Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ikeda, Yoichi*; Umemoto, Yoshihiko*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; Hashimoto, Yuki*; Kitazawa, Takafumi*; Fujita, Masaki*
Materials Transactions, 64(9), p.2254 - 2260, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuya, Yusuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hirata, Yuho; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 9 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:98.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo radiation transport code that can simulate the behavior of most particle species with energies up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ions). Its new version, PHITS3.31, was recently developed and released to the public. In the new version, the compatibility with high-energy nuclear data libraries and the algorithm of the track-structure modes have been improved. In this paper, we summarize the upgraded features of PHITS3.31 with respect to the physics models, utility functions, and application software introduced since the release of PHITS3.02 in 2017.
Furuta, Takuya; Koba, Yusuke*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Chang, W.*; Yonai, Shunsuke*; Matsumoto, Shinnosuke*; Ishikawa, Akihisa*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 67(14), p.145002_1 - 145002_15, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:47.19(Engineering, Biomedical)Carbon ion radiotherapy has an advantage over conventional radiotherapy such that its superior dose concentration on the tumor helps to reduce unwanted dose to surrounding normal tissues. Nevertheless, a little dose to normal tissues, which is a potential risk of secondary cancer, is still unavoidable. The Monte Carlo simulation is a good candidate for the tool to assess secondary cancer risk, including the contributions of secondary particles produced by nuclear reactions. We therefore developed a new dose reconstruction system implementing PHITS as the engine. In this system, the PHITS input is automatically created from the DICOM data sets recorded in the treatment planning. The developed system was validated by comparing to experimental dose distribution in water and treatment plan on an anthropomorphic phantom. This system will be used for retrospective studies using the patient data in National Institute for Quantum and Science and Technology.
Hashimoto, Shoji*; Tanaka, Taku*; Komatsu, Masabumi*; Gonze, M.-A.*; Sakashita, Wataru*; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Nishina, Kazuya*; Ota, Masakazu; Ohashi, Shinta*; Calmon, P.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 238-239, p.106721_1 - 106721_10, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:56.59(Environmental Sciences)This study was aimed at analysing performance of models for radiocesium migration mainly in evergreen coniferous forest in Fukushima, by inter-comparison between models of several research teams. The exercise included two scenarios of countermeasures against the contamination, namely removal of soil surface litter and forest renewal, and a specific konara oak forest scenario in addition to the evergreen forest scenario. All the models reproduced trend of time evolution of radiocesium inventories and concentrations in each of the components in forest such as leaf and organic soil layer. However, the variations between models enlarged in long-term predictions over 50 years after the fallout, meaning continuous field monitoring and model verification/validation is necessary.
Chang, W.*; Koba, Yusuke*; Furuta, Takuya; Yonai, Shunsuke*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Matsumoto, Shinnosuke*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Journal of Radiation Research (Internet), 62(5), p.846 - 855, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:26.61(Biology)With the aim of developing a revaluation tool of treatment plan in carbon-ion radiotherapy using Monte Carlo (MC) simulation, we propose two methods; one is dedicated to identify realistic-tissue materials from a CT image with satisfying the well-calibrated relationship between CT numbers and stopping power ratio (SPR) provided by TPS, and the other is to estimate dose to water considering the particle- and energy-dependent SPR between realistic tissue materials and water. We validated these proposed methods by computing depth dose distribution in homogeneous and heterogeneous phantoms composed of human tissue materials and water irradiated by a 400 MeV/u carbon beam with 8 cm SOBP using a MC simulation code PHITS and comparing with results of conventional treatment planning system (TPS). Our result suggested that use of water as a surrogate of real tissue materials, which is adopted in conventional TPS, is inadequate for dose estimation from secondary particles because their production rates cannot be scaled by SPR of the primary particle in water. We therefore concluded that the proposed methods can play important roles in the reevaluation of the treatment plans in carbon-ion radiotherapy.
 -state of a
-state of a  hypernucleus,
hypernucleus, 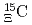
Yoshimoto, Masahiro*; Fujita, Manami; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Ichikawa, Yudai; Ichikawa, Masaya; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2021(7), p.073D02_1 - 073D02_19, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:81.3(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Yoshida, Junya; Akaishi, Takaya; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Masaya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Kim, S.; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011112_1 - 011112_8, 2021/03
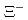 -
- N system
N systemHayakawa, Shuhei; Fujita, Manami; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi*; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(6), p.062501_1 - 062501_6, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:95.34(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ekawa, Hiroyuki; Ashikaga, Sakiko; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi; Kimbara, Shinji*; Nanamura, Takuya; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(2), p.021D02_1 - 021D02_11, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:83.76(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Tsai, P.-E.; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwase, Hiroshi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(6), p.684 - 690, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:775 Percentile:100(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have upgraded many features of the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) and released the new version as PHITS3.02. The accuracy and the applicable energy ranges of the code were greatly improved and extended, respectively, owing to the revisions to the nuclear reaction models and the incorporation of new atomic interaction models. In addition, several user-supportive functions were developed, such as new tallies to efficiently obtain statistically better results, radioisotope source-generation function, and software tools useful for applying PHITS to medical physics. In this paper, we summarize the basic features of PHITS3.02, especially those of the physics models and the functions implemented after the release of PHITS2.52 in 2013.
Hashimoto, Shintaro; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Niita, Koji*
Kaku Deta Nyusu (Internet), (120), p.26 - 34, 2018/06
Particle and heavy-ion transport code system PHITS has been used for calculations of radiation shielding in accelerator facilities. PHITS describes physical phenomena induced by radiation as combination of transport and collision processes. The collision process including nuclear reactions is simulated by the three-step calculation: a generation of a reaction, pre-equilibrium, and compound processes. In the simulation, many physics models are used. This report explains roles of the models in PHITS and shows their developments we recently performed.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Okumura, Keisuke; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.06008_1 - 06008_6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:95.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, has been developed under the collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. It can deal with the transport of nearly all particles up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ion) using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. More than 2,500 researchers and technicians have used the code for a variety of applications such as accelerator design, radiation shielding and protection, medical physics, and space and geosciences. This paper briefly summarizes physics models and functions newly implemented in PHITS between versions 2.52 and 2.82.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Niita, Koji*
Hoshasen, 43(2), p.55 - 58, 2017/05
Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, has been developed under the collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. It can deal with the transport of nearly all particles up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ion) using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. More than 2,500 registered researchers and technicians have used this system for various applications such as accelerator design, radiation shielding and protection, medical physics, and space- and geo-sciences. This paper summarizes the physics models and functions recently implemented in PHITS, between versions 2.52 and 2.88.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hosoyamada, Ryuji*; Niita, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(5), p.617 - 635, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:96 Percentile:99.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)We performed a benchmark study for 58 cases using the recent version 2.88 of the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) in the following fields: particle production cross-sections for nuclear reactions, neutron transport calculations, and electro-magnetic cascade. This paper reports details for 22 cases. In cases of nuclear reactions with energies above 100 MeV and electro-magnetic cascade, overall agreements were found to be satisfactory. On the other hand, PHITS did not reproduce the experimental data for an incident proton energy below 100 MeV, because the intranuclear cascade model INCL4.6 in PHITS is not suitable for the low-energy region. For proton incident reactions over 100 MeV, PHITS did not reproduce fission product yields due to the problem of high-energy fission process in the evaporation model GEM. To overcome these inaccuracies, we are planning to incorporate a high-energy version of the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4.0/HE, and so on.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwase, Hiroshi*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.63 - 69, 2016/09
A general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through the collaboration of several institutes. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. PHITS users apply the code to various research and development fields such as nuclear technology, accelerator design, medical physics, and cosmic-ray research. This presentation briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some new models such as muon-induced nuclear reaction model and a  de-excitation model EBITEM. We will also present the radiation damage cross sections for materials, PKA spectra and kerma factors calculated by PHITS under the IAEA-CRP activity titled "Primary radiation damage cross section."
de-excitation model EBITEM. We will also present the radiation damage cross sections for materials, PKA spectra and kerma factors calculated by PHITS under the IAEA-CRP activity titled "Primary radiation damage cross section."
Furuta, Takuya; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Igaku Butsuri, 36(1), p.50 - 54, 2016/00
An application of Particle and Heavy Ion Transport Code System; PHITS, for medical physics is to simulate treatment planning of radiation therapy. Treatment planning simulation is conducted by constructing patient geometry from patient CT data, calculating radiation transport of external beam, and deducing dose distribution inside patient body. However, it is not easy to extract information such as patient location and CT value distribution from patient CT data or to construct complex accelerator geometry in PHITS format. Therefore, we developed two user assistance programs, DICOM2PHITS and PSFC4PHITS. DICOM2PHITS is a program to construct the voxel PHITS simulation geometry from patient CT DICOM image data. PSFC4PHITS is a program to convert the IAEA phase-space file data to PHITS format to be used as simulation source of PHITS. We explain these two programs by showing some applications in this article.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Furuta, Takuya; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; et al.
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 82, p.110 - 115, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:93.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)The general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through a collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is responsible for managing the entire project. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. This paper briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some important functions useful for particular purposes, such as an event generator mode and beam transport functions.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Furuta, Takuya; Noda, Shusaku; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Iwase, Hiroshi*; Nakashima, Hiroshi; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2014-002, p.69 - 74, 2015/02
A general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through the collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. All components of PHITS such as its source, executable and data-library files are assembled in one package and then distributed to many countries. More than 1,000 researchers apply the code to various research and development fields such as nuclear technology, accelerator design, medical physics, and cosmic-ray research. This presentation briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some important functions for specific applications, such as an event generator mode and a radiation damage calculation function.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Kuga, Naoya*
Igaku Butsuri, 35(2), p.180 - 187, 2015/00
PHITS is a general purpose Monte Carlo particle transport simulation code developed through the collaboration of several institutes mainly in Japan. It can analyze the motion of nearly all radiations over wide energy ranges in 3-dimensional matters. It has been used for various applications including medical physics. This paper reviews the recent improvements of the code, such as implementation of EGS5, new photo-nuclear reaction model, and sumtally function. The review of the biological dose estimation method developed on the basis of the microdosimetric function implemented in PHITS is also given.
Makhsun*; Hashimoto, Takuya*; Sakuma, Takashi*; Takahashi, Haruyuki*; Kamishima, Osamu*; Igawa, Naoki; Danilkin, S. A.*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 83(7), p.074602_1 - 074602_4, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The correlations of atomic thermal displacements in Al were obtained from the analysis of diffuse neutron scattering intensity. The interatomic force constants were determined from the correlation effects using a newly introduced equation. The derived force constants and the crystal structure of Al were used to estimate the phonon dispersion relations, phonon density of states, and specific heat by computer simulation. The calculated phonon dispersion relations and specific heat of Al are similar to those obtained from inelastic neutron scattering and specific heat measurements, respectively.