Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Watanabe, Masatoshi*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 45(2), p.021506_1 - 021506_13, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Sheltering is a key countermeasure for mitigating radiation exposures during nuclear power plant accidents. The effectiveness of sheltering in minimizing inhalation exposure is commonly expressed using the reduction factor, which is the ratio of indoor to outdoor cumulative doses. The indoor dose is primarily influenced by the air exchange rate, penetration factor, and indoor deposition rate. Additionally, the air exchange rate is dependent on wind speed. In previous studies, the reduction factor was often treated as a constant value or calculated under constant wind speed conditions. However, wind speed varies in reality. This study investigated the effect of temporal variations in wind speed on the reduction factor and developed a simplified correction method to account for these variations. The results revealed that temporal variations in wind speed caused the reduction factor to differ by a factor of approximately two. Using the simplified correction method, the corrected reduction factors agreed, on average, within 10% of those calculated using a method that explicitly considers temporal variations in actual wind speed. Additionally, the computational cost was reduced by more than 20 times.

Yamauchi, Hiroki; Metoki, Naoto; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Hong, T.*; Fernandez-Baca, J. A.*; Hagihara, Masato; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Ito, Shinichi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(5), p.054705_1 - 054705_8, 2025/04
 Md produced in the
Md produced in the  He +
He +  Es reaction
Es reactionNishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Orlandi, R.; Kean, K. R.*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Chiera, N. M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 111(4), p.044609_1 - 044609_12, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Hirouchi, Jun; Watanabe, Masatoshi*; Hayashi, Naho; Nagakubo, Azusa; Takahara, Shogo
JAEA-Research 2024-015, 114 Pages, 2025/03
The public living in areas contaminated by nuclear accidents is exposed to radiation in the early phase and over the long term. Even under the same accident scenario, the exposure doses and the effectiveness of sheltering, which is one of the protective measures, vary depending on the meteorological condition and the surrounding environment. The exposure doses and sheltering effectiveness in the early phase are important information for the public and the national and local governments planning a nuclear emergency preparedness. In this report, we evaluate the exposure doses and sheltering effectiveness at sites with nuclear facilities in Japan using OSCAAR, one of the probabilistic risk assessment codes, for five accident scenarios: three scenarios from past severe accident studies; a scenario defined by the Nuclear Regulatory Authority; and a scenario assuming the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident. The sheltering effectiveness differed by approximately 20% among the sites. This was due to the differences in wind speed among the sites.
 martensitic transformation in Ti-12Mo alloy
martensitic transformation in Ti-12Mo alloyChong, Y.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Guo, B.*; Gholizadeh, R.*; Inoue, Koji*; Godfrey, A.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Communications Materials (Internet), 6, p.50_1 - 50_11, 2025/03
Strain-induced  martensitic phase transformation (SIMT) critically affects the mechanical properties of metastable
martensitic phase transformation (SIMT) critically affects the mechanical properties of metastable  titanium alloys. In this study, the effects of
titanium alloys. In this study, the effects of  grain size and oxygen content on SIMT in a Ti-12wt.%Mo alloy were systematically investigated. It is found that SIMT is promoted by a decrease in grain size and in oxygen content. The mechanistic origins of the anomalous grain size dependency and the acute oxygen content dependency of SIMT are discussed based on multi-scale microstructural characterization and state-of-the-art simulations. Grain refinement does not raise the energy barrier for SIMT but rather provides more nucleation sites for strain-induced
grain size and oxygen content on SIMT in a Ti-12wt.%Mo alloy were systematically investigated. It is found that SIMT is promoted by a decrease in grain size and in oxygen content. The mechanistic origins of the anomalous grain size dependency and the acute oxygen content dependency of SIMT are discussed based on multi-scale microstructural characterization and state-of-the-art simulations. Grain refinement does not raise the energy barrier for SIMT but rather provides more nucleation sites for strain-induced  martensite, thereby promoting SIMT in fine-grained Ti-12wt.%Mo alloy. In contrast, for the Ti-12wt.%Mo-0.3 wt.%O alloy, oxygen atoms substantially increase the energy barrier for SIMT, due to a change in the local configuration of oxygen atoms during the phase transformation. In addition, atom probe tomography reveals for the first time that oxygen atoms segregate at
martensite, thereby promoting SIMT in fine-grained Ti-12wt.%Mo alloy. In contrast, for the Ti-12wt.%Mo-0.3 wt.%O alloy, oxygen atoms substantially increase the energy barrier for SIMT, due to a change in the local configuration of oxygen atoms during the phase transformation. In addition, atom probe tomography reveals for the first time that oxygen atoms segregate at 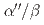 phase boundaries, thereby further restricting the growth of
phase boundaries, thereby further restricting the growth of  martensite.
martensite.
Hirata, Yoshinobu*; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Kaneko, Koji; Hagihara, Masato; Yamaguchi, Hideyuki*; Imaizumi, Teppei*; Nishizu, Takahisa*
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 306, p.141668_1 - 141668_7, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)We used quasi-elastic neutron scattering (QENS) to investigate the effect of the ratio of water to rice on the molecular dynamics of cooked rice starch during retrogradation. X-ray diffraction and differential scanning calorimetric measurements revealed that the degree of recrystallization and change in enthalpy were smaller with an increase in the amount of water added for cooking rice, whereas little difference in the crystallinity of the gelatinized rice starch was detected. The QENS measurements determined that the elastic incoherent structure factor (EISF) values of gelatinized samples were smaller with an increase in the amount of water added for cooking rice, indicating that the molecular dynamics of gelatinized rice starch with higher added water content were spatially more extended.
Hirouchi, Jun; Watanabe, Masatoshi*; Hayashi, Naho; Nagakubo, Azusa; Takahara, Shogo
Journal of Radiological Protection, 45(1), p.011506_1 - 011506_11, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)Public living in areas contaminated by nuclear accidents is exposed to radiation in the early phase and over the long term. Even under similar accident scenarios, radiation doses and sheltering effectiveness, which is one of the protective measures, depend on meteorological conditions and the surrounding environment. Radiation doses and sheltering effectiveness in the early phase of nuclear accidents are crucial information for the public as well as national and local governments planning a nuclear emergency preparedness. In this study, we assessed radiation doses and sheltering effectiveness at sites with nuclear facilities in Japan using the Off-Site Consequence Analysis code for Atmospheric Release accidents, which is one of the level-3 probabilistic risk assessment codes, for five accident scenarios: three scenarios from past severe accident studies, a scenario defined by the Nuclear Regulation Authority in Japan, and a scenario corresponding to the Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident. The sheltering effectiveness differed by up to approximately 50% among the accident scenarios at the same sites and by approximately 20% 50% among sites under the same accident scenario. Differences in the radionuclide composition among the accident scenarios and the differences in wind speeds among the sites primarily caused these differences in sheltering effectiveness.
50% among sites under the same accident scenario. Differences in the radionuclide composition among the accident scenarios and the differences in wind speeds among the sites primarily caused these differences in sheltering effectiveness.
 with geometrically frustrated orthogonal antiferromagnetic dimer
with geometrically frustrated orthogonal antiferromagnetic dimerMetoki, Naoto; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Hagihara, Masato; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kofu, Maiko*; Nakajima, Kenji; Matsuda, Masaaki*
Physical Review B, 111(10), p.104424_1 - 104424_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Inelastic neutron scattering experiments were carried out to understand the unusual successive order in NdB with the frustrated Shatry-Sutherland (SS) lattice. The pseudo-quartet with
with the frustrated Shatry-Sutherland (SS) lattice. The pseudo-quartet with 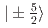 and
and 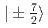 splits into four levels in the magnetically ordered states. The spectra can be explained with the on-site magnetic interaction
splits into four levels in the magnetically ordered states. The spectra can be explained with the on-site magnetic interaction 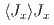 , the coupling of
, the coupling of 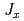 with quadrupole
with quadrupole 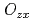 , and the uniaxial crystalline electric field. The
, and the uniaxial crystalline electric field. The  -electron states reproduce the temperature dependences of the in-plane moment
-electron states reproduce the temperature dependences of the in-plane moment 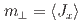 which is the primary order parameter, and a weakly induced
which is the primary order parameter, and a weakly induced 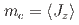 as the secondary order parameter. The magnetic-quadrupole coupling emerges and play essential role under the geometrical frustration, where the Heisenberg interactions are cancelled out.
as the secondary order parameter. The magnetic-quadrupole coupling emerges and play essential role under the geometrical frustration, where the Heisenberg interactions are cancelled out.

 H
H O
OFujihara, Masayoshi; Hagihara, Masato; Koda, Akihiro*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Matsuo, Akira*; Kindo, Koichi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 9(1), p.014406_1 - 014406_9, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:82.77(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) -,
-,  - and X-ray spectra
- and X-ray spectraOshima, Masumi*; Goto, Jun*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Asai, Masato; Shinohara, Hirofumi*; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*; Shen, H.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 10 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The spectrum determination method (SDM) is the method to determine radioactivities by analyzing full spectral shape of  - or
- or  rays through least-squares fitting by referring to standard
rays through least-squares fitting by referring to standard  - and
- and  spectra. In this paper, we have newly applied the SDM to a unified spectrum composed of two spectra measured with a Ge detector and a liquid scintillation counter. By analyzing the unified spectrum, uncertainties of deduced radioactivities have been improved. We applied this method to the unified spectrum including 40 radionuclides with equal intensities, and have deduced their radioactivities correctly.
spectra. In this paper, we have newly applied the SDM to a unified spectrum composed of two spectra measured with a Ge detector and a liquid scintillation counter. By analyzing the unified spectrum, uncertainties of deduced radioactivities have been improved. We applied this method to the unified spectrum including 40 radionuclides with equal intensities, and have deduced their radioactivities correctly.
Zheng, X.-G.*; Yamauchi, Ichihiro*; Hagihara, Masato; Nishibori, Eiji*; Kawae, Tatsuya*; Watanabe, Isao*; Uchiyama, Tomoki*; Chen, Y.*; Xu, C.-N.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.9989_1 - 9989_12, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Toyama, Takeshi*; Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide; Inoue, Koji*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Otsuka, Satoshi; Miyazawa, Takeshi; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Nakashima, Hideharu*; Onuma, Masato*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 599, p.155252_1 - 155252_14, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the stability of oxide nano particles in oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel, which is a promising candidate material for next-generation reactors, under neutron irradiation at high temperature to high doses. MA957, a 14Cr-ODS steel, was irradiated with Joyo in Japan Atomic Energy Agency under irradiation conditions of 130 dpa at 502 C, 154 dpa at 589
C, 154 dpa at 589 C, and 158 dpa at 709
C, and 158 dpa at 709 C. Three-dimensional atom probe (3D-AP) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) observation were performed to characterize the oxide particles in the ODS steels. A high number density of Y-Ti-O particle was observed in the unirradiated and irradiated samples. Almost no change in the morphology of the oxide particles, i.e. average diameter, number density, and chemical composition, has been observed in the samples irradiated to 130 dpa at 502
C. Three-dimensional atom probe (3D-AP) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) observation were performed to characterize the oxide particles in the ODS steels. A high number density of Y-Ti-O particle was observed in the unirradiated and irradiated samples. Almost no change in the morphology of the oxide particles, i.e. average diameter, number density, and chemical composition, has been observed in the samples irradiated to 130 dpa at 502 C and to 154 dpa at 589
C and to 154 dpa at 589 C. A slight decrease in number density was observed in the sample irradiated to 158 dpa at 709
C. A slight decrease in number density was observed in the sample irradiated to 158 dpa at 709 CC. The hardness of any of the irradiated samples was almost unchanged from that of the unirradiated sample. It was revealed that the oxide particles existed stable, and the strength of the material was sufficiently maintained even after being neutron irradiated to high dose of
CC. The hardness of any of the irradiated samples was almost unchanged from that of the unirradiated sample. It was revealed that the oxide particles existed stable, and the strength of the material was sufficiently maintained even after being neutron irradiated to high dose of  160 dpa at high temperature up to 700
160 dpa at high temperature up to 700 C. A part of this study includes the results of MEXT Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program Grant Number JPMXD0219214482.
C. A part of this study includes the results of MEXT Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program Grant Number JPMXD0219214482.
Sogabe, Joji; Ishida, Shinya; Tagami, Hirotaka; Okano, Yasushi; Kamiyama, Kenji; Onoda, Yuichi; Matsuba, Kenichi; Yamano, Hidemasa; Kubo, Shigenobu; Kubota, Ryuzaburo*; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Fuel Cycle (GLOBAL2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
In the frame of France-Japan collaboration, the calculational methodologies were defined and assessed, and the phenomenology and the severe accident consequences were investigated in a pool-type sodium-cooled fast reactor.
 Ba
Ba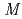 (PO
(PO )
) (
(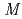 = Mg, Mn, Co, and Ni)
= Mg, Mn, Co, and Ni)Kajita, Yoichi*; Nagai, Takayuki*; Yamagishi, Shigetada*; Kimura, Kenta*; Hagihara, Masato; Kimura, Tsuyoshi*
Chemistry of Materials, 36(15), p.7451 - 7458, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:51.02(Chemistry, Physical)Nagai, Takayuki*; Hagihara, Masato; Yokoi, Rie*; Moriwake, Hiroki*; Kimura, Tsuyoshi*
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 146(33), p.23348 - 23355, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.48(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Oshima, Masumi*; Goto, Jun*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Shinohara, Hirofumi*; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*; Sano, Yuichi*; Asai, Masato; Haraga, Tomoko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(7), p.871 - 882, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Previously we reported a simple algorithmic method of spectral determination method (SDM), which is based on the first principle that a  -ray spectrum obtained for a sample is a linear superposition of individual spectra of the radioactive nuclides included in the sample and demonstrated that the method is valid for
-ray spectrum obtained for a sample is a linear superposition of individual spectra of the radioactive nuclides included in the sample and demonstrated that the method is valid for  -ray determination. Here we apply it to the spectra obtained by liquid scintillation counter (LSC). In LSC measurements quenching is generally observed and we at first developed its correction method to standard spectra. The SDM code reported in the previous investigation is used to analyze the LSC spectra. Based on the analyses done by using the measured spectra, we concluded that the SDM method is valid in the LSC spectra similarly to the
-ray determination. Here we apply it to the spectra obtained by liquid scintillation counter (LSC). In LSC measurements quenching is generally observed and we at first developed its correction method to standard spectra. The SDM code reported in the previous investigation is used to analyze the LSC spectra. Based on the analyses done by using the measured spectra, we concluded that the SDM method is valid in the LSC spectra similarly to the  -ray spectra studied in the previous investigation.
-ray spectra studied in the previous investigation.
 C to 1000
C to 1000 C
CImagawa, Yuya; Hashidate, Ryuta; Miyazawa, Takeshi; Onizawa, Takashi; Otsuka, Satoshi; Yano, Yasuhide; Tanno, Takashi; Kaito, Takeji; Onuma, Masato*; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(6), p.762 - 777, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:71.02(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been developing 9Cr-oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steel as a fuel cladding material for sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs). Previous studies have formulated the creep rupture equation for 650 C to 850
C to 850 C. However, little data have been obtained above 850
C. However, little data have been obtained above 850 C, and no equation has been formulated. This study conducted creep tests to evaluate creep strength at 700
C, and no equation has been formulated. This study conducted creep tests to evaluate creep strength at 700 C to 1000
C to 1000 C. Two creep test methods, the internal pressure and ring creep tests under development, were used, and the validation of the ring creep test method was conducted. The results showed that 9Cr-ODS steel undergoes almost no strength change due to the matrix's phase transformation, and a single equation can express a creep rupture strength from 700
C. Two creep test methods, the internal pressure and ring creep tests under development, were used, and the validation of the ring creep test method was conducted. The results showed that 9Cr-ODS steel undergoes almost no strength change due to the matrix's phase transformation, and a single equation can express a creep rupture strength from 700 C to 1000
C to 1000 C. In validating the ring creep test method, analysis clarified the effect of stress concentration on the specimen. Plastic deformation occurs at high initial stress and may lead to early rupture. The results will be essential for future creep testing and evaluation of neutron-irradiated 9Cr-ODS steel.
C. In validating the ring creep test method, analysis clarified the effect of stress concentration on the specimen. Plastic deformation occurs at high initial stress and may lead to early rupture. The results will be essential for future creep testing and evaluation of neutron-irradiated 9Cr-ODS steel.
Miyazaki, Kanako*; Takehara, Masato*; Minomo, Kenta*; Horie, Kenji*; Takehara, Mami*; Yamasaki, Shinya*; Saito, Takumi*; Onuki, Toshihiko*; Takano, Masahide; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; et al.
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 470(15), p.134104_1 - 134104_11, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.14(Engineering, Environmental)Miyazawa, Takeshi; Tanno, Takashi; Imagawa, Yuya; Hashidate, Ryuta; Yano, Yasuhide; Kaito, Takeji; Otsuka, Satoshi; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Onuma, Masato*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 593, p.155008_1 - 155008_16, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kaneko, Koji; Tabata, Chihiro; Hagihara, Masato; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Oba, Yojiro; Kumada, Takayuki; Kubota, Masato; Kojima, Yuki*; Nabatame, Nozomi; Sasaki, Miki; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 41, p.011015_1 - 011015_6, 2024/03