Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
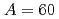
Tamii, Atsushi*; Pellegri, L.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 59(9), p.208_1 - 208_21, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Khalil, A. M. E.*; Han, L.*; Maamoun, I.; Tabish, T. A.*; Chen, Y.*; Eljamal, O.*; Zhang, S.*; Butler, D.*; Memon, F. A.*
Advanced Sustainable Systems (Internet), 6(8), p.2200016_1 - 2200016_16, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.01(Green & Sustainable Science & Technology)Boznar, M. Z.*; Charnock, T. W.*; Chouhan, S. L.*; Grsic, Z.*; Halsall, C.*; Heinrich, G.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Ku a, P.*; Mancini, F.*; et al.
a, P.*; Mancini, F.*; et al.
IAEA-TECDOC-2001, 226 Pages, 2022/06
The IAEA organized a programme from 2012 to 2015 entitled Modelling and Data for Radiological Impact Assessments (MODARIA), which aimed to improve capabilities in the field of environmental radiation dose assessment by acquiring improved data, model testing and comparison of model inputs, assumptions and outputs, reaching a consensus on modelling philosophies, aligning approaches and parameter values, developing improved methods and exchanging information. This publication describes the activities of Working Group 2, Exposures in Contaminated Urban Environments and Effect of Remedial Measures.
Thiessen, K. M.*; Boznar, M. Z.*; Charnock, T. W.*; Chouhan, S. L.*; Federspiel, L.; Gra i
i , B.*; Grsic, Z.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Hulka, J.*; et al.
, B.*; Grsic, Z.*; Helebrant, J.*; Hettrich, S.*; Hulka, J.*; et al.
Journal of Radiological Protection, 42(2), p.020502_1 - 020502_8, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:78.52(Environmental Sciences) Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the
Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the  Fe nucleosynthesis
Fe nucleosynthesisYan, S. Q.*; Li, X. Y.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Lugaro, M.*; Li, Z. H.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Pignatari, M.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Orlandi, R.; Hirose, Kentaro; et al.
Astrophysical Journal, 919(2), p.84_1 - 84_7, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.87(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Soba, A.*; Prudil, A.*; Zhang, J.*; Dethioux, A.*; Han, Z.*; Dostal, M.*; Matocha, V.*; Marelle, V.*; Lasnel-Payan, J.*; Kulacsy, K.*; et al.
Proceedings of TopFuel 2021 (Internet), 10 Pages, 2021/10
 sp
sp HRL LTDE-SD experiments
HRL LTDE-SD experimentsSoler, J. M.*; Meng, S.*; Moreno, L.*; Neretnieks, I.*; Liu, L.*; Kek l
l inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*;
inen, P.*; Hokr, M.*; 
 ha, J.*; Vete
ha, J.*; Vete n
n k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
k, A.*; Reimitz, D.*; et al.
SKB TR-20-17, 71 Pages, 2021/07
Task 9B of the SKB Task Force on Modelling of Groundwater Flow and Transport of Solutes in fractured rock focused on the modelling of experimental results from the LTDE-SD in situ tracer test performed at the  sp
sp Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
Hard Rock Laboratory in Sweden. Ten different modelling teams provided results for this exercise, using different concepts and codes. Three main types of modelling approaches were used: (1) analytical solutions to the transport-retention equations, (2) continuum-porous-medium numerical models, and (3) microstructure-based models accounting for small-scale heterogeneity (i.e. mineral grains and microfracture distributions). The modelling by the different teams allowed the comparison of many different model concepts, especially in terms of potential zonations of rock properties (porosity, diffusion, sorption), such as the presence of a disturbed zone at the rock and fracture surface, the potential effects of micro- and cm-scale fractures.
Dimitriou, P.*; Dillmann, I.*; Singh, B.*; Piksaikin, V.*; Rykaczewski, K. P.*; Tain, J. L.*; Algora, A.*; Banerjee, K.*; Borzov, I. N.*; Cano-Ott, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 173, p.144 - 238, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:96.52(Physics, Nuclear) -delayed neutron emission has been of interest since the discovery of nuclear fission. In nuclear power reactors, delayed-neutron data play a crucial role in reactor kinetics calculations and safe operation.
-delayed neutron emission has been of interest since the discovery of nuclear fission. In nuclear power reactors, delayed-neutron data play a crucial role in reactor kinetics calculations and safe operation.  -delayed neutron data also have a significant impact in the field of nuclear structure and astrophysics especially as nuclei farther away from stability are explored at the new generation of radioactive beam facilities. Several compilations of
-delayed neutron data also have a significant impact in the field of nuclear structure and astrophysics especially as nuclei farther away from stability are explored at the new generation of radioactive beam facilities. Several compilations of  -decay half-lives and delayed-neutron emission probabilities are available, however, complete documentation of measurements and evaluation procedures is often missing for these properties. Efforts to address this gap in nuclear data and create an updated compilation and evaluation of
-decay half-lives and delayed-neutron emission probabilities are available, however, complete documentation of measurements and evaluation procedures is often missing for these properties. Efforts to address this gap in nuclear data and create an updated compilation and evaluation of  -delayed neutron properties were undertaken under the auspices of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) which formed a Coordinated Research Project (CRP) on "Development of a Reference Database of Beta-delayed Neutron Emission Data". In this paper we summarize the work that was performed and present the results of the CRP.
-delayed neutron properties were undertaken under the auspices of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) which formed a Coordinated Research Project (CRP) on "Development of a Reference Database of Beta-delayed Neutron Emission Data". In this paper we summarize the work that was performed and present the results of the CRP.
Dimitriou, P.*; Basunia, S*; Bernstein, L.*; Chen, J.*; Elekes, Z.*; Huang, X.*; Hurst, A.*; Iimura, Hideki; Jain, A. K.*; Kelley, J.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.15004_1 - 15004_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.1(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Evaluated Nuclear Structure Data File (ENSDF) includes the most extensive and comprehensive set of nuclear structure and decay data evaluations performed by the international network of Nuclear Structure and Decay Data evaluators (NSDD) under the auspices of the IAEA. In this report we describe some of the recent NSDD activities and provide future perspectives.
Oyanagi, Koichi*; Takahashi, Saburo*; Cornelissen, L. J.*; Shan, J.*; Daimon, Shunsuke*; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Bauer, G. E. W.*; Van Wees, B. J.*; Saito, Eiji
Nature Communications (Internet), 10, p.4740_1 - 4740_6, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:89.44(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Phan, L. H. S.*; Ohara, Yohei*; Kawata, Ryo*; Liu, X.*; Liu, W.*; Morita, Koji*; Guo, L.*; Kamiyama, Kenji; Tagami, Hirotaka
Proceedings of 12th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-12) (USB Flash Drive), 12 Pages, 2018/10
Self-leveling behavior of core fuel debris beds is one of the key phenomena for the safety assessment of core disruptive accidents (CDAs) in sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). The SIMMER code has been developed for CDA analysis of SFRs, and the code has been successfully applied to numerical simulations for key thermal-hydraulic phenomena involved in CDAs as well as reactor safety assessment. However, in SIMMER's fluid-dynamics model, it is always difficult to represent the strong interactions between solid particles as well as the discrete particle characteristics. To solve this problem, a new method has been developed by combining the multi-fluid model of the SIMMER code with the discrete element method (DEM) for the solid phase to reasonably simulate the particle behaviors as well as the fluid-particle interactions in multi-phase flows. In this study, in order to validate the multi-fluid model of the SIMMER code coupled with DEM, numerical simulations were performed on a series of self-leveling experiments using a gas injection method in cylindrical particle beds. The effects of friction coefficient on the simulation results were investigated by sensitivity analysis. Though more extensive validations are needed, the reasonable agreement between simulation results and corresponding experimental data preliminarily demonstrates the potential ability of the present method in simulating the self-leveling behaviors of debris bed. It is expected that the SIMMER code coupled with DEM is a prospective computational tool for analysis of safety issues related to solid particle debris bed in SFRs.
Ho, D. M. L.*; Nelwamondo, A. N.*; Okubo, Ayako; Rameb ck, H.*; Song, K.*; Han, S.-H.*; Hancke, J. J.*; Holmgren, S.*; Jonsson, S.*; Kataoka, Osamu; et al.
ck, H.*; Song, K.*; Han, S.-H.*; Hancke, J. J.*; Holmgren, S.*; Jonsson, S.*; Kataoka, Osamu; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 315(2), p.353 - 363, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.93(Chemistry, Analytical)The Fourth Collaborative Material Exercise (CMX-4) of the Nuclear Forensics International Technical Working Group (ITWG) registered the largest participation for this exercise in nuclear forensics, with seven of the 17 laboratories participating for the first time. In this paper, participants from five of the first-time laboratories shared their individual experience in this exercise, from preparation to analysis of samples. The exercise proved to be highly useful for testing procedures, repurposing established methods, exercising skills, and improving the understanding of nuclear forensic signatures and their interpretation trough the post-exercise review meeting.
Kristo, M. J.*; Williams, R.*; Gaffney, A. M.*; Kayzar-Boggs, T. M.*; Schorzman, K. C.*; Lagerkvist, P.*; Vesterlund, A.*; Rameb ck, H.*; Nelwamondo, A. N.*; Kotze, D.*; et al.
ck, H.*; Nelwamondo, A. N.*; Kotze, D.*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 315(2), p.425 - 434, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:81.7(Chemistry, Analytical)In a recent international exercise, 10 international nuclear forensics laboratories successfully performed radiochronometry on three low enriched uranium oxide samples, providing 12 analytical results using three different parent-daughter pairs serving as independent chronometers. The vast majority of the results were consistent with one another and consistent with the known processing history of the materials. In general, for these particular samples, mass spectrometry gave more accurate and more precise analytical results than decay counting measurements. In addition, the concordance of the  U-
U-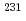 Pa and
Pa and  U-
U- Th chronometers confirmed the validity of the age dating assumptions, increasing confidence in the resulting conclusions.
Th chronometers confirmed the validity of the age dating assumptions, increasing confidence in the resulting conclusions.
 Zr(
Zr( )
)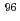 Zr cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on
Zr cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on  -process nucleosynthesis
-process nucleosynthesisYan, S. Q.*; Li, Z. H.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Lugaro, M.*; Karakas, A. I.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mohr, P.*; Su, J.*; Li, Y. J.*; et al.
Astrophysical Journal, 848(2), p.98_1 - 98_8, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:21.48(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Furuta, Takuya; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Han, M. C.*; Yeom, Y. S.*; Kim, C. H.*; Brown, J. L.*; Bolch, W. E.*
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 62(12), p.4798 - 4810, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:47.55(Engineering, Biomedical)A new function to treat tetrahedral-mesh geometry, a type of polygon-mesh geometry, was implemented in the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code Systems (PHITS). Tetrahedral-mesh is suitable to describe complex geometry including curving shapes. In addition, construction of three-dimensional geometry using CAD software becomes possible with file format conversion. We have introduced a function to create decomposition maps of tetrahedral-mesh objects at the initial process so that the computational time for transport process can be reduced. Owing to this function, transport calculation in tetrahedral-mesh geometry can be as fast as that for the geometry in voxel-mesh with the same number of meshes. Due to adaptability of tetrahedrons in size and shape, dosimetrically equivalent objects can be represented by tetrahedrons with much fewer number of meshes compared with the voxels. For dosimetric calculation using computational human phantom, significant acceleration of the computational speed, about 4 times, was confirmed by adopting the tetrahedral mesh instead of the voxel.
 No
NoLopez-Martens, A.*; Henning, G.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Alcorta, M.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Bertone, P. F.*; Boilley, D.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.03001_1 - 03001_6, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:43.94(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Fission barrier height and its angular-momentum dependence have been measured for the first time in the nucleus with the atomic number greater than 100. The entry distribution method, which can determine the excitation energy at which fission starts to dominate the decay process, was applied to  No. The fission barrier of
No. The fission barrier of  No was found to be 6.6 MeV at zero spin, indicating that the
No was found to be 6.6 MeV at zero spin, indicating that the  No is strongly stabilized by the nuclear shell effects.
No is strongly stabilized by the nuclear shell effects.
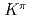 = 8
= 8 two-quasineutron isomer in
two-quasineutron isomer in  Pu
PuHota, S.*; Tandel, S.*; Chowdhury, P.*; Ahmad, I.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Chiara, C. J.*; Greene, J. P.*; Hoffman, C. R.*; Jackson, E. G.*; Janssens, R. V. F.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 94(2), p.021303_1 - 021303_5, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.49(Physics, Nuclear)The decay of a 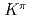 = 8
= 8 isomer in
isomer in  Pu and the collective band structure populating the isomer are studied using deep inelastic excitations with
Pu and the collective band structure populating the isomer are studied using deep inelastic excitations with 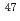 Ti and
Ti and  Pb beams, respectively. Precise measurements of
Pb beams, respectively. Precise measurements of 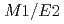 branching ratios in the band confirm a clean 9/2
branching ratios in the band confirm a clean 9/2 [734]
[734]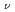
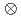 7/2
7/2 [624]
[624]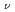 for the isomer, validating the systematics of K
for the isomer, validating the systematics of K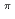 = 8
= 8 two-quasineutron isomers observed in even-
two-quasineutron isomers observed in even- ,
,  = 150 isotones. These isomers around the deformed shell gap at
= 150 isotones. These isomers around the deformed shell gap at  = 152 provide critical benchmarks for theoretical predictions of single-particle energies in this gateway region to superheavy nuclei.
= 152 provide critical benchmarks for theoretical predictions of single-particle energies in this gateway region to superheavy nuclei.
 Zr(n,
Zr(n, )
) Zr cross section with
Zr cross section with 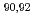 Zr(
Zr( O,
O, O)
O)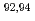 Zr reactions
Zr reactionsYan, S. Q.*; Li, Z. H.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Makii, Hiroyuki; Su, J.*; Li, Y. J.*; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Hirose, Kentaro; Han, Y. L.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 94(1), p.015804_1 - 015804_5, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.49(Physics, Nuclear) No and
No and 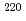 Th
ThHenning, G.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Lopez-Martens, A.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Alcorta, M.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Bertone, P. F.*; Boilley, D.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 113(26), p.262505_1 - 262505_6, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:83.14(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Fission barrier heights of a shell-stabilized superheavy nucleus  No have been determined as a function of spin up to 19
No have been determined as a function of spin up to 19 through the measured distribution of entry points of
through the measured distribution of entry points of  deexcitations in the excitation energy vs. spin plane. The fission barrier height of
deexcitations in the excitation energy vs. spin plane. The fission barrier height of  No was determined to be 6.0 MeV at spin 15
No was determined to be 6.0 MeV at spin 15 , and 6.6 MeV at spin 0
, and 6.6 MeV at spin 0 by extrapolation. This demonstrates that the shell effect actually enlarges the fission barrier in such heavy nuclei and keeps the barrier high even at high spin.
by extrapolation. This demonstrates that the shell effect actually enlarges the fission barrier in such heavy nuclei and keeps the barrier high even at high spin.
Honda, Mitsunori; Yanagida, Masatoshi*; Han, L.*; Miyano, Kenjiro*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 141(17), p.174709_1 - 174709_7, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:29.76(Chemistry, Physical)