Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Jiang, X.*; Hattori, Takanori; Xu, X.*; Li, M.*; Yu, C.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; Yano, Shinichiro*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; et al.
Materials Horizons, 10(3), p.977 - 982, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:87.86(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)As a promising environment-friendly alternative to current vapor-compression refrigeration, solid-state refrigeration based on the barocaloric effect has been attracting world wide attention. Generally, both phases in which a barocaloric effect occurs are present at ambient pressure. Here, instead, we demonstrate that KPF exhibits a colossal barocaloric effect due to the creation of a high-pressure rhombohedral phase. The phase diagram is constructed based on pressure-dependent calorimetric, Raman scattering, and neutron diffraction measurements. The present study is expected to provide an alternative routine to colossal barocaloric effects through the creation of a high-pressure phase.
exhibits a colossal barocaloric effect due to the creation of a high-pressure rhombohedral phase. The phase diagram is constructed based on pressure-dependent calorimetric, Raman scattering, and neutron diffraction measurements. The present study is expected to provide an alternative routine to colossal barocaloric effects through the creation of a high-pressure phase.
 mesocrystal formation
mesocrystal formationLi, Z.*; Piankova, D.*; Yang, Y.*; Kumagai, Yuta; Zschiesche, H.*; Jonsson, M.*; Tarakina, N. V.*; Soroka, I. L.*
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 61(6), p.e202112204_1 - e202112204_9, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.82(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The role of intermediate phases in CeO mesocrystal formation from aqueous Ce(III) solutions subjected to
mesocrystal formation from aqueous Ce(III) solutions subjected to  -radiation was studied. Radiolytically formed hydroxyl radicals convert soluble Ce(III) into less soluble Ce(IV). Transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction studies of samples from different stages of the process allowed the identification of several stages in CeO
-radiation was studied. Radiolytically formed hydroxyl radicals convert soluble Ce(III) into less soluble Ce(IV). Transmission electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction studies of samples from different stages of the process allowed the identification of several stages in CeO mesocrystal evolution following the oxidation to Ce(IV): (1) formation of hydrated Ce(IV)-hydroxides, serving as intermediates in the liquid-to-solid phase transformation; (2) CeO
mesocrystal evolution following the oxidation to Ce(IV): (1) formation of hydrated Ce(IV)-hydroxides, serving as intermediates in the liquid-to-solid phase transformation; (2) CeO primary particle growth inside the intermediate phase; (3) alignment of the primary particles into "pre-mesocrystals" and subsequently to mesocrystals, guided by confinement of the amorphous intermediate phase and accompanied by the formation of mineral bridges. Further alignment of the obtained mesocrystals into supracrystals occurs upon slow drying, making it possible to form complex hierarchical architectures.
primary particle growth inside the intermediate phase; (3) alignment of the primary particles into "pre-mesocrystals" and subsequently to mesocrystals, guided by confinement of the amorphous intermediate phase and accompanied by the formation of mineral bridges. Further alignment of the obtained mesocrystals into supracrystals occurs upon slow drying, making it possible to form complex hierarchical architectures.
 =
=  one-dimensional Ising-like antiferromagnet BaCo
one-dimensional Ising-like antiferromagnet BaCo V
V O
O
Kimura, Shojiro*; Onishi, Hiroaki; Okutani, Akira*; Akaki, Mitsuru*; Narumi, Yasuo*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Okunishi, Koichi*; Kindo, Koichi*; He, Z.*; Taniyama, Tomoyasu*; et al.
Physical Review B, 105(1), p.014417_1 - 014417_9, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:34.67(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Naeem, M.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Lin, W.*; Kai, J.-J.*; Wu, Z.*; Lan, S.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Acta Materialia, 221, p.117371_1 - 117371_18, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:94.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Naeem, M.*; Zhou, H.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; Zhu, Y.*; Wang, X.-L.*
Applied Physics Letters, 119(13), p.131901_1 - 131901_7, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:62.1(Physics, Applied)He, H.*; Naeem, M.*; Zhang, F.*; Zhao, Y.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Wang, B.*; Wu, X.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; et al.
Nano Letters, 21(3), p.1419 - 1426, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:95.34(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Naeem, M.*; He, H.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Zhang, F.*; Wang, B.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; Wu, Y.*; Lu, Z.*; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 188, p.21 - 25, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:56 Percentile:97.51(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)
Guo, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Kawamura, Seiko; Ling, L.*; Wang, J.*; He, L.*; Nakajima, Kenji; Li, B.*; Zhang, Z.*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 4(6), p.064410_1 - 064410_7, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:48.03(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Naeem, M.*; He, H.*; Zhang, F.*; Huang, H.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Wang, B.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 6(13), p.eaax4002_1 - eaax4002_8, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:145 Percentile:99.09(Multidisciplinary Sciences) -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, X.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Zhao, E.*; Zhang, Z.*; Guide, T.*; Le, M. D.*; Avdeev, M.*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Kofu, Maiko; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.942_1 - 942_9, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:90.35(Multidisciplinary Sciences)In high-performance thermoelectric materials, there are two main low thermal conductivity mechanisms: the phonon anharmonic and phonon scattering resulting from the dynamic disorder, which have been successfully revealed by inelastic neutron scattering. Using neutron scattering and ab initio calculations, we report here a mechanism of static local structure distortion combined with phonon-anharmonic-induced ultralow lattice thermal conductivity in  -MgAgSb. Since the transverse acoustic phonons are almost fully scattered by the intrinsic distorted rocksalt sublattice in this compound, the heat is mainly transported by the longitudinal acoustic phonons. The ultralow thermal conductivity in
-MgAgSb. Since the transverse acoustic phonons are almost fully scattered by the intrinsic distorted rocksalt sublattice in this compound, the heat is mainly transported by the longitudinal acoustic phonons. The ultralow thermal conductivity in  -MgAgSb is attributed to its atomic dynamics being altered by the structure distortion, which presents a possible microscopic route to enhance the performance of similar thermoelectric materials.
-MgAgSb is attributed to its atomic dynamics being altered by the structure distortion, which presents a possible microscopic route to enhance the performance of similar thermoelectric materials.
 decay of
decay of 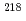 At
AtCubiss, J. G.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Barzakh, A. E.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; Day Goodacre, T.*; Fedorov, D. V.*; Fedosseev, V. N.*; Ferrer, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(6), p.064317_1 - 064317_6, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:53.97(Physics, Nuclear)An  decay of
decay of 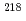 At was studied at the CERN-ISOLDE facility using a laser-ionization technique. Coincidence
At was studied at the CERN-ISOLDE facility using a laser-ionization technique. Coincidence  -
- data were collected for the first time and a more precise half-life value of T
data were collected for the first time and a more precise half-life value of T = 1.27(6) s was measured. A new
= 1.27(6) s was measured. A new  -decay scheme was deduced based on the fine-structure of the
-decay scheme was deduced based on the fine-structure of the  decay. The results lead to a preferred spin and parity assignment of J
decay. The results lead to a preferred spin and parity assignment of J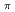 = (3
= (3 ) for the ground state of
) for the ground state of 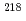 At; however, J
At; however, J = (2)
= (2) cannot be fully excluded.
cannot be fully excluded.
 At revealed by in-source laser spectroscopy
At revealed by in-source laser spectroscopyBarzakh, A. E.*; Cubiss, J. G.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Seliverstov, M. D.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Ascher, P.*; Atanasov, D.*; Beck, D.*; Biero , J.*; et al.
, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(5), p.054317_1 - 054317_9, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:77.09(Physics, Nuclear) Ge
Ge
Wo, H.*; Wang, Q.*; Shen, Y.*; Zhang, X.*; Hao, Y.*; Feng, Y.*; Shen, S.*; He, Z.*; Pan, B.*; Wang, W.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 122(21), p.217003_1 - 217003_5, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:42.69(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -spectroscopy at an intense cold neutron beam facility
-spectroscopy at an intense cold neutron beam facilityJentschel, M.*; Blanc, A.*; de France, G.*; K ster, U.*; Leoni, S.*; Mutti, P.*; Simpson, G.*; Soldner, T.*; Ur, C.*; Urban, W.*; et al.
ster, U.*; Leoni, S.*; Mutti, P.*; Simpson, G.*; Soldner, T.*; Ur, C.*; Urban, W.*; et al.
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 12(11), p.P11003_1 - P11003_33, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:84.92(Instruments & Instrumentation)Li, Z.*; He, T.*; Matsumura, Daiju; Miao, S.*; Wu, A.*; Liu, L.*; Wu, G.*; Chen, P.*
ACS Catalysis, 7(10), p.6762 - 6769, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:158 Percentile:96.49(Chemistry, Physical) Kr
KrFlavigny, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Delaroche, J.-P.*; Girod, M.*; Libert, J.*; Rodriguez, T. R.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Calvet, D.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 118(24), p.242501_1 - 242501_6, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:38 Percentile:86.73(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Zr
ZrPaul, N.*; Corsi, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Authelet, G.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Bally, B.*; Bender, M.*; Calvet, D.*; Ch teau, F.*; et al.
teau, F.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 118(3), p.032501_1 - 032501_7, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:88.64(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -delayed fission and
-delayed fission and  decay of
decay of  At
AtTruesdale, V. L.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ghys, L.*; Huyse, M.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Sels, S.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Barzakh, A.*; Capponi, L.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 94(3), p.034308_1 - 034308_11, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.43(Physics, Nuclear) and W(CO)
and W(CO)
Usoltsev, I.*; Eichler, R.*; Wang, Y.*; Even, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 104(3), p.141 - 151, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:95.03(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Conditions of the production and decomposition of hexacarbonyl complexes of short-lived Mo and W isotopes were investigated to study thermal stability of the heaviest group 6 hexacarbonyl complex Sg(CO) . A tubular flow reactor was tested to decompose the hexacarbonyl complexes and to extract the first bond dissociation energies. A silver was found to be the most appropriate reaction surface to study the decomposition of the group 6 hexacarbonyl. It was found that the surface temperature at which the decomposition occurred was correlated to the first bond dissociation energy of Mo(CO)
. A tubular flow reactor was tested to decompose the hexacarbonyl complexes and to extract the first bond dissociation energies. A silver was found to be the most appropriate reaction surface to study the decomposition of the group 6 hexacarbonyl. It was found that the surface temperature at which the decomposition occurred was correlated to the first bond dissociation energy of Mo(CO) and W(CO)
and W(CO) , indicating that the first bond dissociation energy of Sg(CO)
, indicating that the first bond dissociation energy of Sg(CO) could be determined with this technique.
could be determined with this technique.
Even, J.*; Ackermann, D.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(3), p.2457 - 2466, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.56(Chemistry, Analytical)Rapid In situ synthesis of metal carbonyl complexes has been demonstrated using short-lived isotopes produced in nuclear fission and fusion reactions. The short-lived isotopes with high recoil energy directly react with carbon-monoxides and form carbonyl complexes. Only highly volatile complexes were fast transported in a gas stream to counting and chemistry devices. Short-lived Mo, Tc, Ru, Rh, W, Re, Os, and Ir were found to form volatile carbonyl complexes, while no volataile complex of Hf and Ta were detected. This technique has been applied to a chemical investigation of the superheavy element Sg (atomic number 106), and will be applicable to various fields of nuclear science with short-lived transition metal isotopes.