Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hata, Kuniki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Uchida, Shunsuke
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(4), p.448 - 458, 2024/04
no abstracts in English
Hata, Kuniki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Uchida, Shunsuke; Lister, D. H.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(8), p.867 - 880, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:48.47(Nuclear Science & Technology)One of the major subjects for evaluating the corrosive conditions in the PWR primary coolant was to determine the optimal hydrogen concentration for mitigating PWSCC without any adverse effects on major structural materials. As suitable procedures for evaluating the corrosive conditions in PWR primary coolant, a couple of procedures, i.e., water radiolysis and ECP analyses, were proposed. The previous article showed the radiolysis calculation in the PWR primary coolant, which was followed by an ECP study here. The ECP analysis, a couple of a mixed potential model and an oxide layer growth model, was developed originally for BWR conditions, which was extended to PWR conditions with adding Li (Na
(Na ) and H
) and H effects on the anodic polarization curves. As a result of comparison of the calculated results with INCA in-pile-loop experiment data as well as other experimental data, it was confirmed that the ECPs calculated with the coupled analyses agreed with the measured within
effects on the anodic polarization curves. As a result of comparison of the calculated results with INCA in-pile-loop experiment data as well as other experimental data, it was confirmed that the ECPs calculated with the coupled analyses agreed with the measured within  100mV discrepancies.
100mV discrepancies.
Hata, Kuniki; Kimura, Atsushi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Sato, Tomonori; Kato, Chiaki; Watanabe, Yutaka*
Zairyo To Kankyo, 72(4), p.126 - 130, 2023/04
Gamma-radiolysis experiments with gas-liquid coexistent samples were carried out to investigate effects of gas-phase radiolysis on corrosive environment for materials in solutions under irradiation. After gamma-ray irradiation, hydrogen peroxide, nitrate ion, nitrite ion were detected in the liquid phase. The production yields of nitrate ion and nitrite ion increased with increasing gas-phase volume and oxygen concentration. This result indicated that chemical reactions including oxygen and nitrogen in the gas phase were required for the production of nitrate ion and nitrite ion. To magnify the effects of gas-phase radiolysis in the gas-liquid coexistent samples, absorption dose rate in the liquid phase was reduced by one-hundredth using lead shield. The concentration of hydrogen peroxide and the pH in the shielded liquid phase were similar to those in the irradiated pure water, which did not contact with gas phase. This result indicated that the effects of nitrate ion and nitrite ion dissolved in the liquid phase on water radiolysis were not important in the current experimental system, in which the effects of gas-phase radiolysis were increased by 100-times.
Sato, Tomonori; Hata, Kuniki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Seito, Hajime*; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Tada, Eiji*; Abe, Hiroshi*; Akiyama, Eiji*; Suzuki, Shunichi*
Isotope News, (782), p.40 - 44, 2022/08
The stagnant water in the reactor building at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) is exposed to the radiation from fuel debris and radioactive species. This water contains much amounts of impurities from the seawater which was injected in the emergency cooling. The impurities will affect the radiolysis and corrosive conditions in the water under irradiation. So, the water radiolysis data, corrosion data of steels under irradiations, and the evaluated potential impacts of corrosion in the decommissioning process of 1F are arranged as the database for corrosion under irradiation. This paper introduces the outline of this database.
Hata, Kuniki; Uchida, Shunsuke; Hanawa, Satoshi; Chimi, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of International Symposium on Contribution of Materials Investigations and Operating Experience to LWRs' Safety, Performance and Reliability (Fontevraud 10) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2022/00
Takamizawa, Hisashi; Hata, Kuniki; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Toyama, Takeshi*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 556, p.153203_1 - 153203_10, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:43.41(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Solute clusters (SCs) formed in pressurized water reactor surveillance test specimens neutron-irradiated to a fluence of 1  10
10 n/cm
n/cm were analyzed via atom probe tomography to understand the effect of silicon on solute clustering and irradiation embrittlement of reactor pressure vessel steels. In high-Cu bearing materials, Cu atoms were aggregated at the center of cluster surrounded by the Ni, Mn, and Si atoms like a core-shell structure. In low-Cu bearing materials, Ni, Mn, and Si atoms formed cluster and these solutes were not comprised core-shell structure in SCs. While the number of Cu atoms in clusters was decreased with decreasing nominal Cu content, the number of Si atoms had clearly increased. The cluster radius (
were analyzed via atom probe tomography to understand the effect of silicon on solute clustering and irradiation embrittlement of reactor pressure vessel steels. In high-Cu bearing materials, Cu atoms were aggregated at the center of cluster surrounded by the Ni, Mn, and Si atoms like a core-shell structure. In low-Cu bearing materials, Ni, Mn, and Si atoms formed cluster and these solutes were not comprised core-shell structure in SCs. While the number of Cu atoms in clusters was decreased with decreasing nominal Cu content, the number of Si atoms had clearly increased. The cluster radius ( ) and number density (
) and number density (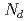 ) decreased and increased, respectively, with increasing nominal Si content. The shift in the reference temperature for nil-ductility transition (
) decreased and increased, respectively, with increasing nominal Si content. The shift in the reference temperature for nil-ductility transition ( RT
RT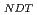 ) showed a good correlation with the square root of volume fraction (
) showed a good correlation with the square root of volume fraction (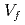 ) multiplied by r (
) multiplied by r (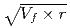 ). This suggested that the dislocation cutting through the particles mechanism dominates the precipitation hardening responsible for irradiation embrittlement. The negative relation between the nominal Si content and
). This suggested that the dislocation cutting through the particles mechanism dominates the precipitation hardening responsible for irradiation embrittlement. The negative relation between the nominal Si content and  RT
RT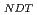 indicated that increasing of nominal Si content reduces the degree of embrittlement.
indicated that increasing of nominal Si content reduces the degree of embrittlement.
Hata, Kuniki
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(12), p.468 - 473, 2021/12
In order to estimate corrosive environment in the contaminated water at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, effects of oxidants, such as H O
O , which were generated from water radiolysis, should be taken into account due to the irradiation field in the reactor building. The process of water radiolysis and the amounts of these oxidants can change depending on the conditions of water and types of radiation. After the accident, a variety of factors, which can affect water radiolysis, such as seawater constituents, surface of oxides, and
, which were generated from water radiolysis, should be taken into account due to the irradiation field in the reactor building. The process of water radiolysis and the amounts of these oxidants can change depending on the conditions of water and types of radiation. After the accident, a variety of factors, which can affect water radiolysis, such as seawater constituents, surface of oxides, and  -radionuclides, had been discussed. In this paper, these effects on radiolysis are reviewed for the better understanding of the corrosive environment in the contaminated water.
-radionuclides, had been discussed. In this paper, these effects on radiolysis are reviewed for the better understanding of the corrosive environment in the contaminated water.
Iwata, Keiko; Hata, Kuniki; Tobita, Toru; Hirota, Takatoshi*; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2021/07
Sato, Tomonori; Hata, Kuniki; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Seito, Hajime*; Tada, Eiji*; Abe, Hiroshi*; Akiyama, Eiji*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-001, 123 Pages, 2021/06
In the implement of the decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), there are many problems to be solved. Specially, the mitigation of the aging degradation by the corrosion of the structural materials is important to implement the decommissioning safely and continuously. However, there are limited data for the environmental factors of corrosion in 1F, and the condition of 1F is continuously changing. So, the literature data for the water radiolysis and the corrosion under irradiation are listed as the database of corrosion under irradiation in this report. And the new obtained radiolysis and corrosion data, which have not been reported in the literature and will be required in the decommissioning of 1F, are reported.
Hata, Kuniki; Takamizawa, Hisashi; Hojo, Tomohiro*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 543, p.152564_1 - 152564_10, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:89.64(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steels for pressurized water reactors (PWRs) with bulk P contents ranging from 0.007 to 0.012wt.% were subjected to neutron irradiation at fluences ranging from 0.3 to 1.2 10
10 n/cm
n/cm (E
(E  1 MeV) in PWRs or a materials testing reactor (MTR). Grain-boundary P segregation was analyzed using Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) on intergranular facets and found to increase with increasing neutron fluence. A rate theory model was also used to simulate the increase in grain-boundary P segregation for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.020wt.%. The increase in grain-boundary P segregation in RPV steel with a bulk P content of 0.015wt.% (the maximum P concentration found in RPV steels used in Japanese nuclear power plants intended for restart) was estimated to be less than 0.1 in monolayer coverage at 1.0
1 MeV) in PWRs or a materials testing reactor (MTR). Grain-boundary P segregation was analyzed using Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) on intergranular facets and found to increase with increasing neutron fluence. A rate theory model was also used to simulate the increase in grain-boundary P segregation for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.020wt.%. The increase in grain-boundary P segregation in RPV steel with a bulk P content of 0.015wt.% (the maximum P concentration found in RPV steels used in Japanese nuclear power plants intended for restart) was estimated to be less than 0.1 in monolayer coverage at 1.0 10
10 n/cm
n/cm (E
(E  1 MeV). A comparison of the PWR data with the MTR data showed that neutron flux had no effect upon grain-boundary P segregation. The effects of grain-boundary P segregation upon changes in irradiation hardening and ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) shifts were also discussed. A linear relationship between irradiation hardening and the DBTT shift with a slope of 0.63 obtained for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.026wt.%, which is higher than that of most U.S. A533B steels. It is concluded that the intergranular embrittlement is unlikely to occur for RPV steels irradiated in PWRs.
1 MeV). A comparison of the PWR data with the MTR data showed that neutron flux had no effect upon grain-boundary P segregation. The effects of grain-boundary P segregation upon changes in irradiation hardening and ductile-brittle transition temperature (DBTT) shifts were also discussed. A linear relationship between irradiation hardening and the DBTT shift with a slope of 0.63 obtained for RPV steels with a bulk P content up to 0.026wt.%, which is higher than that of most U.S. A533B steels. It is concluded that the intergranular embrittlement is unlikely to occur for RPV steels irradiated in PWRs.
Omori, Atsushi*; Akiyama, Eiji*; Abe, Hiroshi*; Hata, Kuniki; Sato, Tomonori; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Seito, Hajime*; Tada, Eiji*; et al.
Zairyo To Kankyo, 69(4), p.107 - 111, 2020/04
To evaluate the effect of oxidants, which are formed by radiolysis of water under gamma ray irradiation, on the corrosion of a carbon steel in humid environment, ozone was introduced as a model oxidant in to humidity-controlled air at 50 C in a thermo-hygrostat chamber. Corrosion monitoring was performed by using an Atmospheric Corrosion Monitor-type (ACM) sensor consisting of a carbon steel anode and an Ag cathode. The output current of the ACM sensor was increased with the increase in relative humidity and it was obviously increased with the increase in the introduced ozone concentration at each relative humidity. The results indicate that ozone accelerates the corrosion of the carbon steel. The effect of ozone on the corrosion acceleration is attributed to the fast reduction reaction and fast dissolution reaction in to water compared to that of oxygen.
C in a thermo-hygrostat chamber. Corrosion monitoring was performed by using an Atmospheric Corrosion Monitor-type (ACM) sensor consisting of a carbon steel anode and an Ag cathode. The output current of the ACM sensor was increased with the increase in relative humidity and it was obviously increased with the increase in the introduced ozone concentration at each relative humidity. The results indicate that ozone accelerates the corrosion of the carbon steel. The effect of ozone on the corrosion acceleration is attributed to the fast reduction reaction and fast dissolution reaction in to water compared to that of oxygen.
Hata, Kuniki; Inoue, Hiroyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(9-10), p.842 - 850, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)To investigate the effect of dissolved species from steels on the radiolysis processes of Cl , radiolysis simulations of solutions containing both Cl
, radiolysis simulations of solutions containing both Cl and Fe
and Fe were carried out. The results showed that the generation of radiolytic products (H
were carried out. The results showed that the generation of radiolytic products (H O
O , O
, O and H
and H ) increased mainly by the addition of Fe
) increased mainly by the addition of Fe , and a drop in the pH was caused by the hydrolysis of Fe
, and a drop in the pH was caused by the hydrolysis of Fe . This pH drop enhanced the reactivity of Cl
. This pH drop enhanced the reactivity of Cl with
with  OH, which induced additional generation of H
OH, which induced additional generation of H O
O and O
and O . These results show that low concentrations of Cl
. These results show that low concentrations of Cl (1
(1  10
10 mol/dm
mol/dm = 35ppm) in the presence of Fe
= 35ppm) in the presence of Fe could influence the generation of H
could influence the generation of H O
O and O
and O during water radiolysis. However, it is considered that these effects of Fe
during water radiolysis. However, it is considered that these effects of Fe and low concentration of Cl
and low concentration of Cl on water radiolysis are less important for corrosion of steels due to the low concentrations of H
on water radiolysis are less important for corrosion of steels due to the low concentrations of H O
O and O
and O generated. The other process, such as dissolution of iron enhanced by FeOOH, might predominantly induce corrosion under the conditions of solutions with low concentrations of H
generated. The other process, such as dissolution of iron enhanced by FeOOH, might predominantly induce corrosion under the conditions of solutions with low concentrations of H O
O and O
and O .
.
Hanawa, Satoshi; Hata, Kuniki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki
Proceedings of 21st International Conference on Water Chemistry in Nuclear Reactor Systems (Internet), 12 Pages, 2019/09
Kasahara, Shigeki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Hata, Kuniki; Hanawa, Satoshi
Zairyo To Kankyo, 68(9), p.240 - 247, 2019/09
In order to study environment assisted cracking mechanism of stainless steel under BWR primary coolant condition, effects of applied load on oxidation in the vicinity of crack tips of CT specimens were evaluated. Loaded CT specimens were immersed in an aqueous condition at 290 C as a simulated BWR coolant condition, and microstructural observation on oxide near the tips of pre-cracks was carried out. Oxide inner layers, which consisted of fine grain magnetite containing Fe and Cr were formed, and oxide outer layers consisting of large grains of Fe
C as a simulated BWR coolant condition, and microstructural observation on oxide near the tips of pre-cracks was carried out. Oxide inner layers, which consisted of fine grain magnetite containing Fe and Cr were formed, and oxide outer layers consisting of large grains of Fe O
O were observed to cover the inner layers. FEM analysis of stress and strain in the loaded CT specimen suggests that both of dislocations due to localized plastic deformation and elastic strain could play important roles to accelerate inner oxide formation in the vicinity of the crack tip of the specimens.
were observed to cover the inner layers. FEM analysis of stress and strain in the loaded CT specimen suggests that both of dislocations due to localized plastic deformation and elastic strain could play important roles to accelerate inner oxide formation in the vicinity of the crack tip of the specimens.
Kasahara, Shigeki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Hata, Kuniki; Fukuya, Koji*; Fujii, Katsuhiko*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors (Internet), p.1345 - 1355, 2019/08
This paper describes empirical equation development of crack growth rates (CGR) in consideration of IASCC of neutron irradiated stainless steel to contribute to structural integrity assessment of BWR reactor internals. Empirical equations of CGR (da/dt) were developed based on a formula of da/dt = M K
K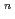 , assuming that "M" and "n" tend to be saturated with increasing neutron fluence. To obtain the empirical equations for normal water chemistry (NWC) and hydrogen water chemistry (HWC) of BWR, a data fitting with least square method was applied to the datasets consisting of F, K and CGR from post irradiation examinations of neutron irradiated stainless steel under simulated NWC and HWC conditions from open literature. As a result, calculated results by the equation for NWC showed good agreement with measured CGR data, meanwhile those for HWC did not. The above difference was seemed to be attributed that CGR data obtained under HWC conditions were scattered extensively.
, assuming that "M" and "n" tend to be saturated with increasing neutron fluence. To obtain the empirical equations for normal water chemistry (NWC) and hydrogen water chemistry (HWC) of BWR, a data fitting with least square method was applied to the datasets consisting of F, K and CGR from post irradiation examinations of neutron irradiated stainless steel under simulated NWC and HWC conditions from open literature. As a result, calculated results by the equation for NWC showed good agreement with measured CGR data, meanwhile those for HWC did not. The above difference was seemed to be attributed that CGR data obtained under HWC conditions were scattered extensively.
Fukuya, Koji*; Fujii, Katsuhiko*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Hata, Kuniki
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors (Internet), p.523 - 531, 2019/08
For structural integrity assessment on reactor internals of light water reactors, empirical equations of tensile properties as a function of neutron dose, and trend curves of stress-strain relations of neutron-irradiated austenitic stainless steels was proposed by fitting to recently developed database. The data in the database were obtained from reports of national projects in Japan and open literature, which was summarized in the form of data sheets. The empirical equations for tensile properties were formulated by using a saturation-type formulae. The equations were for CW 316 and SA 304/316 stainless steels in the temperature range of 280-350 C and the dose range up to 80 dpa. Stress-strain relation curves were reproduced based on the Swift model. Obtained calculated results by the empirical equations and stress-strain relations were reasonably well fitted to experimental data. The effects of composition and cold-working, etc. on tensile properties were discussed.
C and the dose range up to 80 dpa. Stress-strain relation curves were reproduced based on the Swift model. Obtained calculated results by the empirical equations and stress-strain relations were reasonably well fitted to experimental data. The effects of composition and cold-working, etc. on tensile properties were discussed.
 and Br
and Br and its effect on corrosion of a low-alloy steel
and its effect on corrosion of a low-alloy steelHata, Kuniki; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Kojima, Takao*; Kasahara, Shigeki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Tsukada, Takashi; Iwase, Akihiro*
Proceedings of Symposium on Water Chemistry and Corrosion in Nuclear Power Plants in Asia 2017 (AWC 2017) (USB Flash Drive), p.304 - 314, 2017/09
A model simulation of  radiolysis of mixed solutions of NaCl and NaBr was carried out. The simulation result agreed well with the experimental result, and Br
radiolysis of mixed solutions of NaCl and NaBr was carried out. The simulation result agreed well with the experimental result, and Br played an important role in determining the amounts of products from water radiolysis. The simulation result also showed that, in highly pure NaCl solutions, the steady-state concentration of a radolytic product, H
played an important role in determining the amounts of products from water radiolysis. The simulation result also showed that, in highly pure NaCl solutions, the steady-state concentration of a radolytic product, H O
O , was mainly controlled by three reactions (Cl
, was mainly controlled by three reactions (Cl +
+  OH
OH  ClOH
ClOH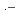 , ClOH
, ClOH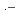
 Cl
Cl +
+  OH, and ClOH
OH, and ClOH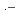 + H
+ H
 Cl
Cl + H
+ H O), which indicated that accurate evaluation of the rate constants of these reactions was very important in improving the radiolysis simulation of solutions containing Cl
O), which indicated that accurate evaluation of the rate constants of these reactions was very important in improving the radiolysis simulation of solutions containing Cl . An immersion test using a low-alloy steel, SQV2A, in the mixed solutions was also carried out under irradiation. The corrosion rate increased or decreased depending on the pH or the concentrations of the halide ions in a similar way to the change in concentration of H
. An immersion test using a low-alloy steel, SQV2A, in the mixed solutions was also carried out under irradiation. The corrosion rate increased or decreased depending on the pH or the concentrations of the halide ions in a similar way to the change in concentration of H O
O produced from water radiolysis, which is affected by the presence of Cl
produced from water radiolysis, which is affected by the presence of Cl and Br
and Br . However, at high pH values (
. However, at high pH values ( 12), the corrosion rate was almost zero even though the concentration of H
12), the corrosion rate was almost zero even though the concentration of H O
O was high. This could be attributed to enhancement of the passivity of test specimens at higher pH values.
was high. This could be attributed to enhancement of the passivity of test specimens at higher pH values.
Hata, Kuniki; Lin, M.*; Yokoya, Akinari*; Fujii, Kentaro*; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Muroya, Yusa*; Katsumura, Yosuke*
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (103), p.29 - 34, 2017/04
Reactivity of edaravone (3-methyl-1-phenyl-2-pyrazolin-5-one), which is known to show high antioxidative properties, with oxidative species, such as hydroxyl radical (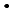 OH) and azide radical (N
OH) and azide radical (N
 ), was investigated by a pulse radiolysis experiment, and generation behavior of edaravone radicals produced through these reactions were observed. It was shown that OH-adducts are produced by the reaction with
), was investigated by a pulse radiolysis experiment, and generation behavior of edaravone radicals produced through these reactions were observed. It was shown that OH-adducts are produced by the reaction with 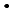 OH in contrast to the other oxidative radicals, which react with edaravone by an electron transfer reaction. Chemical repair properties of edaravone against DNA lesions produced by reactions of DNA with oxidative species were also investigated by a pulse radiolysis experiment with deoxyguanosine monophosphate (dGMP) and a
OH in contrast to the other oxidative radicals, which react with edaravone by an electron transfer reaction. Chemical repair properties of edaravone against DNA lesions produced by reactions of DNA with oxidative species were also investigated by a pulse radiolysis experiment with deoxyguanosine monophosphate (dGMP) and a  -radiolysis experiment with plasmid DNA solutions. It was observed that edaravone reduced dGMP radicals just after produced in a dilute aqueous solution and inhibited some base lesions on plasmid DNA more effectively than single strand breaks. These results show that edaravone may protect living system from oxidative stress, such as radiation, by not only scavenging oxidative species but also reducing precursors of DNA leisons.
-radiolysis experiment with plasmid DNA solutions. It was observed that edaravone reduced dGMP radicals just after produced in a dilute aqueous solution and inhibited some base lesions on plasmid DNA more effectively than single strand breaks. These results show that edaravone may protect living system from oxidative stress, such as radiation, by not only scavenging oxidative species but also reducing precursors of DNA leisons.
Hata, Kuniki
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (103), P. 65, 2017/04
no abstracts in English
Hanawa, Satoshi; Uchida, Shunsuke; Hata, Kuniki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kasahara, Shigeki*; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Proceedings of 20th Nuclear Plant Chemistry International Conference (NPC 2016) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2016/10
The authors proposed and ECP evaluation model introducing irradiation-induced diffusion in the oxide layer to simulate neutron irradiation effect, and predicted with this model that ECP is started to depress from the neutron flux of about ten to the fourteenth per square meter. As the JMTR has in-pile loops applicable to water chemistry experiments, degree of irradiation effect on ECP appears in the in-pile loop was estimated by the model. Under oxygen injected condition, ECP in a capsule becomes constant along the vertical direction due to the presence of high amount of oxygen and hydrogen peroxide in a capsule. However, if neutron irradiation depress ECP, ECP in a capsule along vertical direction wouldn't become constant, and the degree to the decrement is detectable by experiments.