Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
小島 邦洸; 原田 寛之; 田村 文彦; 沖田 英史; 地村 幹; Saha P. K.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2025(1), p.013G01_1 - 013G01_19, 2025/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)本研究は、3GeVシンクロトロン(Rapid cycling synchrotron: RCS)のビーム大強度・高品質化に貢献するものである。大強度の陽子シンクロトロンにおいて、ビーム損失は深刻な装置の放射化をもたらし、ビーム出力の制限に繋がる。そのため、RCSの大強度ビーム安定化には、ビーム損失の更なる低減が不可欠である。特に、加速器のビームを制御する電磁石の配置とビームが進行方向に垂直な方向に行う振動の周期が一定の関係(共鳴条件)を満たすとき、共鳴現象により多大なビーム損失が起きる。この共鳴の発生を避けるため、ビームの振動の周期は共鳴条件を避けるよう慎重に制御されている。一方で、ビーム大強度化に伴って粒子間のクーロン斥力の影響によって個々の粒子の振動数は個別の影響を受け変化するため、共鳴条件はビーム密度に依存した幅を持つようになる。これにより、ビームの振動の周期を制御することによる共鳴条件の回避が難しくなる。RCSではビーム強度が一定以上に達した場合に、半整数共鳴を避けることが困難となるため、これがRCSの最大出力を制限している。そこで、本研究では補正磁場の重畳による半整数共鳴の影響の低減(補正)を試みた。ビーム試験と数値計算の活用により、RCS設計出力と同等な強度を持つビーム条件において、半整数共鳴に起因するビーム損失を1/3にまで低減する補正状況を達成した。本論文では、一連のビーム試験結果に加えて、共鳴補正手法の詳細について報告する。
小島 邦洸; 原田 寛之; 地村 幹; Saha P. K.
Proceedings of 21st Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.118 - 122, 2024/10
本研究は、3GeVシンクロトロン(Rapid cycling synchrotron: RCS)のビーム大強度・高品質化に貢献するものである。RCSでは、設計出力1MWを超える大強度化に向け高度化を進めている。このような大強度陽子加速器において、出力を制限する最大の要因は、ビーム損失に起因する装置の放射化である。一般的にシンクロトロンでは、粒子はある幅の中で振動(ベータトロン振動)しながら進んでおり、その振動数が磁場やビーム自身が作る電場と相互作用し共鳴条件に抵触すると振幅が大きくなり、ダクト内壁等に衝突して損失に至る。そのため、共鳴条件を避けるように、ビームに加える収束力を設定する。しかし、強度が増大するにつれてビームの粒子数密度が高くなり、それに伴って粒子間のクーロン斥力も増大する。各粒子は設定と異なるベータトロン振動数を持ち、共鳴条件に抵触する可能性がある。そこで、振動数が半整数の際に発生する共鳴(半整数共鳴)の影響を補正し、打ち消すことによる安定領域の拡充を試みた。半整数共鳴が励起する強さは、ビームが受ける外力のみで決まり、ビーム強度に依存しない。そのため、まずは空間電荷力の影響が無視できる低強度ビームを用いることで、半整数共鳴の補正を実施した。その結果、この共鳴によるビーム損失を1/10以下にする大幅な低減を実現した。さらに、この補正状況が利用運転時のビームロス低減に寄与することを、大強度ビームを用いた試験により実証した。本発表では、低強度時の共鳴補正手法と実験結果に加えて、大強度時のビーム損失低減などに関して報告する。
河 侑成; 山口 義仁; 長谷川 邦夫; Negyesi, M.*
Proceedings of ASME 2024 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference (PVP 2024) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2024/07
If a flaw in a high-toughness ductile pipe of a power plant is detected during periodic in-service inspection, stress applied at the flaw location of the pipe is compared with an allowable stress. When the applied stress is less than the allowable stress, the plant can operate continuously for a certain evaluation period in accordance with ASME Code Section XI. The flow stress given by the average of yield strength and ultimate tensile strength is an important material parameter for allowable stress. Recently, many fitness-for-service codes and technical reports have adopted conversions from hardness measurement values to yield strength and ultimate tensile strength. In this paper, we introduced the flow stress obtained from converted tensile properties from Vickers hardness using the presented equations for austenitic stainless steel. The allowable stress estimated by the Vickers hardness was compared with the allowable stress determined by actual tensile properties. As a result, the flow stress converted from hardness was about 1.48 times larger than that obtained by actual flow stress. The allowable flaw sizes calculated by the flow stress converted from hardness gave an appropriate indication when the allowable or applied stress was very low. However, the flow stress converted from hardness gave unconservative allowable stress, when the applied stress was large.
Negyesi, M.*; 河 侑成; 長谷川 邦夫; Lacroix, V.*
Proceedings of ASME 2024 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference (PVP 2024) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2024/07
Allowable stresses for pipes are determined by combining failure stresses and safety factors. When predicting the plastic collapse failure stresses for high toughness ductile pipes, flow stresses of the pipe materials are indispensable. The flow stress is usually given by the average of the yield strength and the ultimate tensile strength. Inservice Inspection of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Code Section XI states to use the yield strengths and the ultimate tensile strengths defined by the ASME Code Section II Materials. The ASME Code Section XI also states that actual measured yield strengths and ultimate tensile strengths are possible to be used, alternatively. Values of yield strength and ultimate tensile strength given by the ASME Code Section II are conservative, corresponding to lower bound values. Then, it is easily inferred that the allowable stresses calculated by the code given flow stress are lower than the allowable stresses calculated by the actual measured flow stress. The objective of this paper is to compare the plastic collapse failure and allowable stresses based on both the code and actual flow stresses for pipes with circumferential flaws subjected to bending and tensile loading. In addition, it is demonstrated that allowable flaw sizes based on both flow stresses do not differ much at low allowable stress. However, when the allowable stress is large, the allowable flaw size based on the code flow stress is substantially lower compared to that based on the actual flow stress.
Wang, S.*; Wang, J.*; Zhang, S.*; Wei, D.*; Chen, Y.*; Rong, X.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Liu, X.*; Jiao, Z.*; et al.
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 185, p.245 - 258, 2024/06
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:98.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nanoprecipitates and nanoscale retained austenite (RA) with suitable stability play crucial roles in determining the yield strength (YS) and ductility of ultrahigh strength steels (UHSSs). However, owing to the kinetics incompatibility between nanoprecipitation and austenite reversion, it is highly challenging to simultaneously introduce high-density nanoprecipitates and optimized RA in UHSSs. In this work, through the combination of austenite reversion treatment (ART) and subsequent flash austenitizing (FA), nanoscale chemical heterogeneity was successfully introduced into a low-cost UHSS prior to the aging process. This chemical heterogeneity involved the enrichment of Mn and Ni in the austenite phase. The resulting UHSS exhibited dual-nanoprecipitation of Ni(Al,Mn) and (Mo,Cr) C and nanoscale austenite stabilized via Mn and Ni enrichment. The hard martensitic matrix strengthened by high-density dual-nanoprecipitates constrains the plastic deformation of soft RA with a relatively low fraction, and the presence of relatively stable nanoscale RA with adequate Mn and Ni enrichment leads to a marginal loss in YS but keeps a persistent transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect. As a result, the newly-developed UHSS exhibits an ultrahigh YS of 1.7 GPa, an ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 1.8 GPa, a large uniform elongation (UE) of 8.5 percent, and a total elongation (TE) of 13 percent. The strategy of presetting chemical heterogeneity to introduce proper metastable phases before aging can be extended to other UHSSs and precipitation-hardened alloys.
C and nanoscale austenite stabilized via Mn and Ni enrichment. The hard martensitic matrix strengthened by high-density dual-nanoprecipitates constrains the plastic deformation of soft RA with a relatively low fraction, and the presence of relatively stable nanoscale RA with adequate Mn and Ni enrichment leads to a marginal loss in YS but keeps a persistent transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) effect. As a result, the newly-developed UHSS exhibits an ultrahigh YS of 1.7 GPa, an ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 1.8 GPa, a large uniform elongation (UE) of 8.5 percent, and a total elongation (TE) of 13 percent. The strategy of presetting chemical heterogeneity to introduce proper metastable phases before aging can be extended to other UHSSs and precipitation-hardened alloys.
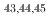 Cl via
Cl via 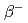 and
and 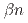 decay
decayTripathi, V.*; Bhattacharya, S.*; Rubino, E.*; Benetti, C.*; Perello, J. F.*; Tabor, S. L.*; Liddick, S. N.*; Bender, P. C.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Carroll, J. J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.044320_1 - 044320_15, 2024/04
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)ミシガン州立大学の国立超伝導サイクロトロン研究所において Caのフラグメンテーション反応によって中性子過剰核
Caのフラグメンテーション反応によって中性子過剰核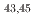 Sを生成し、そこからのベータ崩壊および遅発中性子放出ベータ崩壊によって
Sを生成し、そこからのベータ崩壊および遅発中性子放出ベータ崩壊によって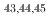 Clの励起状態を得た。得られた実験データをSDPFSDG-MU相互作用を用いた大規模殻模型計算と比較し、よい一致を得た。
Clの励起状態を得た。得られた実験データをSDPFSDG-MU相互作用を用いた大規模殻模型計算と比較し、よい一致を得た。
河 侑成; 下平 昌樹; 勝山 仁哉
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2024/03
国内の原子炉圧力容器(RPV)の溶接継手熱影響部(継手HAZ)は監視試験対象部位である。継手HAZ内には非均質に金属組織が分布し、破壊靭性のばらつきが大きいと考えられるものの、HAZ試験片の採取位置における金属組織の違いが機械的特性及び照射脆化感受性に及ぼす影響は詳細に調べられていなかった。本研究では継手HAZの非均質な組織に着目し、まず未照射材について溶接金属と母材の境界からの距離に応じて3箇所(0.5mm, 1mm及び2mm)の継手HAZ、及び母材から採取した微小試験片(Mini-C(T)試験片)を用いて破壊靭性を評価した。その結果、HAZの破壊靭性は母材と比べてばらつきが大きく、特に溶接金属と母材の境界から0.5mmのHAZにおいて破壊靭性のばらつきが最も大きい傾向を示した。HAZに対する破壊靭性参照温度は採取した3箇所の中で有意な差が得られたものの、いずれの破壊靭性参照温度も母材より低く、破壊靭性値が高いことを確認した。本研究結果により、未照射状態では母材が継手HAZを代表して破壊靭性を保守的に評価できることを確認した。
山本 風海; 守屋 克洋; 沖田 英史; 山田 逸平; 地村 幹; Saha, P. K.; 菖蒲田 義博; 田村 文彦; 山本 昌亘; 森下 卓俊; et al.
Journal of Neutron Research, 26(2-3), p.59 - 67, 2024/01
J-PARC Linacおよび3GeVシンクロトロン(RCS)は、1MWの大強度ビームを中性子実験施設および主リングシンクロトロンに供給するために運転している。これまで進めてきたビーム調整および機器改良により、当初想定よりもはるかに低いビームロス量で1MWのビーム運転を行うことが出来ている。現在のビーム出力はビームロスではなくRCSの高周波加速空胴の電源容量によって制限されている。近年、RCSグループではより少ない消費電力でビームを加速することのできる新しい構造の加速空胴の開発に成功した。この空胴によって、利用運転中に加速空胴で消費される電力を大幅に削減することが出来、さらに1MW以上の大出力での運転も可能となる。これまでの試験結果から、RCSの加速空胴を全て新しい物へ更新すれば、1.5MW以上の大出力も可能となる事が判っている。今後、中性子利用および主リングシンクロトロンの更なる成果創出のため、2MWを目標にRCSで必要な改良について検討を行った。その結果、高周波空胴の更新以外にも、高周波増幅器の増強やビームモニタの増強が必要であることが判ったため、今後順次更新を進める。
沖田 英史; 田村 文彦; 山本 昌亘; 野村 昌弘; 島田 太平; Saha, P. K.; 吉井 正人*; 大森 千広*; 杉山 泰之*; 長谷川 豪志*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2687(7), p.072005_1 - 072005_7, 2024/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)縦方向位相空間トモグラフィは、ビーム進行方向(縦方向)の位相空間分布を得るための有効な測定ツールである。J-PARCシンクロトロン(3GeVシンクロトロン及びメインリング)の大強度運転時の位相空間分布の測定には、空間電荷効果や集束力の非線形性等のビーム物理を考慮したトモグラフィが必要であった。本研究では、ビーム物理を考慮可能なハイブリッドアルゴリズムを採用したCERN's TomographyのJ-PARCシンクロトロンへの導入とベンチマークを実施した。ベンチマークの結果、J-PARCシンクロトロンの大強度運転条件における位相空間分布を高精度に測定可能であることを確認した。
Saha, P. K.; 原田 寛之; 菖蒲田 義博; 田村 文彦; 沖田 英史; 岡部 晃大; 仲野谷 孝充; 畠山 衆一郎; 守屋 克洋; 高柳 智弘; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2687(5), p.052020_1 - 052020_7, 2024/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)In this research, numerical simulation studies and beam tests were performed to minimize the beam loss at high intensity operation of J-PARC RCS. The beam loss usually increases non-linearly with respect to the beam power ramp up at high-intensity. The longitudinal and transverse injection painting used for space charge mitigation at a lower beam energy are optimized to produce a further uniform beam distribution to realize further space charge mitigation. The beam loss at the present operation at a net beam power of nearly 850 kW to the MLF has been kept to a minimum level to achieve a stable user operation. The beam loss at 1 MW beam power has also been sufficiently reduced to remain only 0.05% which is dominated by the unavoidable foil scattering beam loss.
高橋 博樹; Saha, P. K.; 吉本 政弘; 澤邊 祐希*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2687(7), p.072019_1 - 072019_5, 2024/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)J-PARCの3GeVシンクロトロンでは、リフレクティブメモリを用いた同期データシステムを構築している。今後の大強度ビーム運転における、より大きいサイズのデータを扱うという要望に対応するため、新しい同期データ生成手法を考案した。新たな手法は、既存システムにおいては上位計算機が行っている動作を計測系に実装することで、LAN経由のデータ転送による同期データ生成を実現するものである。本研究では、提案した手法を実装した新しい同期データシステムのテストベンチを構築し、性能確認を行った。その結果、LAN経由のデータ転送による新しい同期データシステム開発の目処を得ることができた。本件では、新同期データ生成手法の詳細と性能試験の結果について述べる。
今泉 悠也; 青柳 光裕; 神山 健司; 松場 賢一; Akaev, A.*; Mikisha, A.*; Baklanov, V.*; Vurim, A.*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 194, p.110107_1 - 110107_11, 2023/12
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:43.92(Nuclear Science & Technology)In severe accidents of SFRs, the cooling of the residual core materials, which is called "in-place cooling", is one of the important factors for In-Vessel Retention (IVR). For the evaluation, behavior of the in-place cooling was analyzed by the SIMMER-III code. In order to understand the in-place cooling, method of Phenomena Identification and Ranking Table (PIRT) was applied. Based on the result, an out-of-pile experiment which focused on the extracted factors was conducted. In the experiment, continuous oscillation of sodium level was observed by sodium vaporization and condensation. Analysis for the out-of-pile experiment was conducted by SIMMER-III, but the results were different between the experiment and the analysis. By investigation of the analysis result, it was revealed that the difference was due to occupation of non-condensable gas. Therefore, an analysis model of inter-cell gas mixing was newly developed, and the agreement was significantly improved by the new model.
Soler, J. M.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Pulkkanen, V.-M.*; Moreno, L.*; Iraola, A.*; Trinchero, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Havlov
ha, J.*; Havlov , V.*; Trpko
, V.*; Trpko ov
ov , D.*; et al.
, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Technology, 209(11), p.1765 - 1784, 2023/11
被引用回数:4 パーセンタイル:71.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)The REPRO-TDE test was performed at a depth of about 400 m in the ONKALO underground research facility in Finland. Synthetic groundwater containing radionuclide tracers (HTO, Cl-36, Na-22, Ba-133, Cs-134) was circulated for about four years in a packed-off interval of the injection borehole. Tracer activities were additionally monitored in two observation boreholes. The test was the subject of a modelling exercise by the SKB GWFTS Task Force. Eleven teams participated in the exercise, using different model concepts and approaches. Predictive model calculations were based on laboratory-based information concerning porosities, diffusion coefficients and sorption partition coefficients. After the experimental results were made available, the teams were able to revise their models to reproduce the observations. General conclusions from these back-analysis calculations include the need for reduced effective diffusion coefficients for Cl-36 compared to those applicable to HTO (anion exclusion), the need to implement weaker sorption for Na-22, compared to results from laboratory batch-sorption experiments, and the observation of large differences between the theoretical initial concentrations for the strongly-sorbing Ba-133 and Cs-134 and the first measured values a few hours after tracer injection. Different teams applied different concepts, concerning mainly the implementation of isotropic vs. anisotropic diffusion, or the possible existence of Borehole Disturbed Zones around the different boreholes. The role of microstructure was also addressed in two of the models.
田村 文彦; 沖田 英史; 發知 英明*; Saha, P. K.; 明午 伸一郎; 吉井 正人*; 大森 千広*; 山本 昌亘; 清矢 紀世美*; 杉山 泰之*; et al.
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.64 - 68, 2023/11
J-PARC 3GeVシンクロトロン(RCS)は物質・生命科学実験施設(MLF)およびメインリング(MR)に大強度陽子ビーム供給を行っている。RCSのハーモニック数hは2で、通常は2つのバンチを加速している。MLFのいくつかの実験では1バンチでのビーム供給が好ましいが、この場合1つのRFバケツを空きバケツとして加速を行うため、ビーム強度は半分となってしまう。RCSのハーモニック数を1として加速できれば、1バンチあたりの強度は2倍となり、最大強度での1バンチビーム供が可能となる。一方MRは、バンチあたりの粒子数を設計より上げることができるならば、1バンチずつ8回の入射を行うことで現在の設計ビームパワー1.3MWを超える運転ができる可能性がある。本発表では、主にRCSでの縦方向シミュレーションによるh=1加速の検討について報告する。
 beam at J-PARC RCS
beam at J-PARC RCSSaha, P. K.; 原田 寛之; 米田 仁紀*; 道根 百合奈*; 佐藤 篤*; 柴田 崇統*; 金正 倫計
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.59 - 63, 2023/11
To overcome the issues and practical limitations associated with the stripper foil used for the charge-exchange injection (CEI) of H beam for high-intensity proton accelerators, we are studying a foil-less H
beam for high-intensity proton accelerators, we are studying a foil-less H CEI by using only lasers at J-PARC RCS. To establish our principle, we are preparing for a POP (proof-of-principle) demonstration of 400 MeV H
CEI by using only lasers at J-PARC RCS. To establish our principle, we are preparing for a POP (proof-of-principle) demonstration of 400 MeV H stripping to proton by using lasers. We will use both IR and UV lasers in the process of H
stripping to proton by using lasers. We will use both IR and UV lasers in the process of H stripping to protons. A prototype YAG laser system has been developed through experimental studies of 3 MeV H
stripping to protons. A prototype YAG laser system has been developed through experimental studies of 3 MeV H neutralization. We have also developed a multi-reflection laser cavity system to sufficiently reduce the seed laser energy. We have succeeded for 32 reflections to gain on the laser energy up to 16 to obtain a neutralization fraction of 25%. To realize a perfect benefit of the cavity, we also recently developed higher efficient vacuum windows by which we can achieve the laser energy gain to almost 32, proportional to the number of reflections. As a result, the average power of the seed laser can be reduced to 1/32, which is more useful for the UV laser. The laser setup at the 400 MeV beam line is in progress to start POP experimental studies in 2024.
neutralization. We have also developed a multi-reflection laser cavity system to sufficiently reduce the seed laser energy. We have succeeded for 32 reflections to gain on the laser energy up to 16 to obtain a neutralization fraction of 25%. To realize a perfect benefit of the cavity, we also recently developed higher efficient vacuum windows by which we can achieve the laser energy gain to almost 32, proportional to the number of reflections. As a result, the average power of the seed laser can be reduced to 1/32, which is more useful for the UV laser. The laser setup at the 400 MeV beam line is in progress to start POP experimental studies in 2024.
仲野谷 孝充; 吉本 政弘; Saha, P. K.; 竹田 修*; 佐伯 理生二*; 武藤 正義*
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.937 - 941, 2023/11
J-PARC 3GeVシンクロトロン(RCS: Rapid Cycling Synchrotron)では、前段加速器であるリニアックから入射した400MeVのH ビームを荷電変換フォイルによりH
ビームを荷電変換フォイルによりH ビームに変換して、3GeVまで加速している。これまでRCSでは、HBCフォイル(Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon stripper foil)とカネカ社製のグラフェン薄膜(GTF: Graphene Thin Film)の2種類を荷電変換フォイルとして使用してきた。HBCフォイルとは100
ビームに変換して、3GeVまで加速している。これまでRCSでは、HBCフォイル(Hybrid Boron mixed Carbon stripper foil)とカネカ社製のグラフェン薄膜(GTF: Graphene Thin Film)の2種類を荷電変換フォイルとして使用してきた。HBCフォイルとは100 g/cm
g/cm 以上の厚い炭素フォイルを安定的に作製するために高エネルギー加速器研究機構(KEK)で開発された手法である。当初はKEKで作製されたフォイルを使用してきたが、2017年からは原子力機構でHBCフォイルの作製を開始し、以来これを使用している。近年、アーク蒸着法では作製が困難と言われてきた厚い純炭素フォイルの成膜に成功した。新たな試みとして、この純炭素フォイルを2023年3月からの利用運転で使用した。結果、HBCフォイルとGTFでは使用時間の経過とともに、荷電変換されずにビームダンプに廃棄されるビーム量の増加傾向が観察されたが、純炭素フォイルではこの傾向がなく、安定的に荷電変換が可能であった。本発表ではこれら3種類の荷電変換フォイルの使用状況について報告する。
以上の厚い炭素フォイルを安定的に作製するために高エネルギー加速器研究機構(KEK)で開発された手法である。当初はKEKで作製されたフォイルを使用してきたが、2017年からは原子力機構でHBCフォイルの作製を開始し、以来これを使用している。近年、アーク蒸着法では作製が困難と言われてきた厚い純炭素フォイルの成膜に成功した。新たな試みとして、この純炭素フォイルを2023年3月からの利用運転で使用した。結果、HBCフォイルとGTFでは使用時間の経過とともに、荷電変換されずにビームダンプに廃棄されるビーム量の増加傾向が観察されたが、純炭素フォイルではこの傾向がなく、安定的に荷電変換が可能であった。本発表ではこれら3種類の荷電変換フォイルの使用状況について報告する。
小島 邦洸; 原田 寛之; Saha, P. K.
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.127 - 131, 2023/11
本研究はJ-PARCにある3GeVシンクロトロン(Rapid cycling synchrotron: RCS)のビーム大強度・高品質化に貢献するものである。大強度陽子加速器において出力を制限する最大の要因はビーム損失に起因する装置の放射化である。そのため、ビーム損失の低減は大強度化を目指す上で重要度の高い課題である。現在、RCSでは、設計出力1MWの大強度ビームにおいてビーム損失を0.1%程度にまで低減することに成功している。空間電荷力の影響を受けにくい位相空間内の振幅の大きな粒子はビーム損失の原因となりやすい。つまり、動作点近傍のビーム損失起源となる共鳴の同定と補正は安定領域の拡大とビーム損失の低減をもたらし、より一層の大強度化に貢献する。RCSにおけるビーム損失起源の同定に向け、ビーム重心が水平・進行方向の位相空間内を大振幅で振動するような特殊な入射ビームを用いた実験を実施した。その結果、クロマティシティとシンクロトロン振動で生じるチューンシフトによるビームの2次非構造共鳴(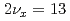 )への抵触がビーム損失に繋がることを明らかにした。さらに、補正四極電磁石6台をそれぞれ励磁し、当該共鳴が補正可能であることを実証した。今後は補正四極電磁石の励磁量の最適化を進めていく。本発表では、これらの実験結果を報告し、ビーム損失起源とその補正手法について議論する。
)への抵触がビーム損失に繋がることを明らかにした。さらに、補正四極電磁石6台をそれぞれ励磁し、当該共鳴が補正可能であることを実証した。今後は補正四極電磁石の励磁量の最適化を進めていく。本発表では、これらの実験結果を報告し、ビーム損失起源とその補正手法について議論する。
Saha, P. K.; 原田 寛之; 岡部 晃大; 沖田 英史; 菖蒲田 義博; 田村 文彦; 山本 風海; 吉本 政弘; 發知 英明*
Proceedings of 68th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High Intensity and High Brightness Hadron Beams (HB2023) (Internet), p.147 - 152, 2023/10
In the 3-GeV RCS of J-PARC we have performed a systematic experimental studies and numerical beam simulations to minimize the beam loss at the designed 1 MW beam power. We have optimized and modified both longitudinal and transverse injection paintings and succeeded obtaining a significant beam loss mitigation throughout the RCS. The beam loss at the collimator and the 1st arc section is reduced to be as much as more than 60% as compared to that using original painting methods. The residual beam loss at 1 MW is estimated to be as low as well below than 0.1%, which is dominated by the beam loss caused by foil scattering of the circulating beam. As a result, we obtained a very stable user operation of the RCS with nearly 1 MW beam power to the MLF with low beam loss and less machine activation.
菖蒲田 義博; 原田 寛之; Saha, P. K.; 高柳 智弘; 田村 文彦; 富樫 智人; 渡辺 泰広; 山本 風海; 山本 昌亘
Proceedings of 68th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High Intensity and High Brightness Hadron Beams (HB2023) (Internet), p.162 - 169, 2023/10
J-PARC 3GeVシンクロトロン(RCS)では、キッカーインピーダンスによってビームが不安定になる。大きな横方向エミッタンスの場合、このビームの不安定性は抑制可能で、横方向のフィードバックシステムなしで、1MWビームを安定的に物質・生命科学実験施設に供給できる。しかし、Main Ringにビームを供給する場合には、より小さな横方向エミッタンスを持つ大強度ビームが必要である。そこで、ダイオードスタックと抵抗器を使用したキッカーインピーダンスを抑制するスキームの実用化をした。これにより、ビームの不安定性を低減しながら、RCSから正常にビームを出射することが可能になった。
山本 風海; 守屋 克洋; 沖田 英史; 山田 逸平; 地村 幹; Saha, P. K.; 菖蒲田 義博; 田村 文彦; 山本 昌亘; 森下 卓俊; et al.
Proceedings of 68th ICFA Advanced Beam Dynamics Workshop on High Intensity and High Brightness Hadron Beams (HB2023) (Internet), p.270 - 273, 2023/10
J-PARC 3GeVシンクロトロン(RCS)は、1MWの大強度ビームを中性子実験施設および主リングシンクロトロンに供給するために運転している。これまで進めてきたビーム調整および機器改良により、当初想定よりもはるかに低いビームロス量で1MWのビーム運転を行うことが出来ている。そのため、現在のビーム出力はビームロスではなく高周波加速空胴の電源容量によって制限されている。近年、RCSグループではより少ない消費電力でビームを加速することのできる新しい構造の加速空胴の開発に成功した。この空胴によって、利用運転中に加速空胴で消費される電力を大幅に削減することが出来、さらに1MW以上の大出力での運転も可能となる。これまでの試験結果から、RCSの加速空胴を全て新しい物へ更新すれば、1.5MW以上の大出力も可能となる事が判っている。今後、中性子利用および主リングシンクロトロンの更なる成果創出のため、2MWを目標にRCSで必要な改良について検討を行った。その結果、高周波空胴の更新以外にも、高周波増幅器の増強やビームモニタの増強が必要であることが判ったため、今後順次更新を進める。