Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nishiyama, Nariaki; Nakajima, Toru; Goto, Akira*; Hakoiwa, Hiroaki; Nagata, Mitsuhiro; Shimada, Koji; Niwa, Masakazu
Earth and Space Science (Internet), 11(6), p.e2023EA003360_1 - e2023EA003360_15, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Earthquakes with magnitudes of 6-7 have been reported even in various active tectonic settings where fault deformation topography have not been detected. Therefore, delineating concealed active faults generating such earthquakes is necessary to reduce earthquake damage; however, few studies exist to provide its clues regarding such faults. The 1984 Western Nagano Earthquake in Japan was a main shock with a magnitude of Mj 6.8 and a depth of 2 km at the source. Solid bedrocks are well-exposed in the earthquake source region; however, no surface rupture have been identified, and the active fault is known to be concealed. In this study, we collected data on striations observed in fractures by geological survey around the source area of the 1984 Western Nagano Earthquake. Using the collected data, the multiple inverse method was used to estimate the stresses that affected the striation formation. Consequently, stresses similar to acting faults in this area were detected in minor faults around the known concealed active fault. This suggests that the minor faults might be part of the damage zone that has been developed around the concealed active fault. Some minor faults were recognized in Quaternary volcanic rocks, confirming that they experienced displacements recently. This study indicates the possibility of detecting concealed active faults in the bedrock by geological survey.
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Terusawa, Shuji*; Goto, Akira*; Nishiyama, Nariaki; Nakajima, Toru; Ishihara, Takanori; Hakoiwa, Hiroaki
Island Arc, 33(1), p.e12516_1 - e12516_16, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:36.99(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)To investigate the geological evidence of near-surface crustal deformations in a high-strain shear zone that has been geodetically identified but not associated with clear tectonic landforms, a fieldwork was conducted in E-W trending southern Kyushu high-strain shear zone, Japan. According to our study, an investigation based on the slip data from minor faults and the occurrences of fracture zones could help to identify a concealed fault that is small in terms of size to record tectonic landforms but can trigger large earthquakes.
Nishiyama, Nariaki; Goto, Akira*; Tsukahara, Yuzuko; Kawamura, Makoto; Umeda, Koji*; Niwa, Masakazu
JAEA-Testing 2022-003, 51 Pages, 2022/09
Advancement of the evaluation technology of the magma activity range is essential as one of the technical issues related to volcanic and igneous activities in the evaluation of the long-term stability of the geological environment in the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. As an effective method, topographical analysis of volcanic edifices is expected to be used to determine the distribution area of dikes. In recent years, the development of computer-based topographic analysis technology has made it possible to simply perform a large volume of work that would otherwise be difficult due to the manual handling. This report describes an analysis method for the shape of contour lines that forms volcanic edifices using GIS software.
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimo, Michito*; Shimada, Koji; Goto, Akira
JAEA-Research 2022-004, 38 Pages, 2022/06
Methane (CH ) seepage to the surface in the early stage of hydrocarbon exploration has attracted increasing attention. Also, detection of CH
) seepage to the surface in the early stage of hydrocarbon exploration has attracted increasing attention. Also, detection of CH -rich fluid emission can be applied to reconnaissance surveys for safety management in geological disposal of radioactive waste because high-temperature fluids that come from slab dehydration along a subduction zone are often rich in CH
-rich fluid emission can be applied to reconnaissance surveys for safety management in geological disposal of radioactive waste because high-temperature fluids that come from slab dehydration along a subduction zone are often rich in CH . These fluids likely migrate along faults and fractures. In this study, we employed a portable analyzer that used a wavelength-scanned cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) with high accuracy (in ppb levels) and short measurement intervals (
. These fluids likely migrate along faults and fractures. In this study, we employed a portable analyzer that used a wavelength-scanned cavity ring-down spectroscopy (CRDS) with high accuracy (in ppb levels) and short measurement intervals ( 1 s). An on-vehicle measurement that employed the CRDS system was performed in the Hongu area in southeast Kii Peninsula, Japan, which included CH
1 s). An on-vehicle measurement that employed the CRDS system was performed in the Hongu area in southeast Kii Peninsula, Japan, which included CH -bearing hot springs (Kawayu and Yunomine). The measurement near the hot springs detected a clear CH
-bearing hot springs (Kawayu and Yunomine). The measurement near the hot springs detected a clear CH anomaly (
anomaly ( 2 ppm) that exceeded the background concentration. The estimation of CH
2 ppm) that exceeded the background concentration. The estimation of CH diffusion in air based on the Gaussian plume model corresponded to the result of the on-vehicle measurement. This study confirmed that the method using the vehicle-mounted CRDS analyzer can help in quickly and easily identifying CH
diffusion in air based on the Gaussian plume model corresponded to the result of the on-vehicle measurement. This study confirmed that the method using the vehicle-mounted CRDS analyzer can help in quickly and easily identifying CH -bearing fluid emissions at the surface. Additionally, directions for use of the analyzer were summarized in this report.
-bearing fluid emissions at the surface. Additionally, directions for use of the analyzer were summarized in this report.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Kokubu, Yoko; Shimada, Koji; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Akiomi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Fujita, Natsuko; et al.
JAEA-Research 2021-007, 65 Pages, 2021/10
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 6th fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. The current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Shimada, Koji; Goto, Akira; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimo, Michito*
Chishitsugaku Zasshi, 127(10), p.I - II, 2021/10
Continuous leaking point of high-temperature fluid (liquid/gas) from underground can be easily grasped by infrared images. We show images confirmed by a FLIR C5 camera that can simultaneously obtain an infrared image and a visible light image at the outcrops of Kawayu Onsen that naturally spring along the river. Outcrops and river surface temperature rise due to hot springs that leaking from riverbanks and riverbeds, rock temperature rise around cracks where gas containing high-concentration methane leaks with hot springs, abandoned fluid pathway due to construction of the bank and damming river for hot spring river bath in winter can be confirmed at a glance. Infrared images may be useful for quick identification of hot fluid leaking points from underground.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Kokubu, Yoko; Shimada, Koji; Shimada, Akiomi; Niwa, Masakazu; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Fujita, Natsuko; Ogita, Yasuhiro; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-012, 48 Pages, 2021/08
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2021. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2021 are described in detail based on the JAEA 3rd Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Kitamura, Akira; Yoshida, Yasushi*; Goto, Takahiro*; Shibutani, Sanae*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 27(2), p.58 - 71, 2020/12
Evaluation and estimation of solubility values are required for a performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive and TRU wastes. Selection of solubility-limiting solid phases (SSPs) that control the solubility of radionuclides is necessary for the evaluation and estimation of solubility values. The authors have developed a methodology for selection of the SSP through a calculation of saturation indices (SIs) using thermodynamic database to show a transparent procedure for the selection. Literature survey should be performed to confirm decision of the SSP from candidate SSPs which generally have larger SIs from realistic point of view for precipitation and solubility control. The authors have selected the SSPs for the elements of interest for the latest Japanese performance assessment in bentonite and cement porewaters after grouping various water compositions.
Goto, Akira; Sasaki, Akimichi*; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Miwa, Atsushi*; Terusawa, Shuji*; Kagohara, Kyoko*; Shimada, Koji
JAEA-Research 2020-013, 88 Pages, 2020/11
Improvement of the investigation techniques to identify active faults is important for the implementation of geological disposal projects from the viewpoint of avoiding locations where permeability increases due to fault displacement. Generally, the existence of active faults is confirmed by aerial photography interpretation of fault displacement topography, which is a topographical trace of fault movement, and on-site geological surveys. However, the investigation method for cases where the topographical traces are unclear is not sufficiently developed. Therefore, to improve existing topographical methods, this study deciphered lineaments up to the rank of poorly defined features, which are almost neglected in general active fault research. The investigation area is one of the geodetic strain concentration zone, called the southern Kyushu shear zone, where the seismogenic faults of the 1997 Kagoshima northwest earthquakes are concealed. We conducted aerial photography interpretation of 62 sheets of 1/25,000 topographic maps, and obtained 1,327 lineaments. Distribution density, direction and length of lineaments were also investigated with topographic and geologic information. As a result, it was clarified that the east-west lineaments in the south Kyushu shear zone predominate in the western part, and the lineaments are densely distributed in the aftershock distribution area of the Kagoshima northwest earthquake. Along with these results, we have compiled a catalog of typical 13 lineaments based on combinations of clarity, direction, length and geomorphic characters of lineaments.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Kokubu, Yoko; Shimada, Koji; Hanamuro, Takahiro; Shimada, Akiomi; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; et al.
JAEA-Research 2020-011, 67 Pages, 2020/10
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 5th fiscal year during the JAEA 3rd Mid- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of the high-level radioactive waste. The planned framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. The current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Ogata, Nobuhisa; Shimada, Koji; Kokubu, Yoko; Niwa, Masakazu; Asamori, Koichi; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; et al.
JAEA-Review 2020-010, 46 Pages, 2020/07
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2020. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2020 are described in detail based on the JAEA 3rd Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2015-2021). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Goto, Akira; Murakami, Masaki*; Sakai, Ryutaro*; Terusawa, Shuji*; Sueoka, Shigeru
JAEA-Review 2020-003, 60 Pages, 2020/03
One of the natural phenomena that may affect the geological disposal system are earthquake and fault activity. Fault displacement due to the earthquake and fault activity will be considered the direct effects. In addition to it, it is necessary to consider the secondary effects include secondary faults formed by the seismic fault activity as well as spring water and mud volcanoes that are generated by fluid movement attributed to the fault activity. This paper introduces previous studies performed focused on the hydraulic effects (spring water and mud volcanoes) and mechanical effects (secondary faults) in order to understand the effects of these secondary phenomena on the geological disposal system. We were able to collect 142 literatures from Japan and overseas by searching for related keywords in Japanese and English. As a result, we compiled case studies of each secondary impact. From the viewpoint of geological disposal, we extracted the following issues for future research and development. As for the sump water induced by earthquakes and faulting, accumulation of information related to its mechanism, affected area, and activity history is required. As for the mud volcanoes, reviewing of the mechanism of anomalous pore water pressure that causing the formation, also development of estimation technique are required. And for the secondary faults, accumulation of the detailed spatial distribution and reviewing of formation mechanism are required.
Tanaka, Taiki*; Narikiyo, Yoshihiro*; Morita, Kosuke*; Fujita, Kunihiro*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Yamaki, Sayaka*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Tanaka, Kengo*; Takeyama, Mirei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_9, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:75.95(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Excitation functions of quasielastic scattering cross sections for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb,
Pb,  Ti +
Ti +  Pb, and
Pb, and  Ca +
Ca +  Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the
Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb and
Pb and  Ti +
Ti +  Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the
Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Shibata, Masahiro; Sawada, Atsushi; Tachi, Yukio; Makino, Hitoshi; Wakasugi, Keiichiro; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Kitamura, Akira; Yoshikawa, Hideki; Oda, Chie; Ishidera, Takamitsu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2014-030, 457 Pages, 2015/03
JAEA and NUMO have conducted a collaborative research work which is designed to enhance the methodology of repository design and post-closure performance assessment in preliminary investigation stage. With regard to (1) study on rock suitability in terms of hydrology, based on some examples of developing method of hydro-geological structure model, acquired knowledge are arranged using the tree diagram, and model uncertainty and its influence on the evaluation items were discussed. With regard to (2) study on scenario development, the developed approach for "defining conditions" has been reevaluated and improved from practical viewpoints. In addition, the uncertainty evaluation for the effect of use of cementitious material, as well as glass dissolution model, was conducted with analytical evaluation. With regard to (3) study on setting radionuclide migration parameters, based on survey of precedent procedures, multiple-approach for distribution coefficient of rocks was established, and the adequacy of the approach was confirmed though its application to sedimentary rock and granitic rock. Besides, an approach for solubility setting was developed including the procedure of selection of solubility limiting solid phase. The adequacy of the approach was confirmed though its application to key radionuclides.
Oe, Kazuhiro*; Attallah, M. F.*; Asai, Masato; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1317 - 1320, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.46(Chemistry, Analytical)A new technique for continuous dissolution of nuclear reaction products transported by a gas-jet system was developed for superheavy element (SHE) chemistry. In this technique, a hydrophobic membrane is utilized to separate an aqueous phase from the gas phase. With this technique, the dissolution efficiencies of short-lived radionuclides of 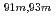 Mo and
Mo and  W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
Shibata, Masahiro; Sawada, Atsushi; Tachi, Yukio; Hayano, Akira; Makino, Hitoshi; Wakasugi, Keiichiro; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Oda, Chie; Kitamura, Akira; Osawa, Hideaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2013-037, 455 Pages, 2013/12
Following FY2011, JAEA and NUMO have conducted a collaborative research work which is designed to enhance the methodology of repository design and performance assessment in preliminary investigation stage. With regard to (1) study on rock suitability in terms of hydrology, the tree diagram of methodology of groundwater travel time has been extended for crystalline rock, in addition, tree diagram for sedimentary rock newly has been organized. With regard to (2) study on scenario development, the existing approach has been improved in terms of a practical task, and applied and tested for near field focusing on the buffer. In addition, the uncertainty of some important processes and its impact on safety functions are discussed though analysis. With regard to (3) study on setting radionuclide migration parameters, the approaches for parameter setting have been developed for sorption for rocks and solubility, and applied and tested through parameter setting exercises for key radionuclides.
 Cm +
Cm +  O reaction
O reactionMurakami, Masashi*; Goto, Shinichi*; Murayama, Hirofumi*; Kojima, Takayuki*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sumita, Takayuki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 88(2), p.024618_1 - 024618_8, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:71.33(Physics, Nuclear)Production cross sections of Rf isotopes in the  Cm +
Cm +  O reaction were measured at the beam energy range of 88.2 to 101.3 MeV by use of a gas-filled recoil ion separator. The excitation functions of
O reaction were measured at the beam energy range of 88.2 to 101.3 MeV by use of a gas-filled recoil ion separator. The excitation functions of 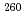 Rf,
Rf, 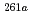 Rf, and
Rf, and  Rf were obtained together with those of spontaneously fissioning nuclides which have few-second half-lives and have been assigned to
Rf were obtained together with those of spontaneously fissioning nuclides which have few-second half-lives and have been assigned to 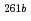 Rf and a longer-lived state of
Rf and a longer-lived state of  Rf. The excitation function of few-second spontaneously fissioning nuclide exhibited the maximum cross section at the
Rf. The excitation function of few-second spontaneously fissioning nuclide exhibited the maximum cross section at the  O beam energy of 94.8 MeV. The shape of the excitation function was almost the same as that of
O beam energy of 94.8 MeV. The shape of the excitation function was almost the same as that of 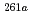 Rf, whereas it was quite different from those of
Rf, whereas it was quite different from those of 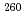 Rf and
Rf and  Rf. A few-second spontaneously fissioning nuclide previously reported as
Rf. A few-second spontaneously fissioning nuclide previously reported as 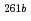 Rf and
Rf and  Rf observed in
Rf observed in Cm +
Cm +  O reaction was identified as
O reaction was identified as 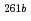 Rf.
Rf.
Koike, Fumihiro*; Funaba, Hisamichi*; Goto, Motoshi*; Kato, Daiji*; Kato, Takako*; Morita, Shigeru*; Murakami, Izumi*; Sakaue, Hiroyuki*; Sudo, Shigeru*; Suzuki, Chihiro*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1545, p.202 - 211, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:82.30(Physics, Applied)Atomic ionic states and transition properties of elements with atomic numbers Z ranging from 50 to 80 are discussed as these are important to the understanding of plasmas containing such heavy elements. As such, data productions and the current status of theoretical calculations in this field are discussed. Further, recent spectroscopic measurements and respective theoretical analyses for W, Gd, and Nd are provided.
Morita, Shigeru*; Dong, C. F.*; Goto, Motoshi*; Kato, Daiji*; Murakami, Izumi*; Sakaue, Hiroyuki*; Hasuo, Masahiro*; Koike, Fumihiro*; Nakamura, Nobuyuki*; Oishi, Tetsutaro*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1545, p.143 - 152, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:99.13(Physics, Applied)Tungsten spectra have been observed from Large Helical Device (LHD) and Compact electron Beam Ion Trap (CoBIT) in wavelength ranges of visible to EUV. The tungsten spectra from LHD are well analyzed based on the knowledge from CoBIT tungsten spectra. The C-R model code has been developed to explain the UTA spectra in details. Radial profiles of EUV spectra from highly ionized tungsten ions have been measured and analyzed by impurity transport simulation code with ADPAK atomic database code to examine the ionization balance determined by ionization and recombination rate coefficients. The ablation cloud of the impurity pellet is directly measured with visible spectroscopy.
 113 of the 113th element
113 of the 113th elementMorita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Ozeki, Kazutaka*; Kudo, Yuki*; Sumita, Takayuki*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Yoneda, Akira*; Tanaka, Kengo*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(10), p.103201_1 - 103201_4, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:179 Percentile:97.24(Physics, Multidisciplinary)An isotope of the 113th element,  113, was produced in a nuclear reaction with a
113, was produced in a nuclear reaction with a  Zn beam on a
Zn beam on a  Bi target. We observed six consecutive
Bi target. We observed six consecutive  decays following the implantation of a heavy particle in nearly the same position in the semiconductor detector, in extremely low background condition. The fifth and sixth decays are fully consistent with the sequential decays of
decays following the implantation of a heavy particle in nearly the same position in the semiconductor detector, in extremely low background condition. The fifth and sixth decays are fully consistent with the sequential decays of  Db and
Db and  Lr both in decay energies and decay times. This indicates that the present decay chain consisted of
Lr both in decay energies and decay times. This indicates that the present decay chain consisted of  113,
113, 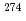 Rg (Z = 111),
Rg (Z = 111), 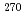 Mt (Z = 109),
Mt (Z = 109),  Bh (Z = 107),
Bh (Z = 107),  Db (Z = 105), and
Db (Z = 105), and  Lr (Z = 103) with firm connections. This result, together with previously reported results from 2004 and 2007, conclusively leads the unambiguous production and identification of the isotope
Lr (Z = 103) with firm connections. This result, together with previously reported results from 2004 and 2007, conclusively leads the unambiguous production and identification of the isotope  113, of the 113th element.
113, of the 113th element.