Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hasemi, Hiroyuki; Kai, Tetsuya
JAEA-Testing 2024-001, 39 Pages, 2024/08
RAIM is an analysis code that analyzes resonance absorption spectra measured at pulsed neutron sources such as the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) to obtain information on nuclear densities and temperatures. By calculating the convolution of the pulse functions of neutron beam and the resonance capture function that is based on the nuclear cross section data, RAIM reproduces the resonance absorption spectrum measured by a pulsed neutron source. Then, RAIM determines the density and temperature of specific nuclides in a sample by performing spectral fitting on the resonance absorption spectrum data. In addition, RAIM is developed to facilitate the analysis of resonance imaging data by minimizing the number of parameters for calculation setup and by providing scripts for processing many resonance absorption spectra measured by a two-dimensional detector at once. This manual explains how to install RAIM on a computer and how to simulate resonance absorption spectra and fit them to measured data.
Hasemi, Hiroyuki; Takahashi, Ryuta*; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kawamura, Seiko; Komine, Ryota
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 41, p.011003_1 - 011003_5, 2024/03
Oikawa, Kenichi; Sato, Hirotaka*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Su, Y. H.; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Hasemi, Hiroyuki
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2605, p.012013_1 - 012013_6, 2023/10
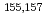 Gd
GdMizuyama, Kazuhito; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Hasemi, Hiroyuki*; Kino, Koichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.11042_1 - 11042_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:75.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)Gadolinium has been used as neutron-absorbing material in a thermal reactor since 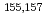 have large thermal neutron capture cross sections. Nevertheless, there is a discrepancy between RPI data and JENDL-4.0 data for
have large thermal neutron capture cross sections. Nevertheless, there is a discrepancy between RPI data and JENDL-4.0 data for  Gd. The criticality in the reactor is very sensitive to the capture cross section. The RPI data made the criticality of Gd-loaded thermal systems in ICSBEP overestimated. Recently, the neutron capture cross sections of
Gd. The criticality in the reactor is very sensitive to the capture cross section. The RPI data made the criticality of Gd-loaded thermal systems in ICSBEP overestimated. Recently, the neutron capture cross sections of 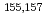 Gd were measured by the neutron time-of-flight (TOF) method using the Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction measurement Instrument (ANNRI) in the J-PARC/MLF. The pulsed neutron beam from the Japan Spallation Neutron Source (JSNS) was used with a double-bunch structure in this measurement, since the incident proton beam is normally delivered in a double-bunch scheme in the J-PARC. In addition to this, it is necessary to take into account the energy resolution of the pulsed neutron beam at the JSNS for the accurate derivation of resolved resonance parameters. In this study, using the least-squares multilevel R-matrix code REFIT modified to include the double bunch structure and the resolution function for the ANNRI, we fitted the calculated capture cross sections of
Gd were measured by the neutron time-of-flight (TOF) method using the Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction measurement Instrument (ANNRI) in the J-PARC/MLF. The pulsed neutron beam from the Japan Spallation Neutron Source (JSNS) was used with a double-bunch structure in this measurement, since the incident proton beam is normally delivered in a double-bunch scheme in the J-PARC. In addition to this, it is necessary to take into account the energy resolution of the pulsed neutron beam at the JSNS for the accurate derivation of resolved resonance parameters. In this study, using the least-squares multilevel R-matrix code REFIT modified to include the double bunch structure and the resolution function for the ANNRI, we fitted the calculated capture cross sections of 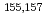 Gd to the experimental data at the ANNRI. We derived the resonance parameters for some low-lying resonances of the two Gd isotopes.
Gd to the experimental data at the ANNRI. We derived the resonance parameters for some low-lying resonances of the two Gd isotopes.
Hasemi, Hiroyuki; Tatsumi, Kazuyoshi; Sato, Hirotaka*; Kamiyama, Takashi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hasemi, Hiroyuki; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Oikawa, Kenichi; Shinohara, Takenao
no journal, ,
Hasemi, Hiroyuki; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Moriyama, Kentaro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kurita, Keisuke; Hasemi, Hiroyuki; Harayama, Isao; Takahashi, Shingo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hasemi, Hiroyuki; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Moriyama, Kentaro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hasemi, Hiroyuki; Tatsumi, Kazuyoshi; Sato, Hirotaka*; Kamiyama, Takashi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kai, Tetsuya; Furuta, Etsuko*; Ishihara, Sachiko*; Hasemi, Hiroyuki*; Shinohara, Takenao; Harada, Masahide; Oikawa, Kenichi; Oi, Motoki; Segawa, Mariko; Iikura, Hiroshi; et al.
no journal, ,
The authors report status of the J-PARC neutron imaging beam-line and a result of cadmium distribution imaging in oil paints by utilizing the neutron transmission ratio of cadmium exhibits local minimum at 0.2 eV as an example of neutron resonance imaging technique. The measurement was carried out by using oil paints labeled cadmium yellow, vanadium yellow, cadmium orange, cadmium red and two kinds of cadmium green. Each oil paint was put on a 15 15 mm aluminum plate, and then was dried. Contrasts were recognized for all oil paint in a conventional neutron radiograph of the samples, while no contrasts were found in the neutron transmission image of 0.2 eV at the positions of vanadium yellow and one of cadmium green. It was found that a distribution of cadmium in oil paints was well demonstrated by the neutron resonance imaging.
15 mm aluminum plate, and then was dried. Contrasts were recognized for all oil paint in a conventional neutron radiograph of the samples, while no contrasts were found in the neutron transmission image of 0.2 eV at the positions of vanadium yellow and one of cadmium green. It was found that a distribution of cadmium in oil paints was well demonstrated by the neutron resonance imaging.
Hasemi, Hiroyuki; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Moriyama, Kentaro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hasemi, Hiroyuki; Nakatani, Takeshi*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Moriyama, Kentaro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Inamura, Yasuhiro; Hasemi, Hiroyuki; Moriyama, Kentaro*; Okazaki, Nobuo*
no journal, ,
Several policy developments on "Open Science" have recently been implemented in Japan to promote open access to scientific research data. These policies have led to the launch of various projects aimed at developing platforms for open science, particularly for managing and publishing research data. In this context, J-PARC's Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF) is encouraged to align with these policies by adopting these platforms. Additionally, MLF plans to offer data search services, enabling users to access experimental data for analysis from outside of J-PARC, although this implementation has not yet been achieved. We now plan to enhance the data flow of metadata and neutron measurement data by upgrading the current systems.
Hasemi, Hiroyuki; Tatsumi, Kazuyoshi; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Oikawa, Kenichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English