Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamaguchi, Akiko; Kurihara, Yuichi*; Nagata, Kojiro*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Higaki, Shogo*; Kobayashi, Toru; Tanida, Hajime; Ohara, Yoshiyuki*; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 661, p.317 - 332, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0no abstracts in English
Higuchi, Yuki*; Yoshimune, Wataru*; Kato, Satoru*; Hibi, Shogo*; Setoyama, Daigo*; Isegawa, Kazuhisa*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Nozaki, Hiroshi*; Harada, Masashi*; et al.
Communications Engineering (Internet), 3, p.33_1 - 33_7, 2024/02
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Terusawa, Shuji*; Goto, Akira*; Nishiyama, Nariaki; Nakajima, Toru; Ishihara, Takanori; Hakoiwa, Hiroaki
Island Arc, 33(1), p.e12516_1 - e12516_16, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0To investigate the geological evidence of near-surface crustal deformations in a high-strain shear zone that has been geodetically identified but not associated with clear tectonic landforms, a fieldwork was conducted in E-W trending southern Kyushu high-strain shear zone, Japan. According to our study, an investigation based on the slip data from minor faults and the occurrences of fracture zones could help to identify a concealed fault that is small in terms of size to record tectonic landforms but can trigger large earthquakes.
Sueoka, Shigeru; Iwano, Hideki*; Danhara, Toru*; Niwa, Masakazu; Kanno, Mizuho; Kohn, B. P.*; Kawamura, Makoto; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kagami, Saya; Ogita, Yasuhiro; et al.
Earth, Planets and Space (Internet), 75(1), p.177_1 - 177_24, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)Fluid-inclusion and thermochronometric analyses have been applied to hydrothermal alteration zones and their host rocks outcropping in the Hongu area of the Kii Peninsula, southwestern Japan in an attempt to detect thermal anomalies related to hydrothermal events and quantify the thermal effects on the host rocks. Hydrothermal events at ca 150 deg. C and ca 200 deg. C were identified by fluid-inclusion microthermometry of quartz veins in the alteration zones. For the host rocks and alteration zones, in the youngest population zircon yielded U-Pb dates ranging between ca 74.7-59.2 Ma, fission-track dates of ca 27.2-16.6 Ma, and (U-Th)/He single-grain dates of ca 23.6-8.7 Ma. Apatite yielded pooled fission-track ages of ca 14.9-9.0 Ma. The zircon U-Pb dates constrain the maximum depositional ages of the sedimentary samples. However, the fission-track and (U-Th)/He dates show no clear trend as a function of distance from the alteration zones. Hence, no thermal anomaly was detected in the surrounding host rocks based on the thermochronometric data patterns. The fission-track and (U-Th)/He dates are rather thought to record regional thermal and exhumation histories rather than a direct thermal imprint of fluid flow, probably because the duration of such activity was too short or because fluid flow occurred before regional cooling events and were later thermally overprinted. Apatite fission-track ages of ca 10 Ma may reflect regional mountain uplift and exhumation related to the obduction of the SW Japan lithospheric sliver onto the Shikoku Basin, or the rapid subduction of the Philippine Sea slab associated with the clockwise rotation of the Southwest Japan Arc.
 Ge
Ge
Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; Kanai-Nakata, Yuina*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Hamamoto, Satoru*; Kiss, Takayuki*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Tanaka, Arata*; Ebihara, Takao*; et al.
New Physics; Sae Mulli, 73(12), p.1062 - 1066, 2023/12
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Sueoka, Shigeru; Fujita, Natsuko; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Fukuda, Shoma; Nakajima, Toru; Kagami, Saya; Ogata, Manabu; et al.
JAEA-Review 2023-017, 27 Pages, 2023/10
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2023. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2023 are described in detail based on the JAEA 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques.
Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Sueoka, Shigeru; Ishihara, Takanori; Ogawa, Hiroki; Hakoiwa, Hiroaki; Watanabe, Tsuyoshi; Nishiyama, Nariaki; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Ogata, Manabu; et al.
JAEA-Research 2023-005, 78 Pages, 2023/10
This annual report documents the progress of research and development (R&D) in the 1st fiscal year of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028) to provide the scientific base for assessing geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques. The current status of R&D activities with previous scientific and technological progress is summarized.
 symmetry for anisotropic
symmetry for anisotropic 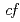 hybridization in the heavy-fermion superconductor CeNi
hybridization in the heavy-fermion superconductor CeNi Ge
Ge
Fujiwara, Hidenori*; Nakatani, Yasuhiro*; Aratani, Hidekazu*; Kanai, Yuina*; Yamagami, Kohei*; Hamamoto, Satoru*; Kiss, Takayuki*; Yamasaki, Atsushi*; Higashiya, Atsushi*; Imada, Shin*; et al.
Physical Review B, 108(16), p.165121_1 - 165121_10, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yoshimune, Wataru*; Higuchi, Yuki*; Kato, Akihiko*; Hibi, Shogo*; Yamaguchi, Satoshi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Nozaki, Hiroshi*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kato, Satoru*
ACS Energy Letters (Internet), 8(8), p.3485 - 3487, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:52.07(Chemistry, Physical)

 Sn
Sn (
( = Rh and Ir)
= Rh and Ir)Shimoda, Ami*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Kuwahara, Keitaro*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Nakao, Hironori*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Ohara, Takashi; Nakao, Akiko*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Ishigaki, Toru*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 38, p.011091_1 - 011091_6, 2023/05
Sueoka, Shigeru; Iwano, Hideki*; Danhara, Toru*; Okamoto, Akira*; Tagami, Takahiro*
Fisshion, Torakku Nyusureta, (35), p.1 - 4, 2022/12
no abstracts in English
Nakajima, Toru; Fukuda, Shoma; Nagata, Mitsuhiro; Danhara, Toru*; Iwano, Hideki*; Sueoka, Shigeru
Fisshion, Torakku Nyusureta, (35), p.34 - 36, 2022/12
In this presentation, we report the results of fission-track etching experiments for the practical use of baddeleyite fission-track dating and a brief discussion of the results.
Fukuda, Shoma; Kohn, B. P.*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Danhara, Toru*; Iwano, Hideki*; Tagami, Takahiro*
Fisshion, Torakku Nyusureta, (35), p.7 - 10, 2022/12
In order to establish the age standard of zircon (U-Th)/He method, we performed zircon (U-Th)/He (hereinafter, ZHe) dating on 4 zircon samples. In this presentation, the Nohi rhyolite and the Mt. Wasso moonstone rhyolite as domestic samples, and Mt. Dromedary and OD-3 were also adopted as age standard zircons of fission-track and U-Pb methods. Consequently, regarding the ZHe age of the Nohi rhyolite indicated younger, which possibly reflected secondary heating, while ones of the others indicated consistent with previous thermochronometric data. Integrated with previously obtained ZHe data about 7 samples, the Utaosa rhyolite in the previous study showed a small age dispersion in grain ages, which infers a suitable candidate for the ZHe age standard. As future prospects, we are planning to conduct geochemical analyses and structure observations of these zircons for exploring the causal factors in age dispersions.
 Se
Se from multilayer VSe
from multilayer VSe films via V- and Se-desorption
films via V- and Se-desorptionSumida, Kazuki; Kusaka, Shotaro*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Kobayashi, Katsuyoshi*; Hirahara, Toru*
Physical Review B, 106(19), p.195421_1 - 195421_7, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Sasao, Eiji; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Akiomi; Shimada, Koji; Watanabe, Takahiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Fujita, Natsuko; Ogita, Yasuhiro; et al.
JAEA-Review 2022-022, 29 Pages, 2022/09
This report is a plan of research and development (R&D) on geosphere stability for long-term isolation of high-level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in fiscal year 2022. The objectives and contents in fiscal year 2022 are described in detail based on the JAEA 4th Medium- and Long-term Plan (fiscal years 2022-2028). In addition, the background of this research is described from the necessity and the significance for site investigation and safety assessment, and the past progress. The plan framework is structured into the following categories: (1) Development and systematization of investigation techniques, (2) Development of models for long-term estimation and effective assessment, (3) Development of dating techniques
Nakajima, Toru; Kawakami, Tetsuo*; Iwano, Hideki*; Danhara, Toru*; Sakai, Harutaka*
Journal of Geophysical Research; Solid Earth, 127(5), p.e2021JB023630_1 - e2021JB023630_33, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:22.72(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The thermochronological methods were applied to the Higher Himalayan Crystalline (HHC) nappe and the underlying Lesser Himalayan sediments (LHS) to elucidate the denudation process of the middle- and upper-crust of eastern Nepal over the geological time scale. The thermochronological inverse analysis was undertaken for new results of fission-track (FT) age and FT length data of zircon and apatite in order to reconstruct the time-temperature (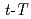 ) paths in the temperature range of 60-350 degree. Eight
) paths in the temperature range of 60-350 degree. Eight 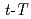 paths obtained along the across-strike section showed that the cooling process of the HHC nappe was characterized by following three aspects: (1) gradual cooling followed by rapid cooling and subsequent gradual cooling, (2) northward-younging of the timing of the rapid cooling, (3) gradual cooling followed by ca. 2 Myr rapid cooling in the frontmost part of the HHC nappe. The observed FT ages and
paths obtained along the across-strike section showed that the cooling process of the HHC nappe was characterized by following three aspects: (1) gradual cooling followed by rapid cooling and subsequent gradual cooling, (2) northward-younging of the timing of the rapid cooling, (3) gradual cooling followed by ca. 2 Myr rapid cooling in the frontmost part of the HHC nappe. The observed FT ages and 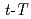 paths were then compared with those predicted by forward thermokinematic modeling. The results of the thermokinematic modeling for the Flat-Ramp-Flat MHT model, in which the HHC and the underlying LHS are denudated accompanied with the movement of the Main Himalayan Thrust (MHT), well reproduced the observed
paths were then compared with those predicted by forward thermokinematic modeling. The results of the thermokinematic modeling for the Flat-Ramp-Flat MHT model, in which the HHC and the underlying LHS are denudated accompanied with the movement of the Main Himalayan Thrust (MHT), well reproduced the observed 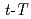 paths and FT ages in eastern Nepal. This suggests that the observed FT ages and
paths and FT ages in eastern Nepal. This suggests that the observed FT ages and 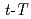 paths reflect a denudation process driven by the movement of the MHT showing the flat-ramp-flat geometry, and that the denudation rate and its spatial distribution have roughly been constant in eastern Nepal since ca. 9 Ma.
paths reflect a denudation process driven by the movement of the MHT showing the flat-ramp-flat geometry, and that the denudation rate and its spatial distribution have roughly been constant in eastern Nepal since ca. 9 Ma.
 )
)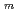 (Bi
(Bi Te
Te )
)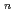 superlattice films by Te desorption from a pristine Bi
superlattice films by Te desorption from a pristine Bi Te
Te film
filmKusaka, Shotaro*; Sasaki, Taisuke*; Sumida, Kazuki; Ichinokura, Satoru*; Ideta, Shinichiro*; Tanaka, Kiyohisa*; Hono, Kazuhiro*; Hirahara, Toru*
Applied Physics Letters, 120(17), p.173102_1 - 173102_5, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:34.67(Physics, Applied)Terasawa, Yukana*; Ohara, Takashi; Sato, Sota*; Yoshida, Satoshi*; Asahi, Toru*
Acta Crystallographica Section E; Crystallographic Communications (Internet), 78(3), p.306 - 312, 2022/03
Yamashita, Keishiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Ohara, Takashi; Munakata, Koji*; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Shimmei, Toru*; Sugiyama, Kazumasa*; Kawamata, Toru*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
High Pressure Research, 42(1), p.121 - 135, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:58.88(Physics, Multidisciplinary)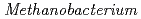 strain induces severe corrosion by retrieving electrons from Fe
strain induces severe corrosion by retrieving electrons from Fe under a freshwater environment
under a freshwater environmentHirano, Shinichi*; Ihara, Sota*; Wakai, Satoshi*; Dotsuta, Yuma; Otani, Kyohei; Kitagaki, Toru; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Okamoto, Akihiro*
Microorganisms (Internet), 10(2), p.270_1 - 270_12, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:84.82(Microbiology)To understand the role of methanogens in corrosion under anoxic conditions in freshwater, we investigated the corrosion activities of methanogens in samples collected from groundwater and rivers. We enriched microorganisms that can grow with CO /NaHCO
/NaHCO and Fe
and Fe as the sole carbon source and electron donor, respectively, in ground fresh water. Electrochemical analysis revealed that
as the sole carbon source and electron donor, respectively, in ground fresh water. Electrochemical analysis revealed that 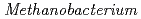 strain can uptake electrons from the cathode at lower than -0.61 V vs SHE and has a redox-active component with electrochemical potential different from those of other previously reported methanogens with extracellular electron transfer ability. This study indicated the corrosion risk by methanogens capable of taking up electrons from Fe
strain can uptake electrons from the cathode at lower than -0.61 V vs SHE and has a redox-active component with electrochemical potential different from those of other previously reported methanogens with extracellular electron transfer ability. This study indicated the corrosion risk by methanogens capable of taking up electrons from Fe in anoxic freshwater environments and the necessity of understanding the corrosion mechanism to contribute to risk diagnosis.
in anoxic freshwater environments and the necessity of understanding the corrosion mechanism to contribute to risk diagnosis.