Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Araki, Shohei; Aizawa, Eiju; Murakami, Takahiko; Arakaki, Yu; Tada, Yuta; Kamikawa, Yutaka; Hasegawa, Kenta; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Sumiya, Masato; Seki, Masakazu; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 217, p.111323_1 - 111323_8, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)JAEA has modified the STACY from a homogeneous system using solution fuel to a heterogeneous system using fuel rods in order to obtain criticality characteristics of fuel debris. The modification of the STACY was completed in December 2023. A series of performance inspections were conducted for the start of experimental operations. A new thermal power calibration is required for the performance inspections in order to operate at less than 200 W, which is the permitted thermal power. However, the thermal power measurement method and calibration data used in the former STACY is no longer available due to the modification of the modified STACY. We measured the thermal power of the STACY using the activation method that was improved to adapt to the measurement condition and calibrated the power meter system. Since the positions where activation foils could be installed were very limited, the thermal power was evaluated using numerical calculations supplemented by experimental data. Neutron flux data at the positions of the activation foil was measured by the activation method. Neutron distribution in the core was calculated by the Monte Carlo code MVP. A response function of the activation foil was calculated using the PHITS. The uncertainty of the thermal power measurement was conservatively estimated to be about 15%. Four operations were conducted for the thermal power measurement. The power meter was calibrated by using three operational data and tested with the one operational data. It was found that the indicated value of the meter adjusted by the STACY before the modification work would tend to overestimate the actual output by about 40%. In addition, the current calibration was able to calibrate the meter to within 3% accuracy.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Onodera, Naoyuki
EPJ Web of Conferences, 302, p.03005_1 - 03005_9, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)We implemented the ensemble data assimilation (DA) method, the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF), into the mesh-refined lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) for turbulent flows. Both the LETKF and the mesh-refined LBM were fully implemented on GPUs, so that they are efficiently computed on modern GPU-based supercomputers. We examined the DA accuracy against the flow around a cylinder. The result showed that our method enabled accurate DA with spatially- and temporarily-sparse observation data; the error of the assimilated velocity field with the observation interval of 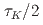 and the observation resolution
and the observation resolution 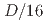 (1.56% of the total computational grids) was smaller than the amplitude of the observation noise, where
(1.56% of the total computational grids) was smaller than the amplitude of the observation noise, where 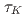 is the period of the K
is the period of the K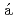 rm
rm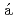 n vortex and
n vortex and  is diameter of the square cylinder.
is diameter of the square cylinder.
Iwata, Yoshihiro; Miyabe, Masabumi; Wells, S. R.*; Yamamoto, Yuta*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research 2024 (FDR2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
In this study, triple and double resonance ionization schemes of atomic Ca were developed, aiming for the separation of odd isotopes by (i) laser polarization-dependent selection rules, and (ii) large isotope shifts of odd Ca isotopes in the Rydberg levels. Separation of odd isotopes was confirmed under the orthogonal condition. Suppression of non-resonant ionization of  Ca by the electric field in the ionization region could further improve the optical isotope selectivity of
Ca by the electric field in the ionization region could further improve the optical isotope selectivity of  Ca.
Ca.
Watanabe, Tsutomu*; Ishikawa, Shuhei*; Kawashima, Masayuki*; Shimoyama, Ko*; Onodera, Naoyuki; Hasegawa, Yuta; Inagaki, Atsushi*
Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 250, p.105783_1 - 105783_17, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.80(Engineering, Civil)This paper presents simulations of drifting snow using a Lagrangian particle dispersion model coupled with a large-eddy simulation code. The model accurately replicates observed features such as mass transport rate dependency on flow velocity and variations in particle size distribution. It also shows that the saltation layer height increases monotonically with flow velocity, contrary to conventional estimates. Additionally, the study confirms the transition from saltation to suspension near the estimated saltation layer height and finds that dense snow streamers are linked to small-scale low-speed streaks in near-surface flows.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Onodera, Naoyuki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 29, 4 Pages, 2024/06
We implemented the ensemble data assimilation (DA) of turbulence by using the mesh-refined lattice Boltzmann method with the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LBM-LETKF). We examined the accuracy of the data assimilation against a turbulent flow around a three-dimensional square cylinder. The DA error was comparable or less than the observation noise when the observation interval was a half of the period of the K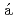 rm
rm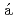 n vortex street and the number of observation points was 0.195% of computational grid points. The LBM-LETKF enables DA of turbulence with spatially- and temporally- sparse observations.
n vortex street and the number of observation points was 0.195% of computational grid points. The LBM-LETKF enables DA of turbulence with spatially- and temporally- sparse observations.
Kawamura, Takuma; Hasegawa, Yuta; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Journal of Visualization, 27(1), p.89 - 107, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:27.40(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)Interactive in-situ steering is an effective tool for debugging, searching for optimal solutions, and analyzing inverse problems in fast and large-scale computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations. We propose an interactive in-situ steering framework for large-scale CFD simulations on GPU supercomputers. This framework employs in-situ particle-based volume rendering (PBVR), in-situ data sampling, and a file-based control that enables interactive communication of steering parameters, compressed particle data, and sampled monitoring data between supercomputers and user PCs. The parallelized PBVR is processed on the host CPU to avoid interference with CFD simulations on the GPU. We apply the proposed framework to a real-time plume dispersion analysis code CityLBM on GPU supercomputers. In the numerical experiment, we address an inverse problem to find a pollutant source from the monitoring data, and demonstrate the effectiveness of the human-in-the-loop approach.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Ina, Takuya; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Fluid Dynamics Research, 55(6), p.065501_1 - 065501_25, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:13.13(Mechanics)We investigate the applicability of the data assimilation (DA) to large eddy simulations (LESs) based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM). We carry out the observing system simulation experiment of a two-dimensional (2D) forced isotropic turbulence, and examine the DA accuracy of the nudging and the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF) with spatially sparse and noisy observation data of flow fields. The advantage of the LETKF is that it does not require computing spatial interpolation and/or an inverse problem between the macroscopic variables (the density and the pressure) and the velocity distribution function of the LBM, while the nudging introduces additional models for them. The numerical experiments with 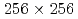 grids and 10% observation noise in the velocity showed that the root mean square error of the velocity in the LETKF with
grids and 10% observation noise in the velocity showed that the root mean square error of the velocity in the LETKF with 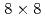 observation points (
observation points (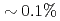 of the total grids) and 64 ensemble members becomes smaller than the observation noise, while the nudging requires an order of magnitude larger number of observation points to achieve the same accuracy. Another advantage of the LETKF is that it well keeps the amplitude of the energy spectrum, while only the phase error becomes larger with more sparse observation. From these results, it was shown that the LETKF enables robust and accurate DA for the 2D LBM with sparse and noisy observation data.
of the total grids) and 64 ensemble members becomes smaller than the observation noise, while the nudging requires an order of magnitude larger number of observation points to achieve the same accuracy. Another advantage of the LETKF is that it well keeps the amplitude of the energy spectrum, while only the phase error becomes larger with more sparse observation. From these results, it was shown that the LETKF enables robust and accurate DA for the 2D LBM with sparse and noisy observation data.
Araki, Shohei; Gunji, Satoshi; Arakaki, Yu; Murakami, Takahiko; Yoshikawa, Tomoki; Hasegawa, Kenta; Tada, Yuta; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Suyama, Kenya
Proceedings of 4th Reactor Physics Asia Conference (RPHA2023) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2023/10
To conduct integrated thermal power measurements for the performance test of the modified STACY, we re-analyzed the experimental data measured in the solution fuel STACY using the activation method. We validated its feasibility under the limited number of activation detectors. The re-analyzed results of the activation method by using MVP and PHITS with JENDL-4.0 indicated that the effect of the difference of the position between activation detectors was small enough, and the results agreed with that of the fission product analysis within almost 10%. It is conceivable that the activation method could be adopted instead of the fission product analysis.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Yuta; Asahi, Yuichi; Inagaki, Atsushi*; Shimose, Kenichi*; Hirano, Kohin*
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 28, 4 Pages, 2023/05
We have developed a multi-scale wind simulation code named CityLBM that can resolve entire cities to detailed streets. CityLBM enables a real time ensemble simulation for several km square area by applying the locally mesh-refined lattice Boltzmann method on GPU supercomputers. On the other hand, real-world wind simulations contain complex boundary conditions that cannot be modeled, so data assimilation techniques are needed to reflect observed data in the simulation. This study proposes an optimization method for ground surface temperature bias based on an ensemble Kalman filter to reproduce wind conditions within urban city blocks. As a verification of CityLBM, an Observing System Simulation Experiment (OSSE) is conducted for the central Tokyo area to estimate boundary conditions from observed near-surface temperature values.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 28, 5 Pages, 2023/05
We implemented and investigated the data assimilation (DA) of two-dimensional isotropic turbulence using the lattice Boltzmann method and the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LBM-LETKF). We carried out the numerical experiment with 256 grids, 256
grids, 256 or less observation points, 10% root mean square (RMS) observation noise in the velocity observation, and 4, 16, or 64 ensemble members. The numerical experiment showed that the accuracy of the LETKF was better than the nudging DA with both dense and sparse observation. The lack of observation points caused the numerical instability in the LETKF, but such a numerical instability can be suppressed by increasing the number of ensemble members. In the sparse observation case (8
or less observation points, 10% root mean square (RMS) observation noise in the velocity observation, and 4, 16, or 64 ensemble members. The numerical experiment showed that the accuracy of the LETKF was better than the nudging DA with both dense and sparse observation. The lack of observation points caused the numerical instability in the LETKF, but such a numerical instability can be suppressed by increasing the number of ensemble members. In the sparse observation case (8 8 observation points) with 64 ensemble members, the root means squared error (RMSE) of the velocity in the LBM-LETKF was smaller than the RMS of the observation noise, while the nudging DA required 32
8 observation points) with 64 ensemble members, the root means squared error (RMSE) of the velocity in the LBM-LETKF was smaller than the RMS of the observation noise, while the nudging DA required 32 32 observation points to obtain the same accuracy. Overall, the LETKF with sufficiently large number of ensemble members was highly accurate and robust, thus, the LETKF was a good choice for the DA of turbulent flows using the LBM.
32 observation points to obtain the same accuracy. Overall, the LETKF with sufficiently large number of ensemble members was highly accurate and robust, thus, the LETKF was a good choice for the DA of turbulent flows using the LBM.
Asahi, Yuichi; Onodera, Naoyuki; Hasegawa, Yuta; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Shiba, Hayato*; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Boundary-Layer Meteorology, 186(3), p.659 - 692, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:25.47(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)We develop a Transformer-based deep learning model to predict the plume concentrations in the urban area under uniform flow conditions. Our model has two distinct input layers: Transformer layers for sequential data and convolutional layers in convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for image-like data. Our model can predict the plume concentration from realistically available data such as the time series monitoring data at a few observation stations and the building shapes and the source location. It is shown that the model can give reasonably accurate prediction with orders of magnitude faster than CFD simulations. It is also shown that the exactly same model can be applied to predict the source location, which also gives reasonable prediction accuracy.
 C
CMiyazawa, Takeshi; Kikuchi, Yuta*; Ando, Masami*; Yu, J.-H.*; Yabuuchi, Kiyohiro*; Nozawa, Takashi*; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu*; Nogami, Shuhei*; Hasegawa, Akira*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 575, p.154239_1 - 154239_11, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:71.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) high energy resolution XAFS
high energy resolution XAFSYamamoto, Naoki*; Matsumura, Daiju; Hagihara, Yuto*; Tanaka, Kei*; Hasegawa, Yuta*; Ishii, Kenji*; Tanaka, Hirohisa*
Journal of Power Sources, 557, p.232508_1 - 232508_10, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.56(Chemistry, Physical)Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Yuta; Nakayama, Hiromasa
Dai-36-Kai Suchi Ryutai Rikigaku Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/12
We have developed a wind simulation code named CityLBM to realize wind digital twins. Mesoscale wind conditions are given as boundary conditions in CityLBM by using a nudging data assimilation method. It is found that conventional approaches with constant nudging coefficients fail to reproduce turbulent intensity in long time simulations, where atmospheric stability conditions change significantly. We propose a dynamic parameter optimization method for the nudging coefficient based on an ensemble Kalman filter. CityLBM was validated against plume dispersion experiments in the complex urban environment of Oklahoma City. The nudging coefficient was updated to reduce the error of the turbulent intensity between the simulation and the observation. The mean error of velocity variance is reduced by  10% compared to the conventional nudging method with a constant nudging coefficient.
10% compared to the conventional nudging method with a constant nudging coefficient.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Dai-36-Kai Suchi Ryutai Rikigaku Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (Internet), 5 Pages, 2022/12
This study implemented and tested the ensemble data assimilation (DA) of turbulent flows using the lattice Boltzmann method and the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LBM-LETKF). The computational code was implemented fully on GPUs. The test was carried out for the 3D turbulent flow around a square cylinder with 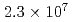 meshes and 32 ensemble members using 32 GPUs. The time interval of the DA in the test was a half of the period of the Kalman vortex shedding. The normalized mean absolute errors (NMAE) of the lift coefficient were 132%, 148%, and 13.2% for the non-DA case, the nudging case (a simpler DA algorithm), and the LETKF case, respectively. It was found that the LETKF achieved good DA accuracy even though the observation was not frequent enough for the small scale turbulence, while the nudging showed systematic delays in its solution, and could not keep the DA accurately.
meshes and 32 ensemble members using 32 GPUs. The time interval of the DA in the test was a half of the period of the Kalman vortex shedding. The normalized mean absolute errors (NMAE) of the lift coefficient were 132%, 148%, and 13.2% for the non-DA case, the nudging case (a simpler DA algorithm), and the LETKF case, respectively. It was found that the LETKF achieved good DA accuracy even though the observation was not frequent enough for the small scale turbulence, while the nudging showed systematic delays in its solution, and could not keep the DA accurately.
Nakayama, Hiromasa; Onodera, Naoyuki; Satoh, Daiki; Nagai, Haruyasu; Hasegawa, Yuta; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(10), p.1314 - 1329, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:60.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)We developed a local-scale high-resolution atmospheric dispersion and dose assessment system (LHADDAS) for safety and consequence assessment of nuclear facilities and emergency response to nuclear accidents or deliberate releases of radioactive materials in built-up urban areas. This system is composed of pre-processing of input files, main calculation by local-scale high-resolution atmospheric dispersion model using large-eddy simulation (LOHDIM-LES) and real-time urban dispersion simulation model based on a lattice Boltzmann method (CityLBM), and post-processing of dose-calculation by simulation code powered by lattice dose-response functions (SIBYL). LHADDAS has a broad utility and offers superior performance in (1) simulating turbulent flows, plume dispersion, and dry deposition under realistic meteorological conditions, (2) performing real-time tracer dispersion simulations using a locally mesh-refined lattice Boltzmann method, and (3) estimating air dose rates of radionuclides from air concentrations and surface deposition in consideration of the influence of individual buildings and structures. This system is promising for safety assessment of nuclear facilities as an alternative to wind tunnel experiments, detailed pre/post-analyses of a local-scale radioactive plume dispersion in case of nuclear accidents, and quick response to emergency situations resulting from deliberate release of radioactive materials by a terrorist attack in an urban central district area.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 4 Pages, 2022/06
We developed GPU implementation of ensemble data assimilation (DA) using the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF) with the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM). The performance test was carried out upto 32 ensembles of two-dimensional isotropic turbulence simulations using the D2Q9 LBM. The computational cost of the LETKF was less than or nearly equal to that of the LBM upto eight ensembles, while the former exceeded the latter at larger ensembles. At 32 ensembles, their computational costs per cycle were respectively 28.3 msec and 5.39 msec. These results suggested that further speedup of the LETKF is needed for practical 3D LBM simulations.
Asahi, Yuichi; Onodera, Naoyuki; Hasegawa, Yuta; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Shiba, Hayato*; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 5 Pages, 2022/06
We have ported the GPU accelerated Lattice Boltzmann Method code "CityLBM" to AMD MI100 GPU. We present the performance of CityLBM achieved on NVIDIA P100, V100, A100 GPUs and AMDMI100 GPU. Using the host to host MPI communications, the performance on MI100 GPU is around 20% better than on V100 GPU. It has turned out that most of the kernels are successfully accelerated except for interpolation kernels for Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) method.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Yuta; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Aoki, Takayuki*
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 4 Pages, 2022/06
We have developed a wind simulation code named CityLBM to realize wind digital twins. Mesoscale wind conditions are given as boundary conditions in CityLBM by using a nudging data assimilation method. It is found that conventional approaches with constant nudging coefficients fail to reproduce turbulent intensity in long time simulations, where atmospheric stability conditions change significantly. We propose a dynamic parameter optimization method for the nudging coefficient based on a particle filter. CityLBM was validated against plume dispersion experiments in the complex urban environment of Oklahoma City. The nudging coefficient was updated to reduce the error of the turbulent intensity between the simulation and the observation, and the atmospheric boundary layer was reproduced throughout the day.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Ina, Takuya; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of 13th Workshop on Latest Advances in Scalable Algorithms for Large-Scale Heterogeneous Systems (ScalAH22) (Internet), p.10 - 17, 2022/00
The ensemble data assimilation of computational fluid dynamics simulations based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) and the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF) is implemented and optimized on a GPU supercomputer based on NVIDIA A100 GPUs. To connect the LBM and LETKF parts, data transpose communication is optimized by overlapping computation, file I/O, and communication based on data dependency in each LETKF kernel. In two dimensional forced isotropic turbulence simulations with the ensemble size of 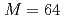 and the number of grid points of
and the number of grid points of 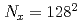 , the optimized implementation achieved
, the optimized implementation achieved 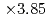 speedup from the naive implementation, in which the LETKF part is not parallelized. The main computing kernel of the local problem is the eigenvalue decomposition (EVD) of
speedup from the naive implementation, in which the LETKF part is not parallelized. The main computing kernel of the local problem is the eigenvalue decomposition (EVD) of 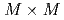 real symmetric dense matrices, which is computed by a newly developed batched EVD in EigenG. The batched EVD in EigenG outperforms that in cuSolver, and
real symmetric dense matrices, which is computed by a newly developed batched EVD in EigenG. The batched EVD in EigenG outperforms that in cuSolver, and 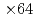 speedup was achieved.
speedup was achieved.