Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shibata, Daisuke*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Hasegawa, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Fukaya, Akane*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2024-014, 54 Pages, 2025/02
XAFS measurements in the soft X-ray region are suitable for evaluating the chemical state of the surface layer of a measurement sample because the X-ray transmittance is low. In this study, the purpose of the study was to confirm the difference between the coagulated surface layer and the inside of the simulated waste glasses by measuring the K-edge of the glass constituent elements boron, oxygen, sodium, and silicon, and the L edge of the waste component cerium. As a result, the B K-edge XANES spectra showed that the proportion of B-O tetracoordinate sp
edge of the waste component cerium. As a result, the B K-edge XANES spectra showed that the proportion of B-O tetracoordinate sp structures (BO
structures (BO ) on the surface layer of the coagulated glass samples was higher than that on the cut surface inside the glass samples, which is expected to improve the water resistance of the coagulated surface. On the other hand, the O K-edge XANES spectra suggested that the O abundance in the coagulated surface layer was lower than that in the cut surface inside the glass samples, and that alkali metal elements may be concentrated in the coagulated surface layer. However, no difference was observed in the Na K-edge XANES spectra between the coagulated surface layer and the cut surface, and no difference was observed in the Si K-edge XANES spectra between the solidified surface and the inside of glass samples. In addition, the Ce L
) on the surface layer of the coagulated glass samples was higher than that on the cut surface inside the glass samples, which is expected to improve the water resistance of the coagulated surface. On the other hand, the O K-edge XANES spectra suggested that the O abundance in the coagulated surface layer was lower than that in the cut surface inside the glass samples, and that alkali metal elements may be concentrated in the coagulated surface layer. However, no difference was observed in the Na K-edge XANES spectra between the coagulated surface layer and the cut surface, and no difference was observed in the Si K-edge XANES spectra between the solidified surface and the inside of glass samples. In addition, the Ce L -edge XANES spectra confirmed that the Ce valence in the surface layer of coagulated glass samples were oxidized compared to the inside of glass samples.
-edge XANES spectra confirmed that the Ce valence in the surface layer of coagulated glass samples were oxidized compared to the inside of glass samples.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Tanaka, Satoshi*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Iwata, Ayako*; Aoki, Yuto; Aoki, Kazuhisa; Yanagisawa, Kenichi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (70), p.3 - 22, 2024/09
Inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F), there are many locations with high radiation levels due to contamination by radioactive materials that leaked from the reactor. These pose a significant obstacle to the smooth progress of decommissioning work. To help solve this issue, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), under a subsidy from the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry's decommissioning and contaminated water management project, is conducting research and development on digital technologies to improve the radiation environment inside the decommissioning site. This project, titled "Development of Technology to Improve the Environment Inside Reactor Buildings (Enhancing Digital Technology for Environment and Source Distribution to Reduce Radiation Exposure)," began in April of FY 2023. In this project, the aim is to develop three interconnected systems: FrontEnd, Pro, and BackEnd. The FrontEnd system, based on the previously developed 3D-ADRES-Indoor (prototype) from FY 2021-2022, will be upgraded to a high-speed digital twin technology usable on-site. The Pro system will carry out detailed analysis in rooms such as the new office building at 1F, while the BackEnd system will serve as a database to centrally manage the collected and analyzed data. This report focuses on the FrontEnd system, which will be used on-site. After point cloud measurement, the system will quickly create a 3D mesh model, estimate the radiation source from dose rate measurements, and refine the position and intensity of the estimated source using recalculation techniques (re-observation instructions and re-estimation). The results of verification tests conducted on Unit 5 are also presented. Furthermore, the report briefly discusses the future research and development plans for this project.
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Shibata, Daisuke*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Hasegawa, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Fukaya, Akane*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2023-004, 45 Pages, 2023/09
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in borosilicate glasses varies with its chemical composition. In this study, simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the chemical state regarding boron (B), silicon (Si) and waste elements of iron (Fe), cesium (Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. To understand the chemical stability of simulated waste glasses, XANES spectra of B K-edge, Fe L , L
, L -edge, and Cs M
-edge, and Cs M , M
, M -edge were measured on the glass surface exposed to the leachate. As a result, it was found that the glass surface exposed to the leachate was changed and it was difficult to obtain a clear XANES spectrum. From the B K-edge XANES spectra on glass surfaces exposed to the leachate, an increase in three-coordination of B-O (BO
-edge were measured on the glass surface exposed to the leachate. As a result, it was found that the glass surface exposed to the leachate was changed and it was difficult to obtain a clear XANES spectrum. From the B K-edge XANES spectra on glass surfaces exposed to the leachate, an increase in three-coordination of B-O (BO ) and a decrease in four-coordination of B-O (BO
) and a decrease in four-coordination of B-O (BO ) were observed compared to the glass surfaces before immersion. The XANES spectra of Fe L
) were observed compared to the glass surfaces before immersion. The XANES spectra of Fe L , L
, L -edge, and Cs M
-edge, and Cs M , M
, M -edge show that as the exposure time in the leachate increases, the Cs present on the glass surface dissolves into the leachate. The XANES spectra of Si K-edge were measured on simulated waste glass surfaces before immersion, and it was confirmed that the change in XANES spectra given by Na
-edge show that as the exposure time in the leachate increases, the Cs present on the glass surface dissolves into the leachate. The XANES spectra of Si K-edge were measured on simulated waste glass surfaces before immersion, and it was confirmed that the change in XANES spectra given by Na O concentration had a larger effect than the waste component concentration.
O concentration had a larger effect than the waste component concentration.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Okumura, Masahiko; Miyamura, Hiroko; Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Sato, Tomoki*; Numata, Yoshiaki*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
The contamination of radioactive materials leaked from the reactor has resulted in numerous hot spots in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) building, posing obstacles to its decommissioning. In order to solve this problem, JAEA has conducted research and development of the digital technique for inverse estimation of radiation source distribution and countermeasures against the estimated source in virtual space for two years from 2021 based on the subsidy program "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management" performed by the funds from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. In this article, we introduce the results of the project and the plan of the renewal project started in April 2023. For the former project, we report the derivative method for LASSO method considering the complex structure inside the building and the character of the source and show the result of the inverse estimation using the method in the real reactor building. Moreover, we explain the platform software "3D-ADRES-Indoor" which integrates these achievements. Finally, we introduce the plan of the latter project.
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 162, p.104792_1 - 104792_19, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Predicting radioactive source distributions inside reactor building rooms based on monitoring air dose rates is one of the most essential steps towards decommissioning of nuclear power plants. However, the attempt is rather a difficult task, because it can be generally mapped onto mathematically ill-posed problem. Then, in order to successfully perform the inverse estimations on radioactive source distributions even in such ill-posed conditions, we suggest that a machine learning method, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) minimizing the loss function, 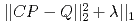 is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 184, p.109686_1 - 109686_12, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:78.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/02
Machida, Masahiko; Shi, W.*; Yamada, Susumu; Miyamura, Hiroko; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji; Aoki, Yuto; Ito, Rintaro; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
Proceedings of Waste Management Symposia 2023 (WM2023) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2023/02
Miwa, Koji*; Fujita, Manami; Harada, Takeshi; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Masaya; Imai, Kenichi*; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Tamura, Hirokazu; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 271, p.04001_1 - 04001_7, 2022/11
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Okumura, Masahiko; Miyamura, Hiroko; Malins, A.; Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Sato, Tomoki*; Numata, Yoshiaki*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; et al.
RIST News, (68), p.3 - 19, 2022/09
no abstracts in English
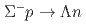 reaction in momentum range 470-650 MeV/
reaction in momentum range 470-650 MeV/
Miwa, Koji*; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai*; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Tamura, Hirokazu; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 128(7), p.072501_1 - 072501_6, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:86.28(Physics, Multidisciplinary)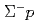 elastic scattering in momentum range 470 to 850 MeV/
elastic scattering in momentum range 470 to 850 MeV/
Miwa, Koji*; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; et al.
Physical Review C, 104(4), p.045204_1 - 045204_20, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:89.34(Physics, Nuclear)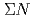 interaction from the
interaction from the 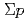 scattering experiment at J-PARC
scattering experiment at J-PARCMiwa, Koji*; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Masaya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1643, p.012174_1 - 012174_6, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:78.92(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Suekuni, Koichiro*; Lee, C. H.*; Tanaka, Hiromi*; Nishibori, Eiji*; Nakamura, Atsushi*; Kasai, Hidetaka*; Mori, Hitoshi*; Usui, Hidetomo*; Ochi, Masayuki*; Hasegawa, Takumi*; et al.
Advanced Materials, 30(13), p.1706230_1 - 1706230_6, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:89.52(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Thermoelectric materials for highly efficient devices must satisfy conflicting requirements of high electrical conductivity and low thermal conductivity. In this paper, we studied the crystal structure and phonon dynamics of tetrahedrites (Cu,Zn) (Sb,As)
(Sb,As) S
S . The results revealed that the Cu atoms in a planar coordination are rattling, which effectively scatter phonons. These findings provide a new strategy for the development of highly efficient thermoelectric materials with planar coordination.
. The results revealed that the Cu atoms in a planar coordination are rattling, which effectively scatter phonons. These findings provide a new strategy for the development of highly efficient thermoelectric materials with planar coordination.
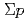 scattering experiment using high intensity pion beams at J-PARC
scattering experiment using high intensity pion beams at J-PARCMiwa, Koji*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hosomi, Kenji; Imai, Kenichi; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Sugimura, Hitoshi; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 17, p.041002_1 - 041002_6, 2017/07
Yamamoto, Masanobu; Ezura, Eiji*; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Nomura, Masahiro; Omori, Chihiro*; Schnase, A.*; Shimada, Taihei; Takagi, Akira*; Takata, Koji*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 8, p.012015_1 - 012015_6, 2015/09
The J-PARC MR provides a coasting proton beam for nuclear physics experiments by slow extraction. The longitudinal emittance should be enlarged until the MR flat top to mitigate the microwave instability. We have investigated a Phase Modulation (PM) method by using a High Frequency Cavity (HFC) to increase the emittance. We have performed extensive simulation studies to find the appropriate parameters of the PM through the particle tracking simulation. We found that the effective HFC frequency has linear dependence with the PM frequency, where the emittance is smoothly enlarged. Furthermore, we found that the required HFC voltage is inverse proportional to the square root of the duration time of the PM. These PM properties will be used for the design of the HFC. We describe the particle tracking simulation results of controlled emittance blow-up by the PM.
Takahashi, Fumiaki; Sato, Kaoru; Endo, Akira; Ono, Koji*; Ban, Nobuhiko*; Hasegawa, Takayuki*; Katsunuma, Yasushi*; Yoshitake, Takayasu*; Kai, Michiaki*
Health Physics, 109(2), p.104 - 112, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.46(Environmental Sciences)A dosimetry system, named WAZA-ARI, is developed to assess accurately radiation doses to persons from Computed Tomography (CT) examination patients in Japan. Organ doses were prepared to application to dose calculations in WAZA-ARI by numerical analyses using average adult Japanese human models with the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS). Experimental studies clarified the radiation configuration on the table for some multi-detector row CT (MDCT) devices. Then, a source model in PHITS could specifically take into account for emissions of X-ray in each MDCT device based on the experiment results. Numerical analyses with PHITS revealed a concordance of organ doses with human body size. The organ doses by the JM phantoms were compared with data obtained using previously developed systems. In addition, the dose calculation in WAZA-ARI were verified with previously reported results by realistic NUBAS phantoms and radiation dose measurement using a physical Japanese model. The results implied that analyses using the Japanese phantoms and PHITS including source models can appropriately give organ dose data with consideration of the MDCT device and physiques of typical Japanese adults.
Yamaji, Tatsuya*; Koizumi, Yasuo; Yamazaki, Kohei*; Otake, Hiroyasu*; Hasegawa, Koji*; Onuki, Akira*; Kanamori, Daisuke*
Konsoryu Shimpojiumu 2015 Koen Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), 2 Pages, 2015/08
Experiments of condensing counter-current two-phase flow in a vertical pipe were performed. This study was intended to examine water accumulation in the up-flow side of steam generator U-tubes of a PWR during the reflux cooling stage of a small break LOCA. It has been apprehended that the water accumulation may result in temporary core liquid level depression. The inner diameter and the length of a test flow channel used in the experiments were 18 mm and 4 m, respectively. The experiments were performed by using steam and water at 0.1 MPa. Two kinds of experiments were conducted; visualization experiments by using a transparent test section and quantitative water accumulation evaluation experiments by using a brass test section. Even if water on the inner surface of the test pipe could not flow downward at the lower portion of the test pipe, a part of water became to flow downward at the upper portion of the test pipe since steam velocity decreased because of condensation. Thus, two-phase mixture level was formed in the upper portion of the test pipe, which resulted in the water accumulation in the pipe. The model to predict the water accumulation was proposed. It predicted the water accumulation reasonably well.
 13MI44 Boreholes)
13MI44 Boreholes)Hasegawa, Takashi; Kawamoto, Koji; Yamada, Nobuto; Onuki, Kenji; Omori, Kazuaki; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Sato, Toshinori
JAEA-Technology 2015-011, 135 Pages, 2015/07
The geological, hydraulic and geochemical data such as rock mass classification, groundwater inflow points and the volume, water pressure, and hydraulic conductivity were obtained from boreholes (13MI38 13MI44) in the -500m Access/Research Gallery-North of Mizunami Underground Research laboratory (MIU). In addition to data acquisition, monitoring systems were installed to observe hydrochemical changes in the groundwater, and rock strain during and after the groundwater recovery experiment.
13MI44) in the -500m Access/Research Gallery-North of Mizunami Underground Research laboratory (MIU). In addition to data acquisition, monitoring systems were installed to observe hydrochemical changes in the groundwater, and rock strain during and after the groundwater recovery experiment.
Honda, Ryotaro*; Miwa, Koji*; Matsumoto, Yuki*; Chiga, Nobuyuki*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Imai, Kenichi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 787, p.157 - 160, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:47.45(Instruments & Instrumentation)A beam position fiber counter consisting of the scintillation fiber and a multi-pixel photon counter was developed in order to handle a 10 MHz secondary pion beam in the J-PARC E40 experiment. This counter was installed at the entrance of the beam line spectrometer at the K1.8 experimental area in J-PARC and used for the momentum reconstruction. In order to suppress the accidental background and reconstruct the beam momentum, a good timing resolution better than 0.8 ns and a good position resolution better than 200  m were simultaneously required for the counter. These requirements were well achieved by reading the 320 fibers with a diameter of 1 mm, which were arranged in a staggered position, with MPPC fiber by fiber. The signal induced from each MPPC was handled with an Extended Analogue SiPM Integrated ReadOut Chip (EASIROC) developed by Omega/IN2P3 in France. In addition, the timing of the discriminated signals from EASIROC was measured by a FPGA-based multi-hit TDC implemented into Spartan-6. Finally, we obtained the timing resolution of 0.68 ns and the position resolution of 190
m were simultaneously required for the counter. These requirements were well achieved by reading the 320 fibers with a diameter of 1 mm, which were arranged in a staggered position, with MPPC fiber by fiber. The signal induced from each MPPC was handled with an Extended Analogue SiPM Integrated ReadOut Chip (EASIROC) developed by Omega/IN2P3 in France. In addition, the timing of the discriminated signals from EASIROC was measured by a FPGA-based multi-hit TDC implemented into Spartan-6. Finally, we obtained the timing resolution of 0.68 ns and the position resolution of 190  m under the 9 MHz beam condition using a pion beam.
m under the 9 MHz beam condition using a pion beam.