Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
河 侑成; 山口 義仁; 長谷川 邦夫; Negyesi, M.*
Proceedings of ASME 2024 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference (PVP 2024) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2024/07
If a flaw in a high-toughness ductile pipe of a power plant is detected during periodic in-service inspection, stress applied at the flaw location of the pipe is compared with an allowable stress. When the applied stress is less than the allowable stress, the plant can operate continuously for a certain evaluation period in accordance with ASME Code Section XI. The flow stress given by the average of yield strength and ultimate tensile strength is an important material parameter for allowable stress. Recently, many fitness-for-service codes and technical reports have adopted conversions from hardness measurement values to yield strength and ultimate tensile strength. In this paper, we introduced the flow stress obtained from converted tensile properties from Vickers hardness using the presented equations for austenitic stainless steel. The allowable stress estimated by the Vickers hardness was compared with the allowable stress determined by actual tensile properties. As a result, the flow stress converted from hardness was about 1.48 times larger than that obtained by actual flow stress. The allowable flaw sizes calculated by the flow stress converted from hardness gave an appropriate indication when the allowable or applied stress was very low. However, the flow stress converted from hardness gave unconservative allowable stress, when the applied stress was large.
Negyesi, M.*; 河 侑成; 長谷川 邦夫; Lacroix, V.*
Proceedings of ASME 2024 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference (PVP 2024) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2024/07
Allowable stresses for pipes are determined by combining failure stresses and safety factors. When predicting the plastic collapse failure stresses for high toughness ductile pipes, flow stresses of the pipe materials are indispensable. The flow stress is usually given by the average of the yield strength and the ultimate tensile strength. Inservice Inspection of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Code Section XI states to use the yield strengths and the ultimate tensile strengths defined by the ASME Code Section II Materials. The ASME Code Section XI also states that actual measured yield strengths and ultimate tensile strengths are possible to be used, alternatively. Values of yield strength and ultimate tensile strength given by the ASME Code Section II are conservative, corresponding to lower bound values. Then, it is easily inferred that the allowable stresses calculated by the code given flow stress are lower than the allowable stresses calculated by the actual measured flow stress. The objective of this paper is to compare the plastic collapse failure and allowable stresses based on both the code and actual flow stresses for pipes with circumferential flaws subjected to bending and tensile loading. In addition, it is demonstrated that allowable flaw sizes based on both flow stresses do not differ much at low allowable stress. However, when the allowable stress is large, the allowable flaw size based on the code flow stress is substantially lower compared to that based on the actual flow stress.
河 侑成; 下平 昌樹; 勝山 仁哉
Transactions of the 27th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT 27) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2024/03
国内の原子炉圧力容器(RPV)の溶接継手熱影響部(継手HAZ)は監視試験対象部位である。継手HAZ内には非均質に金属組織が分布し、破壊靭性のばらつきが大きいと考えられるものの、HAZ試験片の採取位置における金属組織の違いが機械的特性及び照射脆化感受性に及ぼす影響は詳細に調べられていなかった。本研究では継手HAZの非均質な組織に着目し、まず未照射材について溶接金属と母材の境界からの距離に応じて3箇所(0.5mm, 1mm及び2mm)の継手HAZ、及び母材から採取した微小試験片(Mini-C(T)試験片)を用いて破壊靭性を評価した。その結果、HAZの破壊靭性は母材と比べてばらつきが大きく、特に溶接金属と母材の境界から0.5mmのHAZにおいて破壊靭性のばらつきが最も大きい傾向を示した。HAZに対する破壊靭性参照温度は採取した3箇所の中で有意な差が得られたものの、いずれの破壊靭性参照温度も母材より低く、破壊靭性値が高いことを確認した。本研究結果により、未照射状態では母材が継手HAZを代表して破壊靭性を保守的に評価できることを確認した。
下平 昌樹; 河 侑成; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; 鬼沢 邦雄
Proceedings of ASME 2023 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2023) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2023/07
最新の原子炉圧力容器の構造健全性評価においては、マスターカーブ法に基づく正確な破壊靭性参照温度T の取得が必要である。破壊靭性参照温度T
の取得が必要である。破壊靭性参照温度T はMini-C(T)破壊靭性試験片によって取得可能であり、この試験片の寸法や初期亀裂形状に関しては、ASTM規格のE1921や日本電気協会電気技術規程JEAC4216に規定されている。最近、ASTM E1921では評価の正確性や試験を行う上での利便性を向上させるために、何度か予亀裂形状に関する規定の変更が行われてきた。このような規格の改定に伴うMini-C(T)試験片の許容予亀裂形状の変化は、予亀裂先端の塑性拘束状態を変化させ、T
はMini-C(T)破壊靭性試験片によって取得可能であり、この試験片の寸法や初期亀裂形状に関しては、ASTM規格のE1921や日本電気協会電気技術規程JEAC4216に規定されている。最近、ASTM E1921では評価の正確性や試験を行う上での利便性を向上させるために、何度か予亀裂形状に関する規定の変更が行われてきた。このような規格の改定に伴うMini-C(T)試験片の許容予亀裂形状の変化は、予亀裂先端の塑性拘束状態を変化させ、T 評価に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。本研究では、ASTM E1921やJEAC4216に規定される予亀裂形状に関する要求の妥当性について議論するため、Mini-C(T)試験片の予亀裂湾曲が破壊靭性評価に及ぼす影響について、ワイブル応力解析を含む有限要素解析によって定量的に評価した。その結果、ASTM E1921-21で定められた最大湾曲を有する亀裂形状の場合、亀裂先端の塑性拘束が弱められ、理想的な直線状亀裂を有するMini-C(T)試験片で得られる破壊靭性値に比べて高めの破壊靭性値が得られる可能性を示した。また、上述の最大湾曲を許容した場合、非保守的なT
評価に影響を及ぼす可能性がある。本研究では、ASTM E1921やJEAC4216に規定される予亀裂形状に関する要求の妥当性について議論するため、Mini-C(T)試験片の予亀裂湾曲が破壊靭性評価に及ぼす影響について、ワイブル応力解析を含む有限要素解析によって定量的に評価した。その結果、ASTM E1921-21で定められた最大湾曲を有する亀裂形状の場合、亀裂先端の塑性拘束が弱められ、理想的な直線状亀裂を有するMini-C(T)試験片で得られる破壊靭性値に比べて高めの破壊靭性値が得られる可能性を示した。また、上述の最大湾曲を許容した場合、非保守的なT が取得されることをワイブル応力解析によって示した。一方、JEAC4216で許容される最大湾曲を有する亀裂形状の場合は、理想的な直線状亀裂の場合と比べてT
が取得されることをワイブル応力解析によって示した。一方、JEAC4216で許容される最大湾曲を有する亀裂形状の場合は、理想的な直線状亀裂の場合と比べてT の有意な差は見られなかった。
の有意な差は見られなかった。
河 侑成; 飛田 徹; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 145(2), p.021501_1 - 021501_9, 2023/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:14.57(Engineering, Mechanical)The fracture toughness in the heat-affected zone (HAZ), which is located under the weld overlay cladding on the inner surface of the reactor pressure vessel (RPV), was evaluated by considering the inhomogeneous microstructures of the HAZ. In this regard, 0.4T-C(T) specimens and Mini-C(T) specimens were manufactured to clarify the effect of the HAZ on fracture toughness. First, the fracture toughness was evaluated using 0.4T-C(T) specimens targeted on microstructural distribution due to the cladding bead location. The reference temperature (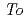 ) of HAZ at middle region of cladding bead was 12
) of HAZ at middle region of cladding bead was 12 C higher than that at overlap cladding beads. Second, the fracture toughness was evaluated using Mini-C(T) specimens focused on the microstructural difference with distance from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal. The
C higher than that at overlap cladding beads. Second, the fracture toughness was evaluated using Mini-C(T) specimens focused on the microstructural difference with distance from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal. The 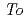 value of the central position located at 3 mm to 7 mm from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal was higher than those of the other positions in HAZ. However, the
value of the central position located at 3 mm to 7 mm from the boundary between the cladding and the base metal was higher than those of the other positions in HAZ. However, the 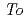 values of HAZ for both 0.4T-C(T) and Mini-C(T) specimens were significantly lower than that of the base metal at a quarter thickness by 40
values of HAZ for both 0.4T-C(T) and Mini-C(T) specimens were significantly lower than that of the base metal at a quarter thickness by 40 C
C 60
60 C. Compared with the literature data that indicated fracture toughness at the inner surface without overlay cladding and the base metal at a quarter thickness, this study concluded that the HAZ under the overlay cladding showed no detrimental effect on the conservatism of the structural integrity assessment of RPV steel.
C. Compared with the literature data that indicated fracture toughness at the inner surface without overlay cladding and the base metal at a quarter thickness, this study concluded that the HAZ under the overlay cladding showed no detrimental effect on the conservatism of the structural integrity assessment of RPV steel.
岩田 景子; 高見澤 悠; 河 侑成; 下平 昌樹; 岡本 芳浩; 本田 充紀; 勝山 仁哉; 西山 裕孝
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 511, p.143 - 152, 2022/01
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:32.42(Instruments & Instrumentation)The main causes of the irradiation embrittlement of RPVs are the formation of a solute cluster and the matrix defect. To investigate these embrittlement mechanisms, it is necessary to complementarily apply microstructure analyses. The extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) technique can detect changes in the atomic structure because of a vacancy-type defect or interstitial atoms introduced by irradiation around selected atoms. In this study, to investigate such microstructural changes due to irradiation, we performed an EXAFS examination for high-copper RPV steels subjected to ion irradiation. We investigated microstructures of the crystal structure around specific element such as Cu, Mn, and Ni, which are known to be the atoms included in the solute atom clusters and lattice defects such as vacancy-type defects. The results indicated that the solute atoms clusteris thought to aggregate in the Fe matrix while maintaining the bcc structure and that not only a vacancy-type defect but also a tensile configuration-type dumbbell pair could be located around both Cu and Ni atoms.
河 侑成; 下平 昌樹; 高見澤 悠; 飛田 徹; 勝山 仁哉; 西山 裕孝
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2021/07
The semi-elliptical crack sized 10 mm in depth  60 mm in length shall be postulated near the inner surface of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) in pressurized thermal shock events. We investigated the fracture toughness distribution in the postulated crack area under the PTS events of unirradiated and highly-neutron irradiated RPV steels. Vickers hardness in heat-affected zone (HAZ) due to stainless overlay cladding and 10 mm from the cladding were higher than that of a quarter thickness position, where the surveillance specimens are machined, for both unirradiated (E1) and irradiated (up to 1
60 mm in length shall be postulated near the inner surface of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) in pressurized thermal shock events. We investigated the fracture toughness distribution in the postulated crack area under the PTS events of unirradiated and highly-neutron irradiated RPV steels. Vickers hardness in heat-affected zone (HAZ) due to stainless overlay cladding and 10 mm from the cladding were higher than that of a quarter thickness position, where the surveillance specimens are machined, for both unirradiated (E1) and irradiated (up to 1  10
10 n/cm
n/cm , WIM) materials. Fracture toughness of HAZ and 10 mm from the cladding was higher for the above highly-neutron irradiated material. The same result was obtained in the unirradiated material. Therefore, it was confirmed that fracture toughness obtained from surveillance specimens can provide conservative assessment of structural integrity of RPV.
, WIM) materials. Fracture toughness of HAZ and 10 mm from the cladding was higher for the above highly-neutron irradiated material. The same result was obtained in the unirradiated material. Therefore, it was confirmed that fracture toughness obtained from surveillance specimens can provide conservative assessment of structural integrity of RPV.
河 侑成; 岡野 成威*; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; 望月 正人*
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2021/07
Residual stress is one of the most important influence factors in the structural integrity assessment of the nuclear components. However, at the present, there are few examples of residual stress measurements for thick butt-welded plates such as the reactor pressure vessels (RPVs). In this study, the residual stresses generated by butt-welding of thick plates of RPV steel, which have almost the same thickness of 140 mm as actual boiling water reactor RPV, were measured for post-welded heat-treated condition using the deep-hole-drilling technique. In addition, thermo-elastic-plastic creep analyses by or without considering the phase transformation in the heat-affected zone using the finite element analyses (FEAs) were performed to evaluate the residual stress produced by butt-welding and post-weld heat treatment. In the analysis considering phase transformation using the commercial FEM analysis code Abaqus, the fractions of the phases, such as martensite, bainite and ferrite, are calculated based on the kinetics of phase transformation. By comparing the analytical results with the experimentally determined values, we found good agreements for the residual stress distributions within the weld and the base material near the welded part. In the presentation, the effect of phase transformation on residual stress distribution of butt-weldment of thick plate will be discussed.
河 侑成; 高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; 塙 悟史; 西山 裕孝
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 461, p.276 - 282, 2019/12
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:41.52(Instruments & Instrumentation)The microstructural distribution in the heat-affected zone (HAZ) under the stainless overlay cladding of low alloy steel was investigated by metallurgical observation and finite element analysis (FEA). The distribution of the coarse-grain (CG) HAZ and the fine-grain (FG) HAZ in low alloy steel by metallurgical observation agreed well with the FEA results. Base metal contained mixed bainite with ferrite, whereas the CGHAZ and the FGHAZ contained mixed lower bainite with martensite and mixed upper bainite with ferrite, respectively. Ferrite fraction in FGHAZ was higher than those other areas. After ion irradiation at a fluence of 0.5 dpa, irradiation hardening and the formation of solute clusters were observed at the base metal, FGHAZ, and the CGHAZ. Atom probe tomography analysis revealed that irradiation hardening increased with increasing volume fraction of clusters, although irradiation hardening at the FGHAZ was greater than that at the CGHAZ, which contained more clusters than the FGHAZ. This difference in irradiation hardening may be due to the differences in the amount of ferrite, carbide precipitates and so on in the different microstructures.
河 侑成; 下平 昌樹; 飛田 徹; 塙 悟史; 山崎 翔太*; 宇野 定則*
2018年度量子科学技術研究開発機構施設共用実施報告書(インターネット), 3 Pages, 2019/09
原子炉圧力容器の母材の内表面から約10mm深さの範囲に生じるステンレスオーバーレイクラッド下溶接熱影響部の照射脆化感受性を調査するための電子線照射試験の準備として、原子炉圧力容器鋼の実機環境相当である290 Cを目標とした照射温度の制御実験を実施した。冷却装置や試料固定治具の製作等を行い、電子線照射時の電流値による試料の発熱と熱伝導による冷却のバランスを調整し、照射温度を290
Cを目標とした照射温度の制御実験を実施した。冷却装置や試料固定治具の製作等を行い、電子線照射時の電流値による試料の発熱と熱伝導による冷却のバランスを調整し、照射温度を290 Cに制御する条件を調べた。その結果、適切な厚さのステンレススペーサーの使用により、290.6
Cに制御する条件を調べた。その結果、適切な厚さのステンレススペーサーの使用により、290.6 C
C 4.7
4.7 C範囲で照射温度を制御できることを確認した。
C範囲で照射温度を制御できることを確認した。
高見澤 悠; 勝山 仁哉; 河 侑成; 飛田 徹; 西山 裕孝; 鬼沢 邦雄
Proceedings of 2019 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2019) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2019/07
原子炉圧力容器鋼の溶接熱影響部(HAZ)について、実際の原子炉圧力容器を模擬した継手溶接材(継手HAZ)及びHAZの代表的な組織を再現した熱処理材を作製し、JRR-3を用いた中性子照射試験及び照射後試験を実施し、照射前後の微細組織変化及び機械的特性変化を調べた。未照射材において、継手HAZ及び細粒HAZの破壊靭性が母材よりも低く、その要因が島状マルテンサイトやフェライト相の存在に因ることを明らかにした。また、粗粒HAZの中性子照射脆化感受性は母材よりも小さい値を示し、継手HAZ及び細粒HAZは母材と同等であることを明らかにした。
河 侑成; 飛田 徹; 大津 拓与; 高見澤 悠; 西山 裕孝
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 140(5), p.051402_1 - 051402_6, 2018/10
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:39.41(Engineering, Mechanical)The applicability of miniature compact tension (Mini-C(T)) specimens to fracture toughness evaluation of neutron-irradiated reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels was investigated. Three types of RPV steels neutron-irradiated to a high-fluence region were prepared and manufactured as Mini-C(T) specimens according to Japan Electric Association Code (JEAC) 4216-2015. Through careful selection of the test temperature by considering previously obtained mechanical properties data, valid fracture toughness, and reference temperature T was obtained with a relatively small number of specimens. Comparing the fracture toughness and T
was obtained with a relatively small number of specimens. Comparing the fracture toughness and T values determined using other larger specimens with those determined using the Mini-C(T) specimens, T
values determined using other larger specimens with those determined using the Mini-C(T) specimens, T values of both unirradiated and irradiated Mini-C(T) specimens were found to be the acceptable margin of error. The scatter of 1T-equivalent fracture toughness values of both unirradiated and irradiated materials obtained using Mini-C(T) specimens did not differ significantly from the values obtained using larger specimens. The correlation between the Charpy 41J transition temperature (T
values of both unirradiated and irradiated Mini-C(T) specimens were found to be the acceptable margin of error. The scatter of 1T-equivalent fracture toughness values of both unirradiated and irradiated materials obtained using Mini-C(T) specimens did not differ significantly from the values obtained using larger specimens. The correlation between the Charpy 41J transition temperature (T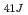 ) and the T
) and the T values agreed very well with that of the data in the literature, regardless of specimen size and fracture toughness of the materials before irradiation. Based on these findings, it was concluded that Mini-C(T) specimens can be applied to fracture toughness evaluation of neutron-irradiated materials without significant specimen size dependence.
values agreed very well with that of the data in the literature, regardless of specimen size and fracture toughness of the materials before irradiation. Based on these findings, it was concluded that Mini-C(T) specimens can be applied to fracture toughness evaluation of neutron-irradiated materials without significant specimen size dependence.
河 侑成; 飛田 徹; 高見澤 悠; 塙 悟史; 西山 裕孝
Proceedings of 2018 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2018), 6 Pages, 2018/07
An evaluation of the fracture toughness of the heat-affected zone (HAZ), which is located under the weld overlay cladding of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV), was performed. Considering inhomogeneous microstructures of the HAZ, 0.4T-C(T) specimens were manufactured from the cladding strips locations, and Mini-C(T) specimens were fabricated from the distanced location as well as under the cladding. The reference temperature (T ) values of HAZ for both 0.4T-C(T) and Mini-C(T) specimens were significantly lower than that of the base metal at a quarter thickness by 40
) values of HAZ for both 0.4T-C(T) and Mini-C(T) specimens were significantly lower than that of the base metal at a quarter thickness by 40 C
C 60
60 C. Compared to the literature data that indicated fracture toughness at the surface without overlay cladding and base metal of a quarter thickness in a pressure vessel plate, this study concluded that the welding thermal history showed no significant effect on the fracture toughness of the inner surface of RPV steel.
C. Compared to the literature data that indicated fracture toughness at the surface without overlay cladding and base metal of a quarter thickness in a pressure vessel plate, this study concluded that the welding thermal history showed no significant effect on the fracture toughness of the inner surface of RPV steel.
岩田 景子; 高見澤 悠; 河 侑成; 岡本 芳浩; 下山 巖; 本田 充紀; 塙 悟史; 西山 裕孝
Photon Factory Activity Report 2017, 2 Pages, 2018/00
原子炉圧力容器内表面のステンレスオーバーレイクラッド直下に生じる溶接熱影響部(HAZ)は熱履歴により結晶粒径や析出物分布の異なる組織が複雑に分布し、母材とは機械的特性が異なることが知られている。本研究では、HAZ組織の特徴を調べるため炭化物分布に着目し、形成元素の一つであるMoの周辺微細構造について分析を行った。HAZ組織の狭い領域毎の構造情報を取得するため、キャピラリレンズを使用した広域X線吸収微細構造(EXAFS)により mオーダーの領域測定を実施した。EXAFS結果からHAZ内で生成が確認されている炭化物種の一つであるMo
mオーダーの領域測定を実施した。EXAFS結果からHAZ内で生成が確認されている炭化物種の一つであるMo Cは粒径の小さい領域に比較的多く分布することが示唆された。
Cは粒径の小さい領域に比較的多く分布することが示唆された。
河 侑成; 飛田 徹; 高見澤 悠; 西山 裕孝
Proceedings of 2017 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2017) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2017/07
圧力容器鋼の破壊靱性評価へのミニチュアC(T)試験片の適用性を調べるため、中性子照射された圧力容器鋼材のシャルピー試験片からミニチュアC(T)試験片を加工するとともに破壊靱性試験に供し、参照温度 を評価した。その結果、ミニチュアC(T)試験片で得られる
を評価した。その結果、ミニチュアC(T)試験片で得られる は疲労予亀裂入りシャルピー型破壊靭性試験片から得られる値とよく一致すること、ミニチュアC(T)試験片から得られる1T-C(T)相当の破壊靱性値のばらつきは疲労予亀裂入りシャルピー型破壊靭性試験片等から得られるものと大差が無いこと、参照温度
は疲労予亀裂入りシャルピー型破壊靭性試験片から得られる値とよく一致すること、ミニチュアC(T)試験片から得られる1T-C(T)相当の破壊靱性値のばらつきは疲労予亀裂入りシャルピー型破壊靭性試験片等から得られるものと大差が無いこと、参照温度 とシャルピー吸収エネルギー41Jレベルの延性脆性遷移温度の関係は、米国データのばらつきの範囲内にあることが明らかになった。
とシャルピー吸収エネルギー41Jレベルの延性脆性遷移温度の関係は、米国データのばらつきの範囲内にあることが明らかになった。
河 侑成; 岩田 景子; 高見澤 悠; 塙 悟史; 西山 裕孝
no journal, ,
低合金鋼の溶接熱影響部(HAZ)における溶質原子クラスタ(クラスタ)の形成を調べるため、クラスタを構成する主要元素であるCuの含有量の異なる二種類の低合金綱にイオン照射を行うとともに3次元アトムプローブで微細組織を分析した。Cu含有量の高い材料では、HAZの組織に応じてクラスタの体積率が異なること、HAZに形成されるクラスタの体積率は母材に比べて高いことを確認した。現在、Cu含有量の低い材料の3次元アトムプローブ分析を進めており、Cu含有量と形成されるクラスタ性状の相関や硬さへの影響等を明らかにする予定である。
河 侑成; 高見澤 悠; 岩田 景子; 飛田 徹; 知見 康弘; 勝山 仁哉; 西山 裕孝
no journal, ,
原子炉圧力容器ステンレスオーバーレイクラッド材について有限要素法解析を行い、溶接入熱による熱影響部の微細構造変化を予測した。その結果に基づいてHAZから粗粒領域と細粒領域を採取し、比較のため1/4厚さ位置の母材試験片を採取してイオン照射を行った。照射前後HAZにおいては母材より照射による硬化量が大きい傾向を示した。また、微細粒領域の場合、位置によって硬化量の変化が異なる結果が得られた。
河 侑成; 高見澤 悠; 塙 悟史; 西山 裕孝
no journal, ,
原子炉圧力容器鋼クラッド溶接熱影響部(HAZ)のイオン照射による微細組織変化を調べるため、粗大粒HAZ, 微細粒HAZ及び母材に対してアトムプローブを用いた溶質原子クラスタ分析を行った。HAZにおけるクラスタの数密度及び体積率は母材に比べて高く、粗大粒HAZで最も大きい値を示した。また、HAZと母材に形成されるクラスタでCu, Mn含有量には違いがない一方で、Ni, Si含有量は粗大粒HAZのクラスタで多いことが明らかになった。金属組織観察及び硬さ測定などの結果から、照射前の結晶粒径や相分率などマクロな組織の違いが溶質原子クラスタの形成等に影響しているものと推測した。
河 侑成; 高見澤 悠; 飛田 徹; 西山 裕孝
no journal, ,
原子炉圧力容器の健全性評価に関する原子力機構における近年の研究内容について発表する。国内の民間規格であるJEAC4216の最新版では、コンパクトテンション型の小型試験片(Mini-C(T))を用いたマスターカーブ法に基づく破壊靭性評価法が示され、JEAC4206の最新版ではマスターカーブ法に基づく破壊靭性曲線が新たに設定されている。その妥当性・保守性を確認するため、化学成分や機械的特性の異なる9種の鋼材に対して、Mini-C(T)から4T-C(T)までの寸法の異なる試験片を用いた破壊靭性試験を実施した。Mini-C(T)を用いて他の試験片と同等の参照温度を得ることができること、またMini-C(T)は照射材に対しても適用できることを示した。さらに、JEAC4206-2016で提案されている破壊靭性下限曲線のデータ包絡率を確認し、下限線の設定が妥当であることを示した。本報告では、今後実施を予定している2軸荷重の大型十字試験体を用いた破壊試験およびクラッド下の溶接熱影響部の照射材の破壊靭性評価の計画についても紹介する。
岩田 景子; 高見澤 悠; 河 侑成; 岡本 芳浩; 下山 巖; 小島 啓*; 眞弓 蓮*; 岩瀬 彰宏*; 永井 康介*; 西山 裕孝
no journal, ,
熱時効された原子炉圧力容器ステンレスオーバーレイクラッド材について、X線吸収を用いて微細組織分析を行った。測定には材料全体の平均的な情報が取得でき、元素選択的に結合距離や化学状態を把握することができるX線吸収微細構造解析を適用した。溶質原子であるMn原子周辺において配位数や結合距離の変化が認められた。