Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kinase, Akari; Goto, Katsunori*; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Sato, Yoshiyuki; Haraga, Tomoko; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2024-004, 60 Pages, 2024/07
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed the samples generated from JRR-2 and JRR-3 and stored at the waste storage facility L. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 20 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc, 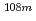 Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2022.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal year 2022.
Hasegawa, Kenta; Goto, Ichiro*; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Ambai, Hiromu; Watanabe, So; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 11(2), p.23-00407_1 - 23-00407_8, 2024/04
Watanabe, So; Takahatake, Yoko; Hasegawa, Kenta; Goto, Ichiro*; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 11(2), p.23-00461_1 - 23-00461_10, 2024/04
Tobita, Minoru*; Goto, Katsunori*; Omori, Takeshi*; Osone, Osamu*; Haraga, Tomoko; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Tsuchida, Daiki; Mitsukai, Akina; Ishimori, Kenichiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-011, 32 Pages, 2023/11
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to the study of radioactivity concentration evaluation methods for radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities, we collected and analyzed concrete samples generated from JRR-3, JRR-4 and JAERI Reprocessing Test Facility. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 23 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Ag,
Ag,  Cs,
Cs,  Ba,
Ba,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2021-2022.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2021-2022.
Okita, Shoichiro; Goto, Minoru
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Nuclear Criticality Safety (ICNC2023) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/10
Iyota, Muneyoshi*; Matsuda, Tomoki*; Sano, Tomokazu*; Shigeta, Masaya*; Shobu, Takahisa; Yumoto, Hirokatsu*; Koyama, Takahisa*; Yamazaki, Hiroshi*; Semba, Yasunori*; Ohashi, Haruhiko*; et al.
Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 94, p.424 - 434, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:66.71(Engineering, Manufacturing)Watanabe, So; Takahatake, Yoko; Hasegawa, Kenta; Goto, Ichiro*; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/05
Hasegawa, Kenta; Goto, Ichiro*; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Ambai, Hiromu; Watanabe, So; Watanabe, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Takeuchi, Masayuki
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2023/05
Okita, Shoichiro; Mizuta, Naoki; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Goto, Minoru; Yoshida, Katsumi*; Nishimura, Yosuke*; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05
Koizumi, Mitsuo; Takahashi, Tone; Hironaka, Kota; Mochimaru, Takanori*; Yamaguchi, Ikuto*; Kimura, Yoshiki; Tanigaki, Minoru*; Masaki, Hiroko*; Harada, Hiroshi*; Goto, Jun*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Annual Meeting 2023 (Internet), 7 Pages, 2023/05
Fukaya, Yuji; Okita, Shoichiro; Sasaki, Koei; Ueta, Shohei; Goto, Minoru; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Yan, X.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 399, p.112033_1 - 112033_9, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kernel migration of TRi-structural ISOtropic (TRISO) fuel for High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) has been analyzed to investigate the potential dominating effects. Kernel migration is a major fuel failure mode and dominant to determine the lifetime of the fuel for High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR). However, this study shows that the result and reliability depend on the evaluation method. The evaluation method used in this study takes into account of actual distribution of Coated Fuel Particles (CFPs) and the resulting heterogeneous fuel temperature calculation with such distribution. The result shows that the Kernel Migration Rate (KMR) is predicted to be about 10% less compared with the most conservative evaluation.
Fukaya, Yuji; Okita, Shoichiro; Kanda, Shun*; Goto, Masaki*; Nakajima, Kunihiro*; Sakon, Atsushi*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Hashimoto, Kengo*; Takahashi, Yoshiyuki*; Unesaki, Hironobu*
KURNS Progress Report 2021, P. 101, 2022/07
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) started the Research and Development (R&D) to improve nuclear prediction techniques for High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors (HTGRs) in 2018. The objectives are to intro-duce the generalized bias factor method to avoid full mock-up experiment for the first commercial HTGR and to improve neutron instrumentation system by virtue of the particular characteristics due to a graphite moderation system. For this end, we composed B7/4"G2/8"p8EU(3)+3/8"p38EU in the B-rack of Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA) in 2021.
Sakon, Atsushi*; Hashimoto, Kengo*; Sano, Tadafumi*; Nakajima, Kunihiro*; Kanda, Shun*; Goto, Masaki*; Fukaya, Yuji; Okita, Shoichiro; Fujimoto, Nozomu*; Takahashi, Yoshiyuki*
KURNS Progress Report 2021, P. 100, 2022/07
The R&D of reactor noise analysis to obtain HTGR nuclear characteristics have been performed with Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA). In the last study, a neutron detector located about 55 cm away of fuel assembly measured the auto power spectral density. However, the prompt neutron decay constants obtained by this detector was different from that of other detectors. The objective of this study is experimental study of reactor noise analysis by the power spectrum method using neutron detector placed outside reactor core.
Fukaya, Yuji; Okita, Shoichiro; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Goto, Minoru; Ohashi, Hirofumi
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 168, p.108911_1 - 108911_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:14.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)A power distribution monitoring system by using a moving detector for a core with a long neutron flight path has been proposed. High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) and Fast Reactor (FR) has a long neutron flight path and the neutrons reach to detector far from fuel assembly in the center of the core unlike Light Water Reactor (LWR). By using the feature, power distribution can be observed with a few detectors by moving the detector and computed tomography technology similar to X-ray Computed Tomography (CT). For a small-sized core, the power distribution can be evaluated only by an ex-core neutron detector. For a large-sized core with inner detectors, the power distribution can be observed with a small number of in-core detectors even if the deployment is limited due to material integrity conditions such as temperature environment. The feasibility is numerically confirmed by simulations of the HTGR core and its detector response. It is expected to observe the power distribution in the core of HTGR and FR, which is difficult continuously to deploy in-core detectors because of high temperature and/or high irradiation damage.
Kusano, Kanya*; Ichimoto, Kiyoshi*; Ishii, Mamoru*; Miyoshi, Yoshizumi*; Yoden, Shigeo*; Akiyoshi, Hideharu*; Asai, Ayumi*; Ebihara, Yusuke*; Fujiwara, Hitoshi*; Goto, Tadanori*; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 73(1), p.159_1 - 159_29, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:39.36(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)The PSTEP is a nationwide research collaboration in Japan and was conducted from April 2015 to March 2020, supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. It has made a significant progress in space weather research and operational forecasts, publishing over 500 refereed journal papers and organizing four international symposiums, various workshops and seminars, and summer school for graduate students at Rikubetsu in 2017. This paper is a summary report of the PSTEP and describes the major research achievements it produced.
Sasaki, Koei; Miura, Shuichiro*; Fukumoto, Kenichi*; Goto, Minoru; Ohashi, Hirofumi
Proceedings of 28th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 28) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2021/08
Cs-Bi and Cs-Sb absorbed graphite samples (Cs-Bi/graphite and Cs-Sb/graphite) were synthesized and their high temperature chemical stabilities were tested up to 1500 C by TG and analyzed by TEM-EDS for the development of Cs trap material in high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) fuel particles. It was observed that Cs was stabilized by Sb but not by Bi in the specimens after the TG test. A rapid weight loss from 800 to 1000
C by TG and analyzed by TEM-EDS for the development of Cs trap material in high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) fuel particles. It was observed that Cs was stabilized by Sb but not by Bi in the specimens after the TG test. A rapid weight loss from 800 to 1000 C may be caused by evaporation of Cs (boiling point: 671
C may be caused by evaporation of Cs (boiling point: 671 C) was seen in the TG result of both specimens. Precipitated Cs-Sb substance in the graphite matrix were not resolved even after the 1500
C) was seen in the TG result of both specimens. Precipitated Cs-Sb substance in the graphite matrix were not resolved even after the 1500 C heating. The chemical composition of the Cs-Sb was specified as Cs
C heating. The chemical composition of the Cs-Sb was specified as Cs Sb. The experimental results suggest that Sb have potential to be a Cs getter material in graphite matrix. Long term heating test should be performed to confirm adaptability of Sb for Cs trap material in HTGR fuel particles.
Sb. The experimental results suggest that Sb have potential to be a Cs getter material in graphite matrix. Long term heating test should be performed to confirm adaptability of Sb for Cs trap material in HTGR fuel particles.
Iizuka, Riko*; Goto, Hirotada*; Shito, Chikara*; Fukuyama, Ko*; Mori, Yuichiro*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.12632_1 - 12632_10, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:27.35(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The Earth's core consist of Fe-Ni alloy with some light elements (H, C, O, Si, S etc.). Hydrogen (H) is the most abundant element in the universe and one of the promising candidates. In this study, we have investigated the effects of sulfur(S) on hydrogenation of iron-hydrous silicate system containing saturated water in the ideal composition of the primitive Earth. We observed a series of phase transitions of Fe, dehydration of the hydrous mineral, and formation of olivine and enstatite with increasing temperature. The FeS formed as the coexisting phase of Fe under high-pressure and temperature condition, but its unit cell volume did not increase, suggesting that FeS is hardly hydrogenated. Recovered samples exhibited that H and S can be incorporated into solid Fe, which lowers the melting temperature as Fe(H )-FeS system. No detection of other light elements (C, O, Si) in solid Fe suggests that they dissolve into molten iron hydride and/or FeS in the later process of Earth's core-mantle differentiation.
)-FeS system. No detection of other light elements (C, O, Si) in solid Fe suggests that they dissolve into molten iron hydride and/or FeS in the later process of Earth's core-mantle differentiation.
Kosugi, Yoshihisa*; Goto, Matato*; Tan, Z.*; Kan, Daisuke*; Isobe, Masahiko*; Yoshii, Kenji; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Fujita, Asaya*; Takagi, Hidenori*; Shimakawa, Yuichi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 11(1), p.12682_1 - 12682_8, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:42.22(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Caloric effects of solids provide more efficient and environment-friendly innovative refrigeration systems compared to the widely-used conventional vapor compressive cooling systems. Exploring novel caloric materials is challenging but critically important in developing future technologies. Here we discovered that the quadruple perovskite structure ferrimagnet BiCu Cr
Cr O
O shows a large multicaloric effect at the first-order charge transition occurred around 190 K. Large latent heat and the corresponding isothermal entropy changes 28.2 J K
shows a large multicaloric effect at the first-order charge transition occurred around 190 K. Large latent heat and the corresponding isothermal entropy changes 28.2 J K kg
kg can be fully utilized by applying both magnetic fields (magnetocaloric effect) and pressure (barocaloric effect). Adiabatic temperature changes reach 3.9 K for the 50 kOe magnetic field and 4.8 K for the 4.9 kbar pressure, and thus highly efficient thermal controls are achieved by multiple ways.
can be fully utilized by applying both magnetic fields (magnetocaloric effect) and pressure (barocaloric effect). Adiabatic temperature changes reach 3.9 K for the 50 kOe magnetic field and 4.8 K for the 4.9 kbar pressure, and thus highly efficient thermal controls are achieved by multiple ways.
Okita, Shoichiro; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(1), p.9 - 16, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Suppressing the kernel migration rates, which depend on both the fuel temperature and the fuel temperature gradient, under normal operation condition is quite important from the viewpoint of the fuel integrity for High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactors. The presence of the ideal axial power distribution to minimize the maximum kernel migration rate allows us to improve efficiency of design work. Therefore, we propose a new method based on Lagrange multiplier method in consideration of thermohydraulic design in order to obtain the ideal axial power distribution to minimize the maximum kernel migration rate. For one of the existing conceptual designs performed by JAEA, the maximum kernel migration rate for the power distribution to minimize the maximum kernel migration rate proposed in this study is lower by approximately 10% than that for the power distribution as a conventional design target to minimize the maximum fuel temperature.
Watanabe, So; Suzuki, Hideya; Goto, Ichiro*; Kofuji, Hirohide; Matsumura, Tatsuro
Nihon Ion Kokan Gakkai-Shi, 29(3), p.71 - 75, 2018/09