Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ide, Shunsuke; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Isayama, Akihiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Yoshida, Maiko; Gormezano, C.*
Nuclear Fusion, 47(11), p.1499 - 1505, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:31.06(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Impact of the electron cyclotron range of frequency wave (ECRF) on the internal transport barriers (ITBs) in a weak shear (WS) plasma has been investigated in JT-60U. It is observed that the ion temperature (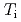 ) ITB in a WS plasma can be degraded by ECRF. It is clarified for the first time that the degradation depends increasingly on the EC power (
) ITB in a WS plasma can be degraded by ECRF. It is clarified for the first time that the degradation depends increasingly on the EC power (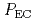 ) but decreasingly on the plasma current (
) but decreasingly on the plasma current (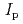 ). Moreover it is confirmed that ECRF affects the toroidal rotation (
). Moreover it is confirmed that ECRF affects the toroidal rotation (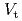 ) indirectly and results in flattening of
) indirectly and results in flattening of 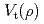 profiles regardless of the direction of the target
profiles regardless of the direction of the target 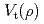 . Furthermore, it is newly found that
. Furthermore, it is newly found that 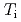 and
and 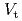 in the whole ITB region are affected with almost no delay from the EC onset even with off-axis EC deposition. These results indicate that the EC injection unveiled a semi-global structure that characterizes
in the whole ITB region are affected with almost no delay from the EC onset even with off-axis EC deposition. These results indicate that the EC injection unveiled a semi-global structure that characterizes 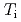 ITB in a WS plasma.
ITB in a WS plasma.
Oyama, Naoyuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Koide, Yoshihiko; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ide, Shunsuke; Nakano, Tomohide; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Hirotaka; Takechi, Manabu; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(7), p.689 - 697, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:48.26(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)After the installation of FSTs in JT-60U, ripple induced fast ion losses have been reduced by 1/2 1/3. The increase in the absorbed power at the same injection power can reduce the required number of NB units to sustain a given
1/3. The increase in the absorbed power at the same injection power can reduce the required number of NB units to sustain a given 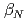 . The smaller recycling level and edge density, which is suitable condition to get higher edge temperature, can be kept longer. The higher edge temperature is essential in keeping the peaked pressure/temperature profile. In addition to this, smaller fast ion losses reduce the effective torque for ctr-rotation and increase in better flexibility of torque input. Then, better quality of
. The smaller recycling level and edge density, which is suitable condition to get higher edge temperature, can be kept longer. The higher edge temperature is essential in keeping the peaked pressure/temperature profile. In addition to this, smaller fast ion losses reduce the effective torque for ctr-rotation and increase in better flexibility of torque input. Then, better quality of  -ITB was obtained in the plasmas with co-rotation. By making use of these advantages to sustain an ITB, the performance of long-pulse ELMy H-mode plasmas was improved in terms of sustained duration time for both high
-ITB was obtained in the plasmas with co-rotation. By making use of these advantages to sustain an ITB, the performance of long-pulse ELMy H-mode plasmas was improved in terms of sustained duration time for both high 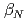 and high thermal confinement enhancement factor (
and high thermal confinement enhancement factor (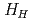 ). High
). High 

 2.3 together with
2.3 together with 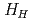
 1 was sustained for 23.1s (
1 was sustained for 23.1s (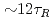 , where
, where 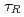 is the current diffusion time.), which also provide high
is the current diffusion time.), which also provide high 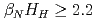 . These long-pulse plasmas are possible candidates for ITER hybrid operation scenario.
. These long-pulse plasmas are possible candidates for ITER hybrid operation scenario.
Gormezano, C.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Luce, T. C.*; Ide, Shunsuke; Becoulet, A.*; Litaudon, X.*; Isayama, Akihiko; Hobirk, J.*; Wade, M. R.*; Oikawa, Toshihiro; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S285 - S336, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:348 Percentile:75.44(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper reviews recent world-wide progress in physics research towards International Thermonuclear Reactor (ITER). This chaper descrives on steady state operation with emphasis on: integrated scenarios, review of presently developed experimental scenarios, actuators for steady state operation, specific control issues to steady state operation, simulation of ITER steady-state and hybrid scenarios.
Fasoli, A.*; Gormezano, C.*; Berk, H. L.*; Breizman, B.*; Briguglio, S.*; Darrow, D. S.*; Gorelenkov, N.*; Heidbrink, W. W.*; Jaun, A.*; Konovalov, S. V.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S264 - S284, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:517 Percentile:84.21(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Shimada, Michiya; Campbell, D. J.*; Mukhovatov, V.*; Fujiwara, Masami*; Kirneva, N.*; Lackner, K.*; Nagami, Masayuki; Pustovitov, V. D.*; Uckan, N.*; Wesley, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S1 - S17, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:802 Percentile:99.92(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The Progress in the ITER Physics Basis document is an update of the ITER Physics Basis (IPB), which was published in 1999. The IPB provided methodologies for projecting the performance of burning plasmas, developed largely through coordinated experimental, modeling and theoretical activities carried out on today's tokamaks (ITER Physics R&D). In the IPB, projections for ITER (1998 Design) were also presented. The IPB also pointed out some outstanding issues. These issues have been addressed by the International Tokamak Physics Activities (ITPA), which were initiated by the European Union, Japan, Russia and the U.S.A.. The new methodologies of projection and control developed through the ITPA are applied to ITER, which was redesigned under revised technical objectives, but will nonetheless meet the programmatic objective of providing an integrated demonstration of the scientific and technological feasibility of fusion energy.
Ide, Shunsuke; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Isayama, Akihiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Yoshida, Maiko; Gormezano, C.*; JT-60 Team
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Impact of an electron cyclotron range of frequency (ECRF) wave on the internal transport barriers (ITBs) in a weak shear (WS) plasma has been investigated in JT-60U. It has been observed that the ITB in the ion temperature (Ti ITB) in a WS plasma can be degraded by an EC injection. It is clarified for the first time that the degradation effect depends increasingly on the EC power (PEC) but decreasingly with plasma current (Ip). Moreover it was confirmed that an EC injection affects the toroidal rotation profile (Vt (r)) indirectly and results in flattening of Vt (r) regardless to the direction of the target Vt (r) peaking, co- (relative to the Ip direction) or counter. Furthermore, it was newly found that the central Ti and Vt are affected with no delay from the EC onset even by an off-axis EC injection. These results suggest that an EC injection acts on background mechanism that has special structure, and EC deposition in any location in this structure gives instantaneous effect.
Oyama, Naoyuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Koide, Yoshihiko; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ide, Shunsuke; Nakano, Tomohide; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Hirotaka; Takechi, Manabu; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
After installation of ferritic steel tiles (FSTs) which reduced fast ion losses due to toroidal field ripple, the performance of long-pulse ELMy H-mode plasmas was improved in terms of sustained duration time for both high normalized beta (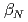 ) and high thermal confinement enhancement factor (
) and high thermal confinement enhancement factor (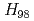 ). High
). High 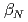
 2.3 together with
2.3 together with 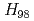
 1 was sustained for 23.1s (
1 was sustained for 23.1s ( 12
12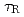 )
) 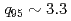 , which also provide high
, which also provide high 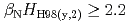 , which is higher than ITER reference scenario. These long-pulse plasmas are possible candidates for ITER hybrid operation scenario.
, which is higher than ITER reference scenario. These long-pulse plasmas are possible candidates for ITER hybrid operation scenario.
Oyama, Naoyuki; Urano, Hajime; Yoshida, Maiko; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Shinohara, Koji; Sakurai, Shinji; Masaki, Kei; Kamiya, Kensaku; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; et al.
Europhysics Conference Abstracts (CD-ROM), 30I, 4 Pages, 2006/00
no abstracts in English
Joffrin, E.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Artaud, J. F.*; Becoulet, A.*; Bertalot, L.*; Budny, R.*; Buratti, P.*; Belo, P.*; Challis, C. D.*; Crisanti, F.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 45(7), p.626 - 634, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:100 Percentile:93.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Joffrin, E.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Artaud, J. F.*; Becoulet, A.*; Budny, R.*; Buratti, P.*; Belo, P.*; Challis, C. D.*; Crisanti, F.*; de Baar, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2004) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
Shimada, Michiya; Campbell, D.*; Stambaugh, R.*; Polevoi, A. R.*; Mukhovatov, V.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Costley, A. E.*; Donn , A. J. H.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Federici, G.*; et al.
, A. J. H.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Federici, G.*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2004) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2004/11
This paper summarises recent progress in the physics basis and its impact on the expected performance of ITER. Significant progress has been made in many outstanding issues and in the development of hybrid and steady state operation scenarios, leading to increased confidence of achieving ITER's goals. Experiments show that tailoring the current profile can improve confinement over the standard H-mode and allow an increase in beta up to the no-wall limit at safety factors  4. Extrapolation to ITER suggests that at the reduced plasma current of
4. Extrapolation to ITER suggests that at the reduced plasma current of  12MA, high Q
12MA, high Q  10 and long pulse (
10 and long pulse ( 1000 s) operation is possible with benign ELMs. Analysis of disruption scenarios has been performed based on guidelines on current quench rates and halo currents, derived from the experimental database. With conservative assumptions, estimated electromagnetic forces on the in-vessel components are below the design target values, confirming the robustness of the ITER design against disruption forces.
1000 s) operation is possible with benign ELMs. Analysis of disruption scenarios has been performed based on guidelines on current quench rates and halo currents, derived from the experimental database. With conservative assumptions, estimated electromagnetic forces on the in-vessel components are below the design target values, confirming the robustness of the ITER design against disruption forces.
Connor, J. W.*; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Garbet, X.*; Gormezano, C.*; Mukhovatov, V.*; Wakatani, Masahiro*; ITB Database Group; ITPA Topical Group on Transport and Internal Barrier Physics*
Nuclear Fusion, 44(4), p.R1 - R49, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:322 Percentile:74.42(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This paper first reviews the present state of theoretical and experimental knowledge regarding the formation and characteristics of ITBs in tokamaks. Specifically, the current status of theoretical modeling of ITBs is presented; then, an international ITB database based on experimental information extracted from some nine tokamaks is described and used to draw some general conclusions concerning the necessary conditions for ITBs to appear, comparing these with the theoretical models. The experimental situation regarding the steady-state, or at least quasi-steady-state, operation of tokamaks is reviewed and finally the issues and prospects for achieving such operational modes in ITER are discussed.
Oyama, Naoyuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Koide, Yoshihiko; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ide, Shunsuke; Nakano, Tomohide; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Hirotaka; Takechi, Manabu; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English