Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Maeda, Makoto; Komeda, Masao
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1301 - 1312, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Ozu, Akira; Toh, Yosuke
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(11), p.4002 - 4018, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Ozu, Akira; Toh, Yosuke
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Virtual Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2021/08
Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Virtual Annual Meeting (Internet), 8 Pages, 2021/08
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Aoi, Nori*; Azaiez, F.*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Kimura, Atsushi; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 103(3), p.034327_1 - 034327_8, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.33(Physics, Nuclear)Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Toh, Yosuke
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.297 - 304, 2020/10
Maeda, Makoto; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kureta, Masatoshi; Ozu, Akira; Komeda, Masao; Toh, Yosuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(7), p.617 - 628, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Proceedings of INMM 60th Annual Meeting (Internet), 7 Pages, 2019/07
Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Heyse, J.*; Paradela, C.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 59th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/07
Ozu, Akira; Maeda, Makoto; Komeda, Masao; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Toh, Yosuke
Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Dai-38-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/04
no abstracts in English
Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Kureta, Masatoshi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Seya, Michio; et al.
EUR-28795-EN (Internet), p.684 - 693, 2017/00
Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Tobita, Hiroshi; Hattori, Kentaro; Shimofusa, Taichi; Ozu, Akira; Kureta, Masatoshi
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 10 Pages, 2016/07
We are working on the development of a non-destructive assay (NDA) measurement system using the Fast Neutron Direct Interrogation (FNDI) method. The FNDI method is a kind of active neutron technique and can measure the total amounts of fissile materials (U-235, Pu-239, Pu-241). We have already carried out design analyses of an NDA measurement system for measuring the debris assuming use of the Three Mile Island (TMI) canister model. The result was presented at the Institute of Nuclear Materials Management (INMM) 56th Annual Meeting. Since then, we have modified the design of the NDA measurement system for the fuel debris and canister models at 1F. In this paper, we provide the calculation and evaluation results using the modified NDA measurement system. Moreover, we provide analytical investigations of the influence of fuel debris including high fissile material content on measurements.
Kimura, Atsushi; Harada, Hideo; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Osamu; Toh, Yosuke; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Igashira, Masayuki*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 51(12), p.180_1 - 180_8, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.63(Physics, Nuclear)Maeda, Makoto; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kureta, Masatoshi; Ozu, Akira; Tobita, Hiroshi; Komeda, Masao; Hattori, Kentaro
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-36-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/12
Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Disaster in March 11th in 2011 is considered to produce fuel debris. It is difficult to measure nondestructively the amount of fissile materials in the fuel debris since the constituents of the debris are unknown and it may contain various materials such as water, metal, and even neutron absorber. A fast neutron direct interrogation (FNDI) method, which has been developed for long years to measure uranium bearing wastes drums, can measure an amount of nuclear materials regardless of a matrix of the wastes drums. We have studied nondestructive assay for nuclear materials in fuel debris by using the FNDI method. In this paper, we report on a design study of a nondestructive measurement system for debris canister and results of the investigation on the applicability of the FNDI method to the fuel debris containing various materials using Monte Carlo simulations.
Kureta, Masatoshi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Seya, Michio
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-36-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/12
The new program "Development of active neutron NDA techniques" has started for non-proliferation applications collaborating with EC-JRC. The final purpose of this program is to establish the measurement techniques for the high radioactive special nuclear material such as MA-Pu fuel for transmutation of minor actinide. In this program, the JAEA will conduct the R&D on active neutron non-destructive measurement techniques, DDA, NRTA, PGA/NRCA and DGS. The development plan and current status of the design study of the active neutron integrated test apparatus named "Active-N" are presented in this report.
 ) cross-sections using multi-nucleon transfer reactions
) cross-sections using multi-nucleon transfer reactionsMakii, Hiroyuki; Ota, Shuya*; Ishii, Tetsuro; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Chiba, Satoshi; Igashira, Masayuki*; Czeszumska, A.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 797, p.83 - 93, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.26(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have installed new experimental apparatus to measure  rays from highly excited states populated by the multi-nucleon transfer reactions with heavy-ion projectiles to determine the (
rays from highly excited states populated by the multi-nucleon transfer reactions with heavy-ion projectiles to determine the ( ) cross sections by means of the surrogate reaction method. Apparatus consists of two anti-Compton LaBr
) cross sections by means of the surrogate reaction method. Apparatus consists of two anti-Compton LaBr (Ce) spectrometers to measure the
(Ce) spectrometers to measure the  rays and a Si
rays and a Si 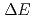 -
- detector system to detect outgoing projectile-like particles. Reactions of 153-MeV
detector system to detect outgoing projectile-like particles. Reactions of 153-MeV  O beams with
O beams with  Gd and
Gd and  Gd targets were used to study the performance of apparatus. By using the LaBr
Gd targets were used to study the performance of apparatus. By using the LaBr (Ce) scintillators with relatively large volume (101.6 mm in diameter and 127 mm in length), we have successfully measured
(Ce) scintillators with relatively large volume (101.6 mm in diameter and 127 mm in length), we have successfully measured  rays from the compound nuclei, which have excitation energy above neutron separation energy, populated by
rays from the compound nuclei, which have excitation energy above neutron separation energy, populated by  Gd(
Gd( O,
O,  O)
O) Gd and
Gd and  Gd(
Gd( O,
O,  O)
O)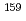 Gd two-neutron transfer reactions. The present study has demonstrated high capability of apparatus to measure the de-excitation
Gd two-neutron transfer reactions. The present study has demonstrated high capability of apparatus to measure the de-excitation  rays in the compound nuclei produced by the multi-nucleon transfer reactions for determination of the (
rays in the compound nuclei produced by the multi-nucleon transfer reactions for determination of the ( ) cross sections by using the surrogate reaction method.
) cross sections by using the surrogate reaction method.
Kureta, Masatoshi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Ozu, Akira; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Tsuchiya, Takahiro*; Seya, Michio; Harada, Hideo; Abousahl, S.*; Heyse, J.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of 37th ESARDA Annual Meeting (Internet), p.111 - 120, 2015/08
The JAEA has just started the new program "Development of active neutron NDA techniques" collaborating with EC-JRC. The final purpose of this program is to establish the measurement techniques for the high radioactive special nuclear material such as MA-Pu fuel for transmutation of minor actinide and for nuclear security applications. In this program, JAEA will conduct the R&D on active neutron non-destructive measurement techniques, DDA, NRTA, PGA/NRCA and DGS.
Kureta, Masatoshi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Ozu, Akira; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Seya, Michio
Proceedings of INMM 56th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/07
The new program "Development of active neutron NDA techniques" has started for non-proliferation applications. The final purpose of this program is to establish the measurement techniques for the high radioactive special nuclear material such as MA-Pu fuel for transmutation of minor actinide. In this program, the JAEA will conduct the R&D on active neutron non-destructive measurement techniques, DDA, NRTA, PGA/NRCA and DGS in collaboration with EC-JRC.
Maeda, Makoto; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kureta, Masatoshi; Ozu, Akira; Tobita, Hiroshi; Komeda, Masao; Hattori, Kentaro
Proceedings of INMM 56th Annual Meeting (Internet), 8 Pages, 2015/07
In Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), it has been started that investigation on applicability of Fast Neutron Direct Interrogation (FNDI) method to fuel debris. FNDI method is expected to be promising non-destructive Assay (NDA) technique which measures total amounts of fissile materials. In this presentation, we report on basic model of non-destructive measurement system designed by using Monte Carlo Code PHITS, the effect of the matrix in debris canister on FNDI method evaluated by using Monte Carlo Code MVP and four dimensional (4 D) visualization results of neutron flux obtained by using visualization tool we have newly developed.
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Takaki, Motonobu*; Miya, Hiroyuki*; Ota, Shinsuke*; Michimasa, Shinichiro*; Shimoura, Susumu*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 6, p.030005_1 - 030005_4, 2015/06