Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hayashi, Naoki; Kawase, Masato; Hatakeyama, Shuichiro; Hiroki, Seiji; Saeki, Riuji; Takahashi, Hiroki; Teruyama, Yuzo*; Toyokawa, Ryoji*; Arakawa, Dai*; Hiramatsu, Shigenori*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 677, p.94 - 106, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:69.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)A beam position monitor (BPM) system at J-PARC RCS is described. The J-PARC RCS is a rapid-cycling proton synchrotron and its designed beam power is 1 MW. A diameter of the BPM detector is larger than 250 mm, however the system has to measure the beam position very accurately. The system should work not only for the high intensity but also for lower intensity. There are 54 BPM around the ring and most of them are placed inside steering magnets because of quite limited space. The BPM detector is an electro static type and it has four electrodes, and a pair of electrode gives a good linear response with diagonal cut shape to detect the charge center precisely. The signal processing unit, which is equipped with 14-bit 40 MSPS ADC and 600 MHz DSP, has been developed. They are controlled via shared memory space and EPICS. It is capable to record full 25 Hz pulse data for averaged mode and it could also store whole waveform data for further analysis, like turn-by-turn position calculation.
Hiroki, Seiji; Abe, Tetsuya; Tanzawa, Sadamitsu
Nuclear Reactors, Nuclear Fusion and Fusion Engineering, p.367 - 403, 2009/09
In recent large tokamak machines, the vacuum leak detection technology is highly important due to mainly a safety reason. However, such machines are huge, complicated, and inaccessible, so the conventional  He leak detection method is not applicable in many cases. In this chapter, the essential technologies developed in JAEA are exhibited. The high-resolution quadrupole mass spectrometer (HR-QMS) has been developed, where 10
He leak detection method is not applicable in many cases. In this chapter, the essential technologies developed in JAEA are exhibited. The high-resolution quadrupole mass spectrometer (HR-QMS) has been developed, where 10 of the
of the  He
He /D
/D
 peak ratio could be obtained. An improved method with fully circulating the water has been demonstrated, where krypton (Kr) was dissolved in water. For 10
peak ratio could be obtained. An improved method with fully circulating the water has been demonstrated, where krypton (Kr) was dissolved in water. For 10 Pa-m
Pa-m /s of two water leaks, the positional accuracy of 12.6% was obtained. Another valuable method has been developed, namely, a unidirectional in-vacuum movable total pressure gauge could detect the minimum 10
/s of two water leaks, the positional accuracy of 12.6% was obtained. Another valuable method has been developed, namely, a unidirectional in-vacuum movable total pressure gauge could detect the minimum 10 Pa-m
Pa-m /s level of air leaks. A special in-vacuum movable QMS head could detect the argon (Ar) leak of 1.9
/s level of air leaks. A special in-vacuum movable QMS head could detect the argon (Ar) leak of 1.9 10
10 Pa-m
Pa-m /s.
/s.
Tanzawa, Sadamitsu; Hiroki, Seiji; Abe, Tetsuya; Shimizu, Katsusuke*; Inoue, Masahiko*; Watanabe, Mitsunori*; Iguchi, Masashi*; Sugimoto, Tomoko*; Inohara, Takashi*; Nakamura, Junichi*
JAEA-Technology 2008-076, 99 Pages, 2008/12
The primary vacuum pumping system of the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) exhausts a helium (He) ash resulting from the DT-burn with excess DT fueling gas, as well as performing a variety of functions such as pump-down, leak testing and wall conditioning. A mechanical based vacuum pumping system has some merits of a continuous pumping, a much lower tritium inventory, a lower operational cost and easy maintenance, comparing with a cryopump system, although demerits of an indispensable magnetic shield and insufficient performance for hydrogen (H ) pumping are well recognized. To overcome the demerits, we newly fabricated and tested a helical grooved pump (HGP) unit suitable for H
) pumping are well recognized. To overcome the demerits, we newly fabricated and tested a helical grooved pump (HGP) unit suitable for H pumping at the ITER divertor pressure of 0.1-10 Pa. Through this R&D, we successfully established many design and manufacturing databases of large HGP units for the lightweight gas pumping. Based on the databases, we conceptually designed the ITER vacuum pumping system mainly comprising the HGP with an optimal pump unit layout and a magnetic shield. We also designed conceptually the reduced cost (RC)-ITER pumping system, where a compound molecular pump combining turbine bladed rotors and helical grooved ones was mainly used. The ITER mechanical based primary pumping system proposed has eventually been a back-up solution, whereas a cryopump based one was formally selected to the ITER for construction.
pumping at the ITER divertor pressure of 0.1-10 Pa. Through this R&D, we successfully established many design and manufacturing databases of large HGP units for the lightweight gas pumping. Based on the databases, we conceptually designed the ITER vacuum pumping system mainly comprising the HGP with an optimal pump unit layout and a magnetic shield. We also designed conceptually the reduced cost (RC)-ITER pumping system, where a compound molecular pump combining turbine bladed rotors and helical grooved ones was mainly used. The ITER mechanical based primary pumping system proposed has eventually been a back-up solution, whereas a cryopump based one was formally selected to the ITER for construction.
Hiroki, Seiji; Hayashi, Naoki; Kawase, Masato; Noda, Fumiaki; Saha, P. K.; Sako, Hiroyuki; Takahashi, Hiroki; Ueno, Akira; Arakida, Yoshio*; Lee, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC '08) (CD-ROM), p.1131 - 1133, 2008/06
A set of six multi-wire profile monitors (MWPMs) has been installed in the injection area of the RCS (Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron), and contributed to the initial commissioning for establishing an optimum injection orbit. The Au coated W wires (0.1 mm dia.) for the H beam are fixed to a ceramic wind frame for two directions (horizontal and vertical with 17.7 deg. tilt, typically 51 wires with 2.9 mm or 9.5 mm distance), and the frame can be scanned for horizontal or vertical direction by using a stepping-motor driven actuator. A combination of the 17.7 deg. tilt wires and the precise scan function provides two step measurements, i.e. a rough profile is obtained only at one shot, and a detailed profile is measured for typically 101 shots (10 mm scan at 0.1 mm interval) thereafter. The beam induced charge signals are amplified, integrated and held by using a signal processing circuit. The signals are sequentially retrieved through multiplexers and digitized for obtaining a beam profile.
beam are fixed to a ceramic wind frame for two directions (horizontal and vertical with 17.7 deg. tilt, typically 51 wires with 2.9 mm or 9.5 mm distance), and the frame can be scanned for horizontal or vertical direction by using a stepping-motor driven actuator. A combination of the 17.7 deg. tilt wires and the precise scan function provides two step measurements, i.e. a rough profile is obtained only at one shot, and a detailed profile is measured for typically 101 shots (10 mm scan at 0.1 mm interval) thereafter. The beam induced charge signals are amplified, integrated and held by using a signal processing circuit. The signals are sequentially retrieved through multiplexers and digitized for obtaining a beam profile.
Hayashi, Naoki; Hiroki, Seiji; Saeki, Riuji; Toyokawa, Ryoji*; Yamamoto, Kazami; Arakawa, Dai*; Hiramatsu, Shigenori*; Lee, S.*; Sato, Kenichiro*; Tejima, Masaki*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC '08) (CD-ROM), p.1128 - 1130, 2008/06
The Beam Position Monitor (BPM) system of the J-PARC RCS has been fabricated, installed and operated successfully during the beam commissioning. There are 54 BPMs around the ring and most of them are placed inside steering magnets. The BPM is electro static type and it has four electrodes. A pair of electrode gives a linear response with diagonal cut shape and they were calibrated before their installation. The signal processing unit, which is equipped with 14-bit 14MSPS ADC and 600MHz DSP, has been developed for the system. In order to measure small signal, especially during the initial phase of the commissioning, careful design also done for cabling. The paper presents the current performance of the system.
Hayashi, Naoki; Hiroki, Seiji; Saeki, Riuji; Toyokawa, Ryoji; Yamamoto, Kazami; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Arakawa, Dai*; Hiramatsu, Shigenori*; Lee, S.*; Sato, Kenichiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 11th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC '08) (CD-ROM), p.1125 - 1127, 2008/06
A 3-GeV Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) has been commissioned recently. During its beam commissioning, various beam diagnostic instrumentation has been used. The multi-wire profile monitor (MWPM) is used to establish injection and H0 dump line. The electron catcher confirms that the beam hits a charge exchange carbon foil and the specified current monitor limits the beam current to the H0 dump. Single pass BPMs and ionization profile monitors (IPM) help to check the one pass orbit without circulation of the beam. The beam position monitor (BPM) can measure both COD and turn-by-turn position. Tune monitor system consists of exciter and its own BPM. The exciter shakes the beam and coherent oscillation. Dedicated BPMs, Fast CT (FCT) and Wall Current Monitor (WCM) are used for RF feedback or feedfoward control. It will describe the performance of each instruments and how they are contributed to the successful beam commissioning.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Hayashi, Naoki; Hiroki, Seiji; Saeki, Riuji; Toyama, Takeshi*; Tejima, Masaki*; Sato, Kenichiro*
Proceedings of 11th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC '08) (CD-ROM), p.382 - 384, 2008/06
Hiroki, Seiji; Tanzawa, Sadamitsu; Arai, Takashi; Abe, Tetsuya
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(1), p.72 - 78, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:38.79(Nuclear Science & Technology)A water leak detection method using krypton as a water soluble tracer has been proposed for fusion reactors with fully circulating the in-vessel cooling water. This method is targeted for applying to the ITER. The water leaks are effused into the vacuum vessel evacuated with a cryopump and the water dissolved Kr is detected with a quadrupole mass spectrometer. When two leak valves with 1 m distance are attached to the test pipe with 30  C heating, two distinct
C heating, two distinct  /
/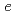 = 84 peak current rises caused by the water leak are successfully detected with the time interval of 39 sec. On the other hand, the water accession length as a function of the traveling time is calculated by considering a natural convection flow caused by the 30
= 84 peak current rises caused by the water leak are successfully detected with the time interval of 39 sec. On the other hand, the water accession length as a function of the traveling time is calculated by considering a natural convection flow caused by the 30  C heating, where the traveling time is 44.6 sec for the 1 m length. This means that the observed positional accuracy is 12.6%, based on the calculation. This method can be applied to the ITER condition.
C heating, where the traveling time is 44.6 sec for the 1 m length. This means that the observed positional accuracy is 12.6%, based on the calculation. This method can be applied to the ITER condition.
Hayashi, Naoki; Hiroki, Seiji; Saha, P. K.; Saeki, Riuji; Toyokawa, Ryoji*; Yamamoto, Kazami; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Arakawa, Dai*; Hiramatsu, Shigenori*; Lee, S.*; et al.
Proceedings of 5th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 33rd Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan (CD-ROM), p.243 - 245, 2008/00
The J-PARC RCS has been beam commissioned since fall 2007. During such a short period, the following items have been established. Establishment of the injection orbit, beam circulation, acceleration up to 3GeV, optics parameters measurements and it achieved 50 kW beam power (4 10
10 ppb). The beam monitor system has an important role for smooth beam commissioning. This paper describes the status of the beam monitor system, BPM, Injection monitors, IPM, current monitor, tune meter and BLM of the RCS.
ppb). The beam monitor system has an important role for smooth beam commissioning. This paper describes the status of the beam monitor system, BPM, Injection monitors, IPM, current monitor, tune meter and BLM of the RCS.
Hayashi, Naoki; Hiroki, Seiji; Sato, Kenichiro; Toyokawa, Ryoji; Arakawa, Dai*; Lee, S.*; Hashimoto, Yoshinori*; Miura, Takako*; Toyama, Takeshi*
KEK Proceedings 2006-15 (CD-ROM), p.128 - 130, 2007/03
The beam diagnostics system for J-PARC synchrotrons (RCS and MR) will be presented. The design of the system will be described for high current machines. Some test results will be reported.
Sato, Kenichiro; Hiroki, Seiji; Lee, S.*; Hayashi, Naoki; Yamamoto, Kazami; Hiramatsu, Shigenori*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Arakawa, Dai*; Igarashi, Zenei*; Saeki, Riuji
Proceedings of 4th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 32nd Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan (CD-ROM), p.297 - 299, 2007/00
At the injection and H0 dump line of J-PARC RCS, different beam monitors have been installed. Main purpose of the beam monitors in the injection line is to generate a beam position and profile to adjust the injection trajectory to the RCS ring. To guide the injected beam precisely is, needless to say, required to reduce the beam loss in the ring. Hence the monitor system is one of the most essential to operate the RCS. At the injection point, there are also some beams that are not match the RCS ring, that is negative and neutral proton beam. H0 dump accepts the unsuitable beams through the H0 dump line. The power limitation of the H0 dump is 4 kW. The monitor system in the dump line is to handle the beam and to monitor the dumped beam power. At the conference these monitor systems will be outlined.
Hayashi, Naoki; Hiroki, Seiji; Kishiro, Junichi*; Teruyama, Yuzo*; Toyokawa, Ryoji; Arakawa, Dai*; Lee, S.*; Miura, Takako*; Toyama, Takeshi*
Proceedings of 2005 Particle Accelerator Conference (PAC '05) (CD-ROM), p.299 - 301, 2005/00
Development of the beam diagnostics system for the J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) Rapid-Cycling Synchrotron is described. The system consists of Beam Position Monitor (BPM), Beam Loss Monitor (BLM), Current monitors (DCCT, SCT, MCT, FCT, WCM), Tune meter system, 324MHz-BPM, Profile monitor, and Halo monitor. BPM electrode is electro-static type and its electronics is designed for both COD and turn-by-turn measurements. Five current monitors have different time constants in order to cover wide frequency range. The tune meter is consisted of RFKO and the beam pick-up electrode. For the continuous injected beam monitoring, 324MHz-BPM detects Linac frequency. Two types of profile monitor are multi-wire for low intensity tuning and the residual gas monitor for non-destructive measurement.
 /He mixed gas under room temperature
/He mixed gas under room temperatureTanzawa, Sadamitsu; Hiroki, Seiji; Abe, Tetsuya
Shinku, 46(3), p.154 - 157, 2003/03
no abstracts in English
Kuroda, Toshimasa*; Hatano, Toshihisa; Miki, Nobuharu*; Hiroki, Seiji; Enoeda, Mikio; Omori, Junji*; Sato, Shinichi*; Akiba, Masato
JAERI-Tech 2002-098, 136 Pages, 2003/02
no abstracts in English
Tanzawa, Sadamitsu; Hiroki, Seiji; Abe, Tetsuya; Futatsuki, Takashi*; Tajima, Yoshinori*
Shinku, 46(1), p.44 - 48, 2003/01
no abstracts in English
Abe, Tetsuya; Kanari, Moriyasu; Tanzawa, Sadamitsu; Hiroki, Seiji
JAERI-Tech 2002-093, 17 Pages, 2002/12
no abstracts in English
Hiroki, Seiji; Abe, Tetsuya; Tanzawa, Sadamitsu; Nakamura, Junichi*; Obayashi, Tetsuro*
JAERI-Tech 2002-056, 11 Pages, 2002/07
no abstracts in English
Shimomura, Yasuo; Tsunematsu, Toshihide; Yamamoto, Shin; Maruyama, So; Mizoguchi, Tadanori*; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Kitamura, Kazunori*; Ioki, Kimihiro*; Inoue, Takashi; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 78(Suppl.), 224 Pages, 2002/01
no abstracts in English
Kanari, Moriyasu; Abe, Tetsuya; Kosaku, Yasuo; Tanzawa, Sadamitsu; Hiroki, Seiji
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 43(12), p.1228 - 1234, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Seki, Masahiro; Hishinuma, Akimichi; Kurihara, Kenichi; Akiba, Masato; Abe, Tetsuya; Ishitsuka, Etsuo; Imai, Tsuyoshi; Enoeda, Mikio; Ohira, Shigeru; Okumura, Yoshikazu; et al.
Kaku Yugoro Kogaku Gairon; Mirai Enerugi Eno Chosen, 246 Pages, 2001/09
no abstracts in English