Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanaka, Taiki*; Morita, Kosuke*; Morimoto, Koji*; Kaji, Daiya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Boll, R. A.*; Brewer, N. T.*; Van Cleve, S.*; Dean, D. J.*; Ishizawa, Satoshi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 124(5), p.052502_1 - 052502_6, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:85.04(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Tanaka, Taiki*; Narikiyo, Yoshihiro*; Morita, Kosuke*; Fujita, Kunihiro*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Yamaki, Sayaka*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Tanaka, Kengo*; Takeyama, Mirei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_9, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:75.18(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Excitation functions of quasielastic scattering cross sections for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb,
Pb,  Ti +
Ti +  Pb, and
Pb, and  Ca +
Ca +  Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the
Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb and
Pb and  Ti +
Ti +  Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the
Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Takai, Shizuka; Hagino, Koichi*
Nuclear Back-end and Transmutation Technology for Waste Disposal, p.3 - 11, 2015/00
One of the major problems of fuel cycle is the disposal of high-level radioactive waste which contains long-lived nuclides and high-decay heating nuclides. Transmuting such nuclides into short-lived or stable nuclides is one possible way to resolve this problem. Neutron capture reactions have been proposed for transmutations of such fission products. However, this transmutation method is not effective for nuclides with small neutron capture cross sections such as  Cs. Recently, the photo-neutron (
Cs. Recently, the photo-neutron ( ,n) reactions via giant dipole resonance with laser Compton scattering
,n) reactions via giant dipole resonance with laser Compton scattering  -rays has been suggested as an alternative method for nuclear transmutations. In this paper, we investigate in detail the effectiveness of the transmutation of
-rays has been suggested as an alternative method for nuclear transmutations. In this paper, we investigate in detail the effectiveness of the transmutation of  Cs quantitatively. For the transmutation of
Cs quantitatively. For the transmutation of  Cs of 1g with photon flux
Cs of 1g with photon flux 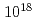 /s,
/s, 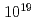 /s and
/s and 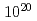 /s for 24 hours, 10%, 70% and 99% reduction of the initial amount of
/s for 24 hours, 10%, 70% and 99% reduction of the initial amount of  Cs is theoretically possible.
Cs is theoretically possible.
 hypernuclei
hypernucleiMinato, Futoshi; Hagino, Koichi*
Physical Review C, 88(6), p.064303_1 - 064303_6, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.64(Physics, Nuclear)Applying the sum rule approach, we investigate the energy of a soft dipole motion in  hypernuclei, which results from a dipole oscillation of a
hypernuclei, which results from a dipole oscillation of a  hyperon against the core nucleus in contrast to usual dipole motion induced by proton and neutron. To this end, we systematically study single-
hyperon against the core nucleus in contrast to usual dipole motion induced by proton and neutron. To this end, we systematically study single- hypernuclei, from
hypernuclei, from 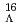 O to
O to 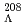 Pb, for which the ground state wave function is obtained in the framework of Hartree-Fock method with several Skyrme-type
Pb, for which the ground state wave function is obtained in the framework of Hartree-Fock method with several Skyrme-type 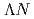 interactions. Our results indicate that the excitation energy of the soft dipole
interactions. Our results indicate that the excitation energy of the soft dipole  mode,
mode, 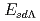 decreases as the mass number increases. We find that the excitation energy is well parametrized as
decreases as the mass number increases. We find that the excitation energy is well parametrized as 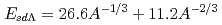 MeV as a function of mass number A.
MeV as a function of mass number A.
 hypernuclei
hypernucleiHagino, Koichi*; Yao, J. M.*; Minato, Futoshi; Li, Z. P.*; Thi Win, M.*
Nuclear Physics A, 914, p.151 - 159, 2013/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:55.63(Physics, Nuclear)We discuss low-lying collective excitations of hypernuclei using the self-consistent mean-field approaches. We first discuss the deformation properties of hypernuclei in the sd-shell region. Based on the relativistic mean-field approach, we show that the oblate deformation of  Si nucleus may disappear when a particle is added to this nucleus. We then discuss the rotational excitations of
Si nucleus may disappear when a particle is added to this nucleus. We then discuss the rotational excitations of  Mg nucleus using the three-dimensional potential energy surface in the deformation plane obtained with the Skyrme-Hartree-Fock method. The deformation of
Mg nucleus using the three-dimensional potential energy surface in the deformation plane obtained with the Skyrme-Hartree-Fock method. The deformation of  Mg nucleus is predicted to be slightly reduced due to an addition of particle. We demonstrate that this leads to a reduction of electromagnetic transition probability,
Mg nucleus is predicted to be slightly reduced due to an addition of particle. We demonstrate that this leads to a reduction of electromagnetic transition probability, 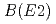 , in the ground state rotational band. We also present an application of random phase approximation to hypernuclei, and show that a new dipole mode appears in hypernuclei, which can be interpreted as an oscillation of particle against the core nucleus.
, in the ground state rotational band. We also present an application of random phase approximation to hypernuclei, and show that a new dipole mode appears in hypernuclei, which can be interpreted as an oscillation of particle against the core nucleus.
Odaka, Hirokazu*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; Takeda, Shinichiro*; Fukuyama, Taro*; Hagino, Koichi*; Saito, Shinya*; Sato, Tamotsu*; Sato, Goro*; Watanabe, Shin*; Kokubun, Motohide*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 695, p.179 - 183, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:82.23(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have developed a new Si/CdTe semiconductor double-sided strip detector (DSD) Compton camera. The camera consists of a 500- m-thick Si-DSD and four layers of 750-
m-thick Si-DSD and four layers of 750- m-thick CdTe-DSDs all of which have common electrode configuration segmented into 128 strips on each side with pitches of 250
m-thick CdTe-DSDs all of which have common electrode configuration segmented into 128 strips on each side with pitches of 250 m. In order to realize high angular resolution and to reduce size of the detector system, a stack of DSDs with short stack pitches of 4 mm is utilized to make the camera. Taking advantage of the excellent energy and position resolutions of the semiconductor devices, the camera achieves high angular resolutions of 4.5 degrees at 356 keV and 3.5 degrees at 662 keV. To obtain such high resolutions together with an acceptable detection efficiency, we demonstrate data reduction methods including energy calibration using Compton scattering continuum and depth sensing in the CdTe-DSD. We also discuss imaging capability of the camera and show simultaneous multi-energy imaging.
m. In order to realize high angular resolution and to reduce size of the detector system, a stack of DSDs with short stack pitches of 4 mm is utilized to make the camera. Taking advantage of the excellent energy and position resolutions of the semiconductor devices, the camera achieves high angular resolutions of 4.5 degrees at 356 keV and 3.5 degrees at 662 keV. To obtain such high resolutions together with an acceptable detection efficiency, we demonstrate data reduction methods including energy calibration using Compton scattering continuum and depth sensing in the CdTe-DSD. We also discuss imaging capability of the camera and show simultaneous multi-energy imaging.
 -ray camera
-ray cameraTakeda, Shinichiro*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; Hagino, Koichi*; Odaka, Hirokazu*; Yuasa, Takayuki*; Ishikawa, Shinnosuke*; Fukuyama, Taro*; Saito, Shinya*; Sato, Tamotsu*; Sato, Goro*; et al.
Physics Procedia, 37, p.859 - 866, 2012/10
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:98.53(Physics, Applied)By using new Compton camera consisting of silicon double-sided strip detector (Si-DSD) and CdTe-DSD developed for the ASTRO-H mission, an experiment was conducted to study its feasibility for advanced hotspot monitoring. In addition to hotspot imaging already provided by commercial imaging systems, the identification of the variety of radioisotopes is realized thanks to the good energy resolution given by the semiconductor detectors. Three radioisotopes of  Ba (356 keV),
Ba (356 keV),  Na (511 keV) and
Na (511 keV) and  Cs (662 keV) were individually imaged by applying event selection in the energy window and the
Cs (662 keV) were individually imaged by applying event selection in the energy window and the  -ray images was correctly overlapped by an optical picture. The detection efficiency of 1.68
-ray images was correctly overlapped by an optical picture. The detection efficiency of 1.68 10
10 (effective area: 1.7
(effective area: 1.7 10
10 cm
cm ) and angular resolution of 3.8
) and angular resolution of 3.8 were obtained by stacking five detector modules for 662 keV
were obtained by stacking five detector modules for 662 keV  -ray. The higher detection efficiency required in a specific use can be achieved by stacking more detector modules.
-ray. The higher detection efficiency required in a specific use can be achieved by stacking more detector modules.
Aritomo, Yoshihiro; Hagino, Koichi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Chiba, Satoshi
Physical Review C, 85(4), p.044614_1 - 044614_15, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:64 Percentile:93.05(Physics, Nuclear)In order to describe heavy-ion fusion reactions around the Coulomb barrier with an actinide target nucleus, we propose a model which combines the coupled-channels approach and a fluctuation-dissipation model for dynamical calculations. Fusion-fission, quasi-fission and deep quasi-fission are separated as different Langevin trajectories on the potential energy surface. Using this model, we analyze the experimental data for the mass distribution of fission fragments (MDFF) in the reactions of 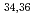 S+
S+ U and
U and  Si+
Si+ U at several incident energies around the Coulomb barrier. We find that the time scale in the quasi-fission as well as the deformation of fission fragments at the scission point are different between the
U at several incident energies around the Coulomb barrier. We find that the time scale in the quasi-fission as well as the deformation of fission fragments at the scission point are different between the  Si+
Si+ U and
U and  S+
S+ U systems, causing different mass asymmetries of the quasi-fission.
U systems, causing different mass asymmetries of the quasi-fission.
 hypernuclei
hypernucleiMinato, Futoshi; Hagino, Koichi*
Physical Review C, 85(2), p.024316_1 - 024316_10, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:54.66(Physics, Nuclear)Using the Hartree-Fock plus random-phase-approximation (HF+RPA), we study the impurity effect of  hyperon on the collective vibrational excitations of double-
hyperon on the collective vibrational excitations of double- hypernuclei. To this end, we employ a Skyrme-type
hypernuclei. To this end, we employ a Skyrme-type 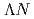 and
and 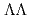 interactions for the HF calculations, and the residual interactions for RPA derived with the same interactions. We find that inclusion of two
interactions for the HF calculations, and the residual interactions for RPA derived with the same interactions. We find that inclusion of two  hyperons in
hyperons in  O shifts the energy of the collective states towards higher energies. In particular, the energy of the giant monopole resonance of
O shifts the energy of the collective states towards higher energies. In particular, the energy of the giant monopole resonance of 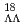 O, as well as that of
O, as well as that of 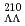 Pb, becomes larger. This implies that the effective incompressibility modulus increases due to the impurity effect of
Pb, becomes larger. This implies that the effective incompressibility modulus increases due to the impurity effect of  particle, if the
particle, if the  -stability condition is not imposed.
-stability condition is not imposed.
 U target nucleus
U target nucleusNishio, Katsuhisa; Ikezoe, Hiroshi; Hofmann, S.*; Ackermann, D.*; Antalic, S.*; Aritomo, Yoshihiro; Comas, V. F.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Gorshkov, A.*; Graeger, R.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Gorshkov, A.*; Graeger, R.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 17, p.09005_1 - 09005_4, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:46.91(Physics, Nuclear)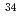 S+
S+ U and synthesis of the new isotope
U and synthesis of the new isotope 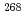 Hs
HsNishio, Katsuhisa; Hofmann, S.*; He berger, F. P.*; Ackermann, D.*; Antalic, S.*; Aritomo, Yoshihiro; Comas, V. F.*; D
berger, F. P.*; Ackermann, D.*; Antalic, S.*; Aritomo, Yoshihiro; Comas, V. F.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Gorshkov, A.*; Graeger, R.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Gorshkov, A.*; Graeger, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 82(2), p.024611_1 - 024611_9, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:83 Percentile:95.90(Physics, Nuclear) hypernuclei with the Skyrme-Hartree-Fock approach
hypernuclei with the Skyrme-Hartree-Fock approachMinato, Futoshi; Chiba, Satoshi; Hagino, Koichi*
Nuclear Physics A, 831(3-4), p.150 - 162, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:73.17(Physics, Nuclear)Fission-related phenomena of heavy  hypernuclei are discussed with the constraint Skyrme-Hartree-Fock+BCS (SHF+BCS) method, in which a similar Skyrme-type interaction is employed also for the interaction between a
hypernuclei are discussed with the constraint Skyrme-Hartree-Fock+BCS (SHF+BCS) method, in which a similar Skyrme-type interaction is employed also for the interaction between a  particle and a nucleon. Assuming that the
particle and a nucleon. Assuming that the  particle adiabatically follows the fission motion, we discuss the fission barrier height of
particle adiabatically follows the fission motion, we discuss the fission barrier height of 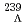 U. We find that the fission barrier height increases slightly when the
U. We find that the fission barrier height increases slightly when the  particle occupies the lowest level. In this case, the
particle occupies the lowest level. In this case, the  particle is always attached to the heavier fission fragment. This indicates that one may produce heavy neutron-rich
particle is always attached to the heavier fission fragment. This indicates that one may produce heavy neutron-rich  hypernuclei through fission, whose weak decay is helpful for the nuclear transmutation of long-lived fission products. We also discuss cases where the
hypernuclei through fission, whose weak decay is helpful for the nuclear transmutation of long-lived fission products. We also discuss cases where the  particle occupies a higher single-particle level.
particle occupies a higher single-particle level.
 -decay half-lives at finite temperatures for
-decay half-lives at finite temperatures for  =82 isotones
=82 isotonesMinato, Futoshi; Hagino, Koichi*
Physical Review C, 80(6), p.065808_1 - 065808_7, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:52.62(Physics, Nuclear)Using the finite temperature quasi-particle random phase approximation (FTQRPA) on the basis of finite temperature Skyrme-Hartree-Fock + BCS method, we study 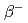 -decay half-lives for even-even neutron magic nuclei with
-decay half-lives for even-even neutron magic nuclei with  =82 in a finite temperature environment. We find that the
=82 in a finite temperature environment. We find that the 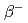 -decay half-life first decreases as the temperature increases for all the nuclei we study, although the thermal effect is found to be small at temperatures relevant to
-decay half-life first decreases as the temperature increases for all the nuclei we study, although the thermal effect is found to be small at temperatures relevant to  -process nucleosynthesis. Our calculations indicate that the half-life begins to increase at high temperatures for open shell nuclei. We discuss this behavior in connection to the pairing phase transition.
-process nucleosynthesis. Our calculations indicate that the half-life begins to increase at high temperatures for open shell nuclei. We discuss this behavior in connection to the pairing phase transition.
Hagino, Koichi*; Minato, Futoshi
Physical Review C, 80(4), p.047301_1 - 047301_4, 2009/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.50(Physics, Nuclear)We investigate the applicability of the finite temperature random phase approximation (RPA) using a solvable Lipkin model. We show that the finite temperature RPA reproduces reasonably well the temperature dependence of total strength, both for the positive energy (i.e., the excitation) and the negative energy (i.e., the de-excitation) parts. This is the case even at very low temperatures, which may be relevant to astrophysical purposes.
Zamrun, F. M.*; Hagino, Koichi*; Mitsuoka, Shinichi; Ikezoe, Hiroshi
Physical Review C, 77(3), p.034604_1 - 034604_11, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:81.26(Physics, Nuclear)Hirose, Kentaro; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Ikezoe, Hiroshi*; Orlandi, R.; L guillon, R.; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
guillon, R.; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 hypernuclei with the Skyrme-Hartree-Fock approach
hypernuclei with the Skyrme-Hartree-Fock approachMinato, Futoshi; Hagino, Koichi*; Chiba, Satoshi
no journal, ,
It has been shown that the shape of a few deformed nuclei change toward spherical when a  particle is added to them. This is caused because the interaction between a
particle is added to them. This is caused because the interaction between a  particle and a nucleon is attractive. This fact has motivated us to investigate the influence of
particle and a nucleon is attractive. This fact has motivated us to investigate the influence of  particle on the fission of heavy nuclei. We will discuss the fission-related phenomena of heavy
particle on the fission of heavy nuclei. We will discuss the fission-related phenomena of heavy  hypernuclei with the constraint Skyrme-Hartree-Fock+BCS (SHF+BCS) method. We employ a Skyrme-type interaction for the
hypernuclei with the constraint Skyrme-Hartree-Fock+BCS (SHF+BCS) method. We employ a Skyrme-type interaction for the 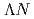 interaction and assume adiabaticity, that is, the
interaction and assume adiabaticity, that is, the  particle is assumed to be in the lowest state at all deformations. Our result confirms that the
particle is assumed to be in the lowest state at all deformations. Our result confirms that the  particle is stuck to the heavier fission fragment, which is consistent with the experimental result of CERN. We will also discuss the deformation of heavy
particle is stuck to the heavier fission fragment, which is consistent with the experimental result of CERN. We will also discuss the deformation of heavy  hypernuclei and the
hypernuclei and the  particle motion inside the core nuclei.
particle motion inside the core nuclei.
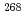 Hs produced in the subbarrier fusion reaction of
Hs produced in the subbarrier fusion reaction of 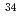 S+
S+ U
UNishio, Katsuhisa; Hofmann, S.*; He berger, F. P.*; Ackermann, D.*; Antalic, S.*; Comas, V. F.*; D
berger, F. P.*; Ackermann, D.*; Antalic, S.*; Comas, V. F.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Gorshkov, A.*; Graeger, R.*; Heinz, S.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Gorshkov, A.*; Graeger, R.*; Heinz, S.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hirose, Kentaro; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ikezoe, Hiroshi; Mitsuoka, Shinichi; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
no journal, ,
Minato, Futoshi; Chiba, Satoshi; Hagino, Koichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -decay half-lives at finite temperatures with the Skyrme-QRPA
-decay half-lives at finite temperatures with the Skyrme-QRPAMinato, Futoshi; Hagino, Koichi*
no journal, ,
Using the finite-temperature quasiparticle random phase approximation (FTQRPA) on the basis of the finite temperature Skyrme-Hartree-Fock+Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) method, we study  -decay half-lives for even-even nuclei in a finite-temperature environment. We find that the
-decay half-lives for even-even nuclei in a finite-temperature environment. We find that the  -decay half-life first decreases as the temperature increases for all the nuclei we study, although the thermal effect is found to be small at temperatures relevant to r-process nucleosynthesis. Our calculations indicate that the half-life begins to increase at high temperatures for open-shell nuclei. We discuss this behavior in connection to the pairing phase transition.
-decay half-life first decreases as the temperature increases for all the nuclei we study, although the thermal effect is found to be small at temperatures relevant to r-process nucleosynthesis. Our calculations indicate that the half-life begins to increase at high temperatures for open-shell nuclei. We discuss this behavior in connection to the pairing phase transition.