Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kitamura, Ryo; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Miyao, Tomoaki*
Proceedings of 21st Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.233 - 234, 2024/10
Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Tongu, Hiromu*; Hayano, Hitoshi*; Geng, R. L.*
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 19(9), p.P09037_1 - P09037_15, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Fuwa, Yasuhiro
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 34(5), p.4904504_1 - 4904504_4, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A permanent magnet can be used to generate an axisymmetric uniform magnetic field over a long distance. To satisfy Ampere's law, which states that the line-integral value of the magnetic field is zero, a magnetic field region of opposite polarity appears somewhere along the axis while maintaining uniformity in a certain range along the axis. Using this configuration, a magnetic field generator for a Faraday rotation device for laser light was fabricated. This device has a large bore of 30 mm in diameter to handle ultra-high-power lasers and can hold a large crystal disc for Faraday rotation. The irregularity in the central plane is less than 1% within the bore diameter. This configuration can also be applied to long axisymmetric beam transport magnets. This technique can be extended to control the gradient of the magnetic field distributions, such as the focusing field of a klystron.
Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Terunuma, Nobuhiro*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 34(5), p.4004005_1 - 4004005_5, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)We are developing a correction magnet for charged particle beams using permanent magnets. By rotating the rod of the permanent magnet that generates the magnetic field, the magnetic field can be changed to bipolarity. To verify the principle of this bi-polarity change, a prototype was built, and its performance was evaluated. The performance evaluation of the prototype machine revealed that the inhomogeneity of the remanent magnetization of the permanent magnet has a significant effect on the multipole component. To suppress this effect, a compensating magnet with additional anisotropic intermediate poles is being considered.
Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.531 - 534, 2023/11
In the J-PARC LINAC, the beam current and pulse width are being upgraded in order to increase the beam output power for the next decade. MEBT1 (Medium Energy Beam Transport 1) is located between the RFQ and the DTL to form an intermediate bunch structure for matching the transverse and longitudinal beams and for injection into the rapid cycling synchrotron in the later stage. Since the beam energy in MEBT1 section is low (3 MeV), the space-charge effect is expected to increase as the beam intensity increases. In this study, a new magnet has been designed and fabricated to suppress the beam loss caused by the space-charge effect. The new magnet is a combined-function magnet that can generate superimposed multipole components for beam focusing and space-charge effect compensation in a small space, and a permanent magnet is used to reduce the power consumption and the size of the equipment. In this presentation, the design of the magnet and its effect on beam dynamics will be discussed.
Ono, Ayato; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Horino, Koki*; Sugita, Moe; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Ikoma, Naoya*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.871 - 876, 2023/11
In J-PARC, an ignitron is used for the crowbar device of the klystron power supply to excite the RF acceleration voltage in a Linac cavity. Mercury, that is used in the ignitron, would be prohibition of use in the future due to environmental protection. Therefore, we designed a semiconductor crowbar switch for short-circuit protection of klystron using a MOS gate thyristor. We have manufactured an oval-type board module that realizes an operating output of 3kV, 40kA, and 50us per board. Because a high voltage of 120 kV is applied on each board, we adopted a self-power supply method to supply a electricity for the control system. This method can create the electricity from a high-voltage DCDC converter. We confirmed the operating performance on a 1/2 scale (60 kV, 40 kA) of the voltage in the existing ignitron system (120 kV, 40 kA). We also studied a test circuit in a higher voltage range of more than 90 kV. Our latest result is well promising for an alternative system of ignitron.
Kitamura, Ryo; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Ito, Daito*
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.280 - 281, 2023/11
In the J-PARC linac, an RF chopper produces a characteristic time structure in the beam bunch at the injection into the 3-GeV synchrotron. Incomplete chopped beam derived from the transient response of the RF chopper results in the beam loss. The investigation of the particle tracking and the countermeasure for the beam loss are reported using the particle-in-cell simulation.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Takahashi, Hiroki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Chimura, Motoki; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Hayashi, Naoki; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Sawabe, Yuki*; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro*
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.839 - 843, 2023/11
In the J -PARC 3GeV synchrotron accelerator (RCS), a new signal processing system for beam monitors is been developing to replace the existing system for the main beam monitors that monitor the stability of the accelerator: beam loss monitor, beam position monitor and beam current monitor. The new system will consist of a TAG server and an ADC module that can be used commonly for the three main monitors. The main design concepts of the new system are: (1) the TAG server divides various beam J-PARC tag information to each ADC module, (2) the ADC module converts acquisition data from beam monitors to digital signals by ADC and performs high-speed analysis by FPGA with switching analysis methods to suit each monitor, (3) the ADC module periodically outputs the analysis data with tag information by packing the signal processing data of all shots for about 10 seconds, and also outputs any one shot data on-demand, and (4) the raw waveform data, the latest four shots of FFT-related data in the process of analysis and bunch data for each cycle are stored in the internal memory of the ADC module, and the data can be read out as needed. In this presentation, we will report on the progress of the data acquisition test of tag information reading and beam monitor signals using the prototype under development.
Nakano, Hideto; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Mizobata, Satoshi*
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.577 - 578, 2023/11
In the J-PARC linac, klystrons are used as RF source. To improve the stability of RF power supply, the replacement of klystrons with semiconductor amplifiers is under consideration. Since the output of a semiconductor amplifier is relatively small, klystrons were installed in high power sections. Progresses of semiconductor production technology have allowed to manufacture semiconductor amplifiers that are expected be practical use. In the J-PARC linac, the installation in a debuncher 2 cavity with relatively small output power is planed. Characteristics test of a prototype semiconductor amplifier were conducted before full scale installation.
Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Ono, Ayato; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Horino, Koki*; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Sugita, Moe; Yamamoto, Kazami; Oguri, Hidetomo; Kinsho, Michikazu; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.242 - 246, 2023/01
At J-PARC, semiconductor short pulse power supplies to replace kicker power supplies and semiconductor long pulse power supplies to replace klystron power supply systems are under construction. We have fabricated a 40kV/2kA/1.2 s unit power supply that employs a linear transformer drivers (LTD) system for kickers. Currently, we are working on a high voltage insulating cylinder insulator that suppresses corona discharges using only the insulator structure, without using insulating oil. In addition, the MARX system was adopted for klystron power supply system. A main circuit unit for 8kV/60A/830
s unit power supply that employs a linear transformer drivers (LTD) system for kickers. Currently, we are working on a high voltage insulating cylinder insulator that suppresses corona discharges using only the insulator structure, without using insulating oil. In addition, the MARX system was adopted for klystron power supply system. A main circuit unit for 8kV/60A/830 s rectangular pulse output and an 800V/60A correction circuit unit that improves the flat top droop from 10% to 1% were manufactured. Furthermore, a 2.2kV/2.4kW high voltage SiC inverter charger has been fabricated for this MARX power supply. The presentation will report the evaluation results of each test and prospects for semiconductor pulse power supplies.
s rectangular pulse output and an 800V/60A correction circuit unit that improves the flat top droop from 10% to 1% were manufactured. Furthermore, a 2.2kV/2.4kW high voltage SiC inverter charger has been fabricated for this MARX power supply. The presentation will report the evaluation results of each test and prospects for semiconductor pulse power supplies.
Ono, Ayato; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Horino, Koki*; Sugita, Moe; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Ikoma, Naoya*; et al.
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.395 - 399, 2023/01
At J-PARC, an ignitron is used for the crowbar device of the klystron power supply for high-frequency acceleration of a linear accelerator. Ignitron uses mercury, which is of limited use worldwide, and is expected to be discontinued in the future. Therefore, we designed a semiconductor crowbar switch for short-circuit protection of klystron using a MOS gate thyristor. We have manufactured an oval-type board module that realizes an operating output of 3 kV, 40 kA, and 50  s per board. For the control power supply to each board module assuming a high voltage of 120 kV, we adopted a self-power supply method that creates a control power supply with a high-voltage DCDC converter from the voltage shared and charged by each board module. It was possible to confirm the operating performance on a 1/2 scale (60 kV, 40 kA) against the voltage of the existing equipment (120 kV, 40 kA) by connecting twenty oval board modules in series. The output test result will be reported.
s per board. For the control power supply to each board module assuming a high voltage of 120 kV, we adopted a self-power supply method that creates a control power supply with a high-voltage DCDC converter from the voltage shared and charged by each board module. It was possible to confirm the operating performance on a 1/2 scale (60 kV, 40 kA) against the voltage of the existing equipment (120 kV, 40 kA) by connecting twenty oval board modules in series. The output test result will be reported.
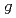 -2 and electric dipole moment experiment
-2 and electric dipole moment experimentNakazawa, Yuga*; Cicek, E.*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Hayashizaki, Noriyosu*; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Iwata, Yoshiyuki*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Mibe, Tsutomu*; et al.
Physical Review Accelerators and Beams (Internet), 25(11), p.110101_1 - 110101_9, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:43.00(Physics, Nuclear)We conducted a high-power test of a prototype cavity of a 324-MHz interdigital H-mode drift tube linac (IH-DTL) for the precise measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic moment (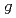 -2) and electric dipole moment (EDM). This prototype cavity (short IH) was developed to verify the fabrication methodology for the IH-DTL cavity with a monolithic drift tube structure. The electromagnetic field distribution was measured and compared with the finite element method simulation results, and the fabrication accuracy of the monolithic drift tube was confirmed to satisfy the requirements. After 40 h of conditioning, the short IH was stably operated with an rf power of 88 kW, which corresponds to a 10% higher accelerating field than the design field (E0) of 3.0 MV/m. In addition, the thermal characteristics and frequency response were measured, verifying that the experimental data were consistent with the three-dimensional model. In this paper, the design, fabrication, and low-power and high-power tests of this IH-DTL for muon acceleration are described.
-2) and electric dipole moment (EDM). This prototype cavity (short IH) was developed to verify the fabrication methodology for the IH-DTL cavity with a monolithic drift tube structure. The electromagnetic field distribution was measured and compared with the finite element method simulation results, and the fabrication accuracy of the monolithic drift tube was confirmed to satisfy the requirements. After 40 h of conditioning, the short IH was stably operated with an rf power of 88 kW, which corresponds to a 10% higher accelerating field than the design field (E0) of 3.0 MV/m. In addition, the thermal characteristics and frequency response were measured, verifying that the experimental data were consistent with the three-dimensional model. In this paper, the design, fabrication, and low-power and high-power tests of this IH-DTL for muon acceleration are described.
Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 32(6), p.4006705_1 - 4006705_5, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.40(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Space charge compensation technique using multipole magnetic field components has been proposed to transport high intensity beam in the J-PARC linac. In order to realize this compensation technique, a compact size permanent hybrid multi-pole magnet would be suitable. A magnet system for the simultaneous production of quadrupole and adjustable octupole components using permanent magnet materials and have manufactured a first model of the magnet systems.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Otani, Masashi*; Cicek, E.*; Ego, Hiroyasu*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; et al.
Proceedings of 31st International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2022) (Internet), p.636 - 641, 2022/09
The muon linac project for the precise measurement of the muon anomalous magnetic and electric dipole moments, which is currently one of the hottest issues of the elementary particle physics, is in progress at J-PARC. The muons from the J-PARC muon facility are once cooled to room temperature, then accelerated up to 212 MeV with a normalized emittance of 1.5  mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
mm mrad and a momentum spread of 0.1%. Four types of accelerating structures are adopted to obtain the efficient acceleration with a wide beta range from 0.01 to 0.94. The project is moving into the construction phase. We already demonstrated the re-acceleration scheme of the decelerated muons using a 324-MHz RFQ in 2017. The high-power test of the 324-MHz Interdigital H-mode (IH) DTL using a prototype cavity was performed in 2021. The fabrication of the first module of 14 modules of the 1296-MHz Disk and Washer (DAW) CCL will be done to confirm the production process. Moreover, the final design of the travelling wave accelerating structure for the high beta region is also proceeding. In this paper, the recent progress toward the realization of the world first muon linac will be presented.
Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro
Proceedings of 31st International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2022) (Internet), p.364 - 367, 2022/09
MEBT1 (Medium Energy Beam Transport 1) of the J-PARC LINAC is a 3 MeV beam transport system located between the RFQ (Radio Frequency Quadrupole) and DTL (Drift Tube Linac). In the MEBT1, the beam-optical matching for injection into DLT and chopping for injection into acceleration phase of 3 GeV synchrotron, located downstream to the LINAC, are performed. The characteristics of MEBT1 are an important factor in determining the beam quality in the J-PARC accelerator facility. To achieve beam power of 1 MW and beyond, improving the stability and reliability of MEBT1 is an important development issue. The application of permanent magnets to the beam focusing system to the MEBT1 is under consideration to achieve improved stability and reliability. In this presentation, we report the design of focusing magnets using permanent magnet material and the results of the lattice study of MEBT1 with permanent magnets.
Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Kondo, Akihiro*
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 32(6), p.4007304_1 - 4007304_4, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)High-field magnets are often demanded advanced scientific studies. Although a hybrid coil design comprising Nb-Ti, Nb Sn, and HTS (High-Temperature Superconductors) are potential candidates for such application, the costs of Nb
Sn, and HTS (High-Temperature Superconductors) are potential candidates for such application, the costs of Nb Sn and HTS are expensive compared with Nb-Ti. By generating an additional field of about 1 T by permanent magnets, the required amounts of superconducting material may be reduced. Magnetic properties of some magnetic materials have been studied by other works at temperatures as low as 100 K. The remanent field of conventional NdFeB magnets decreases at 100 K due to spin reorientation. PrFeB magnets consisting of praseodymium (Pr) instead of neodymium (Nd) do not show such degradation and the coercivity of PrFeB at 100 K is 7 T. In this study, the B-H curve, as a primary magnetic property, of a PrFeB magnet sample was measured in the temperature range down to 4 K. As a result, no decrease in magnetization of the praseodymium magnets, and the coercivity was 10 T.
Sn and HTS are expensive compared with Nb-Ti. By generating an additional field of about 1 T by permanent magnets, the required amounts of superconducting material may be reduced. Magnetic properties of some magnetic materials have been studied by other works at temperatures as low as 100 K. The remanent field of conventional NdFeB magnets decreases at 100 K due to spin reorientation. PrFeB magnets consisting of praseodymium (Pr) instead of neodymium (Nd) do not show such degradation and the coercivity of PrFeB at 100 K is 7 T. In this study, the B-H curve, as a primary magnetic property, of a PrFeB magnet sample was measured in the temperature range down to 4 K. As a result, no decrease in magnetization of the praseodymium magnets, and the coercivity was 10 T.
Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Tongu, Hiromu*; Hayano, Hitoshi*; Geng, R. L.*
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on RF Superconductivity (SRF 2021) (Internet), p.323 - 325, 2022/05
In order to evaluate the performance of a superconducting cavity, we are developing a mapping system to measure the distribution of cavity temperature, field emission X-rays, and trapped magnetic flux with high positional resolution. In order to construct a system with high positional resolution, a large number of sensors are required. However, as the number of sensors increases, so does the amount of wiring, which increases the complexity of the wiring in the cryogenic apparatus, and also increases the heat transfer through the wiring, which disturb efficient operation of cavity tests. We are developing an efficient mapping system with a multiplexer that scans the readout signal on the same circuit as the sensor in the cryogenic dewar where the cavity test is conducted. In this presentation, we report the outline and test results of the mapping system under development
Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Ono, Ayato; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Mizobata, Satoshi*; Fang, Z.*
Proceedings of 17th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.780 - 782, 2020/09
In the J-PARC linac, High Voltage DC power supplies (HVDC) to drive klystrons. These HVDCs are modulating-anode power supplies with a rated voltage of 110 kV and are operated by connecting up to four klystrons to a single HVDC. Since multiple klystrons are driven by a single HVDC, a voltage droop in the capacitor bank of the HVDC occurs in the beam pulse. This effect causes a decrease in the output power of the klystron. Half of the existing HVDC in J-PARC were installed at the J-PARC construction, and the other half were installed at the LINAC 400 MeV upgrade, and the capacitors show signs of age-related degradation. In the near future, the capacitors will be necessary to be replaced partially or completely. On the replacement of the capacitors, it will be necessary to re-evaluate the operating behavior of the HVDC when the capacitor bank configuration is changed. In this presentation, we evaluated the effect of the voltage droop on the klystron with the present configuration and the effect of changing the capacitor bank configuration with numerical and experimental results, and we discussed the countermeasure for the stable beam operation.
Yako, Tomoki*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Abe, Masashi*; Kurihara, Toshikazu*; Fukuda, Masafumi*; Sato, Masaharu*; Sugimura, Takashi*; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Takamiya, Koichi*; Iinuma, Yuto*
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1003 - 1005, 2019/10
Permanent magnets are used as materials for beam optics elements, but it is known that radiation demagnetization occurs in neodymium magnets and samarium cobalt magnets. However, there is not enough information on the radiation demagnetization of ferrite magnets which is weak in strength but inexpensive. In order to verify the suitability of the ferrite magnet as a beam optics element, radiation demagnetization experiments by neutron irradiation of the ferrite magnet were carried out at the Kyoto University Research Reactor (KUR). In the experiment, neutron fluence up to 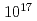 cm
cm was irradiated, and no significant demagnetization was detected on the fluence.
was irradiated, and no significant demagnetization was detected on the fluence.
Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirane, Tatsuya; Fang, Z.*; Fukui, Yuji*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Mizobata, Satoshi*; Iwama, Yuhei*; Sato, Yoshikatsu*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.611 - 613, 2019/10
In the J-PARC linac, a proton accelerator is operated using 45 units of 324 MHz and 972 MHz klystrons. In the future stabilization and advancement of the accelerator, it is important to acquire the klystron output characteristics near the maximum output accurately. In order to understand this characteristics, measurement of the characteristics of the replaced klystron for some reason such as discharge, as well as the new klystron. However, such measurements have not been performed because of the risk of damage including peripheral equipment due to discharge and the temporal interference with the operation of the accelerator. Therefore, we set up a klystron test stand in the linac building and measured the high-voltage characteristics and input/output characteristics of the klystron under various operating parameters. By using this measurement result, the characteristics of klystron can be obtained before installation, and it becomes possible to determine the optimum operation parameters and make effective plan of klystron replacements. In addition, basic data for predicting the degradation tendency of klystron was acquired by comparing the characteristics of the used and used klystron.