Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Niu, X.*; Elakneswaran, Y.*; Li, A.*; Seralathan, S.*; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Hiraki, Yoshihisa; Sato, Junya; Osugi, Takeshi; Walkley, B.*
Cement and Concrete Research, 190, p.107814_1 - 107814_17, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology) -
- transitions
transitionsYang, Q.*; Yang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Fei, Y.*; Li, F.*; Zheng, H.*; Li, K.*; Han, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; Zhu, P.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.7778_1 - 7778_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:88.19(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Luminescent materials that simultaneously embody bright singlet and triplet excitons hold great potential in optoelectronics, signage, and information encryption. However, achieving high-performance white-light emission is severely hampered by their inherent unbalanced contribution of fluorescence and phosphorescence. Herein, we address this challenge by pressure treatment engineering via hydrogen bonding cooperativity effect to realize the mixture of n- -
- transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
Imatomi, Daisuke*; Ishikawa, Ryosuke*; Nakata, Akira*; Ito, Tatsuya; Han, K.*; Nagasako, Makoto*; Xu, X.*; Omori, Toshihiro*; Kainuma, Ryosuke*
Journal of Phase Equilibria and Diffusion, 45(1), p.3 - 17, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.66(Chemistry, Physical)Phase equilibria in the Mn-Zn binary system were experimentally determined by chemical composition examination, crystal structure determination, and thermal analysis. Major changes were detected for the  ,
,  , and
, and  phases. The
phases. The  -B2 single-phase region could not be confirmed in the studied system because a disordered body-centered cubic structure, which is identical to the
-B2 single-phase region could not be confirmed in the studied system because a disordered body-centered cubic structure, which is identical to the  Mn phase, was confirmed in a quenched sample from the previously proposed region of
Mn phase, was confirmed in a quenched sample from the previously proposed region of  phase. The
phase. The  phase has been controversial whether the phase is separated into
phase has been controversial whether the phase is separated into  ,
, 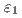 , and
, and 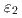 phases or not. By studying a diffusion couple and several alloy compositions, it was established that the
phases or not. By studying a diffusion couple and several alloy compositions, it was established that the  ,
, 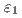 , and
, and 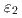 phases are not separate and comprise a single
phases are not separate and comprise a single  phase. Furthermore, the
phase. Furthermore, the  phase is not present in the Zn-rich region of the system because the corresponding invariant reactions were not detected via thermal analysis.
phase is not present in the Zn-rich region of the system because the corresponding invariant reactions were not detected via thermal analysis.
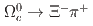 and search for
and search for 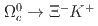 and
and  decays at Belle
decays at BelleHan, X.*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*; 170 of others*
Journal of High Energy Physics (Internet), 2023(1), p.55_1 - 55_12, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:57.15(Physics, Particles & Fields) /La
/La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO heterostructures
heterostructuresZhang, J.*; Chen, M.*; Chen, J.*; Yamamoto, Kei; Wang, H.*; Hamdi, M.*; Sun, Y.*; Wagner, K.*; He, W.*; Zhang, Y.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 12, p.7258_1 - 7258_8, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:77.31(Multidisciplinary Sciences) Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the
Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the  Fe nucleosynthesis
Fe nucleosynthesisYan, S. Q.*; Li, X. Y.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Lugaro, M.*; Li, Z. H.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Pignatari, M.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Orlandi, R.; Hirose, Kentaro; et al.
Astrophysical Journal, 919(2), p.84_1 - 84_7, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.27(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Han, X.*; Shen, X.*; Yamamoto, Toshihiro*; Nakajima, Ken*; Sun, Haomin; Hibiki, Takashi*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 178, p.121637_1 - 121637_24, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:76.84(Thermodynamics)Gao, D.*; Tang, X.*; Wang, X.*; Yang, X.*; Zhang, P.*; Che, G.*; Han, J.*; Hattori, Takanori; Wang, Y.*; Dong, X.*; et al.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 23(35), p.19503 - 19510, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:42.22(Chemistry, Physical)Pressure-induced phase transition and polymerization of nitrogen-rich molecules are widely focused due to its extreme importance for the development of green high energy density materials. Here, we present a study of the phase transition and chemical reaction of 1H-tetrazole up to 100 GPa by using  Raman, IR, X-ray diffraction, neutron diffraction techniques and theoretical calculation. A phase transition above 2.6 GPa was identified and the high-pressure structure was determined with one molecule in a unit cell. The 1H-tetrazole polymerizes reversibly below 100 GPa, probably through a carbon-nitrogen bonding instead of nitrogen-nitrogen bonding. Our studies updated the structure model of the high pressure phase of 1H-tetrazole, and presented the possible intermolecular bonding route for the first time, which gives new insights to understand the phase transition and chemical reaction of nitrogen-rich compounds, and benefit for designing new high energy density materials.
Raman, IR, X-ray diffraction, neutron diffraction techniques and theoretical calculation. A phase transition above 2.6 GPa was identified and the high-pressure structure was determined with one molecule in a unit cell. The 1H-tetrazole polymerizes reversibly below 100 GPa, probably through a carbon-nitrogen bonding instead of nitrogen-nitrogen bonding. Our studies updated the structure model of the high pressure phase of 1H-tetrazole, and presented the possible intermolecular bonding route for the first time, which gives new insights to understand the phase transition and chemical reaction of nitrogen-rich compounds, and benefit for designing new high energy density materials.
Yao, Y.*; Cai, R.*; Yang, S.-H.*; Xing, W.*; Ma, Y.*; Mori, Michiyasu; Ji, Y.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Xie, X.-C.*; Han, W.*
Physical Review B, 104(10), p.104414_1 - 104414_6, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:41.33(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Dimitriou, P.*; Dillmann, I.*; Singh, B.*; Piksaikin, V.*; Rykaczewski, K. P.*; Tain, J. L.*; Algora, A.*; Banerjee, K.*; Borzov, I. N.*; Cano-Ott, D.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 173, p.144 - 238, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:95.46(Physics, Nuclear) -delayed neutron emission has been of interest since the discovery of nuclear fission. In nuclear power reactors, delayed-neutron data play a crucial role in reactor kinetics calculations and safe operation.
-delayed neutron emission has been of interest since the discovery of nuclear fission. In nuclear power reactors, delayed-neutron data play a crucial role in reactor kinetics calculations and safe operation.  -delayed neutron data also have a significant impact in the field of nuclear structure and astrophysics especially as nuclei farther away from stability are explored at the new generation of radioactive beam facilities. Several compilations of
-delayed neutron data also have a significant impact in the field of nuclear structure and astrophysics especially as nuclei farther away from stability are explored at the new generation of radioactive beam facilities. Several compilations of  -decay half-lives and delayed-neutron emission probabilities are available, however, complete documentation of measurements and evaluation procedures is often missing for these properties. Efforts to address this gap in nuclear data and create an updated compilation and evaluation of
-decay half-lives and delayed-neutron emission probabilities are available, however, complete documentation of measurements and evaluation procedures is often missing for these properties. Efforts to address this gap in nuclear data and create an updated compilation and evaluation of  -delayed neutron properties were undertaken under the auspices of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) which formed a Coordinated Research Project (CRP) on "Development of a Reference Database of Beta-delayed Neutron Emission Data". In this paper we summarize the work that was performed and present the results of the CRP.
-delayed neutron properties were undertaken under the auspices of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) which formed a Coordinated Research Project (CRP) on "Development of a Reference Database of Beta-delayed Neutron Emission Data". In this paper we summarize the work that was performed and present the results of the CRP.
Dimitriou, P.*; Basunia, S*; Bernstein, L.*; Chen, J.*; Elekes, Z.*; Huang, X.*; Hurst, A.*; Iimura, Hideki; Jain, A. K.*; Kelley, J.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.15004_1 - 15004_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Evaluated Nuclear Structure Data File (ENSDF) includes the most extensive and comprehensive set of nuclear structure and decay data evaluations performed by the international network of Nuclear Structure and Decay Data evaluators (NSDD) under the auspices of the IAEA. In this report we describe some of the recent NSDD activities and provide future perspectives.
 6 rod bundle
6 rod bundleHan, X.*; Shen, X.*; Yamamoto, Toshihiro*; Nakajima, Ken*; Sun, Haomin; Hibiki, Takashi*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 144, p.118696_1 - 118696_19, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:73.38(Thermodynamics)Phan, L. H. S.*; Ohara, Yohei*; Kawata, Ryo*; Liu, X.*; Liu, W.*; Morita, Koji*; Guo, L.*; Kamiyama, Kenji; Tagami, Hirotaka
Proceedings of 12th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation and Safety (NUTHOS-12) (USB Flash Drive), 12 Pages, 2018/10
Self-leveling behavior of core fuel debris beds is one of the key phenomena for the safety assessment of core disruptive accidents (CDAs) in sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). The SIMMER code has been developed for CDA analysis of SFRs, and the code has been successfully applied to numerical simulations for key thermal-hydraulic phenomena involved in CDAs as well as reactor safety assessment. However, in SIMMER's fluid-dynamics model, it is always difficult to represent the strong interactions between solid particles as well as the discrete particle characteristics. To solve this problem, a new method has been developed by combining the multi-fluid model of the SIMMER code with the discrete element method (DEM) for the solid phase to reasonably simulate the particle behaviors as well as the fluid-particle interactions in multi-phase flows. In this study, in order to validate the multi-fluid model of the SIMMER code coupled with DEM, numerical simulations were performed on a series of self-leveling experiments using a gas injection method in cylindrical particle beds. The effects of friction coefficient on the simulation results were investigated by sensitivity analysis. Though more extensive validations are needed, the reasonable agreement between simulation results and corresponding experimental data preliminarily demonstrates the potential ability of the present method in simulating the self-leveling behaviors of debris bed. It is expected that the SIMMER code coupled with DEM is a prospective computational tool for analysis of safety issues related to solid particle debris bed in SFRs.
 Zr(n,
Zr(n, )
) Zr cross section with
Zr cross section with  Zr(
Zr( O,
O, O)
O)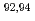 Zr reactions
Zr reactionsYan, S. Q.*; Li, Z. H.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Makii, Hiroyuki; Su, J.*; Li, Y. J.*; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Hirose, Kentaro; Han, Y. L.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 94(1), p.015804_1 - 015804_5, 2016/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.14(Physics, Nuclear)Deng, Z.*; Zhao, K.*; Gu, B.; Han, W.*; Zhu, J. L.*; Wang, X. C.*; Li, X.*; Liu, Q. Q.*; Yu, R. C.*; Goko, Tatsuo*; et al.
Physical Review B, 88(8), p.081203_1 - 081203_5, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:77 Percentile:91.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) /SrTiO
/SrTiO (110) interface
(110) interfaceAnnadi, A.*; Zhang, Q.*; Renshaw Wang, X.*; Tuzla, N.*; Gopinadhan, K.*; L , W. M.*; Roy Barman, A.*; Liu, Z. Q.*; Srivastava, A.*; Saha, S.*; et al.
, W. M.*; Roy Barman, A.*; Liu, Z. Q.*; Srivastava, A.*; Saha, S.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 4, p.1838_1 - 1838_7, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:103 Percentile:94.51(Multidisciplinary Sciences)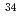 P
PBender, P. C.*; Tabor, S. L.*; Tripathi, V.*; Hoffman, C. R.*; Hamilton, L.*; Volya, A.*; Clark, R. M.*; Fallon, P.*; Macchiavelli, A. O.*; Paschalis, S.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 85(4), p.044305_1 - 044305_10, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:54.56(Physics, Nuclear)The available experimental information on 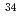 P has been greatly increased through the analysis of
P has been greatly increased through the analysis of  decays in coincidence with protons from the interaction of an
decays in coincidence with protons from the interaction of an  O beam at 24 MeV with an
O beam at 24 MeV with an  O target. Light charged particles from the reaction were detected with Microball, and multiple
O target. Light charged particles from the reaction were detected with Microball, and multiple  ray coincidences with Gammasphere. Many newly observed
ray coincidences with Gammasphere. Many newly observed  transitions have been identified and placed in the level scheme. Additionally, for most states, spins have been assigned based on measured
transitions have been identified and placed in the level scheme. Additionally, for most states, spins have been assigned based on measured  ray angular distributions while parities were inferred from lifetimes determined through Doppler-broadened line-shape analysis. Most of the states observed have been interpreted in terms of shell-model calculations using the WBP-a and SDPF-NR interactions having one particle in the 0
ray angular distributions while parities were inferred from lifetimes determined through Doppler-broadened line-shape analysis. Most of the states observed have been interpreted in terms of shell-model calculations using the WBP-a and SDPF-NR interactions having one particle in the 0
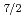 or 1
or 1
 orbital. The two calculations agree almost equally well with the data resulting in root-mean-square differences of about 200 keV. However, two of a few high-lying states may be associated with stretched
orbital. The two calculations agree almost equally well with the data resulting in root-mean-square differences of about 200 keV. However, two of a few high-lying states may be associated with stretched 

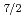
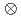


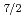 states, but the calculations over-predict their energies by 2-3 MeV. Furthermore, a newly observed long-lived 7919-keV state is established for which no explanation is available at present.
states, but the calculations over-predict their energies by 2-3 MeV. Furthermore, a newly observed long-lived 7919-keV state is established for which no explanation is available at present.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:75.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 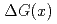 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:193 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 isomer in
isomer in  Rf
RfRobinson, A. P.*; Khoo, T. L.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Ahmad, I.*; Asai, Masato; Back, B. B.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Chowdhury, P.*; Davids, C. N.*; Greene, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064311_1 - 064311_7, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:85.36(Physics, Nuclear)We have identified an isomer with a half-life of 17  s in
s in  Rf through a calorimetric conversion electron measurement tagged with implanted
Rf through a calorimetric conversion electron measurement tagged with implanted  Rf nuclei using the fragment mass analyzer at Argonne National Laboratory. The low population yield for this isomer suggests that this isomer should not be a 2-quasiparticle high-
Rf nuclei using the fragment mass analyzer at Argonne National Laboratory. The low population yield for this isomer suggests that this isomer should not be a 2-quasiparticle high- isomer which is typically observed in the N = 152 isotones, but should be a 4-quasiparticle one. Possible reasons of the non-observation of a 2-quasiparticle isomer are this isomer decays by fission with a half-life similar to that of the ground state of
isomer which is typically observed in the N = 152 isotones, but should be a 4-quasiparticle one. Possible reasons of the non-observation of a 2-quasiparticle isomer are this isomer decays by fission with a half-life similar to that of the ground state of  Rf. Another possibility, that there is no 2-quasiparticle isomer at all, would imply an abrupt termination of axially symmetric deformed shape at Z=104.
Rf. Another possibility, that there is no 2-quasiparticle isomer at all, would imply an abrupt termination of axially symmetric deformed shape at Z=104.