Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Gd and
Gd and  Gd in the thermal energy region with the Li-glass detectors and NaI(Tl) spectrometer installed in J-PARC
Gd in the thermal energy region with the Li-glass detectors and NaI(Tl) spectrometer installed in J-PARC MLF
MLF ANNRI
ANNRIKimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Terada, Kazushi*; Hori, Junichi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.678 - 696, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Goux, P.*; Glessgen, F.*; Gazzola, E.*; Singh Reen, M.*; Focillon, W.*; Gonin, M.*; Tanaka, Tomoyuki*; Hagiwara, Kaito*; Ali, A.*; Sudo, Takashi*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2023(6), p.063H01_1 - 063H01_15, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Multidisciplinary) I(n,
I(n,  ) using fast neutron source in the "YAYOI" reactor
) using fast neutron source in the "YAYOI" reactorNakamura, Shoji; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Harada, Hideo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(7), p.851 - 865, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The present study performed integral experiments of  I using a fast-neutron source reactor "YAYOI" of the University of Tokyo to validate evaluated nuclear data libraries. The iodine-129 sample and flux monitors were irradiated by fast neutrons in the Glory hole of the YAYOI reactor. Reaction rates of
I using a fast-neutron source reactor "YAYOI" of the University of Tokyo to validate evaluated nuclear data libraries. The iodine-129 sample and flux monitors were irradiated by fast neutrons in the Glory hole of the YAYOI reactor. Reaction rates of  I were obtained by measurement of decay gamma-rays emitted from
I were obtained by measurement of decay gamma-rays emitted from 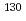 I. The validity of the fast-neutron flux spectrum in the Glory hole was confirmed by the
I. The validity of the fast-neutron flux spectrum in the Glory hole was confirmed by the 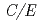 ratios of the reaction rates of flux monitors. The experimental reaction rate of
ratios of the reaction rates of flux monitors. The experimental reaction rate of  I was compared with that calculated with both the fast-neutron flux spectrum and evaluated nuclear data libraries. The present study revealed that the evaluated nuclear data of
I was compared with that calculated with both the fast-neutron flux spectrum and evaluated nuclear data libraries. The present study revealed that the evaluated nuclear data of  I cited in JENDL-4.0 should be reduced as much as 18% in neutron energies ranging from 10 keV to 3 MeV, and supported the reported data by Noguere
I cited in JENDL-4.0 should be reduced as much as 18% in neutron energies ranging from 10 keV to 3 MeV, and supported the reported data by Noguere 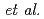 below 100 keV.
below 100 keV.
Nakamura, Shoji; Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Toh, Yosuke; Harada, Hideo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(12), p.1318 - 1329, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The present study performed fast-neutron capture cross-section measurement of  Tc by an activation method using a fast-neutron source reactor "YAYOI" of the University of Tokyo. Technetium-99 samples were irradiated with reactor neutrons using a pneumatic system. Reaction rates of
Tc by an activation method using a fast-neutron source reactor "YAYOI" of the University of Tokyo. Technetium-99 samples were irradiated with reactor neutrons using a pneumatic system. Reaction rates of  Tc were obtained by measuring decay gamma rays emitted from
Tc were obtained by measuring decay gamma rays emitted from  Tc. The neutron flux at an irradiation position was monitored with gold foils. The fast-neutron capture cross section of
Tc. The neutron flux at an irradiation position was monitored with gold foils. The fast-neutron capture cross section of  Tc at neutron energy of 85 keV was derived as 0.432
Tc at neutron energy of 85 keV was derived as 0.432 0.023 barn by using the reaction rates of
0.023 barn by using the reaction rates of  Tc, evaluated cross-section data and the fast-neutron flux spectrum of the YAYOI reactor. The present study agreed with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4.0.
Tc, evaluated cross-section data and the fast-neutron flux spectrum of the YAYOI reactor. The present study agreed with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4.0.
Harada, Hideo
Applied Sciences (Internet), 11(14), p.6558_1 - 6558_20, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)For accuracy improvement of neutron activation analysis and neutron capture cross section, bias effects are investigated on g- and s-factors in the Westcott convention. As origins of biases, a joining function shape, neutron temperature and sample temperature, have been investigated. Biases are quantitatively deduced for two 1/v isotopes ( Au,
Au,  Co) and six non-1/v isotopes (
Co) and six non-1/v isotopes ( Am,
Am,  Eu,
Eu, 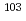 Rh,
Rh,  In,
In,  Hf,
Hf,  Ra). The s-factor calculated with a joining function deduced recently by a detailed Monte Carlo simulation is compared to s-factors calculated with traditional joining functions by Westcott. The results show the bias induced by sample temperature is small as the order of 0.1% for g-factor and the order of 1% for s-factor. On the other hand, biases induced by a joining function shape for s-factor depend significantly on both isotopes and neutron temperature. As the result, reaction rates are also affected significantly as well. The bias size on reaction rate is given in the case of epithermal neutron index r = 0.1, for the eight isotopes.
Ra). The s-factor calculated with a joining function deduced recently by a detailed Monte Carlo simulation is compared to s-factors calculated with traditional joining functions by Westcott. The results show the bias induced by sample temperature is small as the order of 0.1% for g-factor and the order of 1% for s-factor. On the other hand, biases induced by a joining function shape for s-factor depend significantly on both isotopes and neutron temperature. As the result, reaction rates are also affected significantly as well. The bias size on reaction rate is given in the case of epithermal neutron index r = 0.1, for the eight isotopes.
Kawase, Shoichiro*; Kimura, Atsushi; Harada, Hideo; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Nakamura, Shoji; Segawa, Mariko; Toh, Yosuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(7), p.764 - 786, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)Harada, Hideo
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (129), p.35 - 43, 2021/06
This paper explained the activities of the International Nuclear Data Evaluation Co-operation (WPEC)'s subgroup SG-41, which was carried out to improve the accuracy of nuclear data. In this paper, by focusing on how to deal with discrepant data, the method of deriving recommended values from multiple measurement results was reviewed. It also explained how to derive the recommended values, including exercises.
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Aoi, Nori*; Azaiez, F.*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Kimura, Atsushi; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 103(3), p.034327_1 - 034327_8, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:57.13(Physics, Nuclear)Dupont, E.*; Bossant, M.*; Capote, R.*; Carlson, A. D.*; Danon, Y.*; Fleming, M.*; Ge, Z.*; Harada, Hideo; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.15005_1 - 15005_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:99.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)Fleming, M.*; Bernard, D.*; Brown, D.*; Chadwick, M. B.*; De Saint Jean, C.*; Dupont, E.*; Ge, Z.*; Harada, Hideo; Hawari, A.*; Herman, M.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.15002_1 - 15002_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.1(Nuclear Science & Technology)Harada, Hideo; Takayama, Naoki; Komeda, Masao
Journal of Physics Communications (Internet), 4(8), p.085004_1 - 085004_17, 2020/08
A new convention of epithermal neutron spectrum is formulated for improving accuracy of resonance integrals. The new type function is proposed as an approximating function of epithermal neutron spectrum based on calculations by the state-of-art Monte Carlo code MVP-3. Bias effects on determination of resonance integrals due to utilizing approximating functions of the traditional types and the new type are compared. The other bias effect is also investigated, which is caused by neglecting position dependence of a neutron spectrum inside an irradiation capsule. For demonstrating the bias effects due to these assumptions on neutron spectrum quantitatively in a practical case, the thermal neutron-capture cross section and resonance integral of  Cs measured at a research reactor JRR-3 are re-evaluated. A superior property of the proposed new convention is discussed. The experimental method is proposed to determine the new shape factor
Cs measured at a research reactor JRR-3 are re-evaluated. A superior property of the proposed new convention is discussed. The experimental method is proposed to determine the new shape factor  introduced in the convention by a combinational use of triple flux monitors (
introduced in the convention by a combinational use of triple flux monitors ( Au,
Au,  Co and
Co and  Zr), and its analytical methodology is formulated.
Zr), and its analytical methodology is formulated.
Ma, F.; Kopecky, S.*; Alaerts, G.*; Harada, Hideo; Heyse, J.*; Kitatani, Fumito; Noguere, G.*; Paradela, C.*;  alamon, L.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
alamon, L.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 35(3), p.478 - 488, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.14(Chemistry, Analytical) U(n, f) cross section relative to the
U(n, f) cross section relative to the  Li(n, t) and
Li(n, t) and  B(n,
B(n,  ) standards from thermal to 170 keV neutron energy range at n_TOF
) standards from thermal to 170 keV neutron energy range at n_TOFAmaducci, S.*; Harada, Hideo; Kimura, Atsushi; 118 of others*
European Physical Journal A, 55(7), p.120_1 - 120_19, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:90.38(Physics, Nuclear)The  U(n, f) cross section was measured at n_TOF relative to
U(n, f) cross section was measured at n_TOF relative to  Li(n, t) and
Li(n, t) and  B(n,
B(n,  ), in a wide energy range (25 meV
), in a wide energy range (25 meV 170 keV) with 1.5% systematic uncertainty, making use of a stack of six samples and six silicon detectors placed in the neutron beam. The present results indicate that the cross section in the 9
170 keV) with 1.5% systematic uncertainty, making use of a stack of six samples and six silicon detectors placed in the neutron beam. The present results indicate that the cross section in the 9 18 keV neutron energy range is indeed overestimated by almost 5% in the recently released evaluated data files ENDF/B-VIII.0 and JEFF3.3. Furthermore, these new high-resolution data confirm the existence of resonance-like structures in the keV neutron energy region. From the present data, a value of 249.7
18 keV neutron energy range is indeed overestimated by almost 5% in the recently released evaluated data files ENDF/B-VIII.0 and JEFF3.3. Furthermore, these new high-resolution data confirm the existence of resonance-like structures in the keV neutron energy region. From the present data, a value of 249.7 1.4(stat)
1.4(stat) 0.94(syst) b eV has been extracted for the cross section integral between 7.8 and 11 eV, confirming the value of 247.5
0.94(syst) b eV has been extracted for the cross section integral between 7.8 and 11 eV, confirming the value of 247.5 3 b eV recently established as a standard.
3 b eV recently established as a standard.
 scintillation detector equipped with specially-designed shield for neutron resonance capture analysis
scintillation detector equipped with specially-designed shield for neutron resonance capture analysisTsuchiya, Harufumi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 932, p.16 - 26, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation) Am neutron capture and total cross sections with ANNRI at J-PARC
Am neutron capture and total cross sections with ANNRI at J-PARCKimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Terada, Kazushi*; Nakao, Taro*; Mizuyama, Kazuhito*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Igashira, Masayuki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(6), p.479 - 492, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:84.54(Nuclear Science & Technology)Hagiwara, Kaito*; Yano, Takatomi*; Das, P. K.*; Lorenz, S.*; Ou, Iwa*; Sakuda, Makoto*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Harada, Hideo; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(2), p.023D01_1 - 023D01_26, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:87.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Gd(n,
Gd(n, ) induced by thermal and epithermal neutrons
) induced by thermal and epithermal neutronsMastromarco, M.*; Manna, A.*; Aberle, O.*; Andrzejewski, J.*; Harada, Hideo; Kimura, Atsushi; n_TOF Collaboration*; 116 of others*
European Physical Journal A, 55(1), p.9_1 - 9_20, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:92.58(Physics, Nuclear)Nakamura, Shoji; Terada, Kazushi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakao, Taro*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Harada, Hideo; Uehara, Akihiro*; Takamiya, Koichi*; Fujii, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(1), p.123 - 129, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.15(Nuclear Science & Technology)Accurate data of  -ray emission probabilities are frequently needed when one quantitatively determines the amount of isotope by
-ray emission probabilities are frequently needed when one quantitatively determines the amount of isotope by  -ray measurements or obtains neutron capture cross-sections using them. Americium-243, one of the most important minor actinides, produces
-ray measurements or obtains neutron capture cross-sections using them. Americium-243, one of the most important minor actinides, produces  Am after neutron capture. The 744-keV
Am after neutron capture. The 744-keV  -ray decaying from the ground state of
-ray decaying from the ground state of  Am has a relatively large
Am has a relatively large  -ray emission probability c.a. 66%, however, its uncertainty is as large as 29%. The uncertainty of the
-ray emission probability c.a. 66%, however, its uncertainty is as large as 29%. The uncertainty of the  -ray emission probability leads to a major factor of the systematic uncertainty on determining an amount of isotope, and therefore the
-ray emission probability leads to a major factor of the systematic uncertainty on determining an amount of isotope, and therefore the  -ray emission probability was measured by using an activation method and an examined level structure of
-ray emission probability was measured by using an activation method and an examined level structure of  Cm. In this study, the emission probability of 744-keV
Cm. In this study, the emission probability of 744-keV  ray was derived as 66.5
ray was derived as 66.5 1.1%, and its uncertainty was improved from 29% to 2%.
1.1%, and its uncertainty was improved from 29% to 2%.
 Am with ANNRI at J-PARC
Am with ANNRI at J-PARCTerada, Kazushi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakao, Taro*; Nakamura, Shoji; Mizuyama, Kazuhito*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Harada, Hideo; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Igashira, Masayuki*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(10), p.1198 - 1211, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:88.27(Nuclear Science & Technology) Be(n,p)
Be(n,p) Li reaction and the cosmological lithium problem; Measurement of the cross section in a wide energy range at n_TOF at CERN
Li reaction and the cosmological lithium problem; Measurement of the cross section in a wide energy range at n_TOF at CERNDamone, L.*; Barbagallo, M.*; Mastromarco, M.*; Cosentino, L.*; Harada, Hideo; Kimura, Atsushi; n_TOF Collaboration*; 152 of others*
Physical Review Letters, 121(4), p.042701_1 - 042701_7, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:91.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)