gaussian distribution of resistance and capacitance. The distribution parameters well explained the glassy nature of the electric and dielectric properties between 100 and 200 K and the distribution variations of charge- and magnetic-ordered domains underlying the glass nature.
Unno, Masayoshi*; Ishikawa, Kumiko*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Tamada, Taro; Hagiwara, Yoshinori*; Sugishima, Masakazu*; Wada, Kei*; Yamada, Taro*; Tomoyori, Katsuaki; Hosoya, Takaaki*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 137(16), p.5452 - 5460, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:62.81(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Phycocyanobilin, a light-harvesting and photoreceptor pigment in higher plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, is synthesized from biliverdin IX (BV) by phycocyanobilin:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PcyA) via two steps of two-proton-coupled two-electron reduction. We determined the neutron structure of PcyA from cyanobacteria complexed with BV, revealing the exact location of the hydrogen atoms involved in catalysis. Notably, approximately half of the BV bound to PcyA was BVH
(BV) by phycocyanobilin:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PcyA) via two steps of two-proton-coupled two-electron reduction. We determined the neutron structure of PcyA from cyanobacteria complexed with BV, revealing the exact location of the hydrogen atoms involved in catalysis. Notably, approximately half of the BV bound to PcyA was BVH , a state in which all four pyrrole nitrogen atoms were protonated. The protonation states of BV complemented the protonation of adjacent Asp105. The "axial "water molecule that interacts with the neutral pyrrole nitrogen of the A-ring was identified. His88 N
, a state in which all four pyrrole nitrogen atoms were protonated. The protonation states of BV complemented the protonation of adjacent Asp105. The "axial "water molecule that interacts with the neutral pyrrole nitrogen of the A-ring was identified. His88 N was protonated to form a hydrogen bond with the lactam O atom of the BV A-ring. His88 and His74 were linked by hydrogen bonds via H
was protonated to form a hydrogen bond with the lactam O atom of the BV A-ring. His88 and His74 were linked by hydrogen bonds via H O
O . These results imply that Asp105, His88, and the axial water molecule contribute to proton transfer during PcyA catalysis.
. These results imply that Asp105, His88, and the axial water molecule contribute to proton transfer during PcyA catalysis.
 Fe
Fe O
O (R=Yb and Lu)
(R=Yb and Lu)Yoshii, Kenji; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Fukuyama, Ryota*; Nagata, Tomoko*; Kambe, Takashi*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Mori, Shigeo*
Solid State Communications, 173, p.34 - 37, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:19.11(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have investigated the magnetic properties of R Fe
Fe O
O (R=Yb and Lu), which belongs to the homologous family of electronic ferroelectric RFe
(R=Yb and Lu), which belongs to the homologous family of electronic ferroelectric RFe O
O . Magnetization measurements show ferrimagnetic ordering at the Neel temperature (T
. Magnetization measurements show ferrimagnetic ordering at the Neel temperature (T ) of about 270 K, which is slightly higher than that of RFe
) of about 270 K, which is slightly higher than that of RFe O
O (T
(T about 230-250 K). Observation of spin glass and exchange bias shows a coexistence of ferromagnetic and antiferromagneticinteractions, similarly to RFe
about 230-250 K). Observation of spin glass and exchange bias shows a coexistence of ferromagnetic and antiferromagneticinteractions, similarly to RFe O
O . This situation gives rise to a complex magnetic change and a broad peak of magnetic entropy change. Some characteristics, such as refrigeration temperatures higher than in RFe
. This situation gives rise to a complex magnetic change and a broad peak of magnetic entropy change. Some characteristics, such as refrigeration temperatures higher than in RFe O
O , seem to offer a possibility of this system to applications.
, seem to offer a possibility of this system to applications.
 Fe
Fe O
O (
( =Y, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu and In)
=Y, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu and In)Yoshii, Kenji; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Nishihata, Yasuo; Maeda, Daisuke*; Fukuyama, Ryota*; Nagata, Tomoko*; Kano, Jun*; Kambe, Takashi*; Horibe, Yoichi*; Mori, Shigeo*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(3), p.033704_1 - 033704_4, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:58.45(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Exchange bias (EB) behavior has been observed for multiferroic  Fe
Fe O
O (
( =Y, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu and In). The materials with the small
=Y, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu and In). The materials with the small 
 ions (
ions ( =Tm, Yb, Lu and In) exhibit large EB fields (
=Tm, Yb, Lu and In) exhibit large EB fields (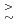 1 kOe) below
1 kOe) below  100-150 K. This property is rooted in a magnetically glassy state, arising from the competition between ferro- and antiferromagnetic domain interactions. In addition, the exchange bias field tends to be more enhanced for smaller
100-150 K. This property is rooted in a magnetically glassy state, arising from the competition between ferro- and antiferromagnetic domain interactions. In addition, the exchange bias field tends to be more enhanced for smaller 
 ions. Hence, the EB is controlled by the substitution at the
ions. Hence, the EB is controlled by the substitution at the  -site in this series.
-site in this series.
 Na
Na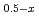 Li
Li )TiO
)TiO
Fukunaga, Masanori; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Fukuyama, Ryota*; Saito, Hiroyuki; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 35(1), p.111 - 114, 2010/03
High-pressure synthesis of bismuth based perovskite (Bi Na
Na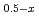 Li
Li )TiO
)TiO (BNLT) (
(BNLT) ( =0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.25, 0.4, 0.5) was demonstrated. Single phase BNLTs with perovskite structure were successfully synthesized for
=0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.25, 0.4, 0.5) was demonstrated. Single phase BNLTs with perovskite structure were successfully synthesized for 
 0.1 by the solid state reaction method. The solid phase reaction occurred in the pressure range of 6-10 GPa, and in the temperature range of 800-1200
0.1 by the solid state reaction method. The solid phase reaction occurred in the pressure range of 6-10 GPa, and in the temperature range of 800-1200  C. Two thermal anomalies were observed in single phase perovskite BNLT (
C. Two thermal anomalies were observed in single phase perovskite BNLT ( =0.1) as well as (Bi,Na)TiO
=0.1) as well as (Bi,Na)TiO . The cusp like anomaly at 210
. The cusp like anomaly at 210  C was assigned to a rhombohedral-tetragonal structural phase transition. The finished products of
C was assigned to a rhombohedral-tetragonal structural phase transition. The finished products of 
 0.2 included three kinds of impurities, which were affected by the selection of starting materials.
0.2 included three kinds of impurities, which were affected by the selection of starting materials.
 Fe
Fe O
O
Yoshii, Kenji; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Fukuyama, Ryota*; Nagata, Tomoko*; Kambe, Takashi*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Mori, Shigeo*
no journal, ,
The rare-earth iron oxides R Fe
Fe O
O (R=Yb and Lu) are materials closely related to a multiferroic system RFe
(R=Yb and Lu) are materials closely related to a multiferroic system RFe O
O , which shows a new type of ferroelectiricy (i.e., electronic ferroelectiricy) at 330 K owing to real-space charge ordering of Fe ions. In this work, we have investigated detailed magnetic properties of a single crystalline LuFe
, which shows a new type of ferroelectiricy (i.e., electronic ferroelectiricy) at 330 K owing to real-space charge ordering of Fe ions. In this work, we have investigated detailed magnetic properties of a single crystalline LuFe O
O . It was found that this oxide shows the magnetic transition temperature of 270 K, which is higher than that of the corresponding RFe
. It was found that this oxide shows the magnetic transition temperature of 270 K, which is higher than that of the corresponding RFe O
O (LuFe
(LuFe O
O ), 240-250 K. AC magnetic susceptibility measurements exhibited spin-glass behavior at around the magnetic transition temperature. In addition, exchange bias and magnetocaloric effect were observed at low temperatures, similarly to RFe
), 240-250 K. AC magnetic susceptibility measurements exhibited spin-glass behavior at around the magnetic transition temperature. In addition, exchange bias and magnetocaloric effect were observed at low temperatures, similarly to RFe O
O . These phenomena are explained in connection with several factors, such as a coexistence of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic interactions between Fe ions.
. These phenomena are explained in connection with several factors, such as a coexistence of ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic interactions between Fe ions.
 Fe
Fe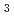 O
O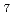 using impedance spectroscopy
using impedance spectroscopyFukada, Yukimasa*; Fukuyama, Ryota*; Fujiwara, Kosuke*; Yoshii, Kenji; Ikeda, Naoshi*
no journal, ,

Kuroda, Tomoko*; Fukuyama, Ryota*; Kitamura, Satoshi*; Matsuo, Yoji*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Kambe, Takashi*; Agui, Akane; Kimizuka, Noboru*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Fe
Fe O
O system using impedance spectroscopy
system using impedance spectroscopyFukada, Yukimasa*; Yoshii, Kenji; Fujiwara, Kosuke*; Fukuyama, Ryota*; Ikeda, Naoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 O
O
Maeda, Daisuke*; Fukuyama, Ryota*; Kitamura, Satoshi*; Funae, Takeshi*; Matsuo, Yoji*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Kambe, Takashi*; Kimizuka, Noboru*; Yoshii, Kenji
no journal, ,
We have investigated the successive phase transition in YFe O
O , which shows charge-ordering-induced ferroelectricity below about 330 K. This material has been reported to show complex phase transitions below 330 K. In this work we have studied the structure and physical properties of YFe
, which shows charge-ordering-induced ferroelectricity below about 330 K. This material has been reported to show complex phase transitions below 330 K. In this work we have studied the structure and physical properties of YFe O
O synthesized in a variety of preparation conditions, and have found that slight changes of the conditions led to drastic alternations of physical properties. Details of the results will be shown at the conference.
synthesized in a variety of preparation conditions, and have found that slight changes of the conditions led to drastic alternations of physical properties. Details of the results will be shown at the conference.
 Fe
Fe O
O
Fukuyama, Ryota*; Yoshii, Kenji; Kuroda, Tomoko*; Kitamura, Satoshi*; Funae, Takeshi*; Matsuo, Yoji*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Kimizuka, Noboru*; Kambe, Takashi*
no journal, ,
We have investigated the physical properties of Lu Fe
Fe O
O , which has a related structure to the electronic ferroelectric RFe
, which has a related structure to the electronic ferroelectric RFe O
O (R: rare earths). Magnetic measurements showed that its magnetic transition temperature was about 260-270 K. Dielectric measurements showed that dielectric constants at room temperature were about 10000. This material also showed a magneto-dielectric effect at around room temperature, a result which is interesting from the viewpoints of both fundamental and applied science.
(R: rare earths). Magnetic measurements showed that its magnetic transition temperature was about 260-270 K. Dielectric measurements showed that dielectric constants at room temperature were about 10000. This material also showed a magneto-dielectric effect at around room temperature, a result which is interesting from the viewpoints of both fundamental and applied science.