Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Hashimoto, Shintaro
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (123), p.53 - 59, 2019/06
The 2019 International Conference on Nuclear Data for Science and Technology (ND2019) was held at the China National Convention Center on May 19-24, 2019. The series of the ND conferences are the largest conferences in nuclear data research field that are held every three years. In this paper, as a part of the conference reports of ND2019, the authors gave summaries of the presentations on nuclear data evaluation and theory conducted at the conference.
Kofu, Maiko; Hashimoto, Naoki*; Akiba, Hiroshi*; Kobayashi, Hirokazu*; Kitagawa, Hiroshi*; Iida, Kazuki*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Yamamuro, Osamu*
Physical Review B, 96(5), p.054304_1 - 054304_7, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:58.3(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The vibrational states of hydrogen atoms in bulk and nanocrystalline palladium were examined in a wide energy region 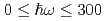 meV using neutron spectroscopy. In bulk PdH
meV using neutron spectroscopy. In bulk PdH , the vibrational excitations of H atoms were roughly reproduced by the quantum harmonic oscillator (QHO) model. In PdH
, the vibrational excitations of H atoms were roughly reproduced by the quantum harmonic oscillator (QHO) model. In PdH nanocrystals with a diameter of 8 nm, however, additional vibrational excitations were found at energies above 80 meV. The energies and intensities of the additional states were not explained by QHO but reasonably described as vibrations in a highly anharmonic trumpet-like potential. The additional excitations are attributed to the vibrations of H atoms at tetrahedral sites in the subsurface region stabilized by surface effects. This is an experimental work which clearly detects hydrogen vibration
nanocrystals with a diameter of 8 nm, however, additional vibrational excitations were found at energies above 80 meV. The energies and intensities of the additional states were not explained by QHO but reasonably described as vibrations in a highly anharmonic trumpet-like potential. The additional excitations are attributed to the vibrations of H atoms at tetrahedral sites in the subsurface region stabilized by surface effects. This is an experimental work which clearly detects hydrogen vibration  metal nanoparticles.
metal nanoparticles.
 Li(
Li( ,
, ) reactions
) reactionsHashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*
Energy Procedia, 71, p.191 - 196, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:93.1(Energy & Fuels)Accelerator-based neutron sources using proton- and deuteron-induced reactions have been utilized for scientific and medical applications, such as irradiation testing of fusion reactor materials at IFMIF and BNCT. Quasi-monoenergetic neutron beams using  Li(
Li( ,
, )
) Be are of special importance for calibrating a detector and measuring cross sections for neutron induced reactions. PHITS can deal with the transport of incident protons as well as secondary neutrons using various physics models, and it can estimate particle fluxes in the beam line and energy deposition in shielding materials. Therefore, PHITS is a useful code for neutron source design in accelerator facilities. However, nuclear reaction models implemented in PHITS, such as INC, were not enough to reproduce the peak structure in neutron spectra of experimental data, since these models do not consider the transition process of
Be are of special importance for calibrating a detector and measuring cross sections for neutron induced reactions. PHITS can deal with the transport of incident protons as well as secondary neutrons using various physics models, and it can estimate particle fluxes in the beam line and energy deposition in shielding materials. Therefore, PHITS is a useful code for neutron source design in accelerator facilities. However, nuclear reaction models implemented in PHITS, such as INC, were not enough to reproduce the peak structure in neutron spectra of experimental data, since these models do not consider the transition process of  Li(
Li( ,
, )
) Be. We have developed a new option that adds peaks obtained by the DWBA method, which gives cross sections of the transition on the basis of quantum mechanics, to results calculated by the INC model. We had applied this option to estimate neutron spectra in the reactions at incident energies below 50 MeV. Results of the INC model using the option had been in good agreement with experimental data. In this study, we extended the applicable incident energy range up to 400 MeV for the
Be. We have developed a new option that adds peaks obtained by the DWBA method, which gives cross sections of the transition on the basis of quantum mechanics, to results calculated by the INC model. We had applied this option to estimate neutron spectra in the reactions at incident energies below 50 MeV. Results of the INC model using the option had been in good agreement with experimental data. In this study, we extended the applicable incident energy range up to 400 MeV for the  Li(
Li( ,
,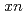 ) reactions. We will show the comparison between the calculated result and experimental data, and discuss the validity of the option for the reactions.
) reactions. We will show the comparison between the calculated result and experimental data, and discuss the validity of the option for the reactions.
Makhsun*; Hashimoto, Takuya*; Sakuma, Takashi*; Takahashi, Haruyuki*; Kamishima, Osamu*; Igawa, Naoki; Danilkin, S. A.*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(7), p.074602_1 - 074602_4, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The correlations of atomic thermal displacements in Al were obtained from the analysis of diffuse neutron scattering intensity. The interatomic force constants were determined from the correlation effects using a newly introduced equation. The derived force constants and the crystal structure of Al were used to estimate the phonon dispersion relations, phonon density of states, and specific heat by computer simulation. The calculated phonon dispersion relations and specific heat of Al are similar to those obtained from inelastic neutron scattering and specific heat measurements, respectively.
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*
Nuclear Data Sheets, 118, p.258 - 261, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.03(Physics, Nuclear)Particle transport simulation codes based on the Monte Carlo technique are utilized to predict interaction of radiations with materials. The codes describe the transport of all particles, e.g. photons, electrons, nucleons, and heavy ions by various models for physical processes and nuclear reaction. In particular, nuclear reaction processes are essential parts for the accurate prediction. Recently, accelerator-based neutron sources using proton or deuteron beams with energies from 10 to 100 MeV come to be utilized for scientific and medical applications. For neutron source design, accurate description of neutron yields created by nuclear reactions is required in the simulation. However, the Intra-Nuclear Cascade type models used in most of the simulation codes are not enough to reproduce experimental data because of neglecting quantum mechanical effects. In this study, we combined the cascade type models and an event generator using the DWBA (Distorted Wave Born Approximation) calculation, which is a theoretical model based on quantum mechanics. We verified that the calculated results with the combination model can reproduce experimental data of neutron spectra in deuteron-induced reactions. We will also present the validity of the combination model for proton-induced reactions.
Nagai, Yasuki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Saeki, Hideya; Motoishi, Shoji; Sonoda, Nozomi; Kawabata, Masako; Harada, Hideo; Kin, Tadahiro*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 82(6), p.064201_1 - 064201_7, 2013/06
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:85.02(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Nagai, Yasuki; Kin, Tadahiro; Segawa, Mariko; Harada, Hideo; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Ochiai, Kentaro; Takakura, Kosuke; Konno, Chikara; et al.
Proceedings in Radiochemistry, 1(1), p.327 - 329, 2011/09
Authors proposed a new route to produce  Mo by the
Mo by the  Mo(
Mo( ,2
,2 )
) Mo reaction, which has some characteristic features. Such as the reaction cross section is large, about 1.5 barn at 12
Mo reaction, which has some characteristic features. Such as the reaction cross section is large, about 1.5 barn at 12 

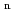
 17 MeV, which is 10 times larger than the thermal-neutron capture cross section of
17 MeV, which is 10 times larger than the thermal-neutron capture cross section of  Mo. Second, the cross sections of the (
Mo. Second, the cross sections of the ( ,
, ), (
), ( ,
,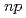 ), and (
), and ( ,
, ) reactions are less than a few mb at
) reactions are less than a few mb at 
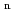 = 14 MeV. Third, a large amount of
= 14 MeV. Third, a large amount of  Mo target materials can be used, compared to that for proton beam irradiation on
Mo target materials can be used, compared to that for proton beam irradiation on  Mo. Fourth, intense neutrons with energy of 12-17 MeV are already available. In the present work we have measured all
Mo. Fourth, intense neutrons with energy of 12-17 MeV are already available. In the present work we have measured all  -rays emitted from activities produced by bombarding a natural Mo target with neutrons from the D(
-rays emitted from activities produced by bombarding a natural Mo target with neutrons from the D( H,
H, )
) He reaction at Fusion Neutronics Source Facility (FNS) at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to study characteristic features mentioned above more in detail. The neutron flux was about 10
He reaction at Fusion Neutronics Source Facility (FNS) at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to study characteristic features mentioned above more in detail. The neutron flux was about 10 n/cm
n/cm s. The experimental results at FNS will be discussed in the conference.
s. The experimental results at FNS will be discussed in the conference.
 Cu
Cu O
O
Sato, H.*; Ishikawa, Norito; Iwase, Akihiro; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Hashimoto, Takeo*; Michikami, Osamu*
Physica C, 378-381(Part1), p.527 - 530, 2002/10
no abstracts in English
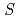
 -scaling of lattice parameter change in high ion-velocity region (
-scaling of lattice parameter change in high ion-velocity region (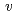
 2.6
2.6 10
10 cm/s) in ion-irradiated EuBa
cm/s) in ion-irradiated EuBa Cu
Cu O
O
Ishikawa, Norito; Iwase, Akihiro; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Michikami, Osamu*; Wakana, Hironori*; Hashimoto, Takeo*; Kambara, Tadashi*; M ller, C.*; Neumann, R.*
ller, C.*; Neumann, R.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 193(1-4), p.278 - 282, 2002/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:47.9(Instruments & Instrumentation)Swift heavy ions with wide energy range of 80MeV-3.84GeV have been irradiated to EuBa Cu
Cu O
O oxide superconductors, and the lattice parameter change due to elecronic excitation has been measured. In the high ion-velocity region, the change in lattice parameter per unit fluence varies as the 4th power of the electronic stopping power. However, in the low-velocity region, the deviation from the 4th power dependence is observed. The results are analyzed by using the primary ionization rate, and it is found that the results support that the Coulomb explosion triggers the atomic displacements.
oxide superconductors, and the lattice parameter change due to elecronic excitation has been measured. In the high ion-velocity region, the change in lattice parameter per unit fluence varies as the 4th power of the electronic stopping power. However, in the low-velocity region, the deviation from the 4th power dependence is observed. The results are analyzed by using the primary ionization rate, and it is found that the results support that the Coulomb explosion triggers the atomic displacements.
 Cu
Cu O
O
Ishikawa, Norito; Iwase, Akihiro; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Michikami, Osamu*; Wakana, Hironori*; Hashimoto, Takeo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 191(1-4), p.606 - 609, 2002/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.5(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Sonoda, Katsumi*; Yamamoto, Yasushi*; Hashimoto, Osamu*; Ono, Toshio*; Tomita, Haruhiko*; Udagawa, Akira; Egusa, Shigenori; Sasuga, Tsuneo; Seguchi, Tadao; Tamura, Naoyuki
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 28(10), p.1950 - 1956, 1989/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Udagawa, Akira; Egusa, Shigenori; Sasuga, Tsuneo; Seguchi, Tadao; Ono, Toshio*; *; *; *; Hashimoto, Osamu*; Sonoda, Katsumi*; et al.
JAERI-M 88-047, 27 Pages, 1988/03
no abstracts in English
Egusa, Shigenori; Udagawa, Akira; Hashimoto, Osamu*; Ono, Toshio*; *; Sonoda, Katsumi*
Journal of Materials Science Letters, 7, p.503 - 505, 1988/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:42.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Sonoda, Katsumi*; Hashimoto, Osamu*; *; Ono, Toshio*; *; Udagawa, Akira; Egusa, Shigenori; Sasuga, Tsuneo; Seguchi, Tadao; Tamura, Naoyuki
EIM-87-152, p.11 - 24, 1987/00
no abstracts in English
Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Hashimoto, Masashi; Nagai, Yasuki*; Kin, Tadahiro; Segawa, Mariko; Harada, Hideo; Konno, Chikara; Ochiai, Kentaro; Takakura, Kosuke; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; et al.
no journal, ,
 Tc is the most important radioisotope used as nuclear medicine which is mostly produced by using only five nuclear reactors. Recently, two of the present authors proposed a new route to produce
Tc is the most important radioisotope used as nuclear medicine which is mostly produced by using only five nuclear reactors. Recently, two of the present authors proposed a new route to produce  Mo by the
Mo by the  Mo(n,2n)
Mo(n,2n) Mo reaction, which has the following characteristic features. (1) First, the reaction cross section is large. Second, the cross sections of the (n,
Mo reaction, which has the following characteristic features. (1) First, the reaction cross section is large. Second, the cross sections of the (n, ), (n,np), and (n,p) reactions are less than a few mb at En = 14 MeV. Third, a large amount of
), (n,np), and (n,p) reactions are less than a few mb at En = 14 MeV. Third, a large amount of  Mo target materials can be used, compared to that for proton beam irradiation on
Mo target materials can be used, compared to that for proton beam irradiation on  Mo. In the present work we have measured all
Mo. In the present work we have measured all  -rays emitted from activities produced by bombarding a natural Mo target with neutrons from the D(
-rays emitted from activities produced by bombarding a natural Mo target with neutrons from the D( H,n)
H,n) He reaction at FNS at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to study characteristic features mentioned above more in detail. The experimental results at FNS will be discussed in the conference.
He reaction at FNS at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) to study characteristic features mentioned above more in detail. The experimental results at FNS will be discussed in the conference.
Chiba, Satoshi; Aritomo, Yoshihiro*; Koura, Hiroyuki; Iwamoto, Osamu; Utsuno, Yutaka; Hashimoto, Shintaro
no journal, ,
Results of research in the surrogate reaction carried out at JAEA will be reported.
Nakayama, Shinsuke*; Araki, Shohei*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ye, T.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*
no journal, ,
A code system to calculate the cross sections for deuteron-induced reaction has been developed to create a deuteron nuclear data library that is important for the accelerator neutron sources. The (d,xn) reactions below 20 MeV that are important for the neutron source have been analyzed. It was found that the calculated results agree with the experimental data of the angular distribution at forward angles to the N-13 ground state by the proton stripping reactions for the deuteron induced reaction on C-12. The results of the analyses of the neutron yields for the C thick target will be reported.
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Osamu; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*
no journal, ,
PHITS has been used for many purposes such as radiation shielding in accelerator facilities. The PHITS result involves not only statistical error related to the number of trials in the Monte Carlo method but also systematic error attributed to uncertainty of nuclear data and nuclear reaction model. We developed a method to estimate the influence of covariance of JENDL on the PHITS result. In this method, we change the cross section within the covariance, and execute PHITS using each cross section. The result depends on the cross section. We regard its variance as the systematic error. PHITS can give both the statistical and systematic errors. We can discuss the reliability of the result of the radiation shielding. This method is applied to estimate the systematic error of neutron flux in neutron shielding calculations. The systematic error of the calculated flux depends on the depth in shielding material due to the number of scattering.
Taniguchi, Takumi; Irisawa, Keita; Ito, Yuzuru; Namiki, Masahiro; Osugi, Takeshi; Abe, Tomohisa; Sato, Junya; Sakakibara, Tetsuro; Nakazawa, Osamu; Meguro, Yoshihiro; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Osamu; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*
no journal, ,
PHITS has been used for many purposes such as radiation shielding in accelerator facilities. The PHITS result includes not only statistical error related to the number of trials in the Monte Carlo method but also systematic error attributed to uncertainty of nuclear data and nuclear reaction model. In the previous study, we developed a method to estimate the influence of uncertainty of nuclear data for neutrons below 20 MeV on PHITS results. In this study, we evaluated uncertainty of a cross section model to also consider neutrons above 20 MeV. In the method, we change the cross section within the uncertainty, and execute PHITS using each cross section. Because the result depends on the cross section, we regard its variance as the systematic error. We applied the method to estimate the systematic error of 100 MeV neutron flux in neutron shielding calculations. The systematic error of the calculated flux depends on the depth in shielding material due to the number of scattering.