Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Honda, Mitsunori; Kaneta, Yui; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Goto, Takuya*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
Ten years have passed since the earthquake and nuclear power plant accident at 1F that occurred in 2011, and the contaminated soil generated in Fukushima Prefecture is now being managed as removed soil at intermediate storage facilities. In the course of developing technology to remove cesium from the removed soil, we have focused on the functionality of crystalline minerals after removal of cesium, and have been investigating their potential as thermoelectric materials. In this study, we report on the evaluation of thermoelectric properties (electrical conductivity, thermal diffusivity, and Seebeck coefficient) and structural analysis of crystalline minerals.
Honda, Mitsunori; Kaneta, Yui; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Goto, Takuya*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
Ten years have passed since the Great East Japan Earthquake and the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, and the contaminated soil generated in Fukushima Prefecture has been decontaminated and managed as removal soil. We have been conducting research on the volume reduction and recycling of Fukushima weathered biotite, which is known to be a strong adsorbent of radioactive Cs contained in the removed soil. In this study, thermoelectric properties (Seebeck coefficient, electrical conductivity, and thermal diffusivity) of soil clay minerals and molten salt-electrolyzed soil clay minerals were evaluated in order to clarify their properties as thermoelectric materials.
Wako, Toshinobu*; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Honda, Mitsunori
no journal, ,
This report investigates the effect of heat transfer due to contact with measurement terminals on the measurement results of thermoelectric material properties using heat transfer simulation. In thermoelectric conversion technology, miniaturization and thinning of elements are being studied for their compatibility with compact power supplies for the IoT, etc. In order to achieve this, it is necessary to accurately measure thermoelectric properties of minute materials, and it is essential to evaluate the results in the entire measurement system.
Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Matsumura, Hiroshi*; Wako, Toshinobu*; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Honda, Mitsunori
no journal, ,
We have been developing new thermoelectric materials from soil clay minerals treated by molten salt electrolysis, and have been evaluating their basic properties. In this study, we report the results of the measurement of thermal conductivity of soil clay minerals, which is essential for the determination of thermoelectric performance index.
Honda, Mitsunori; Kaneta, Yui; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Goto, Takuya*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
Twelve years have passed since the 1F accident that occurred in 2011, and contaminated soil generated in Fukushima Prefecture is being managed as removed soil. We have focused on the functionality of several crystalline minerals obtained in the process of developing a technology to remove Cs from the removed soil, and are examining their potential as thermoelectric conversion materials. In this study, we report on the evaluation of thermoelectric properties (electrical conductivity, thermal diffusivity, and Seebeck coefficient) of the crystalline minerals.
Honda, Mitsunori; Kaneta, Yui; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Iino, Chiaki*; Oda, Masato*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Goto, Takuya*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
no journal, ,
In this study, thermoelectric properties (electrical conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and thermal diffusivity) were evaluated (OZMA-1-S1) for polycrystalline minerals obtained by systematically changing the conditions of WB and the molten treatment. The Seebeck coefficient and thermal diffusivity were evaluated on the same sample. Macroscopic and microscopic structures were identified by various X-ray analyses and first-principles calculations. As for the electrical conductivity results of WB, the biotite material is usually known as an electrical insulator at room temperature, but after grinding, classification, molten salt treatment, and sintering, it was found to have electrical conductivity on the order of 1.49  10
10 (
( V/K) in the temperature range 650-850
V/K) in the temperature range 650-850 C, indicating that it has semiconducting electrical conductivity properties. Seebeck coefficient measurements in the same temperature range showed a high value of -2.0
C, indicating that it has semiconducting electrical conductivity properties. Seebeck coefficient measurements in the same temperature range showed a high value of -2.0 10
10 (
( V/K). Calculating the dimensionless performance index
V/K). Calculating the dimensionless performance index 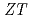 from the obtained results,
from the obtained results, 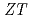 =0.29 was obtained. Regarding the thermoelectric property evaluation results for the molten salt treated polycrystalline minerals, higher electrical conductivity properties than WB were obtained for the same temperature range. These results suggest that WB can be used to show useful thermoelectric properties in the high temperature region above 650
=0.29 was obtained. Regarding the thermoelectric property evaluation results for the molten salt treated polycrystalline minerals, higher electrical conductivity properties than WB were obtained for the same temperature range. These results suggest that WB can be used to show useful thermoelectric properties in the high temperature region above 650 C.
C.
Hayakawa, Kosetsu; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Honda, Mitsunori
no journal, ,
Okumoto, Shunsuke*; Iino, Chiaki*; Oda, Masato*; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Honda, Mitsunori
no journal, ,
As part of research and development for environmental restoration of Fukushima, we have conducted study on Cs removal from weathered biotite using molten salt method. 99.9999% or less of Cs removal and formation of crystalline minerals such as ordinary Augite and wadalite were confirmed, but the atomic-level reaction mechanism of the reaction process and products is necessary. In this study, the stable structure of wadalite was investigated using first-principles calculations, and the reaction mechanism was investigated using the obtained stable structure.
Ono, Tatsumi*; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Oda, Masato*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Honda, Mitsunori; Muraguchi, Masakazu*
no journal, ,
The contact thermal resistance of each interface in the measurement of thermal conductivity using the one-way steady-state heat flow comparison method was decomposed into elements and extracted by performing actual measurements. This method provides a guideline for correcting errors in measurement results due to contact resistance between test rods. In the future, we will further improve the accuracy of the measurement system by correcting for contact thermal resistance.
Hayakawa, Kosetsu; Masebo, Yumeno*; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Kojima, Yoichiro*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Honda, Mitsunori
no journal, ,
Soil clay minerals are expected to be a new thermoelectric material in the high temperature range, but the mechanism of their thermoelectricity has not been clarified yet. We have focused on weathered biotite (WB), a soil clay mineral composed of elements such as Si, Fe, Al, Mg, and K. We have found that the structure of WB changes under high temperature conditions, which can be observed by infrared absorption spectroscopy. In-situ observation by infrared absorption spectroscopy has shown that the structure of WB changes under high temperature conditions. However, the detailed structure has not yet been identified. In this study, we developed a method for synchrotron XAFS analysis of WB at high temperatures, where thermoelectric properties are observed, and succeeded in obtaining data from room temperature up to 873K.
 intercalation into weathered biotite
intercalation into weathered biotiteMasebo, Yumeno*; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Honda, Mitsunori
no journal, ,
Natural minerals are expected as new thermoelectric materials, among which we focus on weathered biotite (WB), a kind of layered silicate mineral. WB consists of tetrahedral and octahedral sheets overlapping each other in layers, with interlayers between them. The interlayer contains K and other substances. However, the effect of the amount and type of interlayer material adsorbed on the structure has not yet been clarified. It has been known that Cs can intercalate into the interlayer of WB, but the amount of adsorption into the interlayer has not been fully investigated. In this study, we investigated the relationship between the amount of Cs adsorption and structure when Cs
can intercalate into the interlayer of WB, but the amount of adsorption into the interlayer has not been fully investigated. In this study, we investigated the relationship between the amount of Cs adsorption and structure when Cs was intercalated into WB, and obtained Cs adsorption amounts of 0.9%, 1.7%, 3.8%, and 4.8%. XRD analysis showed that the interlayer distance increased from 9.84
was intercalated into WB, and obtained Cs adsorption amounts of 0.9%, 1.7%, 3.8%, and 4.8%. XRD analysis showed that the interlayer distance increased from 9.84 , 9.91
, 9.91 , 9.90
, 9.90 to 9.92
to 9.92 as the adsorption amount increased.
as the adsorption amount increased.
Honda, Mitsunori; Kaneta, Yui; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Goto, Takuya*
no journal, ,
Our research focuses on the use of weathered biotite (WB) as an alternative material to thermoelectric materials, which have traditionally been made from rare and toxic elements. After WB was crushed and classified, crystals with conductivity comparable to that of Si semiconductors in the temperature range of 650-850 C were obtained by heat treatment using the molten salt method. In this study, we report on the results of the dimensionless evaluation index ZT calculated from the conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and thermal diffusion measurements in the high temperature range, and the thermal conductivity calculated from the specific heat and specific gravity.
C were obtained by heat treatment using the molten salt method. In this study, we report on the results of the dimensionless evaluation index ZT calculated from the conductivity, Seebeck coefficient, and thermal diffusion measurements in the high temperature range, and the thermal conductivity calculated from the specific heat and specific gravity.
Hayakawa, Kosetsu*; Masebo, Yumeno*; Muraguchi, Masakazu*; Kojima, Yoichiro*; Oda, Masato*; Iino, Chiaki*; Ishii, Hiroyuki*; Honda, Mitsunori
no journal, ,
We have been studying the development of functional materials derived from WB as an application of molten-salt treatment technology. We have experimentally demonstrated that Sr can be adsorbed on the interlayer of WB by molten-salt treatment. However, the correlation between Cs adsorption and Sr adsorption has not yet been clarified, although Sr adsorption was examined for Cs adsorbed WB in a previous study. Therefore, in this study, the amount and structure of Sr adsorption with and without Cs adsorption were investigated using XRF, XRD and XAFS. The results showed that the Sr adsorption dependence may differ depending on the presence or absence of Cs in WB.