Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Lan, Z.*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Morace, A.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Wei, T.*; Tatsumi, Yuta*; Koizumi, Mitsuo; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 15, p.5365_1 - 5365_7, 2024/07
 Ni
NiShizuma, Toshiyuki*; Omer, M.; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Minato, Futoshi*; Matsuba, Shunya*; Miyamoto, Shuji*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Utsuno, Yutaka
Physical Review C, 109(1), p.014302_1 - 014302_7, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.11(Physics, Nuclear) ,
,  , and X-ray spectrum analysis
, and X-ray spectrum analysisOshima, Masumi*; Goto, Jun*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Asai, Masato; Kin, Tadahiro*; Shinohara, Hirofumi*
Isotope News, (790), p.19 - 23, 2023/12
When analyzing samples that contain many radionuclides at various concentrations, such as radioactive waste or fuel debris, it is difficult to apply general spectrum analysis methods and is necessary to chemically separate each nuclide before quantifying it. The chemical separation is especially essential for analysis using a liquid scintillation counter (LSC). In this report, the authors explain the newly developed spectral determination method (SDM) in which the entire spectrum is fitted to quantify radioactivity of nuclides mixed in a sample. By applying the SDM to  - and X-ray spectrum measured by LSC and
- and X-ray spectrum measured by LSC and  -ray spectrum measured by Ge detector simultaneously, the authors demonstrated that radioactivity of 40 radionuclides mixed in a sample at concentrations varying by two orders could be quantified, which is useful to simplify chemical separation process in radionuclide quantification.
-ray spectrum measured by Ge detector simultaneously, the authors demonstrated that radioactivity of 40 radionuclides mixed in a sample at concentrations varying by two orders could be quantified, which is useful to simplify chemical separation process in radionuclide quantification.
 method
methodNauchi, Yasushi*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Kimura, Yasuhiko; Suyama, Kenya; Kashima, Takao*; Futakami, Kazuhiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1050, p.168109_1 - 168109_9, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Instruments & Instrumentation)Measurement of neutrons from spent nuclear fuel is performed in this study using the H method, which detects 2.223 MeV
method, which detects 2.223 MeV  rays from neutron capture reaction of hydrogen using a highly pure germanium (HPGe) detector. The detection of the 2.223 MeV
rays from neutron capture reaction of hydrogen using a highly pure germanium (HPGe) detector. The detection of the 2.223 MeV  ray is affected by intense
ray is affected by intense  ray emission from fission products (FPs) because the emission rate of
ray emission from fission products (FPs) because the emission rate of  rays from the FP is seven orders of magnitude higher than the emission rate of neutrons. To shield the intense
rays from the FP is seven orders of magnitude higher than the emission rate of neutrons. To shield the intense  ray from the FP, the HPGe detector is placed off the axis of a collimator, whereas a polyethylene block is placed on the axis. In this geometry, the detector is shielded from the intense
ray from the FP, the HPGe detector is placed off the axis of a collimator, whereas a polyethylene block is placed on the axis. In this geometry, the detector is shielded from the intense  rays from the FP, but the detector can measure 2.223 MeV
rays from the FP, but the detector can measure 2.223 MeV  rays from the H
rays from the H reactions in the polyethylene block. The measured count rate of the 2.223 MeV
reactions in the polyethylene block. The measured count rate of the 2.223 MeV  rays is consistent with the expected rate within the statistical error, which is calculated based on the nuclide composition, which is primary
rays is consistent with the expected rate within the statistical error, which is calculated based on the nuclide composition, which is primary  Cm, estimated via depletion and decay calculations. Accordingly, the H
Cm, estimated via depletion and decay calculations. Accordingly, the H method is considered feasible to quantify the number of neutron leakage from spent nuclear fuel assembly, which is applicable to certify burn up of the assembly.
method is considered feasible to quantify the number of neutron leakage from spent nuclear fuel assembly, which is applicable to certify burn up of the assembly.
Yogo, Akifumi*; Lan, Z.*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*; Mirfayzi, S. R.*; Wei, T.*; Mori, Takato*; Golovin, D.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Iwata, Natsumi*; et al.
Physical Review X, 13(1), p.011011_1 - 011011_12, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:93.39(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Cs activity in spent nuclear fuel with calculated detector response function
Cs activity in spent nuclear fuel with calculated detector response functionSato, Shunsuke*; Nauchi, Yasushi*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Kimura, Yasuhiko; Kashima, Takao*; Futakami, Kazuhiro*; Suyama, Kenya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.615 - 623, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new non-destructive method for evaluating  Cs activity in spent nuclear fuels was proposed and experimentally demonstrated for physical measurements in burnup credit implementation.
Cs activity in spent nuclear fuels was proposed and experimentally demonstrated for physical measurements in burnup credit implementation.  Cs activities were quantified using gamma ray measurements and numerical detector response simulations without reference fuels, in which
Cs activities were quantified using gamma ray measurements and numerical detector response simulations without reference fuels, in which  Cs activities are well known. Fuel samples were obtained from a lead use assembly (LUA) irradiated in a commercial pressurized water reactor (PWR) up to 53 GWd/t. Gamma rays emitted from the samples were measured using a bismuth germinate (BGO) scintillation detector through a collimator attached to a hot cell. The detection efficiency of gamma rays with the detector was calculated using the PHITS particle transport calculation code considering the measurement geometry. The relative activities of
Cs activities are well known. Fuel samples were obtained from a lead use assembly (LUA) irradiated in a commercial pressurized water reactor (PWR) up to 53 GWd/t. Gamma rays emitted from the samples were measured using a bismuth germinate (BGO) scintillation detector through a collimator attached to a hot cell. The detection efficiency of gamma rays with the detector was calculated using the PHITS particle transport calculation code considering the measurement geometry. The relative activities of  Cs,
Cs,  Cs, and
Cs, and  Eu in the sample were measured with a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector for more accurate simulations of the detector response for the samples. The absolute efficiency of the detector was calibrated by measuring a standard gamma ray source in another geometry.
Eu in the sample were measured with a high-purity germanium (HPGe) detector for more accurate simulations of the detector response for the samples. The absolute efficiency of the detector was calibrated by measuring a standard gamma ray source in another geometry.  Cs activity in the fuel samples was quantified using the measured count rate and detection efficiency. The quantified
Cs activity in the fuel samples was quantified using the measured count rate and detection efficiency. The quantified  Cs activities agreed well with those estimated using the MVP-BURN depletion calculation code.
Cs activities agreed well with those estimated using the MVP-BURN depletion calculation code.
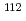 Cd(
Cd( )
) Cd reaction in an
Cd reaction in an  -process branching point
-process branching pointHayakawa, Takehito*; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Chiba, Satoshi*; Kajino, Toshitaka*
Physical Review C, 103(4), p.045801_1 - 045801_5, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.58(Physics, Nuclear) Pb
PbShizuma, Toshiyuki*; Minato, Futoshi; Omer, M.*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Miyamoto, Shuji*
Physical Review C, 103(2), p.024309_1 - 024309_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:54.40(Physics, Nuclear)Low-lying dipole transitions in  Pb were measured via nuclear photon scattering using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The electric (
Pb were measured via nuclear photon scattering using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The electric ( ) and magnetic (
) and magnetic ( ) dipole strengths were extracted for excitation energies up to 6.8 MeV. The present (
) dipole strengths were extracted for excitation energies up to 6.8 MeV. The present (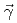 ,
,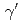 ) results, combined with (
) results, combined with ( ,
, ) data from the literature, were used to investigate the
) data from the literature, were used to investigate the  and
and  photoabsorption cross sections near the neutron separation energy by comparison with predictions of the particle-vibration coupling on top of the quasi-particle random phase approximation (PVC+QRPA).
photoabsorption cross sections near the neutron separation energy by comparison with predictions of the particle-vibration coupling on top of the quasi-particle random phase approximation (PVC+QRPA).
Hatsukawa, Yuichi*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Hashimoto, Kazuyuki*; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tanimori, Toru*; Sonoda, Shinya*; Kabuki, Shigeto*; et al.
PLOS ONE (Internet), 13(12), p.e0208909_1 - e0208909_12, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:29.51(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Imaging of  Tc radioisotope was conducted using an electron tracking-Compton camera (ETCC).
Tc radioisotope was conducted using an electron tracking-Compton camera (ETCC).  Tc emits 204, 582, and 835 keV
Tc emits 204, 582, and 835 keV  rays, and was produced in the
rays, and was produced in the  Mo(p,n)
Mo(p,n) Tc reaction with a
Tc reaction with a  Mo-enriched target. The recycling of the
Mo-enriched target. The recycling of the  Mo-enriched molybdenum trioxide was investigated, and the recycled yield of
Mo-enriched molybdenum trioxide was investigated, and the recycled yield of  Mo was achieved to be 70% - 90%. The images were obtained with each of the three
Mo was achieved to be 70% - 90%. The images were obtained with each of the three  rays. Results showed that the spatial resolution increases with increasing
rays. Results showed that the spatial resolution increases with increasing  -ray energy, and suggested that the ETCC with high-energy
-ray energy, and suggested that the ETCC with high-energy  -ray emitters such as
-ray emitters such as  Tc is useful for the medical imaging of deep tissue and organs in the human body.
Tc is useful for the medical imaging of deep tissue and organs in the human body.
 Cr
CrShizuma, Toshiyuki*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Daito, Izuru*; Ogaki, Hideaki*; Miyamoto, Shuji*; Minato, Futoshi
Physical Review C, 96(4), p.044316_1 - 044316_10, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:58.65(Physics, Nuclear)The low-lying dipole strength in  Cr was measured in nuclear resonance fluorescence experiments using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The parities of the excited dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered
Cr was measured in nuclear resonance fluorescence experiments using a quasi-monochromatic, linearly polarized photon beam. The parities of the excited dipole states were determined by the intensity asymmetry of resonantly scattered  -rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The summed magnetic dipole (M1) strength was determined as
-rays with respect to the polarization plane of the incident photon beam. The summed magnetic dipole (M1) strength was determined as 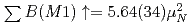 at excitation energies between 7.5 and 12.1 MeV; the summed electric dipole (E1) strength was obtained as
at excitation energies between 7.5 and 12.1 MeV; the summed electric dipole (E1) strength was obtained as 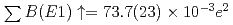 fm
fm . The observed M1 and E1 strengths were compared via random phase approximation calculations using the Skyrme interaction. The effects of 2 particle-2 hole configuration mixing and tensor force on dipole strength distributions were investigated.
. The observed M1 and E1 strengths were compared via random phase approximation calculations using the Skyrme interaction. The effects of 2 particle-2 hole configuration mixing and tensor force on dipole strength distributions were investigated.
 -ray beams
-ray beamsHayakawa, Takehito; Miyamoto, Shuji*; Hajima, Ryoichi; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Amano, So*; Hashimoto, Satoshi*; Misawa, Tsuyoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(12), p.2064 - 2071, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:48.81(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have proposed a new selective isotope transmutation method using photonuclear reactions with quasi-monochromatic  -ray beams. This method is based on the fact that the particle threshold of a long-lived fission product (LLFP) such as
-ray beams. This method is based on the fact that the particle threshold of a long-lived fission product (LLFP) such as  Zr,
Zr,  Pd, or
Pd, or  Se is lower than those of stable isotopes of the same chemical element. Therefore, this method has an excellent advantage that LLFPs cannot, in principle, be produced newly even if the target materials include stable isotopes in addition to a LLFP. Laser Compton scattering
Se is lower than those of stable isotopes of the same chemical element. Therefore, this method has an excellent advantage that LLFPs cannot, in principle, be produced newly even if the target materials include stable isotopes in addition to a LLFP. Laser Compton scattering  -ray sources and neutron capture
-ray sources and neutron capture  -rays in nuclear reactors are candidates for this method.
-rays in nuclear reactors are candidates for this method.
 Cd(
Cd( )
) Cd reaction using neutron beams at J-PARC
Cd reaction using neutron beams at J-PARCHayakawa, Takehito*; Toh, Yosuke; Huang, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Harada, Hideo; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Chiba, Satoshi*; Kajino, Toshitaka*
Physical Review C, 94(5), p.055803_1 - 055803_6, 2016/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.12(Physics, Nuclear)Omer, M.; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Angell, C.*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Seya, Michio; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2016/07
Isotope-specific  -rays emitted in the nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) process provide a good technique for a non-destructive detection and assay of nuclear materials. We are developing technologies relevant to
-rays emitted in the nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF) process provide a good technique for a non-destructive detection and assay of nuclear materials. We are developing technologies relevant to  -ray nondestructive detection and assay utilizing NRF. A Monte Carlo code to simulate NRF process is necessary for design and evaluation of NDA systems. We are developing NRFGeant4, a Geant4-based simulation code, for this purpose. In NRF experiments, highly-enriched targets are generally used such that the NRF signals are dominant and easily measured. In contrast, a real situation may involve very small contents of isotopes of interest. This results in a difficulty in measuring NRF signals because of the interference with other interactions, e.g. elastic scattering. For example, a typical nuclear fuel pellet contains about 90% of
-ray nondestructive detection and assay utilizing NRF. A Monte Carlo code to simulate NRF process is necessary for design and evaluation of NDA systems. We are developing NRFGeant4, a Geant4-based simulation code, for this purpose. In NRF experiments, highly-enriched targets are generally used such that the NRF signals are dominant and easily measured. In contrast, a real situation may involve very small contents of isotopes of interest. This results in a difficulty in measuring NRF signals because of the interference with other interactions, e.g. elastic scattering. For example, a typical nuclear fuel pellet contains about 90% of  U as a host material and less than 1% of
U as a host material and less than 1% of  Pu as an isotope of interest. When measuring NRF of
Pu as an isotope of interest. When measuring NRF of  Pu, there would be a huge background coming from the elastic scattering of
Pu, there would be a huge background coming from the elastic scattering of  U. Therefore, an estimation of the elastic scattering with the host material is essential for precise determination of isotope of interest. Satisfying estimation of elastic scattering is currently not available except for some calculations. In the present study, we upgrade our simulation code to include the calculation of elastic scattering events.
U. Therefore, an estimation of the elastic scattering with the host material is essential for precise determination of isotope of interest. Satisfying estimation of elastic scattering is currently not available except for some calculations. In the present study, we upgrade our simulation code to include the calculation of elastic scattering events.
Hayakawa, Takehito; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Harada, Hideo
EPJ Web of Conferences, 122, p.05003_1 - 05003_5, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.06(Physics, Nuclear)Many isotopes heavier than iron are synthesized by the slow neutron capture reaction process (s-process) in stars. Isomers in stable isotopes have sometimes an important role as a branching point. An isomer with a half-life of 14.1 y in  Cd is a branching point from which a nucleosynthesis flow reaches to a rare isotope
Cd is a branching point from which a nucleosynthesis flow reaches to a rare isotope  Sn. The astrophysical origin of
Sn. The astrophysical origin of  Sn has remained still an open question. The s-process abundance of
Sn has remained still an open question. The s-process abundance of  Sn depends on the ratio of the
Sn depends on the ratio of the 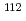 Cd(n,
Cd(n,  )
) Cdm reaction cross section to the
Cdm reaction cross section to the 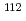 Cd(n,
Cd(n,  )
) Cd
Cd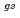 reaction cross section. However, the isomer production ratio has not been measured in the energy region higher than the thermal energy. We measured
reaction cross section. However, the isomer production ratio has not been measured in the energy region higher than the thermal energy. We measured  -rays using the HPGe detectors with neutrons at ANNRI.
-rays using the HPGe detectors with neutrons at ANNRI.
 Fe(
Fe( , n)
, n) Fe reaction with a linearly polarized
Fe reaction with a linearly polarized  -ray beam
-ray beamHayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Miyamoto, Shuji*; Amano, Sho*; Takemoto, Akinori*; Yamaguchi, Masashi*; Horikawa, Ken*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Chiba, Satoshi*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
Physical Review C, 93(4), p.044313_1 - 044313_4, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:48.70(Physics, Nuclear)We have measured the azimuthal anisotropy of neutrons emitted from the  Fe(
Fe( , n)
, n) Fe reaction with a linearly polarized
Fe reaction with a linearly polarized  ray beam generated by laser Compton scattering at NewSUBARU. Neutron yields at the polar angle of 90
ray beam generated by laser Compton scattering at NewSUBARU. Neutron yields at the polar angle of 90 have been measured as a function of the azimuthal angle
have been measured as a function of the azimuthal angle  between the detector and the linear polarization plane of the ray beam. The azimuthal anisotropy of neutrons measured at seven angles has been well reproduced using a theoretically predicted function of
between the detector and the linear polarization plane of the ray beam. The azimuthal anisotropy of neutrons measured at seven angles has been well reproduced using a theoretically predicted function of  +
+  cos(2
cos(2 ).
).
 -ray beams
-ray beamsHajima, Ryoichi; Sawamura, Masaru; Nagai, Ryoji; Nishimori, Nobuyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Angell, C.
Proceedings of 12th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.79 - 83, 2015/09
Generation of energy-tunable narrow-bandwidth  -rays via Laser Compton Scattering (LCS) is of great interest for scientific studies and applications of MeV photons which interact with nuclei. We are developing technologies relevant to generation of high-brightness LCS
-rays via Laser Compton Scattering (LCS) is of great interest for scientific studies and applications of MeV photons which interact with nuclei. We are developing technologies relevant to generation of high-brightness LCS  -ray beams. One of the promising applications of such
-ray beams. One of the promising applications of such  -rays is the nondestructive detection and assay of nuclides which are necessary for nuclear security and safeguards. We summarize R-and-D status of LCS
-rays is the nondestructive detection and assay of nuclides which are necessary for nuclear security and safeguards. We summarize R-and-D status of LCS  -ray sources and overview future applications.
-ray sources and overview future applications.
 -ray, positron, and neutron source from ultra-intense laser-matter interactions
-ray, positron, and neutron source from ultra-intense laser-matter interactionsNakamura, Tatsufumi*; Hayakawa, Takehito
Physics of Plasmas, 22(8), p.083113_1 - 083113_6, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:40.64(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In ultra-intense laser-matter interactions,  -rays are effectively generated via the radiation reaction effect. Since a significant fraction of the laser energy is converted into
-rays are effectively generated via the radiation reaction effect. Since a significant fraction of the laser energy is converted into  -rays, understanding of the energy transport inside of the target is important. We have developed a Particle-in-Cell code which includes generation of the
-rays, understanding of the energy transport inside of the target is important. We have developed a Particle-in-Cell code which includes generation of the  -rays, their energy transport, and photo-nuclear reactions. Using the code, we have proposed a collimated, mono-energetic positron beams with hundreds of MeV are generated by using thick targets. Neutron beams are also effectively generated by using beryllium targets via photo-nuclear reactions.
-rays, their energy transport, and photo-nuclear reactions. Using the code, we have proposed a collimated, mono-energetic positron beams with hundreds of MeV are generated by using thick targets. Neutron beams are also effectively generated by using beryllium targets via photo-nuclear reactions.
Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hajima, Ryoichi; Hayakawa, Takehito; Angell, C.; Seya, Michio
Proceedings of 37th ESARDA Annual Meeting (Internet), p.838 - 845, 2015/08
Nondestructive assay (NDA) of nuclear materials is an important technology for nuclear security and safeguard applications. We have proposed an NDA system based on nuclear resonance fluorescence (NRF). In the proposed detection system, an energy-tunable and mono-energetic  -ray source generated by Compton scattering of laser light (laser Compton scattering; LCS) with high-energy electrons is used. The NRF measurement can be more efficient by using a mono-energetic
-ray source generated by Compton scattering of laser light (laser Compton scattering; LCS) with high-energy electrons is used. The NRF measurement can be more efficient by using a mono-energetic  -ray beam, which has been demonstrated in recent NRF measurements. We have started a research and development program of the LCS
-ray beam, which has been demonstrated in recent NRF measurements. We have started a research and development program of the LCS  -ray NDA systems, which includes demonstration of LCS
-ray NDA systems, which includes demonstration of LCS  -ray generation from an energy recovery linac (ERL), establishment of detection system, and benchmark of Monte Carlo simulation. The R&D status including recent results on the demonstrations of the LCS photon generation as well as the measurement principles will be reported.
-ray generation from an energy recovery linac (ERL), establishment of detection system, and benchmark of Monte Carlo simulation. The R&D status including recent results on the demonstrations of the LCS photon generation as well as the measurement principles will be reported.
Angell, C.; Hayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Hajima, Ryoichi; Quiter, B. J.*; Ludewigt, B. L.*; Karwowski, H. J.*; Rich, G.*; Silano, J.*
Proceedings of INMM 56th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/07
 -rays
-raysHayakawa, Takehito; Miyamoto, Shuji*
Isotope News, (734), p.12 - 16, 2015/06
It was predicted in 1950's that the neutron angular distribution in ( ,n) reactions with a 100% linearly polarized
,n) reactions with a 100% linearly polarized  -ray beam for dipole excitation should be anisotropic.However, it has not been experimentally confirmed over half a century becuase of the lack of useful linear polarized
-ray beam for dipole excitation should be anisotropic.However, it has not been experimentally confirmed over half a century becuase of the lack of useful linear polarized  -ray beam. The laser Compton scattering (LCS)
-ray beam. The laser Compton scattering (LCS)  -ray beam has been developed. We can use almost 100% linear polarized photon beam. We have verified experimentally the neutron angular distribution on
-ray beam has been developed. We can use almost 100% linear polarized photon beam. We have verified experimentally the neutron angular distribution on  Au,
Au,  I, and natural Cu using linearly polarized laser Compton scattering
I, and natural Cu using linearly polarized laser Compton scattering  -rays at NewSUBARU. The result suggests the (polarized
-rays at NewSUBARU. The result suggests the (polarized  ,n) reaction is a novel tool to study the nuclear physics.
,n) reaction is a novel tool to study the nuclear physics.