Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 signatures in two-dimensional cone beam interferometry
signatures in two-dimensional cone beam interferometrySarenac, D.*; Gorbet, G.*; Clark, C. W.*; Cory, D. G.*; Ekinci, H.*; Henderson, M. E.*; Huber, M. G.*; Hussey, D. S.*; Kapahi, C.*; Kienzle, P. A.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(3), p.L032054_1 - L032054_8, 2024/09
Sarenac, D.*; Gorbet, G.*; Kapahi, C.*; Clark, C. W.*; Cory, D. G.*; Ekinci, H.*; Garrad, D. V.*; Henderson, M. E.*; Huber, M. G.*; Hussey, D.*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 6(2), p.023260_1 - 023260_15, 2024/06
 Ca studied with fusion reactions induced by a reaccelerated rare isotope beam
Ca studied with fusion reactions induced by a reaccelerated rare isotope beamAsh, J.*; Iwasaki, Hironori*; Mijatovi , T.*; Budner, T.*; Elder, R.*; Elman, B.*; Friedman, M.*; Gade, A.*; Grinder, M.*; Henderson, J.*; et al.
, T.*; Budner, T.*; Elder, R.*; Elman, B.*; Friedman, M.*; Gade, A.*; Grinder, M.*; Henderson, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 103(5), p.L051302_1 - L051302_6, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:35.67(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 98 in multi-nucleon transfer reactions of
98 in multi-nucleon transfer reactions of  Ca+
Ca+ Cm
CmDevaraja, H. M.*; Heinz, S.*; Beliuskina, O.*; Hofmann, S.*; Hornung, C.*; M nzenberg, G.*; Ackermann, D.*; Gupta, M.*; Gambhir, Y. K.*; Henderson, R. A.*; et al.
nzenberg, G.*; Ackermann, D.*; Gupta, M.*; Gambhir, Y. K.*; Henderson, R. A.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 55(2), p.25_1 - 25_9, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.80(Physics, Nuclear)Hofmann, S.*; Heinz, S.*; Mann, R.*; Maurer, J.*; M nzenberg, G.*; Antalic, S.*; Barth, W.*; Burkhard, K. G.*; Dahl, L.*; Eberhardt, K.*; et al.
nzenberg, G.*; Antalic, S.*; Barth, W.*; Burkhard, K. G.*; Dahl, L.*; Eberhardt, K.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 52(6), p.180_1 - 180_34, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:200 Percentile:93.94(Physics, Nuclear)Hofmann, S.*; Heinz, S.*; Mann, R.*; Maurer, J.*; M nzenberg, G.*; Antalic, S.*; Barth, W.*; Dahl, L.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Grzywacz, R.*; et al.
nzenberg, G.*; Antalic, S.*; Barth, W.*; Dahl, L.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Grzywacz, R.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 52(4), p.116_1 - 116_12, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:87.07(Physics, Nuclear) 92 in multinucleon transfer reactions
92 in multinucleon transfer reactionsDevaraja, H. M.*; Heinz, S.*; Beliuskina, O.*; Comas, V. F.*; Hofmann, S.*; Hornung, C.*; M nzenberg, G.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ackermann, D.*; Gambhir, Y. K.*; et al.
nzenberg, G.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ackermann, D.*; Gambhir, Y. K.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 748, p.199 - 203, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:73 Percentile:96.87(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Takahashi, Koji; Kajiwara, Ken; Oda, Yasuhisa; Sakamoto, Keishi; Omori, Toshimichi*; Henderson, M.*
Fusion Science and Technology, 67(4), p.718 - 731, 2015/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.44(Nuclear Science & Technology)Development of an electron cyclotron (EC) equatorial launcher has been undergoing a series of prototype tests and design enhancements intending to improve reliability and functionality of the launcher. The design enhancements include adaptation of the launcher steering angles such that one of three beam rows of the launcher is necessary flipped to perform counter current drive (to conform to a new ITER physics requirement). Also the top and bottom steering rows have been tilted with angle of 5 so that the top and bottom beam row can access from on axis to near mid-radius. Furthermore, the position of the focusing mirror that forms a quasi-optical in-vessel millimeter wave transmission line is modified to increase the nuclear shielding capability. High power experiment of the mm-wave launching system mock-up fabricated in basis of the design confirmed the successful steering capability of 20
so that the top and bottom beam row can access from on axis to near mid-radius. Furthermore, the position of the focusing mirror that forms a quasi-optical in-vessel millimeter wave transmission line is modified to increase the nuclear shielding capability. High power experiment of the mm-wave launching system mock-up fabricated in basis of the design confirmed the successful steering capability of 20
 40
40 . It was measured that some of stray RF propagated in the beam duct and generated some heat on the duct at a certain condition of mm-wave transmission. Prototype tests also include the fabrication of the blanket shield module and the partial port plug mock-up and have shown no serious technological issue on the fabrication and the cooling functionality.
. It was measured that some of stray RF propagated in the beam duct and generated some heat on the duct at a certain condition of mm-wave transmission. Prototype tests also include the fabrication of the blanket shield module and the partial port plug mock-up and have shown no serious technological issue on the fabrication and the cooling functionality.
Takahashi, Koji; Iida, Hiromasa*; Kobayashi, Noriyuki*; Kajiwara, Ken; Sakamoto, Keishi; Omori, Toshimichi*; Henderson, M.*
Fusion Science and Technology, 63(1T), p.156 - 159, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Nuclear analysis of the ITER equatorial EC launcher has been carried out to determine heat and/or particle loads on its components and also to evaluate the possibility of "hands-on maintainability" (personnel accessibility) to the launcher back-end. Monte Carlo code "MCNP5" is applied to simulate the radiation leak from fusion plasma to the special region around the launcher. The results indicate a significant radiation leak at the gaps between the port walls and port plug frame and at the waveguide bundles in the launcher. Another significant neutron leakage is through the port wall consisting of only stainless steel but without light isotopes such as water. The shut down dose rates was estimated at the port interspace behind the launcher at the level of the required value of 100  Sv/h. This analysis offers the potential to modify the launchers shielding layout to minimize the above leakage and further reduce the shut down dose rates in the regions of personnel access.
Sv/h. This analysis offers the potential to modify the launchers shielding layout to minimize the above leakage and further reduce the shut down dose rates in the regions of personnel access.
Takahashi, Koji; Kajiwara, Ken; Oda, Yasuhisa; Kobayashi, Noriyuki*; Sakamoto, Keishi; Omori, Toshimichi*; Henderson, M.*
Proceedings of 24th IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2012) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/03
The ITER equatorial EC launcher is making a large technology to injecting  20 M and CW operation. The design of the shield blanket structure that tolerates thermal and electromagnetic load is attained. The port plug structure considering the fabrication process applying HIP and TIG-welding are designed. The mm-wave design that enables to guide the wave power of
20 M and CW operation. The design of the shield blanket structure that tolerates thermal and electromagnetic load is attained. The port plug structure considering the fabrication process applying HIP and TIG-welding are designed. The mm-wave design that enables to guide the wave power of  20 MW into plasma with toroidal steering capability of 20
20 MW into plasma with toroidal steering capability of 20
 40
40 and efficiency of 98.4
and efficiency of 98.4  99% assuming HE11 fundamental wave mode + TEM000 gaussian mode are proceeded. Reduction of the heat load to 2.1 MW/m
99% assuming HE11 fundamental wave mode + TEM000 gaussian mode are proceeded. Reduction of the heat load to 2.1 MW/m on the steering mirror are attained. These results allow the transmission of 2.0 MW per a waveguide and the required radiation profile from the launcher. The full scale mock-up of the mm-wave launching system consisting of the waveguides and the mirrors and the subcomponents such as the steering mechanism of the mirror, the cooling water lines and etc., are fabricated to investigate the design availability. High power (0.5 MW) experiment of the mock-up confirmed the expected wave beam propagation and steering capability of 20
on the steering mirror are attained. These results allow the transmission of 2.0 MW per a waveguide and the required radiation profile from the launcher. The full scale mock-up of the mm-wave launching system consisting of the waveguides and the mirrors and the subcomponents such as the steering mechanism of the mirror, the cooling water lines and etc., are fabricated to investigate the design availability. High power (0.5 MW) experiment of the mock-up confirmed the expected wave beam propagation and steering capability of 20
 40
40 . The mock-up of the shield blanket module and the partial mock-up of the port plug structure are fabricated based on the present design to investigate the manufacturability and the performance of the cooling water flow. The results will reflect back to the fabrication design of the structural components of the equatorial launcher.
. The mock-up of the shield blanket module and the partial mock-up of the port plug structure are fabricated based on the present design to investigate the manufacturability and the performance of the cooling water flow. The results will reflect back to the fabrication design of the structural components of the equatorial launcher.
Takahashi, Koji; Kajiwara, Ken; Oda, Yasuhisa; Sakamoto, Keishi; Omori, Toshimichi*; Henderson, M.*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 88(2), p.85 - 93, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:54.83(Nuclear Science & Technology)The design of the torus diamond window for the ITER electron cyclotron heating and current drive (EC H&CD) system has advanced considering a reliable and manufacturable structure. The diamond window prototype was fabricated in basis of the design and the high power experiment was carried out to verify the millimeter wave transmission capability. Transmission of 740 kW-100 sec was demonstrated and no significant temperature increase of the window structure and no damage on the diamond disk was obtained. The saturation of the cooling water for the window was observed and loss tangent of 7.8  10
10 , which was the lowest value that we had ever obtained at JAEA, was evaluated. This result indicates that the diamond window design is feasible and promising the high power more than 1 MW transmission.
, which was the lowest value that we had ever obtained at JAEA, was evaluated. This result indicates that the diamond window design is feasible and promising the high power more than 1 MW transmission.
 Ca +
Ca +  Cm
Cm 
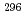 116
116 studied at the GSI-SHIP
studied at the GSI-SHIPHofmann, S.*; Heinz, S.*; Mann, R.*; Maurer, J.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Ackermann, D.*; Antalic, S.*; Barth, B.*; Block, M.*; Burkhard, H. G.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 48(5), p.62_1 - 62_23, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:178 Percentile:98.83(Physics, Nuclear)Kajiwara, Ken; Oda, Yasuhisa; Kasugai, Atsushi; Takahashi, Koji; Sakamoto, Keishi; Darbos, C.*; Henderson, M. A.*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(6-8), p.955 - 958, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:58.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)Takahashi, Koji; Kajiwara, Ken; Okazaki, Yukio*; Oda, Yasuhisa; Sakamoto, Keishi; Omori, Toshimichi*; Henderson, M.*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(6-8), p.982 - 986, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to optimize the physics performance of ITER, the millimeter (mm) wave design of the equatorial electron cyclotron launcher is modified so that one-third of the total mm-wave injection power can be flipped to drive plasma current in the counter direction. The design change to perform the poloidal beam tilting of 5 at top and bottom beam row is conducted so that more efficient central power deposition is achievable. The opening shape in the blanket shield module (BSM) structure is also optimized to minimize the degradation of the mm-wave transmission efficiency. The degradation is only 0.3%. The modularization design of the steering mirror components and the internal shield, the application of a rail structure to perform the alignment of the steering mirror installation and the space allocation behind the BSM structure are implemented to increase the reliability, the manufacturability and the maintenability of the launcher design.
at top and bottom beam row is conducted so that more efficient central power deposition is achievable. The opening shape in the blanket shield module (BSM) structure is also optimized to minimize the degradation of the mm-wave transmission efficiency. The degradation is only 0.3%. The modularization design of the steering mirror components and the internal shield, the application of a rail structure to perform the alignment of the steering mirror installation and the space allocation behind the BSM structure are implemented to increase the reliability, the manufacturability and the maintenability of the launcher design.
Takahashi, Koji; Kajiwara, Ken; Oda, Yasuhisa; Kasugai, Atsushi; Kobayashi, Noriyuki*; Sakamoto, Keishi; Doane, J.*; Olstad, R.*; Henderson, M.*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 82(6), p.063506_1 - 063506_7, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:62.27(Instruments & Instrumentation)High power, long pulse millimeter (mm) wave experiments of the RF test stand (RFTS) of JAEA were performed. The system consists of a 1 MW/170 GHz gyrotron, a long and short distance transmission line (TL) and an equatorial launcher (EL) mock-up. The RFTS has an ITER-relevant configuration, i.e., that is consisted by a 1 MW-170 GHz gyrotron, mm wave TL and EL mock-up. The TL is composed of a matching optics unit, evacuated circular corrugated waveguides, 6 miter bends, an in-line waveguide switch, an isolation valve. The Gaussian-like beam radiation with the steering capability of 20-40 from the EL mock-up was also successfully proved. The high power long pulse power transmission test was conducted with the metallic load replaced by the EL mock-up, and the transmission of 1 MW/800 s and 0.5 MW/1000 sec were successfully demonstrated with no arcing and no damages. The transmission efficiency of the TL was 96%. The results prove the feasibility of the ITER electron cyclotron heating and current drive system.
from the EL mock-up was also successfully proved. The high power long pulse power transmission test was conducted with the metallic load replaced by the EL mock-up, and the transmission of 1 MW/800 s and 0.5 MW/1000 sec were successfully demonstrated with no arcing and no damages. The transmission efficiency of the TL was 96%. The results prove the feasibility of the ITER electron cyclotron heating and current drive system.
Kajiwara, Ken; Kasugai, Atsushi; Oda, Yasuhisa; Takahashi, Koji; Sakamoto, Keishi; Darbos, C.*; Henderson, M.*
Journal of Infrared, Millimeter, and Terahertz Waves, 32(3), p.329 - 336, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:57.66(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Jacquinot, J.*; Albajar, F.*; Beaumont, B.*; Becoulet, A.*; Bonicelli, T.*; Bora, D.*; Campbell, D.*; Chakraborty, A.*; Darbos, C.*; Decamps, H.*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 84(2-6), p.125 - 130, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:81.14(Nuclear Science & Technology)The electron cyclotron (EC), ion cyclotron (IC), neutral beam (NB) and, lower hybrid (LH) systems for ITER have been reviewed in 2007/2008 in light of progress of physics and technology. Although the overall specifications are unchanged, notable changes have been approved. Firstly, the full 73MW should be commissioned and available on a routine basis before the D/T phase. Secondly, the possibility to operate the NB at full power during the hydrogen phase requiring new shine through protection; IC with 2 antennas with increased robustness; 2 MW transmission systems to provide an easier upgrading of the EC power; the addition of a building dedicated to the RF power sources and to a testing facility for acceptance of diagnostics and heating port plugs. Thirdly, the need of a plan for developing, in time for the active phase, a CD system such as LH suitable for very long pulse operation of ITER was recognized.
Kobayashi, Noriyuki; Bigelow, T.*; Bonicelli, T.*; Cirant, S.*; Denisov, G.*; Heidinger, R.*; Henderson, M.*; Hogge, J.-P.*; Piosczyk, B.*; Ramponi, G.*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 933, p.413 - 416, 2007/10
Since the EDA 2001, Design of Electron Cyclotron Heating and Current Drive (ECH&CD) System have been modified due to progress of physics understanding and change of interface. Nominal RF power 20 MW is injected by four upper launchers or one equatorial launcher. RF beams are steered by a front steering mirror. DCHV power supply will be composed of IGBT pulse step modulators because of high frequency modulation and design flexibility to three different types of 170 GHz gyrotrons from three parties. The RF power is transmitted by 63.5 mm dia corrugated waveguide and switched by a waveguide switch between the upper launcher and the equatorial launcher. A start-up system for initial discharge is composed of three 127.5 GHz gyrotrons and dedicated DCHV power supply. Three of transmission lines are shared between 170 GHz and 127.5 GHz gyrotrons to inject start-up RF beam through the equatorial launcher. R&Ds for high power long pulse have been on-going to obtain a reliable ITER ECH&CD system.
Oikawa, Toshihiro; Polevoi, A. R.*; Bonoli, P. T.*; Campbell, D. J.*; Henderson, M.*
no journal, ,
We have been developing physics models and computational codes for heating and current drive of NB, EC and LH. A NB code has been developed in JAEA and on the Monte-Carlo scheme with employing the Suzuki model for the ionization process, which are based on the most recent atomic data. An EC code, also developed in JAEA, is based on the ray-tracing and quasi-linear Fokker-Planck equation. A LH code, which was introduced from MIT, employs a 2D equivalent collision operator in the 1D Fokker-Planck code. Then the LH code shows a good agreement with fully 2D codes. A design changes of the NB and its injection port in 2007 made the range of the NB injection angle narrower than in the EDA2001, then the NBCD profile shifts inward by a minor radius of  0.05. The LH spectrum has to have a relatively high value of
0.05. The LH spectrum has to have a relatively high value of 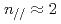 because of the accessibility condition. With this spectrum, LHCD is 0.83MA in the reference steady-state scenario for a 20MW injection from an equatorial port.
because of the accessibility condition. With this spectrum, LHCD is 0.83MA in the reference steady-state scenario for a 20MW injection from an equatorial port.
Kajiwara, Ken; Oda, Yasuhisa; Kasugai, Atsushi; Takahashi, Koji; Sakamoto, Keishi; Henderson, M.*; Darbos, C.*
no journal, ,