Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsumoto, Hideki*; Tomita, Masanori*; Otsuka, Kensuke*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Maeda, Munetoshi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Yokota, Yuichiro; Suzuki, Michiyo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Ikeda, Hiroko; et al.
JAEA-Review 2014-050, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2013, P. 76, 2015/03
The objective of this project is to elucidate molecular mechanisms for the induction of radioadaptive response through radiation-induced bystander responses induced by irradiation with heavy ion microbeams in JAEA. We found that the adaptive response was induced by Ar (520 MeV  Ar
Ar ) microbeam-irradiation of a limited number of cells, followed by the broad beam-irradiation and that the adaptive response was almost completely suppressed by the addition of carboxy-PTIO, as a nitric oxide (NO) scavenger. In addition, we found several genes induced specifically and preferentially when radioadaptive response could be induced. We confirmed that
) microbeam-irradiation of a limited number of cells, followed by the broad beam-irradiation and that the adaptive response was almost completely suppressed by the addition of carboxy-PTIO, as a nitric oxide (NO) scavenger. In addition, we found several genes induced specifically and preferentially when radioadaptive response could be induced. We confirmed that 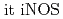 expression was specifically induced only when radioadaptive response could be induced. Our findings strongly suggested that radioadaptive response can be induced by NO-mediated bystander responses evoked by irradiation with heavy ion microbeams.
expression was specifically induced only when radioadaptive response could be induced. Our findings strongly suggested that radioadaptive response can be induced by NO-mediated bystander responses evoked by irradiation with heavy ion microbeams.
Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Konishi, Teruaki*; Imaseki, Hitoshi*; Yasuda, Keisuke*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Takagi, Keiichi*; Hatori, Satoshi*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 50(Suppl.A), p.A29 - A47, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:72.75(Biology)Takagi, Keiichi*; Tanaka, Yoshikazu*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Endo, Nobuyuki*
Heisei-18-Nendo Zaidan Hojin Wakasawan Enerugi Kenkyu Senta Kenkyu Seika Hokokushu, 9, P. 95, 2007/09
no abstracts in English
Matsumoto, Hideki*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Takahashi, Akihisa*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kakizaki, Takehiko; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 111, 2007/02
Matsumoto, Hideki*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Takahashi, Akihisa*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Wada, Seiichi*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Funayama, Tomoo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kakizaki, Takehiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Izumi, Yoshinobu*; Matsuo, Yoichiro*; Sakamoto, Ayako; Takagi, Keiichi*; Hatashita, Masanori*; Kojima, Takao*; Shimizu, Kikuo*
no journal, ,
In cases of ion-beam irradiations, several features of deep interest can be observed, contrasting with the low-LET radiations such as  -rays. In order to elucidate the induction mechanisms of mutations peculiar to ion beams, carbon-ion beams with LETs of 13 keV/
-rays. In order to elucidate the induction mechanisms of mutations peculiar to ion beams, carbon-ion beams with LETs of 13 keV/ m - 107 keV/
m - 107 keV/ m and proton beam with LET of 0.45 keV/
m and proton beam with LET of 0.45 keV/ m were irradiated to budding yeast. Carbon-ion beams and proton beam irradiation were performed in TIARA or HIMAC, and WERC, respectively. After irradiations, survival ratios and mutation frequencies were analyzed as well as sequencing and gene expression analyses. In order to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of mutagenesis caused by radiations, we used
m were irradiated to budding yeast. Carbon-ion beams and proton beam irradiation were performed in TIARA or HIMAC, and WERC, respectively. After irradiations, survival ratios and mutation frequencies were analyzed as well as sequencing and gene expression analyses. In order to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of mutagenesis caused by radiations, we used 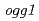 (BER-) which is deficient in the elimination of 8-oxodGTP and
(BER-) which is deficient in the elimination of 8-oxodGTP and 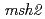 (MMR-) deficient in the mismatch-repair function. For comparison, we also used
(MMR-) deficient in the mismatch-repair function. For comparison, we also used 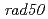 (NHEJ-) and
(NHEJ-) and 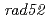 (HR-) that were deficient in the double-strand breaks (DSBs)-repair function.
(HR-) that were deficient in the double-strand breaks (DSBs)-repair function.