Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*
Physical Review B, 111(22), p.224413_1 - 224413_6, 2025/06
The crystal and magnetic structures of antiferromagnetic Mn deuterides formed by hydrogenating Mn metal at high temperature and high pressure, fcc  -MnDx and hcp
-MnDx and hcp  -MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from
-MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from  700 to
700 to  450 K and remained down to 300 K. N
450 K and remained down to 300 K. N el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for
el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for  -MnD
-MnD . For
. For  -MnD
-MnD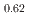 , saturation magnetic moment and N
, saturation magnetic moment and N el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1)
el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1) 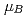 and 347(3) K, respectively. The N
and 347(3) K, respectively. The N el temperatures determined for
el temperatures determined for  -MnD
-MnD and
and  -MnD
-MnD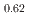 are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N
are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
 hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH
hydridosilicate at high pressures; A Bridge to BaSiH polyhydride
polyhydrideBeyer, D. C.*; Spektor, K.*; Vekilova, O. Y.*; Grins, J.*; Barros Brant Carvalho, P. H.*; Leinbach, L. J.*; Sannemo-Targama, M.*; Bhat, S.*; Baran, V.*; Etter, M.*; et al.
ACS Omega (Internet), 10(15), p.15029 - 15035, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Hydridosilicates featuring SiH octahedral moieties represent a rather new class of compounds with potential properties relating to hydrogen storage and hydride ion conductivity. Here, we report on the new representative BaSiH
octahedral moieties represent a rather new class of compounds with potential properties relating to hydrogen storage and hydride ion conductivity. Here, we report on the new representative BaSiH obtained from reacting the Zintl phase hydride BaSiH
obtained from reacting the Zintl phase hydride BaSiH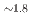 with H
with H fluid at pressures above 4 GPa and subsequent decompression to ambient pressure. It consists of complex SiH
fluid at pressures above 4 GPa and subsequent decompression to ambient pressure. It consists of complex SiH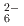 ions, which are octahedrally coordinated by Ba
ions, which are octahedrally coordinated by Ba counterions. The arrangement of Ba and Si atoms deviates only slightly from an ideal fcc NaCl structure. IR and Raman spectroscopy showed SiH
counterions. The arrangement of Ba and Si atoms deviates only slightly from an ideal fcc NaCl structure. IR and Raman spectroscopy showed SiH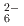 bending and stretching modes in the ranges 800-1200 and 1400-1800 cm
bending and stretching modes in the ranges 800-1200 and 1400-1800 cm , respectively. BaSiH
, respectively. BaSiH is thermally stable up to 95
is thermally stable up to 95 C above which decomposition into BaH
C above which decomposition into BaH and Si takes place. DFT calculations indicated a direct band gap of 2.5 eV. The discovery of BaSiH
and Si takes place. DFT calculations indicated a direct band gap of 2.5 eV. The discovery of BaSiH consolidates the compound class of hydridosilicates, accessible from hydrogenations of silicides at gigapascal pressures (
consolidates the compound class of hydridosilicates, accessible from hydrogenations of silicides at gigapascal pressures (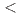 10 GPa). The structural properties of BaSiH
10 GPa). The structural properties of BaSiH suggest that it presents an intermediate (or precursor) for further hydrogenation at considerably higher pressures to the predicted superconducting polyhydride BaSiH
suggest that it presents an intermediate (or precursor) for further hydrogenation at considerably higher pressures to the predicted superconducting polyhydride BaSiH .
.
Li, F.*; Tang, X.*; Fei, Y.*; Zhang, J.*; Liu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Che, G.*; Zhao, Z.*; Zheng, Y.*; Fang, Y.*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 147(17), p.14054 - 14059, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We synthesized a crystalline graphane nanoribbon (GANR) via pressure-induced polymerization of 2,2'-bipyrazine (BPZ). By performing Rietveld refinement of in situ neutron diffraction data, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, infrared spectra, and theoretical calculation, we found that BPZ experienced Diels-Alder polymerization between the 

 stacked aromatic rings, and formed extended boat-GANR structures with exceptional long-range order. The unreacted -C=N- groups bridge the two ends of the boat, and ready for further functionalization. The GANR has a bandgap of 2.25 eV, with booming photoelectric response (
stacked aromatic rings, and formed extended boat-GANR structures with exceptional long-range order. The unreacted -C=N- groups bridge the two ends of the boat, and ready for further functionalization. The GANR has a bandgap of 2.25 eV, with booming photoelectric response (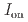 /
/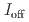 =18.8). Our work highlights that the high-pressure topochemical polymerization is a promising method for the precise synthesis of graphane with specific structure and desired properties.
=18.8). Our work highlights that the high-pressure topochemical polymerization is a promising method for the precise synthesis of graphane with specific structure and desired properties.
 under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation study
under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation studyEfthimiopoulos, I.*; Klotz, S.*; Kunc, K.*; Baptiste, B.*; Chauvigne, P.*; Hattori, Takanori
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134103_1 - 134103_13, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a comprehensive study of the high pressure behaviour of ReO using X-ray and neutron diffraction, Raman scattering and first-principles calculations to 15 GPa. We show that the ambient pressure
using X-ray and neutron diffraction, Raman scattering and first-principles calculations to 15 GPa. We show that the ambient pressure 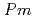
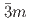 structure converts at 0.7 GPa in a continuous phase transition directly to a cubic phase with space group
structure converts at 0.7 GPa in a continuous phase transition directly to a cubic phase with space group 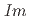
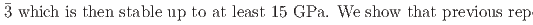 and rhombohedral
and rhombohedral 
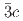 structures in this pressure range are an artifact due to an alteration of the sample by high-flux synchrotron X-ray radiation. The structural pressure dependence of the
structures in this pressure range are an artifact due to an alteration of the sample by high-flux synchrotron X-ray radiation. The structural pressure dependence of the 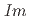
 O samples are presented. The data shed light onto the unusual transition and densification mechanism due to progressive tilting of essentially rigid ReO
O samples are presented. The data shed light onto the unusual transition and densification mechanism due to progressive tilting of essentially rigid ReO octahedra.
octahedra.
 GeTe
GeTe to hydrostatic pressure
to hydrostatic pressureWang, Y.*; Zeng, X.-T.*; Li, B.*; Su, C.*; Hattori, Takanori; Sheng, X.-L.*; Jin, W.*
Chinese Physics B, 34(4), p.046203_1 - 046203_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Two-dimensional van der Waals ferromagnet Fe GeTe
GeTe (FGT) holds a great potential for applications in spintronic devices, due to its high Curie temperature, easy tunability, and excellent structural stability in air. In this study, we have performed high-pressure neutron powder diffraction (NPD) up to 5 GPa, to investigate the evolution of its structural and magnetic properties with hydrostatic pressure. The NPD data clearly reveal the robustness of the ferromagnetism in FGT, despite of an apparent suppression by hydrostatic pressure. As the pressure increases from 0 to 5 GPa, the Curie temperature is found to decrease monotonically from 225(5) K to 175(5) K, together with a dramatically suppressed ordered moment of Fe, which is well supported by the first-principles calculations. Although no pressure-driven structural phase transition is observed up to 5 GPa, quantitative analysis on the changes of bond lengths and bond angles indicate a significant modification of the exchange interactions, which accounts for the pressure-induced suppression of the ferromagnetism in FGT.
(FGT) holds a great potential for applications in spintronic devices, due to its high Curie temperature, easy tunability, and excellent structural stability in air. In this study, we have performed high-pressure neutron powder diffraction (NPD) up to 5 GPa, to investigate the evolution of its structural and magnetic properties with hydrostatic pressure. The NPD data clearly reveal the robustness of the ferromagnetism in FGT, despite of an apparent suppression by hydrostatic pressure. As the pressure increases from 0 to 5 GPa, the Curie temperature is found to decrease monotonically from 225(5) K to 175(5) K, together with a dramatically suppressed ordered moment of Fe, which is well supported by the first-principles calculations. Although no pressure-driven structural phase transition is observed up to 5 GPa, quantitative analysis on the changes of bond lengths and bond angles indicate a significant modification of the exchange interactions, which accounts for the pressure-induced suppression of the ferromagnetism in FGT.
Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Hattori, Takanori
Koatsuryoku No Kagaku To Gijutsu, 35(1), p.4 - 11, 2025/03
Iron reacts with hydrogen to form solid solutions with body-centered cubic, face-centered cubic, hexagonal close packed, and double hexagonal close packed structures at high temperatures and high pressures. Neutron diffraction is the most powerful tool for determining the occupation sites and occupancies of hydrogen atoms dissolved in a metal lattice. Structural parameters, including hydrogen occupation sites and occupancies, are refined via Rietveld analysis for neutron diffraction data. We present our expertise in Rietveld refinement of iron hydrides accumulated over 10 years.
Okazaki, Nobuo*; Hattori, Takanori
CROSS Reports (Internet), 3, p.001_1 - 001_8, 2025/02
There have been requests for remote analysis of measured data at the BL11 PLANET beamline in the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), but a system to perform this analysis on a regular basis has not been established. In order to meet this demand, a system for remote analysis was established using NoMachine, which is widely used as a remote desktop connection environment. This system is built on the cloud, and users can analyze data from anywhere with an Internet environment by using the NoMachine client.
Yang, X.*; Che, G.*; Wang, Y.*; Zhang, P.*; Tang, X.*; Lang, P.*; Gao, D.*; Wang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Nano Letters, 25(3), p.1028 - 1035, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Saturated sp -carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
-carbon nanothreads (CNTh) have garnered significant interest due to their predicted high Young's modulus and thermal conductivity. While the incorporation of heteroatoms into the central ring has been shown to influence the formation of CNTh and yield chemically homogeneous products, the impact of pendant groups on the polymerization process remains underexplored. In this study, we investigate the pressure-induced polymerization of phenol, revealing two phase transitions occurring below 0.5 and 4 GPa. Above 20 GPa, phenol polymerizes into degree-4 CNThs featuring hydroxyl and carbonyl groups. Hydrogen transfer of hydroxyl groups was found to hinder the formation of degree-6 nanothreads. Our findings highlight the crucial role of the hydroxyl group in halting further intracolumn polymerization and offer valuable insights for future mechanism research and nanomaterial synthesis.
Che, G.*; Fei, Y.*; Tang, X.*; Zhao, Z.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Wang, X.*; Ju, J.*; Dong, X.*; Wang, Y.*; et al.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 27(2), p.1112 - 1118, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:65.57(Chemistry, Physical)Pressure-induced polymerization (PIP) of aromatic molecules has emerged as an effective method for synthesizing various carbon-based materials. In this work, PIP of 1,4-difluorobenzene (1,4-DFB) was investigated.  high-pressure investigations of 1,4-DFB reveal a phase transition at approximately 12.0 GPa and an irreversible chemical reaction at 18.7 GPa. Structural analysis of the product and the kinetics of the reaction uncovered the formation of pseudohexagonal stacked fluoro-diamond nanothreads with linear growth. Compared to the crystal structures of benzene under high pressure, 1,4-DFB exhibits higher compression along the [001] axis. The anisotropic compression is attributed to the stronger H
high-pressure investigations of 1,4-DFB reveal a phase transition at approximately 12.0 GPa and an irreversible chemical reaction at 18.7 GPa. Structural analysis of the product and the kinetics of the reaction uncovered the formation of pseudohexagonal stacked fluoro-diamond nanothreads with linear growth. Compared to the crystal structures of benzene under high pressure, 1,4-DFB exhibits higher compression along the [001] axis. The anisotropic compression is attributed to the stronger H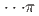 interaction along the [01
interaction along the [01 ] axis and the potential compression-inhibiting H
] axis and the potential compression-inhibiting H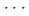 F interactions along the [100] and [010] axes, and it facilitates a possible reaction pathway along the [01
F interactions along the [100] and [010] axes, and it facilitates a possible reaction pathway along the [01 ] axis. This work emphasizes the crucial role of functionalization in modulating molecular stacking and influencing the reaction pathway.
] axis. This work emphasizes the crucial role of functionalization in modulating molecular stacking and influencing the reaction pathway.
Xu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Liang, S.*; Zhang, J.*; Fei, Y.*; Wang, Y.*; Gao, D.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Dong, X.*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), p.2445 - 2451, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)The Alder-ene reaction is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen, and it provides an efficient method to construct the C-C bond. Traditionally, this reaction requires catalysts, high temperatures, or photocatalysis. In this study, we reported a high-pressure-induced solid-state Alder-ene reaction of 1-hexene at room temperature without a catalyst. 1-Hexene crystallizes at 4.3 GPa and polymerizes at 18 GPa, forming olefins. By exploring gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, we discovered that 1-hexene generates dimeric products through the Alder-ene reaction under high pressures. The in situ neutron diffraction shows that the reaction process did not obey the topochemical rule. A six-membered ring transition state including one C-H  bond and two alkene
bond and two alkene  bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
Yamashita, Keishiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Machida, Shinichi*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
Acta Crystallographica Section B; Structural Science, Crystal Engineering and Materials (Internet), 80(6), p.695 - 705, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)So far, the odd hydration number has been missing in the water-rich magnesium chloride hydrate series (MgCl

 H
H O). In this study, we have identified magnesium chloride heptahydrate, MgCl
O). In this study, we have identified magnesium chloride heptahydrate, MgCl
 7H
7H O (or MgCl
O (or MgCl
 7D
7D O) which forms at high pressures and high temperatures of above 2 GPa and above 300 K, respectively. Its structure has been determined by a combination of
O) which forms at high pressures and high temperatures of above 2 GPa and above 300 K, respectively. Its structure has been determined by a combination of  single crystal X-ray diffraction at 2.5 GPa and 298 K and powder neutron diffraction at 3.1 GPa and 300 K. The results showed an orientational disorder of water molecules, which was also examined by the density-functional-theory calculations. The disorder involves the reconnection of hydrogen bonds, which differs from those in water ice phases and known disordered salt hydrates. The shrinkage by compression occurs mainly in one direction. In the plane perpendicular to this most compressible direction, oxygen and chlorine atoms are in a hexagonal-like arrangement.
single crystal X-ray diffraction at 2.5 GPa and 298 K and powder neutron diffraction at 3.1 GPa and 300 K. The results showed an orientational disorder of water molecules, which was also examined by the density-functional-theory calculations. The disorder involves the reconnection of hydrogen bonds, which differs from those in water ice phases and known disordered salt hydrates. The shrinkage by compression occurs mainly in one direction. In the plane perpendicular to this most compressible direction, oxygen and chlorine atoms are in a hexagonal-like arrangement.
Hattori, Takanori; Komatsu, Kazuki*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 66(12), p.618 - 622, 2024/12
, 66(12), p.618 - 622, 2024/12
The high-pressure neutron diffractometer PLANET is the first beamline dedicated to high-pressure neutron experiments in Japan. It was constructed at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) in the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) located at Tokai-mura in Ibaraki Prefecture. Energy-dispersive data measurement using pulsed neutrons, state-of-the-art optical instruments, and a high-pressure device enable us to analyze the structure of crystals, liquids, and glasses over a wide range of pressure and temperature with unprecedented accuracy. In this paper, we will show how this has been achieved and introduce the recently published results on the symmetrization of hydrogen bonds in ice.
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Sugimoto, Hidehiko*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Endo, Naruki*; Katayama, Yoshinori*; Iizuka, Riko*; Sato, Toyoto*; Matsuo, Motoaki*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.8861_1 - 8861_2, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In our previous article (Nature Commun. 5, 5063 (2014)), the site occupancies of D atoms dissolved in an fcc Fe metal lattice were investigated via Rietveld refinement of neutron powder diffraction patterns collected at 988 K and 6.3 GPa. The fcc metal lattice has two interstitial sites available for accommodating D atoms: octahedral and tetrahedral sites. The Rietveld refinement revealed that D atoms occupied mainly the octahedral sites with occupancy of 0.532 and slightly the tetrahedral sites with occupancy of 0.056. Subsequent density-functional-theory (DFT) calculations by Antonov (Phys. Rev. Mater. 2019)) showed that the occupation energy on the tetrahedral site was significantly higher than that on the octahedral site; the tetrahedral site occupation was unlikely to occur even at temperatures as high as 988 K. We reexamined the site occupancies of D-atom by Rietveld refinement including extinction correction. As a result, the octahedral occupancy was increased to 0.60 and the tetrahedral occupancy was reduced to zero. The occupation of only the octahedral site for D atom is consistent with the DFT calculation, although in contrast to the previous results.
 S
S under pressure
under pressureKosaka, Yusuke*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori
Koatsuryoku No Kagaku To Gijutsu, 34(3), p.121 - 126, 2024/09
Transition-metal intercalated dichalcogenides have attracted attention due to the observation of chiral helimagnetism (CHM) and chiral soliton lattice in CrNb S
S . It forms a chiral monoaxial crystal structure with a space group P6
. It forms a chiral monoaxial crystal structure with a space group P6 22. To examine the pressure effect on the CHM period of CrNb
22. To examine the pressure effect on the CHM period of CrNb S
S , we performed small-angle neutron scattering experiments with a piston-cylinder pressure cell up to 1.2 GPa. We observed a decrease in the magnetic transition temperature with increasing pressure. Moreover, the CHM period decreased with increasing pressure. Compared to the decrease of the lattice constant, that of the CHM period is much larger. This indicates that applying pressure weakens the amplitude of Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction.
, we performed small-angle neutron scattering experiments with a piston-cylinder pressure cell up to 1.2 GPa. We observed a decrease in the magnetic transition temperature with increasing pressure. Moreover, the CHM period decreased with increasing pressure. Compared to the decrease of the lattice constant, that of the CHM period is much larger. This indicates that applying pressure weakens the amplitude of Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction.
Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Nakano, Satoshi*; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Abe, Jun*
Koatsuryoku No Kagaku To Gijutsu, 34(3), p.134 - 142, 2024/09
A diamond anvil cell (DAC) for high-pressure neutron diffraction experiments has been developed at the PLANET beamline, Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility, in J-PARC. The conically supported diamond anvils were used for high-pressure generation. We succeeded in obtaining the neutron data for D O ice up to 69.4 GPa. In addition, the gasket materials suitable for the neutron diffraction measurements were investigated. 11 kinds of alloys were tested and SUS304, Inconel718 and M2052 (73Mn-20Cu-5Ni-2Fe, at%) alloys showed excellent performance. Especially, M2052 null-matrix alloy has proven to be useful for neutron diffraction experiments where the beam inevitably hits the gasket. We then obtained refinable neutron diffraction profiles in Rietveld analysis from D
O ice up to 69.4 GPa. In addition, the gasket materials suitable for the neutron diffraction measurements were investigated. 11 kinds of alloys were tested and SUS304, Inconel718 and M2052 (73Mn-20Cu-5Ni-2Fe, at%) alloys showed excellent performance. Especially, M2052 null-matrix alloy has proven to be useful for neutron diffraction experiments where the beam inevitably hits the gasket. We then obtained refinable neutron diffraction profiles in Rietveld analysis from D O ice at least up to 43.3 GPa.
O ice at least up to 43.3 GPa.
 -
- transitions
transitionsYang, Q.*; Yang, X.*; Wang, Y.*; Fei, Y.*; Li, F.*; Zheng, H.*; Li, K.*; Han, Y.*; Hattori, Takanori; Zhu, P.*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.7778_1 - 7778_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:88.46(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Luminescent materials that simultaneously embody bright singlet and triplet excitons hold great potential in optoelectronics, signage, and information encryption. However, achieving high-performance white-light emission is severely hampered by their inherent unbalanced contribution of fluorescence and phosphorescence. Herein, we address this challenge by pressure treatment engineering via hydrogen bonding cooperativity effect to realize the mixture of n- -
- transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
transitions, where the triplet state emission was boosted from 7% to 40% in isophthalic acid (IPA). A superior white-light emission based on hybrid fluorescence and phosphorescence was harvested in pressure-treated IPA, and the photoluminescence quantum yield was increased to 75% from the initial 19% (blue-light emission). In-situ high-pressure IR spectra, X ray diffraction, and neutron diffraction reveal continuous strengthening of the hydrogen bonds with the increase of pressure. Furthermore, this enhanced hydrogen bond is retained down to the ambient conditions after pressure treatment, awarding the targeted IPA efficient intersystem crossing for balanced singlet/triplet excitons population and resulting in efficient white-light emission. This work not only proposes a route for brightening triplet states in organic small molecule, but also regulates the ratio of singlet and triplet excitons to construct high-performance white-light emission.
He, X.*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iizuka, Riko*; Okajima, Hajime*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Goto, Hirotada*; et al.
Journal of Molecular Structure, 1310, p.138271_1 - 138271_8, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)High-pressure responses of the O-D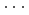 F hydrogen bonds in deuterated magnesium hydroxyfluoride were investigated using neutron powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The Rietveld analysis at ambient conditions revealed a chemical formula of Mg(OD)
F hydrogen bonds in deuterated magnesium hydroxyfluoride were investigated using neutron powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. The Rietveld analysis at ambient conditions revealed a chemical formula of Mg(OD)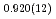 F
F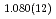 and hydroxyl group/fluorine disorder (OD/F disorder) in the crystal structure, which gave rise to two hydrogen-bonding configurations. The Rietveld analysis showed the hydrogen-bonding geometries remains up to 9.8 GPa, indicating no pressure-induced strengthening of hydrogen bonds. The Raman spectra at ambient conditions showed three hydroxyl stretching bands at 2613, 2694, and 2718 cm
and hydroxyl group/fluorine disorder (OD/F disorder) in the crystal structure, which gave rise to two hydrogen-bonding configurations. The Rietveld analysis showed the hydrogen-bonding geometries remains up to 9.8 GPa, indicating no pressure-induced strengthening of hydrogen bonds. The Raman spectra at ambient conditions showed three hydroxyl stretching bands at 2613, 2694, and 2718 cm . The high frequencies of the O-D stretching modes indicated that the hydroxyls should be involved in weak or none hydrogen-bonding interactions. Up to 20.2 GPa, the mode initially centered at 2694 cm
. The high frequencies of the O-D stretching modes indicated that the hydroxyls should be involved in weak or none hydrogen-bonding interactions. Up to 20.2 GPa, the mode initially centered at 2694 cm displayed a pressure-induced blue shift, revealing no strengthening of hydrogen bonds under compression. We discuss the existence of hydrogen bonds and the causes of the blue-shifting hydroxyls at ambient and at high pressures.
displayed a pressure-induced blue shift, revealing no strengthening of hydrogen bonds under compression. We discuss the existence of hydrogen bonds and the causes of the blue-shifting hydroxyls at ambient and at high pressures.
Zhang, Z.*; Hattori, Takanori; Song, R.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; Zhang, Z.*; Li, B.*
Journal of Applied Physics, 136(3), p.035105_1 - 035105_8, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:40.97(Physics, Applied)Solid-state refrigeration using barocaloric materials is environmentally friendly and highly efficient, making it a subject of global interest over the past decade. Here, we report giant barocaloric effects in sodium hexafluorophosphate (NaPF ) and sodium hexafluoroarsenate (NaAsF
) and sodium hexafluoroarsenate (NaAsF ) that both undergo a cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transition near room temperature. We have determined that the low-temperature phase structure of NaPF
) that both undergo a cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transition near room temperature. We have determined that the low-temperature phase structure of NaPF is a rhombohedral structure with space group R
is a rhombohedral structure with space group R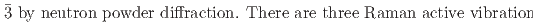 and NaAsF
and NaAsF , i.e., F
, i.e., F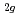 , E
, E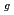 , and A
, and A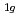 . The phase transition temperature varies with pressure at a rate of dT
. The phase transition temperature varies with pressure at a rate of dT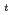 /dP = 250 and 310 K/GPa for NaPF
/dP = 250 and 310 K/GPa for NaPF and NaAsF
and NaAsF . The pressure-induced entropy changes of NaPF
. The pressure-induced entropy changes of NaPF and NaAsF
and NaAsF are determined to be around 45.2 and 35.6J kg
are determined to be around 45.2 and 35.6J kg K
K , respectively. The saturation driving pressure is about 40 MPa. The pressure-dependent neutron powder diffraction suggests that the barocaloric effects are related to the pressure-induced cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transitions.
, respectively. The saturation driving pressure is about 40 MPa. The pressure-dependent neutron powder diffraction suggests that the barocaloric effects are related to the pressure-induced cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transitions.
Hattori, Takanori; Suzuki, Koji*; Miyo, Tatsuya*; Ito, Takayoshi*; Machida, Shinichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1064, p.169448_1 - 169448_9, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The authors regret that the abstract and summary explain that the cup diameter of a standard double-toroidal anvils is 1.5 mm. This is incorrect; the standard diameter is 4.0 mm. The authors would like to apologise for any inconvenience caused.
 O ice observed by neutron diffraction
O ice observed by neutron diffractionKomatsu, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Klotz, S.*; Machida, Shinichi*; Yamashita, Keishiro*; Ito, Hayate*; Kobayashi, Hiroki*; Irifune, Tetsuo*; Shimmei, Toru*; Sano, Asami; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.5100_1 - 5100_7, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:72.77(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Hydrogen bond symmetrisation is the phenomenon where a hydrogen atom is located at the centre of a hydrogen bond. Theoretical studies predict that hydrogen bonds in ice VII eventually undergo symmetrisation upon increasing pressure, involving nuclear quantum effect with significant isotope effect and drastic changes in the elastic properties through several intermediate states with varying hydrogen distribution. Despite numerous experimental studies conducted, the location of hydrogen and hence the transition pressures reported up to date remain inconsistent. Here we report the atomic distribution of deuterium in D O ice using neutron diffraction above 100 GPa and observe for the first time the transition from a bimodal to a unimodal distribution of deuterium at around 80 GPa. At the transition pressure, a significant narrowing of the peak widths of 110 was also observed, attributed to the structural relaxation by the change of elastic properties.
O ice using neutron diffraction above 100 GPa and observe for the first time the transition from a bimodal to a unimodal distribution of deuterium at around 80 GPa. At the transition pressure, a significant narrowing of the peak widths of 110 was also observed, attributed to the structural relaxation by the change of elastic properties.