Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanaka, Taiki*; Narikiyo, Yoshihiro*; Morita, Kosuke*; Fujita, Kunihiro*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Yamaki, Sayaka*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Tanaka, Kengo*; Takeyama, Mirei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_9, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:75.18(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Excitation functions of quasielastic scattering cross sections for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb,
Pb,  Ti +
Ti +  Pb, and
Pb, and  Ca +
Ca +  Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the
Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb and
Pb and  Ti +
Ti +  Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the
Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
 No
NoLopez-Martens, A.*; Henning, G.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Alcorta, M.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Bertone, P. F.*; Boilley, D.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.03001_1 - 03001_6, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:42.06(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Fission barrier height and its angular-momentum dependence have been measured for the first time in the nucleus with the atomic number greater than 100. The entry distribution method, which can determine the excitation energy at which fission starts to dominate the decay process, was applied to  No. The fission barrier of
No. The fission barrier of  No was found to be 6.6 MeV at zero spin, indicating that the
No was found to be 6.6 MeV at zero spin, indicating that the  No is strongly stabilized by the nuclear shell effects.
No is strongly stabilized by the nuclear shell effects.
 No and
No and 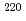 Th
ThHenning, G.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Lopez-Martens, A.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Alcorta, M.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Bertone, P. F.*; Boilley, D.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 113(26), p.262505_1 - 262505_6, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:81.81(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Fission barrier heights of a shell-stabilized superheavy nucleus  No have been determined as a function of spin up to 19
No have been determined as a function of spin up to 19 through the measured distribution of entry points of
through the measured distribution of entry points of  deexcitations in the excitation energy vs. spin plane. The fission barrier height of
deexcitations in the excitation energy vs. spin plane. The fission barrier height of  No was determined to be 6.0 MeV at spin 15
No was determined to be 6.0 MeV at spin 15 , and 6.6 MeV at spin 0
, and 6.6 MeV at spin 0 by extrapolation. This demonstrates that the shell effect actually enlarges the fission barrier in such heavy nuclei and keeps the barrier high even at high spin.
by extrapolation. This demonstrates that the shell effect actually enlarges the fission barrier in such heavy nuclei and keeps the barrier high even at high spin.
 No
NoHenning, G.*; Lopez-Martens, A.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Alcorta, M.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Bertone, P. F.*; Boilley, D.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 66, p.02046_1 - 02046_8, 2014/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.16(Physics, Nuclear)Fission barrier heights of  No have been determined through the entry distribution method. The entry distribution is the initial distribution of excitation energy and spin from which the
No have been determined through the entry distribution method. The entry distribution is the initial distribution of excitation energy and spin from which the  deexcitation starts in the fusion-evaporation reaction. The initial distribution is extracted from measured
deexcitation starts in the fusion-evaporation reaction. The initial distribution is extracted from measured  -ray multiplicity and total
-ray multiplicity and total  -ray energy. This paper describes the details of the entry distribution method, and reports the first determination of the fission barrier heights of
-ray energy. This paper describes the details of the entry distribution method, and reports the first determination of the fission barrier heights of  No, which is the heaviest nucleus whose fission barrier has been measured.
No, which is the heaviest nucleus whose fission barrier has been measured.
 -ray spectroscopy of a superheavy element; The
-ray spectroscopy of a superheavy element; The  Rf
RfRubert, J.*; Dorvaux, O.*; Gall, B. J. P.*; Greenlees, P. T.*; Asfari, Z.*; Piot, J.*; Andersson, L. L.*; Asai, Masato; Cox, D. M.*; Dechery, F.*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 420, p.012010_1 - 012010_10, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)The first prompt in-beam  -ray spectroscopy of a superheavy element,
-ray spectroscopy of a superheavy element,  Rf, has been performed successfully. A development of an intense isotopically enriched
Rf, has been performed successfully. A development of an intense isotopically enriched  Ti beam using the MIVOC method enabled us to perform this experiment. A rotational band up to a spin of 20
Ti beam using the MIVOC method enabled us to perform this experiment. A rotational band up to a spin of 20  has been discovered in
has been discovered in  Rf, and its moment of inertia has been extracted. These data suggest that there is no evidence of a significant deformed shell gap at
Rf, and its moment of inertia has been extracted. These data suggest that there is no evidence of a significant deformed shell gap at  = 104.
= 104.
 =104 nucleus
=104 nucleus  Rf
RfGreenlees, P. T.*; Rubert, J.*; Piot, J.*; Gall, B. J. P.*; Andersson, L. L.*; Asai, Masato; Asfari, Z.*; Cox, D. M.*; Dechery, F.*; Dorvaux, O.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 109(1), p.012501_1 - 012501_5, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:62 Percentile:88.45(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Rotational band structure of the  =104 nucleus
=104 nucleus  Rf has been observed for the first time using an in-beam
Rf has been observed for the first time using an in-beam  -ray spectroscopic technique. This nucleus is the heaviest among the nuclei whose rotational band structure has ever been observed. Thus, the present result provides valuable information on the single-particle shell structure and pairing interaction in the heaviest extreme of nuclei. The deduced moment of inertia indicates that there is no deformed shell gap at
-ray spectroscopic technique. This nucleus is the heaviest among the nuclei whose rotational band structure has ever been observed. Thus, the present result provides valuable information on the single-particle shell structure and pairing interaction in the heaviest extreme of nuclei. The deduced moment of inertia indicates that there is no deformed shell gap at  =104, which is predicted in a number of current self-consistent mean-field models.
=104, which is predicted in a number of current self-consistent mean-field models.
Hidaka, Hiroshi*; Kagami, Saya; Bentridi, S.*; Gall, B.*
no journal, ,
It is known that 16 parts (called as reactor zones, hereafter RZs) of the Oklo uranium deposit in the Republic of Gabon, central Africa, functioned as natural fission reactors around two billion years ago. Isotopic data sets of several elements, particularly rare earth elements (REEs) and noble gases, of the Oklo RZs materials, show the results caused by a combination of nuclear fission, neutron captures, and radioactive decays and provide useful information on the determination of nuclear parameters during the reactor criticality, construction of the model for the reactor criticality by numerical simulation, evaluation of geochemical behaviours of fission products in geological media, and so on. In this study, two kinds of the Oklo reactor materials collected from RZs 13 and 16 were used. We are now planning to determine the isotopic compositions of REEs and Hf of the Oklo reactor materials by TIMS and/or MC-ICP-MS to reconstruct the energy spectra of neutrons generated in the RZs.
Hidaka, Hiroshi*; Saito, Takaharu*; Hashiguchi, Minako*; Kagami, Saya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Gall, B.*
no journal, ,
It is known that 16 parts (called as reactor zones, hereafter RZs) of the Oklo uranium deposit in the Republic of Gabon, central Africa, functioned as natural fission reactors around two billion years ago. Many elements of the Oklo RZs materials show variations in their isotopic compositions caused by a combination of nuclear fission, neutron captures, and radioactive decays. Isotopic data sets of several elements, particularly rare earth elements (REEs), of the Oklo RZs materials provide useful information on the determination of nuclear parameters during the reactor criticality, construction of the model for the reactor criticality by numerical simulation, evaluation of geochemical behaviours of fission products in geological media, and so on. In this study, two kinds of the Oklo reactor materials collected from RZs 13 and 16 were used. The isotopic compositions of Sm, Gd, Er, Yb and Hf of the Oklo reactor materials were newly determined by TIMS and/or MC-ICP-MS. We are now planning to combine the data from several REE and Hf isotopes to reconstruct the energy spectra of neutrons generated in the RZs.