Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samples
-edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samplesLi, W.*; Yamada, Shinya*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Sekizawa, Oki*; Suga, Hiroki*; Uruga, Tomoya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1240, p.340755_1 - 340755_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.9(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Okumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I.-H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(5), p.2101704_1 - 2101704_4, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.15(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A superconducting transition-edge sensor (TES) microcalorimeter is an ideal X-ray detector for experiments at accelerator facilities because of good energy resolution and high efficiency. To study the performance of the TES detector with a high-intensity pulsed charged-particle beam, we measured X-ray spectra with a pulsed muon beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in Japan. We found substantial temporal shifts of the X-ray energy correlated with the arrival time of the pulsed muon beam, which was reasonably explained by pulse pileup due to the incidence of energetic particles from the initial pulsed beam.
 X rays
X raysOkumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I. H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:79.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed electronic  X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic
X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic 
 and
and 
 X rays together with the hypersatellite
X rays together with the hypersatellite 
 X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the
X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the  -shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic
-shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic  - and
- and  -shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
-shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
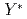 in nuclei through C
in nuclei through C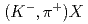 spectrum at 1.8 GeV/
spectrum at 1.8 GeV/ in the J-PARC E05 experiment
in the J-PARC E05 experimentHonda, Ryotaro*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hosomi, Kenji; Imai, Kenichi; Ichikawa, Yudai; Nanamura, Takuya; Naruki, Megumi; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 26, p.023014_1 - 023014_4, 2019/11
 Li
Li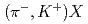 reaction to search for
reaction to search for 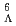 H
HHonda, Ryotaro*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Hosomi, Kenji; Ichikawa, Yudai; Imai, Kenichi; Nagamiya, Shoji; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Sugimura, Hitoshi; et al.
Physical Review C, 96(1), p.014005_1 - 014005_23, 2017/07
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:73.79(Physics, Nuclear)Hayakawa, Masato; Suzuki, Shigeaki*; Shimoyama, Kazuhito; Umeda, Ryota; Yoshida, Eiichi; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Shigeaki*; Hayakawa, Masato; Shimoyama, Kazuhito; Umeda, Ryota; Yoshida, Eiichi; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
We are conducting dismantling inspection of large-scale sodium component that we have been using in sodium environment for a long time. We got the cover gas area sodium deposition rate of the large tank used for several decades. As a result of examination based on the data and past findings, it was possible to derive the recommended value "1.0e-10 g/cm /s" for the cover gas region sodium adhesion rate of the plant operating in the low temperature range (150 to 200
/s" for the cover gas region sodium adhesion rate of the plant operating in the low temperature range (150 to 200 C). For disassembling large sodium equipment, it is possible to estimate and evaluate sodium adhesion amount based on this recommended value and operation history. With this evaluation, it became possible to increase the reliability of disassembly technology for safety measures and safety management related to sodium fires etc.
C). For disassembling large sodium equipment, it is possible to estimate and evaluate sodium adhesion amount based on this recommended value and operation history. With this evaluation, it became possible to increase the reliability of disassembly technology for safety measures and safety management related to sodium fires etc.
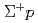 scattering events in the J-PARC E40 experiment
scattering events in the J-PARC E40 experimentNanamura, Takuya; Ichikawa, Yudai; Hayakawa, Shuhei; Yoshida, Junya; Miwa, Koji*; Honda, Ryotaro*; Akazawa, Yuya*; Yamamoto, Takeshi
no journal, ,
Hyperon-nucleon scattering experiment is one of the powerful methods for studying YN interaction. However, it is difficult due to short lifetime of hyperon. 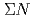 scattering experiments were performed as KEK E251 and KEK E289 in order to measure the differential cross sections. In these experiments, statistics were limited to less than 100 events and differential cross section had too large statistical errors to restrict baryon-baryon interaction models. J-PARC E40 experiment aims for measuring cross sections of
scattering experiments were performed as KEK E251 and KEK E289 in order to measure the differential cross sections. In these experiments, statistics were limited to less than 100 events and differential cross section had too large statistical errors to restrict baryon-baryon interaction models. J-PARC E40 experiment aims for measuring cross sections of 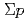 scatterings with high statistics (
scatterings with high statistics (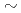 10000 events) by overcoming difficulties of hyperon-nucleon scattering experiment. By using high rate (
10000 events) by overcoming difficulties of hyperon-nucleon scattering experiment. By using high rate ( 19M /spill)
19M /spill)  beam and large acceptance spectrometer, we can produce and tag large amount of
beam and large acceptance spectrometer, we can produce and tag large amount of  beam. LH
beam. LH target and surrounding detector system CATCH enable us to reconstruct reactions from two body kinematics. Our experimental group completed
target and surrounding detector system CATCH enable us to reconstruct reactions from two body kinematics. Our experimental group completed 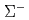 data taking and about half of
data taking and about half of 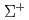 data taking by 2019 Apr. Left data taking will be performed in the end of this fiscal year.
data taking by 2019 Apr. Left data taking will be performed in the end of this fiscal year.
Yomogida, Takumi; Yamada, Shinya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; Sato, Toshiki*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Okada, Shinji*; Toyama, Yuichi*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Noda, Hirofumi*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Biotite is known as a host phase that retains uranium (U) in uranium deposits at Ningyo-Toge and Tono, and it is expected that the distribution of U in biotite will provide insight into the concentration and long-term immobilization of U. However, biotite contains rubidium (Rb), which interferes with X-ray fluorescence analysis, making it difficult to accurately determine the distribution of U-Rb in biotite by measurement using a conventional solid state detector (SSD). In this study, we developed a method to use a transition edge sensor (TES) as a detector in microbeam X-ray fluorescence analysis, which enables us to detect X-ray fluorescence with an energy resolution of about 20 eV and to obtain a Rb K line at 13.373 keV and a U L
line at 13.373 keV and a U L line at 13.612 keV can be completely separated. Therefore,the developed method enables us to accurately determine the distribution of U-Rb in biotite.
line at 13.612 keV can be completely separated. Therefore,the developed method enables us to accurately determine the distribution of U-Rb in biotite.
Yomogida, Takumi; Yamada, Shinya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; Sato, Toshiki*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Okada, Shinji*; Toyama, Yuichi*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Noda, Hirofumi*; Isobe, Tadaaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
The reduction of uranium on biotite was studied to obtain insight into the immobilization of uranium in the environment. The chemical species of uranium in biotite were studied using a superconducting transition edge sensor and an X-ray emission spectrometer to remove interference from rubidium in biotite. As a result, the speciation of uranium in biotite collected from former uranium deposits was possible. The XANES spectra of the biotite indicated that the uranium in the biotite was partially reduced.