Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Watabe, Hiroshi*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Yu, K. N.*; Zivkovic, M.*; Krstic, D.*; Nikezic, D.*; Kim, K. M.*; Yamaya, Taiga*; Kawachi, Naoki*; Tanaka, Hiroki*; et al.
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 200(2), p.130 - 142, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:46.61(Environmental Sciences)Previously, we have developed DynamicMC for modelling relative movement of ORNL phantom in a radiation field for MCNP. Using this software, 3-dimensional dose distributions in a phantom irradiated by a certain mono-energetic source can be deduced through its graphical user interface (GUI). In this study, we extended DynamicMC to be used in combination with the PHITS by providing it with a higher flexibility for dynamic movement for a less sophisticated anthropomorphic phantom. We anticipate that the present work and the developed open-source tools will be in the interest of nuclear radiation physics community for research and teaching purposes.
 RecFOR proteins in homologous recombination
RecFOR proteins in homologous recombinationSato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Ishaque, A. M.*; Oba, Hirofumi*; Yamada, Mitsugu; Tejima, Kohei; Onodera, Takefumi; Narumi, Issei
DNA Repair, 11(4), p.410 - 418, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:60.52(Genetics & Heredity)In an effort to gain insights into the role of  RecFOR proteins in homologous recombination, we generated
RecFOR proteins in homologous recombination, we generated 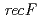 ,
, 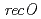 and
and 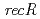 disruptant strains and characterized the disruption effects. Disruption of
disruptant strains and characterized the disruption effects. Disruption of 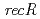 resulted in severe reduction of the transformation efficiency. On the other hand, the
resulted in severe reduction of the transformation efficiency. On the other hand, the 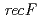 disruptant strain was the most sensitive phenotype to
disruptant strain was the most sensitive phenotype to  rays, UV irradiation and mitomycin C among the three disruptants. In the
rays, UV irradiation and mitomycin C among the three disruptants. In the 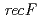 disruptant strain, the intracellular level of the LexA1 protein did not decrease following
disruptant strain, the intracellular level of the LexA1 protein did not decrease following  irradiation. These results demonstrate that the RecF protein plays a crucial role in the homologous recombination repair process by facilitating RecA activation. Thus, the RecF and RecR proteins are involved in the RecA activation and the stability of incoming DNA, respectively, during RecA-mediated homologous recombination processes that initiated the ESDSA pathway in
irradiation. These results demonstrate that the RecF protein plays a crucial role in the homologous recombination repair process by facilitating RecA activation. Thus, the RecF and RecR proteins are involved in the RecA activation and the stability of incoming DNA, respectively, during RecA-mediated homologous recombination processes that initiated the ESDSA pathway in  .
.
Haque, M. M.*; Alam, M. M.*; Ferdows, M.; Postelnicu, A.*
European Journal of Scientific Research, 53(3), p.491 - 515, 2011/05
Unsteady MHD heat and mass transfer by free convective micropolar fluid flow over an infinite vertical porous medium under the action of transverse magnetic field with thermal diffusion have been studied numerically in the presence of constant heat source. This investigation is performed for both cooling and heating problem with constant suction velocity when the medium is subjected to constant heat and mass fluxes. A finite difference technique with stability and convergence analysis is used to solve the non-dimensional momentum, angular momentum, energy and concentration equations. The computed values of fluid velocity, angular velocity, temperature and concentration distributions, wall shear stress, wall couple stress, Nusselt number and Sherwood number are shown graphically. Finally, a qualitative comparison with previous work is tabulated.
Sultana, M.*; Haque, M. M.*; Alam, M. M.*; Ferdows, M.; Postelnicu, A.*
European Journal of Scientific Research, 53(3), p.477 - 490, 2011/05
A unsteady MHD heat transfer by free convective micropolar fluid flow through an infinite vertical porous medium under the action of strong magnetic field have been studied numerically with induced magnetic field. This investigation is performed for the turbulent boundary layer cooling problem with constant suction velocity. The unconditionally stable implicit finite difference technique is used to solve the non-dimensional momentum, angular momentum, magnetic induction and energy equations. The computed values of fluid velocity, angular velocity, induced magnetic field and temperature distributions as well as the steady-state wall shear stress, wall couple stress, current density and Nusselt number are shown graphically. Finally, the important findings are listed here.
Makuuchi, Keizo; Haque, M. H.*; Ikeda, Kenichi*; Yoshii, Fumio; Kume, Tamikazu
Nihon Ratekkusu Arerugi Kenkyukai Kaishi, 4(1), p.7 - 10, 2001/01
no abstracts in English
Haque, M. H.*; Makuuchi, Keizo; Mitomo, Hiroshi*; Ikeda, K.*; Yoshii, Fumio; Kume, Tamikazu
IAEA-SM-365/17, p.34 - 35, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Haque, M. E.*; Yoshii, Fumio; Makuuchi, Keizo
Macromolecular Reports, A32(Suppl.3), p.249 - 254, 1995/00
no abstracts in English