Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
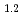 Ni
Ni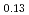 Mn
Mn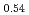 Co
Co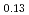 O
O in a lithium-ion battery
in a lithium-ion batteryKonishi, Hiroaki*; Hirano, Tatsumi*; Takamatsu, Daiko*; Gunji, Akira*; Feng, X.*; Furutsuki, Sho*; Okumura, Takafumi*; Terada, Shohei*; Tamura, Kazuhisa
Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 262, p.294 - 300, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:47.54(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The potential in each state of charge (SOC) during charging of Li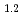 Ni
Ni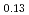 Mn
Mn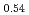 Co
Co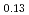 O
O is higher than that during discharging. To clarify the effect of chargedischarge operating conditions on the electrochemical reaction, Li
is higher than that during discharging. To clarify the effect of chargedischarge operating conditions on the electrochemical reaction, Li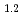 Ni
Ni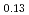 Mn
Mn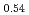 Co
Co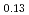 O
O was charged and discharged under various charge-discharge operating ranges, and OCP, crystal structure, and oxidation states of the ransition metals were evaluated by electrochemical measurement, XRD, and XAFS. These results indicate that OCP, lattice parameters, and oxidation states of the transition metals of Li
was charged and discharged under various charge-discharge operating ranges, and OCP, crystal structure, and oxidation states of the ransition metals were evaluated by electrochemical measurement, XRD, and XAFS. These results indicate that OCP, lattice parameters, and oxidation states of the transition metals of Li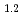 Ni
Ni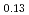 Mn
Mn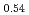 Co
Co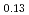 O
O in each SOC are not constant. The XRD results indicate that two phases, namely, LiNi
in each SOC are not constant. The XRD results indicate that two phases, namely, LiNi Mn
Mn Co
Co O
O -like and Li
-like and Li MnO
MnO -like, exist in Li
-like, exist in Li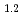 Ni
Ni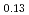 Mn
Mn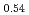 Co
Co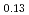 O
O .
.
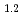 Ni
Ni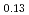 Mn
Mn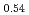 Co
Co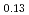 O
O used for lithium ion batteries
used for lithium ion batteriesKonishi, Hiroaki*; Hirano, Tatsumi*; Takamatsu, Daiko*; Gunji, Akira*; Feng, X.*; Furutsuki, Sho*; Okumura, Takafumi*; Terada, Shohei*; Tamura, Kazuhisa
Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 258, p.225 - 231, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:43.89(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Li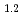 Ni
Ni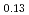 Mn
Mn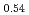 Co
Co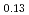 O
O is known as one of the cathode electrode material for Li ion batteries and its structure during charge and discharge process was investigated using electrochemical method and X-ray diffraction. It was found that in the charge process the structure changes in the order of Li
is known as one of the cathode electrode material for Li ion batteries and its structure during charge and discharge process was investigated using electrochemical method and X-ray diffraction. It was found that in the charge process the structure changes in the order of Li MnO
MnO , LiNi
, LiNi Mn
Mn Co
Co O
O , and Li
, and Li MnO
MnO . On the other hand, in the discharge process, the structure changes in the order of Li
. On the other hand, in the discharge process, the structure changes in the order of Li MnO
MnO and LiNi
and LiNi Mn
Mn Co
Co O
O .
.
Magara, Masaaki; Usuda, Shigekazu; Sakurai, Satoshi; Watanabe, Kazuo; Esaka, Fumitaka; Hirayama, Fumio; Lee, C. G.; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Kono, Nobuaki; Inagawa, Jun; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 46th Annual Meeting (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2005/00
JAERI has been developing analytical techniques for ultra-trace amounts of nuclear materials in the environmental samples in order to contribute to the strengthened safeguards system. Development of essential techniques for bulk and particle analysis of the environmental swipe sample has been established as an ultra-trace analytical method of uranium and plutonium. In January 2003, JAERI was qualified as a member of the IAEA network analytical laboratories for environmental samples. Since then, JAERI has conducted the analysis of domestic and the IAEA samples. From Japanese fiscal year 2003, the second phase of the project was started for the development of advanced techniques, such as analyzing minor actinides and fission products as well as uranium and plutonium, particle analysis using fission-track technique, more efficient particle analysis using ICP-TOFMS and screening by X-ray fluorescent analysis. This paper deals with the progress in the development of the new techniques, applications and future perspective.