Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Gu, G. H.*; Jeong, S. G.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Cho, J.*; Kim, H. S.*; 4 of others*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 223, p.308 - 324, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Gu, Y. Q.*; Gu, Y. M.*; Liu, F.*; Kawamura, Seiko; Murai, Naoki; Zhao, J.*
Physical Review Letters, 132(24), p.246702_1 - 246702_7, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:92.84(Multidisciplinary Sciences) ;
;  SR studies and charge-spin percolation model
SR studies and charge-spin percolation modelSheng, Q.*; Kaneko, Tatsuya*; Yamakawa, Kohtaro*; Guguchia, Z.*; Gong, Z.*; Zhao, G.*; Dai, G.*; Jin, C.*; Guo, S.*; Fu, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 4(3), p.033172_1 - 033172_14, 2022/09
 K
K (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )
) As
As studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scatteringSuzuki, Hakuto*; Zhao, G.*; Okamoto, Jun*; Sakamoto, Shoya*; Chen, Z.-Y.*; Nonaka, Yosuke*; Shibata, Goro; Zhao, K.*; Chen, B.*; Wu, W.-B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(6), p.064710_1 - 064710_5, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)
Hao, Y. Q.*; Wo, H. L.*; Gu, Y. M.*; Zhang, X. W.*; Gu, Y. Q.*; Zheng, S. Y.*; Zhao, Y.*; Xu, G. Y.*; Lynn, J. W.*; Nakajima, Kenji; et al.
Science China; Physics, Mechanics & Astronomy, 64(3), p.237411_1 - 237411_6, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:69.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Wang, Y.*; Jia, G.*; Cui, X.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, Q.*; Gu, L.*; Zheng, L.*; Li, L. H.*; Wu, Q.*; Singh, D. J.*; et al.
Chem, 7(2), p.436 - 449, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:297 Percentile:99.75(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Lai, W.-H.*; Wang, H.*; Zheng, L.*; Jiang, Q.*; Yan, Z.-C.*; Wang, L.*; Yoshikawa, Hirofumi*; Matsumura, Daiju; Sun, Q.*; Wang, Y.-X.*; et al.
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 59(49), p.22171 - 22178, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:105 Percentile:95.70(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Iwatsuki, Teruki; Onoe, Hironori; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Ozaki, Yusuke; Wang, Y.*; Hadgu, T.*; Jove-Colon, C. F.*; Kalinina, E.*; Hokr, M.*; Balv n, A.*; et al.
n, A.*; et al.
JAEA-Research 2018-018, 140 Pages, 2019/03
DECOVALEX-2019 Task C aims to develop modelling and prediction methods using numerical simulation based on the water-filling experiment to examine the post drift-closure environment recovery processes. In this intermediate report, the results of Step 1 (Modelling and prediction of environmental disturbance by CTD excavation) are summarized from each of the research teams (JAEA, Sandia National Laboratories, Technical University of Liberec). Groundwater inflow rates to the tunnel during the excavation, hydraulic drawdown, and variation of chlorine concentration at monitoring boreholes in the vicinity of the tunnel were chosen as comparison metrics for Step1 by mutual agreement amongst the research teams. It is likely to be possible to foresee the scales of inflow rate and hydraulic drawdown based on a data from the pilot borehole by current simulation techniques.
Kalinina, E. A.*; Hadgu, T.*; Wang, Y.*; Ozaki, Yusuke; Iwatsuki, Teruki
Proceedings of 2nd International Discrete Fracture Network Engineering Conference (DFNE 2018) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2018/06
The Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory is located in the Tono area (Central Japan). Its main purpose is providing a scientific basis for the research and development of technologies needed for deep geological disposal of radioactive waste in fractured crystalline rocks. The current work is focused on the experiments in the research tunnel (500 m depth). The collected tunnel and borehole data were shared with the participants of DEvelopment of COupled models and their VALidation against EXperiments (DECOVALEX) project. This study describes how these data were used to (1) develop the fracture model of the granite rocks around the research tunnel and (2) validate the model.
Hadgu, T.*; Kalinina, E.*; Wang, Y.*; Ozaki, Yusuke; Iwatsuki, Teruki
Proceedings of 2nd International Discrete Fracture Network Engineering Conference (DFNE 2018) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2018/06
Experimental hydrology data from the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory in Central Japan have been used to develop a site-scale fracture model and a flow model for the study area. The discrete fracture network model was upscaled to a continuum model to be used in flow simulations. A flow model was developed centered on the research tunnel, and using a highly refined regular mesh. In this study development and utilization of the model is presented. The modeling analysis used permeability and porosity fields from the discrete fracture network model as well as a homogenous model using fixed values of permeability and porosity. The simulations were designed to reproduce hydrology of the modeling area and to predict inflow of water into the research tunnel during excavation. Modeling results were compared with the project hydrology data. Successful matching of the experimental data was obtained for simulations based on the discrete fracture network model.
Gu, Y. J.*; Klimo, O.*; Kumar, D.*; Liu, Y.*; Singh, S. K.*; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Bulanov, S. V.; Weber, S.*; Korn, G.*
Physical Review E, 93(1), p.013203_1 - 013203_6, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:86.28(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Liu, Y.*; Klimo, O.*; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Bulanov, S. V.; Gu, Y.*; Weber, S.*; Korn, G.*
Physics of Plasmas, 22(11), p.112302_1 - 112302_8, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:12.55(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Gu, Y. J.*; Klimo, O.*; Kumar, D.*; Bulanov, S. V.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Weber, S.*; Korn, G.*
Physics of Plasmas, 22(10), p.103113_1 - 103113_9, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:41.44(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Deng, Z.*; Zhao, K.*; Gu, B.; Han, W.*; Zhu, J. L.*; Wang, X. C.*; Li, X.*; Liu, Q. Q.*; Yu, R. C.*; Goko, Tatsuo*; et al.
Physical Review B, 88(8), p.081203_1 - 081203_5, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:77 Percentile:91.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) /SrTiO
/SrTiO (110) interface
(110) interfaceAnnadi, A.*; Zhang, Q.*; Renshaw Wang, X.*; Tuzla, N.*; Gopinadhan, K.*; L , W. M.*; Roy Barman, A.*; Liu, Z. Q.*; Srivastava, A.*; Saha, S.*; et al.
, W. M.*; Roy Barman, A.*; Liu, Z. Q.*; Srivastava, A.*; Saha, S.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 4, p.1838_1 - 1838_7, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:103 Percentile:94.51(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Deng, Z.*; Jin, C. Q.*; Liu, Q. Q.*; Wang, X. C.*; Zhu, J. L.*; Feng, S. M.*; Chen, L. C.*; Yu, R. C.*; Arguello, C.*; Goko, Tatsuo*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 2, p.1425_1 - 1425_5, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:172 Percentile:93.60(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In a prototypical ferromagnet (Ga,Mn)As based on a III-V semiconductor, substitution of divalent Mn atoms into trivalent Ga sites leads to severely limited chemical solubility and metastable specimens available only as thin films. The doping of hole carriers via (Ga,Mn) substitution also prohibits electron doping. To overcome these difficulties, Masek et al. theoretically proposed systems based on a I-II-V semiconductor LiZnAs, where isovalent (Zn,Mn) substitution is decoupled from carrier doping with excess/deficient Li concentrations. Here we show successful synthesis of Li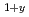 (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )As in bulk materials. We reported that ferromagnetism with a critical temperature of up to 50 K is observed in nominally Li-excess compounds, which have p-type carriers.
)As in bulk materials. We reported that ferromagnetism with a critical temperature of up to 50 K is observed in nominally Li-excess compounds, which have p-type carriers.
Gu, B.; Ziman, T.*; Guo, G.-Y.*; Nagaosa, Naoto; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Journal of Applied Physics, 109(7), p.07C502_1 - 07C502_3, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.46(Physics, Applied)We show theoretically a novel route to obtain giant room temperature spin Hall effect (SHE) using surface-assisted skew scattering. By a combined approach of density functional theory and the quantum Monte Carlo (QMC) method, we have studied the SHE due to a Pt impurity in different Au hosts. We show that the spin Hall angle (SHA) could become larger than 0.1 on the Au (111) surface, and decreases by about a half on the Au (001) surface, while it is small in bulk Au. The QMC results show that the spin-orbit interaction (SOI) of the Pt impurity on the Au (001) and Au (111) surfaces is enhanced, because the Pt 5 levels are lifted to the Fermi level due to the valence fluctuations. In addition, there are two SOI channels on the Au (111) surface, while only one for Pt either on the Au (001) surface or in bulk Au.
levels are lifted to the Fermi level due to the valence fluctuations. In addition, there are two SOI channels on the Au (111) surface, while only one for Pt either on the Au (001) surface or in bulk Au.
Gu, B.; Sugai, Isamu*; Ziman, T.*; Guo, G. Y.*; Nagaosa, Naoto; Seki, Takeshi*; Takanashi, Koki; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Physical Review Letters, 105(21), p.216401_1 - 216401_4, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:71 Percentile:89.78(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Gu, B.; Gan, J.-Y.*; Bulut, N.*; Ziman, T.*; Guo, G.-Y.*; Nagaosa, Naoto*; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Physical Review Letters, 105(8), p.086401_1 - 086401_4, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:78.69(Physics, Multidisciplinary)By quantum Monte Carlo simulation of a realistic multi-orbital Anderson impurity model, we have studied the spin-orbit interaction (SOI) of an Fe impurity in Au host metal. We have shown, for the first time, that the SOI is strongly renormalized by the quantum spin fluctuation. Based on this mechanism, we could explain why the gigantic spin hall effect in Au with Fe impurities was observed in recent experiment, while it is not visible in the anomalous hall effect. In addition, we have shown that the SOI is strongly renormalized by the coulomb correlation  . Based on this picture, we could explain past discrepancies in the calculated orbital angular momenta for an Fe impurity in Au host.
. Based on this picture, we could explain past discrepancies in the calculated orbital angular momenta for an Fe impurity in Au host.