Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*
Physical Review B, 111(22), p.224413_1 - 224413_6, 2025/06
The crystal and magnetic structures of antiferromagnetic Mn deuterides formed by hydrogenating Mn metal at high temperature and high pressure, fcc  -MnDx and hcp
-MnDx and hcp  -MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from
-MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from  700 to
700 to  450 K and remained down to 300 K. N
450 K and remained down to 300 K. N el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for
el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for  -MnD
-MnD . For
. For  -MnD
-MnD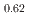 , saturation magnetic moment and N
, saturation magnetic moment and N el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1)
el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1) 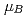 and 347(3) K, respectively. The N
and 347(3) K, respectively. The N el temperatures determined for
el temperatures determined for  -MnD
-MnD and
and  -MnD
-MnD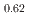 are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N
are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Hattori, Takanori
Koatsuryoku No Kagaku To Gijutsu, 35(1), p.4 - 11, 2025/03
Iron reacts with hydrogen to form solid solutions with body-centered cubic, face-centered cubic, hexagonal close packed, and double hexagonal close packed structures at high temperatures and high pressures. Neutron diffraction is the most powerful tool for determining the occupation sites and occupancies of hydrogen atoms dissolved in a metal lattice. Structural parameters, including hydrogen occupation sites and occupancies, are refined via Rietveld analysis for neutron diffraction data. We present our expertise in Rietveld refinement of iron hydrides accumulated over 10 years.
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Sugimoto, Hidehiko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Endo, Naruki*; Katayama, Yoshinori*; Iizuka, Riko*; Sato, Toyoto*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.8861_1 - 8861_2, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In our previous article (Nature Commun. 5, 5063 (2014)), the site occupancies of D atoms dissolved in an fcc Fe metal lattice were investigated via Rietveld refinement of neutron powder diffraction patterns collected at 988 K and 6.3 GPa. The fcc metal lattice has two interstitial sites available for accommodating D atoms: octahedral and tetrahedral sites. The Rietveld refinement revealed that D atoms occupied mainly the octahedral sites with occupancy of 0.532 and slightly the tetrahedral sites with occupancy of 0.056. Subsequent density-functional-theory (DFT) calculations by Antonov (Phys. Rev. Mater. 2019)) showed that the occupation energy on the tetrahedral site was significantly higher than that on the octahedral site; the tetrahedral site occupation was unlikely to occur even at temperatures as high as 988 K. We reexamined the site occupancies of D-atom by Rietveld refinement including extinction correction. As a result, the octahedral occupancy was increased to 0.60 and the tetrahedral occupancy was reduced to zero. The occupation of only the octahedral site for D atom is consistent with the DFT calculation, although in contrast to the previous results.
 Ni
Ni D
D at high
at high 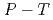 conditions
conditionsShito, Chikara*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Kakizawa, Sho*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iizuka, Riko*; Abe, Jun*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori
American Mineralogist, 108(4), p.659 - 666, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:71.52(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The phase relation and crystal structure of Fe Ni
Ni H
H (D
(D ) at high pressures and temperatures up to 12 GPa and 1000 K were clarified by in-situ X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements. Under
) at high pressures and temperatures up to 12 GPa and 1000 K were clarified by in-situ X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements. Under 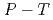 conditions of the present study, no deuterium atoms occupied tetragonal (
conditions of the present study, no deuterium atoms occupied tetragonal ( ) sites of face-centered cubic (fcc) Fe
) sites of face-centered cubic (fcc) Fe Ni
Ni D
D unlike fcc FeH
unlike fcc FeH (D
(D ). The deuterium-induced volume expansion per deuterium
). The deuterium-induced volume expansion per deuterium 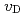 was determined as 2.45(4)
was determined as 2.45(4) 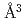 and 3.31(6)
and 3.31(6) 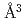 for fcc and hcp phases, respectively, which were significantly larger than the corresponding values for FeD
for fcc and hcp phases, respectively, which were significantly larger than the corresponding values for FeD . The
. The 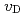 value slightly increased with increasing temperature. This study suggests that only 10% of nickel in iron drastically changes the behaviors of hydrogen in metal. Assuming that
value slightly increased with increasing temperature. This study suggests that only 10% of nickel in iron drastically changes the behaviors of hydrogen in metal. Assuming that 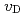 is constant regardless of pressure, the maximum hydrogen content in the Earth's inner core is estimated to be one to two times the amount of hydrogen in the oceans.
is constant regardless of pressure, the maximum hydrogen content in the Earth's inner core is estimated to be one to two times the amount of hydrogen in the oceans.
 Si
Si at 14.7 GPa and 800 K
at 14.7 GPa and 800 KMori, Yuichiro*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Kakizawa, Sho*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Shito, Chikara*; Iizuka, Riko*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; et al.
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 116(6), p.309 - 313, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.84(Mineralogy)The Earth's core is believed to contain some light elements because it is 10% less dense than pure Fe under the corresponding pressure and temperature conditions. Hydrogen, a promising candidate among light elements, has phase relations and physical properties that have been investigated mainly for the Fe-H system. This study specifically examined an Fe-Si-H system using in-situ neutron diffraction experiments to investigate the site occupancy of deuterium of hcp-Fez Si
Si hydride at 14.7 GPa and 800 K. Results of Rietveld refinement indicate hcp-Fe
hydride at 14.7 GPa and 800 K. Results of Rietveld refinement indicate hcp-Fe Si
Si hydride as having deuterium (D) occupancy of 0.24(2) exclusively at the interstitial octahedral site in the hcp lattice. The effect on the site occupancy of D by addition of 2.6 wt% Si into Fe (Fe
hydride as having deuterium (D) occupancy of 0.24(2) exclusively at the interstitial octahedral site in the hcp lattice. The effect on the site occupancy of D by addition of 2.6 wt% Si into Fe (Fe Si
Si ) was negligible compared to results obtained from an earlier study of an Fe-D system (Machida et al., 2019).
) was negligible compared to results obtained from an earlier study of an Fe-D system (Machida et al., 2019).
Saito, Hiroyuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 587, p.412153_1 - 412153_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:25.28(Physics, Condensed Matter)The site occupancy of deuterium (D) atoms in face-centered-cubic nickel (fcc Ni) was measured along a cooling path from 1073 to 300 K at an initial pressure of 3.36 GPa via in situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms predominantly occupy the octahedral (O) sites and slightly occupy the tetrahedral (T) sites of the fcc metal lattice. The O-site occupancy increases from 0.4 to 0.85 as the temperature is lowered from 1073 to 300 K. Meanwhile, the T-site occupancy remains c.a. 0.02. The temperature-independent behavior of the T-site occupancy is unusual, and its process is not yet understood. From the linear relation between the expanded lattice volume and D content, a D-induced volume expansion of 2.09(13) 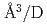 atom was obtained. This value is in agreement with the values of 2.14-2.2
atom was obtained. This value is in agreement with the values of 2.14-2.2 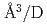 atom previously reported for Ni and Ni
atom previously reported for Ni and Ni Fe
Fe alloy.
alloy.
Saito, Hiroyuki*; Machida, Akihiko*; Iizuka, Riko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 10, p.9934_1 - 9934_8, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:19.41(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Neutron powder diffraction profiles were collected for iron deuteride (FeDx) while the temperature decreased from 1023 to 300 K for a pressure range of 4-6 GPa. The  ' deuteride with a double hexagonal close-packed (dhcp) structure, which coexisted with other stable or metastable deutrides at each temperature and pressure condition, formed solid solutions with a composition of FeD
' deuteride with a double hexagonal close-packed (dhcp) structure, which coexisted with other stable or metastable deutrides at each temperature and pressure condition, formed solid solutions with a composition of FeD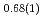 at 673 K and 6.1 GPa and FeD
at 673 K and 6.1 GPa and FeD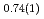 at 603 K and 4.8 GPa. Upon stepwise cooling to 300 K, the D-content x increased to a stoichiometric value of 1.0 to form monodeuteride FeD
at 603 K and 4.8 GPa. Upon stepwise cooling to 300 K, the D-content x increased to a stoichiometric value of 1.0 to form monodeuteride FeD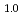 . In the dhcp FeD
. In the dhcp FeD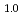 at 300 K and 4.2 GPa, dissolved D atoms fully occupied the octahedral interstitial sites, slightly displaced from the octahedral centers in the dhcp metal lattice, and the dhcp sequence of close-packed Fe planes contained hcp-stacking faults at 12%. Magnetic moments with 2.11
at 300 K and 4.2 GPa, dissolved D atoms fully occupied the octahedral interstitial sites, slightly displaced from the octahedral centers in the dhcp metal lattice, and the dhcp sequence of close-packed Fe planes contained hcp-stacking faults at 12%. Magnetic moments with 2.11  0.06 B/Fe-atom aligned ferromagnetically in parallel on the Fe planes.
0.06 B/Fe-atom aligned ferromagnetically in parallel on the Fe planes.
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 9(1), p.12290_1 - 12290_9, 2019/08
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:83.40(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Hexagonal close-packed iron hydride, hcp FeHx, is absent from the conventional phase diagram of the Fe-H system, although hcp metallic Fe exists stably over extensive temperature ( ) and pressure (
) and pressure ( ) conditions, including those corresponding to the Earth's inner core.
) conditions, including those corresponding to the Earth's inner core. 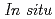 X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements at temperatures ranging from 298 to 1073 K and H pressures ranging from 4 to 7 GPa revealed that the hcp hydride was formed for FeH
X-ray and neutron diffraction measurements at temperatures ranging from 298 to 1073 K and H pressures ranging from 4 to 7 GPa revealed that the hcp hydride was formed for FeH compositions when
compositions when 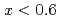 . Hydrogen atoms occupied the octahedral interstitial sites of the host metal lattice both partially and randomly. The hcp hydride exhibited a H-induced volume expansion of 2.48(5)
. Hydrogen atoms occupied the octahedral interstitial sites of the host metal lattice both partially and randomly. The hcp hydride exhibited a H-induced volume expansion of 2.48(5) 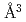 /H-atom, which was larger than that of the face-centered cubic (fcc) hydride. The hcp hydride showed an increase in
/H-atom, which was larger than that of the face-centered cubic (fcc) hydride. The hcp hydride showed an increase in  with
with  , whereas the fcc hydride showed a corresponding decrease. The present study provides guidance for further investigations of the Fe-H system over an extensive
, whereas the fcc hydride showed a corresponding decrease. The present study provides guidance for further investigations of the Fe-H system over an extensive  -
- -
- region.
region.
Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami
Hamon, 25(1), p.26 - 31, 2015/02
The deuterization process of fcc Fe to form solid1solution fcc FeD was investigated by
was investigated by 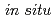 neutron diffraction measurements at high temperature and high pressure. In a completely deuterized specimen at 988 K and 6.3 GPa, deuterium atoms occupy the octahedral and tetrahedral interstitial sites with an occupancy of 0.532(9) and 0.056(5), respectively, giving a deuterium composition
neutron diffraction measurements at high temperature and high pressure. In a completely deuterized specimen at 988 K and 6.3 GPa, deuterium atoms occupy the octahedral and tetrahedral interstitial sites with an occupancy of 0.532(9) and 0.056(5), respectively, giving a deuterium composition  of 0.64(1). During deuterization, the metal-lattice expands approximately linearly with deuterium composition at a rate of 2.21
of 0.64(1). During deuterization, the metal-lattice expands approximately linearly with deuterium composition at a rate of 2.21 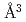 per deuterium atom. The minor occupation of tetrahedral site is likely driven by the intersite movement of deuterium atoms along the
per deuterium atom. The minor occupation of tetrahedral site is likely driven by the intersite movement of deuterium atoms along the  111
111 direction in the fcc metal lattice. These results provide implications for the light elements in the Earth's core and the mechanism of hydrogen embrittlement of ferrous metals.
direction in the fcc metal lattice. These results provide implications for the light elements in the Earth's core and the mechanism of hydrogen embrittlement of ferrous metals.
Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Machida, Akihiko; Saito, Hiroyuki; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami
Hamon, 25(1), p.26 - 31, 2015/02
The deuterization process of fcc Fe to form solid-solution fcc FeD was investigated by in situ neutron diffraction measurements at high temperature and high pressure. In a completely deuterized specimen at 988 K and 6.3 GPa, deuterium atoms occupy the octahedral and tetrahedral interstitial sites with an occupancy of 0.532(9) and 0.056(5), respectively, giving a deuterium composition
was investigated by in situ neutron diffraction measurements at high temperature and high pressure. In a completely deuterized specimen at 988 K and 6.3 GPa, deuterium atoms occupy the octahedral and tetrahedral interstitial sites with an occupancy of 0.532(9) and 0.056(5), respectively, giving a deuterium composition  of 0.64(1). During deuterization, the metal-lattice expands approximately linearly with deuterium composition at a rate of 2.21
of 0.64(1). During deuterization, the metal-lattice expands approximately linearly with deuterium composition at a rate of 2.21 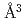 per deuterium atom. The minor occupation of tetrahedral site is likely driven by the intersite movement of deuterium atoms along the
per deuterium atom. The minor occupation of tetrahedral site is likely driven by the intersite movement of deuterium atoms along the 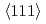 direction in the fcc metal lattice. These results provide implications for the light elements in the Earth's core and the mechanism of hydrogen embrittlement of ferrous metals.
direction in the fcc metal lattice. These results provide implications for the light elements in the Earth's core and the mechanism of hydrogen embrittlement of ferrous metals.
Machida, Akihiko; Saito, Hiroyuki; Sugimoto, Hidehiko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Endo, Naruki*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Iizuka, Riko*; Sato, Toyoto*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 5, p.5063_1 - 5063_6, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:66 Percentile:87.34(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Iron hydride FeH , is thermodynamically stable only at high hydrogen pressure of several GPa. To investigate the hydrogenation process and hydrogen state in iron hydride, it is necessary to carry out the in-situ measurement under high pressure and high temperature. In this study, we performed the in-situ neutron diffraction measurement of Fe-D system using the high pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET in the MLF, J-PARC, and determined the deuterium occupying sites and occupancies in fcc-FeD
, is thermodynamically stable only at high hydrogen pressure of several GPa. To investigate the hydrogenation process and hydrogen state in iron hydride, it is necessary to carry out the in-situ measurement under high pressure and high temperature. In this study, we performed the in-situ neutron diffraction measurement of Fe-D system using the high pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET in the MLF, J-PARC, and determined the deuterium occupying sites and occupancies in fcc-FeD . We found the minor occupation of tetrahedral sites under high pressure and high temperature. We considered the mechanism of the minor occupation based on the Quantum-mechanical calculation.
. We found the minor occupation of tetrahedral sites under high pressure and high temperature. We considered the mechanism of the minor occupation based on the Quantum-mechanical calculation.
Machida, Akihiko; Honda, Mitsunori*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*
Hamon, 23(2), p.131 - 136, 2013/05
Recently, we have revealed formation of NaCl-type LaD using synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction and neutron diffraction measurements under high pressure. Previously, we have found that LaH decomposes into two phases, which have different hydrogen compositions, the H-poor and H-rich phases, at 11 GPa at room temperature by synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction. Recent neutron diffraction measurements on LaD
decomposes into two phases, which have different hydrogen compositions, the H-poor and H-rich phases, at 11 GPa at room temperature by synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction. Recent neutron diffraction measurements on LaD confirmed the formation of a NaCl-type LaD as the D-poor phase. This is the first observation of a formation of the rare-earth metal monodeuteride. Present result indicates that that rare-earth metal can form a series of stoichiometric hydrides, such as mono-, di-, and trihydride with the fcc metal lattice.
confirmed the formation of a NaCl-type LaD as the D-poor phase. This is the first observation of a formation of the rare-earth metal monodeuteride. Present result indicates that that rare-earth metal can form a series of stoichiometric hydrides, such as mono-, di-, and trihydride with the fcc metal lattice.
Kanasaki, Masato; Hattori, Atsuto; Sakaki, Hironao; Fukuda, Yuji; Yogo, Akifumi; Jinno, Satoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Ogura, Koichi; Kondo, Kiminori; Oda, Keiji*; et al.
Radiation Measurements, 50, p.46 - 49, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:71.45(Nuclear Science & Technology)A precise measurement has been made utilizing a stacked CR-39 detectors unit for laser accelerated high intensity protons. The proton beams are derived from a thin polyimide target exposed to an high intense Ti:sapphire laser 8 J energy and 40 fs duration. The sample sets, stacked radiochromic film and CR-39 detectors covered with 13  m aluminum filter, are irradiated under vacuum condition. By analyzing the etch pits on the last layer of CR-39 which recorded etchable tracks, the proton energy in high energy region is evaluate more precisely than in the past. The residual ranges for each particle in the last layer has been obtained from etch pit growth curves with multi-stepetching technique. The maximum energy of proton is 14.39
m aluminum filter, are irradiated under vacuum condition. By analyzing the etch pits on the last layer of CR-39 which recorded etchable tracks, the proton energy in high energy region is evaluate more precisely than in the past. The residual ranges for each particle in the last layer has been obtained from etch pit growth curves with multi-stepetching technique. The maximum energy of proton is 14.39 0.05 MeV. This method allows us to measure the maximum energy of proton precisely, which is obtained up to the hundredth place in unit of MeV in the laser-driven particle acceleration experiment.
0.05 MeV. This method allows us to measure the maximum energy of proton precisely, which is obtained up to the hundredth place in unit of MeV in the laser-driven particle acceleration experiment.

Machida, Akihiko; Honda, Mitsunori*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Watanuki, Tetsu; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Oshita, Hidetoshi*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 108(20), p.205501_1 - 205501_5, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:70.52(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hydrogen atoms absorbed in a metal occupy the interstitial sites of the metal lattice. In an fcc metal lattice, each metal atom has two tetrahedral (T) and one octahedral (O) sites that can accommodate hydrogen. Rare-earth metal La forms T-site occupied LaH and fully occupied LaH
and fully occupied LaH . O-site occupied or NaCl-type monohydride has yet to be reported for rare-earth metals. Previous X-ray diffraction measurements revealed the pressure-induced decomposition of an fcc-LaH
. O-site occupied or NaCl-type monohydride has yet to be reported for rare-earth metals. Previous X-ray diffraction measurements revealed the pressure-induced decomposition of an fcc-LaH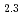 into H-rich and H-poor phases around 11 GPa. The present neutron diffraction measurements on LaD
into H-rich and H-poor phases around 11 GPa. The present neutron diffraction measurements on LaD confirm the formation of NaCl-type LaD as a counterpart of the D-rich LaD
confirm the formation of NaCl-type LaD as a counterpart of the D-rich LaD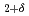 by disproportionation. First-principle calculations demonstrate that the NaCl-type LaH is stabilized at high pressures. Finding the NaCl-type LaH will pave the way for investigations on the site-dependent nature of hydrogen-metal interactions.
by disproportionation. First-principle calculations demonstrate that the NaCl-type LaH is stabilized at high pressures. Finding the NaCl-type LaH will pave the way for investigations on the site-dependent nature of hydrogen-metal interactions.
Kanasaki, Masato; Fukuda, Yuji; Sakaki, Hironao; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kondo, Kiminori; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Hattori, Atsuto*; Oda, Keiji*; Yamauchi, Tomoya*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 88(5), p.261 - 275, 2012/05
CR-39 solid state nuclear track detector, which was developed for optical lens, has been applied for various field such as radon surveys, measurement of galactic cosmic ray, cell irradiation experiment and so on. The CR-39 detectors have the great advantages of being insensitive to high energy photons and electrons and capable of detecting only ions in the mixed fields such as laser driven relativistic plasmas. Though there are some analytical methods of CR-39 to diagnose ion beam, unfortunately, only few researchers in the field of plasma know the methods. This article looks at how to use CR-39 detectors and introduce the accomplishment of the joint study JAEA and Kobe Univ. for application of CR-39 detectors to ion beam diagnosis.
Katayama, Yoshinori; Hattori, Takanori; Saito, Hiroyuki; Ikeda, Takashi; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Fukui, Hiroshi*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
Physical Review B, 81(1), p.014109_1 - 014109_6, 2010/01
Times Cited Count:73 Percentile:90.03(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The structure of liquid water was studied along the melting curve up to 17.1 GPa and 850 K by in situ X-ray diffraction. At low pressures, the local structure changed toward a simple liquid-like structure through an increase in the coordination number of water molecules. Once densely packed structure of water molecules was achieved around 4 GPa, the volume was reduced through the decrease of the intermolecular distance on further compression. Classical molecular dynamics simulations well reproduced the experimental results although the degree of agreement depended on pressure. Limitations of the pair potential model were discussed.
Hattori, Takanori; Saito, Hiroyuki; Kaneko, Hiroshi; Okajima, Yuka; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Utsumi, Wataru
KEK Proceedings 2007-7, p.56 - 60, 2007/12
We introduce high-pressure study on amorphous materials using a multi-anvils press equipped with the X-ray transparent cBN anvils. First, we mention merits of the angle-dispersive X-ray diffraction system compared with the conventional energy-dispersive system. Next, we show the results of the verification of the high-pressure formation of the elemental bulk metallic glass as an example. Finally, the characteristics of X-ray absorption are shown both for the combinational sintered diamond anvils and the presently used cBN anvils.
Hattori, Takanori; Saito, Hiroyuki; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Kaneko, Hiroshi; Okajima, Yuka; Utsumi, Wataru
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 49(3), p.179 - 185, 2007/06
The high-pressure formation of the bulk metallic glass of elemental Zr and Ti, which has been recently reported, is verified by a newly developed angle dispersive X-ray diffraction (ADX) system using a large volume multi-anvil apparatus equipped with X-ray transparent anvils. The ADX data revealed that Zr and Ti remain as a crystalline form at high-pressure and temperature condition where the amorphization has been reported. The misinterpretation in the previous papers is attributed to the anomalous rapid grain growth that is related to the characteristic lattice dynamic and the resulting anomalously fast self diffusion in the high-temperature phases of Zr and Ti.
Hattori, Takanori; Saito, Hiroyuki; Utsumi, Wataru; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Kaneko, Hiroshi; Okajima, Yuka
SPring-8 Riyosha Joho, 12(1), p.45 - 50, 2007/01
no abstracts in English
Hattori, Takanori; Saito, Hiroyuki; Kaneko, Hiroshi; Okajima, Yuka; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Utsumi, Wataru
Physical Review Letters, 96(25), p.255504_1 - 255504_4, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:74.58(Physics, Multidisciplinary)To verify the high-pressure formation of the bulk metallic glass in elemental Zr and Ti, which Zhang and Zhao and Y. Wang  recently reported, the high-pressure states were investigated by our newly developed
recently reported, the high-pressure states were investigated by our newly developed 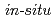 angle-dispersive X-ray diffraction using a two-dimensional detector and X-ray transparent anvils. Despite the disappearance of all the Bragg peaks in the one-dimensional energy-dispersive data, two-dimensional angle-dispersive data showed several intense Bragg spots even at the conditions where the amorphization was reported. This finding suggests that Zr and Ti do not transform into an amorphous state, but that their grain size becomes large, which causes the missing Bragg peaks in energy-dispersive data.
angle-dispersive X-ray diffraction using a two-dimensional detector and X-ray transparent anvils. Despite the disappearance of all the Bragg peaks in the one-dimensional energy-dispersive data, two-dimensional angle-dispersive data showed several intense Bragg spots even at the conditions where the amorphization was reported. This finding suggests that Zr and Ti do not transform into an amorphous state, but that their grain size becomes large, which causes the missing Bragg peaks in energy-dispersive data.