Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Gao, S.*; Ito, Tatsuya; Yamashita, Takayuki*; Harjo, S.; Zhao, L.*; Wang, Q.*
Scripta Materialia, 264, p.116726_1 - 116726_6, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Go, J.*; Park, M.-H.*; Gao, S.*; Matsumiya, Hisashi*; Gong, W.; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 1014, p.178749_1 - 178749_10, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:95.66(Chemistry, Physical)Xu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Liang, S.*; Zhang, J.*; Fei, Y.*; Wang, Y.*; Gao, D.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Dong, X.*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), p.2445 - 2451, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)The Alder-ene reaction is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen, and it provides an efficient method to construct the C-C bond. Traditionally, this reaction requires catalysts, high temperatures, or photocatalysis. In this study, we reported a high-pressure-induced solid-state Alder-ene reaction of 1-hexene at room temperature without a catalyst. 1-Hexene crystallizes at 4.3 GPa and polymerizes at 18 GPa, forming olefins. By exploring gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, we discovered that 1-hexene generates dimeric products through the Alder-ene reaction under high pressures. The in situ neutron diffraction shows that the reaction process did not obey the topochemical rule. A six-membered ring transition state including one C-H  bond and two alkene
bond and two alkene  bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
Mao, W.*; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Ito, Tatsuya; Harjo, S.; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 278, p.120233_1 - 120233_13, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:96.74(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) neutron diffraction revealing the achievement of excellent combination of strength and ductility in metastable austenitic steel by grain refinement
neutron diffraction revealing the achievement of excellent combination of strength and ductility in metastable austenitic steel by grain refinementMao, W.; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Morooka, Satoshi; Gao, S.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 176, p.69 - 82, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:59.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The yield stress of Fe-24Ni-0.3C (wt.%) metastable austenitic steel increased 3.5 times (158  551 MPa) when the average grain size decreased from 35
551 MPa) when the average grain size decreased from 35  m (coarse-grained [CG]) to 0.5
m (coarse-grained [CG]) to 0.5  m (ultrafine-grained [UFG]), whereas the tensile elongation was kept large (0.87
m (ultrafine-grained [UFG]), whereas the tensile elongation was kept large (0.87  0.82).
0.82).  neutron diffraction measurements of the CG and UFG Fe-24Ni-0.3C steels were performed during tensile deformation at room temperature to quantitatively elucidate the influence of grain size on the mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms. The initial stages of plastic deformation in the CG and UFG samples were dominated by dislocation slip, with deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT) also occurring in the later stage of deformation. Results show that grain refinement increases the initiation stress of DIMT largely and suppresses the rate of DIMT concerning the strain, which is attributed to the following effects. (i) Grain refinement increased the stabilization of austenite and considerably delayed the initiation of DIMT in the
neutron diffraction measurements of the CG and UFG Fe-24Ni-0.3C steels were performed during tensile deformation at room temperature to quantitatively elucidate the influence of grain size on the mechanical properties and deformation mechanisms. The initial stages of plastic deformation in the CG and UFG samples were dominated by dislocation slip, with deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT) also occurring in the later stage of deformation. Results show that grain refinement increases the initiation stress of DIMT largely and suppresses the rate of DIMT concerning the strain, which is attributed to the following effects. (i) Grain refinement increased the stabilization of austenite and considerably delayed the initiation of DIMT in the  111
111 //LD (LD: loading direction) austenite grains, which were the most stable grains for DIMT. As a result, most of the
//LD (LD: loading direction) austenite grains, which were the most stable grains for DIMT. As a result, most of the  111
111 //LD austenite grains in the UFG specimens failed to transform into martensite. (ii) Grain refinement also suppressed the autocatalytic effect of the martensitic transformation. Nevertheless, the DIMT with the low transformation rate in the UFG specimen was more efficient in increasing the flow stress and more appropriate to maintain uniform deformation than that in the CG specimen during deformation. The above phenomena mutually contributed to the excellent combination of strength and ductility of the UFG metastable austenitic steel.
//LD austenite grains in the UFG specimens failed to transform into martensite. (ii) Grain refinement also suppressed the autocatalytic effect of the martensitic transformation. Nevertheless, the DIMT with the low transformation rate in the UFG specimen was more efficient in increasing the flow stress and more appropriate to maintain uniform deformation than that in the CG specimen during deformation. The above phenomena mutually contributed to the excellent combination of strength and ductility of the UFG metastable austenitic steel.
 Be ground-state molecular structure using
Be ground-state molecular structure using  Be(
Be(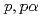 )
) He triple differential reaction cross-section measurements
He triple differential reaction cross-section measurementsLi, P. J.*; Beaumel, D.*; Lee, J.*; Assi , M.*; Chen, S.*; Franchoo, S.*; Gibelin, J.*; Hammache, F.*; Harada, T.*; Kanada-En'yo, Yoshiko*; et al.
, M.*; Chen, S.*; Franchoo, S.*; Gibelin, J.*; Hammache, F.*; Harada, T.*; Kanada-En'yo, Yoshiko*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 131(21), p.212501_1 - 212501_7, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:94.59(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The cluster structure of the neutron-rich isotope  Be has been probed via the (
Be has been probed via the (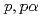 ) reaction. The triple differential cross-section was extracted and compared to distorted-wave impulse approximation reaction calculations performed in a microscopic framework using the Tohsaki-Horiuchi-Schuck-R
) reaction. The triple differential cross-section was extracted and compared to distorted-wave impulse approximation reaction calculations performed in a microscopic framework using the Tohsaki-Horiuchi-Schuck-R pke wave function and the wave function deduced from Antisymmetrized Molecular Dynamics calculations. The remarkable agreement between calculated and measured cross-sections in both shape and magnitude validates the description of the
pke wave function and the wave function deduced from Antisymmetrized Molecular Dynamics calculations. The remarkable agreement between calculated and measured cross-sections in both shape and magnitude validates the description of the  Be ground-state as a rather compact nuclear molecule.
Be ground-state as a rather compact nuclear molecule.
 ders band deformation in an ultrafine grain stainless steel by combining
ders band deformation in an ultrafine grain stainless steel by combining  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation analysis
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation analysisMao, W.; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Scripta Materialia, 235, p.115642_1 - 115642_6, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:86.78(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)In the present study, a hybrid  neutron diffraction and digital image correlation measurement was performed on tensile deformation of an ultrafine grain (UFG) stainless steel exhibiting a huge L
neutron diffraction and digital image correlation measurement was performed on tensile deformation of an ultrafine grain (UFG) stainless steel exhibiting a huge L ders band deformation to evaluate the individual contribution of the austenite matrix and the deformation-induced martensite to the strain hardening during the propagation of the band. Quantitative analysis revealed that the strain hardening of the austenite matrix was insufficient to maintain a uniform deformation when the flow stress was greatly enhanced by the UFG structure. The strain hardening required for the L
ders band deformation to evaluate the individual contribution of the austenite matrix and the deformation-induced martensite to the strain hardening during the propagation of the band. Quantitative analysis revealed that the strain hardening of the austenite matrix was insufficient to maintain a uniform deformation when the flow stress was greatly enhanced by the UFG structure. The strain hardening required for the L ders band to propagate was mostly provided by the formation of martensite and the high internal stress within it.
ders band to propagate was mostly provided by the formation of martensite and the high internal stress within it.
Mao, W.; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Bai, Y.*; Harjo, S.; Park, M.-H.*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 256, p.119139_1 - 119139_16, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:98.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP)-assisted steels exhibit an excellent combination of strength and ductility due to enhanced strain hardening rate associated with deformation-induced martensitic transformation (DIMT). Quantitative evaluation on the role of DIMT in strain hardening behavior of TRIP-assisted steels and alloys can provide guidance for designing advanced materials with strength and ductility synergy, which is, however, difficult since the phase composition keeps changing and both stress and plastic strain are dynamically partitioned among constituent phases during deformation. In the present study, tensile deformation with  neutron diffraction measurement was performed on an Fe-24Ni-0.3C (wt.%) TRIP-assisted austenitic steel. The analysis method based on stress partitioning and phase fractions measured by neutron diffraction was proposed, by which the tensile flow stress and the strain hardening rate of the specimen were resolved into factors associated with each phase, i.e., the austenite matrix, deformation-induced martensite, and the transformation rate of DIMT after differentiation, and then the role of each factor in the global strain hardening behavior was discussed. In addition, the plastic strain partitioning between austenite and martensite was indirectly estimated using the dislocation density measured by diffraction profile analysis, which constructed the full picture of stress and strain partitioning between austenite and martensite in the material. The results suggested that both the transformation rate and the phase stress borne by the deformation-induced martensite played important roles in the global tensile properties of the material. The proposed decomposition analysis method could be widely applied to investigating mechanical behavior of multi-phase alloys exhibiting the TRIP phenomenon.
neutron diffraction measurement was performed on an Fe-24Ni-0.3C (wt.%) TRIP-assisted austenitic steel. The analysis method based on stress partitioning and phase fractions measured by neutron diffraction was proposed, by which the tensile flow stress and the strain hardening rate of the specimen were resolved into factors associated with each phase, i.e., the austenite matrix, deformation-induced martensite, and the transformation rate of DIMT after differentiation, and then the role of each factor in the global strain hardening behavior was discussed. In addition, the plastic strain partitioning between austenite and martensite was indirectly estimated using the dislocation density measured by diffraction profile analysis, which constructed the full picture of stress and strain partitioning between austenite and martensite in the material. The results suggested that both the transformation rate and the phase stress borne by the deformation-induced martensite played important roles in the global tensile properties of the material. The proposed decomposition analysis method could be widely applied to investigating mechanical behavior of multi-phase alloys exhibiting the TRIP phenomenon.
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:93.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary) 100 MeV/nucleon
100 MeV/nucleonPohl, T.*; Sun, Y. L.*; Obertelli, A.*; Lee, J.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Cai, B. S.*; Yuan, C. X.*; Brown, B. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 130(17), p.172501_1 - 172501_8, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:87.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We report on the first proton-induced single proton- and neutron-removal reactions from the neutron deficient  O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at
O nucleus with large Fermi-surface asymmetry at  100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
100 MeV/nucleon. Our results provide the first quantitative contributions of multiple reaction mechanisms including the quasifree knockout, inelastic scattering, and nucleon transfer processes. It is shown that the inelastic scattering and nucleon transfer, usually neglected at such energy regime, contribute about 50% and 30% to the loosely bound proton and deeply bound neutron removal, respectively.
Chen, J.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Zhang, J.*; Ma, J.*; Wang, H.*; Sun, Y.*; Chen, M.*; Liu, S.*; Gao, P.*; Yu, D.*; et al.
Physical Review Applied (Internet), 19(2), p.024046_1 - 024046_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:62.75(Physics, Applied) isomers in
isomers in  Cf
CfOrlandi, R.; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sato, Tetsuya; Ito, Yuta; Suzaki, Fumi; Nagame, Yuichiro*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064301_1 - 064301_11, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:52.14(Physics, Nuclear) neutron diffraction and electron microscopy study
neutron diffraction and electron microscopy studyZheng, R.*; Gong, W.; Du, J.-P.*; Gao, S.*; Liu, M.*; Li, G.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Ma, C.*; Ogata, Shigenobu*; et al.
Acta Materialia, 238, p.118243_1 - 118243_15, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:97.03(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Brumm, S.*; Gabrielli, F.*; Sanchez-Espinoza, V.*; Groudev, P.*; Ou, P.*; Zhang, W.*; Malkhasyan, A.*; Bocanegra, R.*; Herranz, L. E.*; Berda , M.*; et al.
, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th European Review Meeting on Severe Accident Research (ERMSAR 2022) (Internet), 13 Pages, 2022/05
Liu, M.*; Gong, W.; Zheng, R.*; Li, J.*; Zhang, Z.*; Gao, S.*; Ma, C.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 226, p.117629_1 - 117629_13, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:85 Percentile:99.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Mao, W.; Gao, S.*; Bai, Y.*; Park, M.-H.*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 17, p.2690 - 2700, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:80.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Metastable austenitic steels having ultrafine grained (UFG) microstructures can be fabricated by conventional cold rolling and annealing processes by utilizing the deformation-induced martensitic transformation during cold rolling and its reverse transformation to austenite upon annealing. However, such processes are not applicable when the austenite has high mechanical stability against deformation-induced martensitic transformation, since there is no sufficient amount of martensite formed during cold rolling. In the present study, a two-step cold rolling and annealing process was applied to an Fe-24Ni-0.3C metastable austenitic steel having high mechanical stability. Prior to the cold rolling, a repetitive subzero treatment and reverse annealing treatment were applied. Such a treatment dramatically decreased the mechanical stability of the austenite and greatly accelerated the formation of deformation-induced martensite during the following cold rolling processes. As a result, the grain refinement was significantly promoted, and a fully recrystallized specimen with a mean austenite grain size of 0.5 mm was successfully fabricated, which exhibited both high strength and high ductility.
Tremsin, A. S.*; Gao, Y.*; Makinde, A.*; Bilheux, H. Z.*; Bilheux, J. C.*; An, K.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Oikawa, Kenichi
Additive Manufacturing, 46, p.102130_1 - 102130_20, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:60.07(Engineering, Manufacturing) Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the
Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the  Fe nucleosynthesis
Fe nucleosynthesisYan, S. Q.*; Li, X. Y.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Lugaro, M.*; Li, Z. H.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Pignatari, M.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Orlandi, R.; Hirose, Kentaro; et al.
Astrophysical Journal, 919(2), p.84_1 - 84_7, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.27(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Tremsin, A. S.*; Bilheux, H. Z.*; Bilheux, J. C.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Oikawa, Kenichi; Gao, Y.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1009, p.165493_1 - 165493_12, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.33(Instruments & Instrumentation)Harjo, S.; Kubota, Satoru*; Gong, W.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Gao, S.*
Acta Materialia, 196, p.584 - 594, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:58.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)