Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 rays in the
rays in the  La(
La(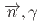 )
) La reaction
La reactionOkuizumi, Mao*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; et al.
Physical Review C, 111(3), p.034611_1 - 034611_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear) for brittle fracture in ductile-brittle transition temperature region
for brittle fracture in ductile-brittle transition temperature regionHojo, Kiminobu*; Hirota, Takatoshi*; Nagoshi, Yasuto*; Fukahori, Takuya*; Shimizu, Kazuma*; Shimodaira, Masaki; Ogawa, Takuya*; Yashirodai, Kenji*; Ohata, Mitsuru*; Minami, Fumiyoshi*
Proceedings of ASME 2024 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference (PVP 2024) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2024/07
no abstracts in English
 -odd/
-odd/ -odd interactions on the 0.75 eV
-odd interactions on the 0.75 eV  -wave resonance in
-wave resonance in 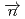 +
+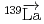 forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beam
forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beamNakabe, Rintaro*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Gudkov, V.*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kambara, Wataru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.L041602_1 - L041602_4, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:23.17(Physics, Nuclear) rays from a neutron-induced
rays from a neutron-induced  -wave resonance of
-wave resonance of  Xe
XeOkudaira, Takuya*; Tani, Yuika*; Endo, Shunsuke; Doskow, J.*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kameda, Kento*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Luxnat, M.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 107(5), p.054602_1 - 054602_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:76.15(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 rays in the
rays in the 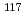 Sn(
Sn( )
)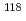 Sn reaction
Sn reactionEndo, Shunsuke; Okudaira, Takuya*; Abe, Ryota*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Oku, Takayuki; Sakai, Kenji; Shima, Tatsushi*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064601_1 - 064601_7, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:72.81(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 rays from the
rays from the  -wave resonance of
-wave resonance of 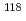 Sn
SnKoga, Jun*; Takada, Shusuke*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Niinomi, Yudai*; Okudaira, Takuya*; et al.
Physical Review C, 105(5), p.054615_1 - 054615_5, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:72.81(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 rays in the
rays in the  La(
La( )
) La
La reaction
reactionOkudaira, Takuya*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; Niinomi, Yudai*; Sakai, Kenji; et al.
Physical Review C, 104(1), p.014601_1 - 014601_6, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:64.07(Physics, Nuclear)Hirota, Takatoshi*; Nagoshi, Yasuto*; Hojo, Kiminobu*; Okada, Hiroshi*; Takahashi, Akiyuki*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Ueda, Takashi*; Ogawa, Takuya*; Yashirodai, Kenji*; Ohata, Mitsuru*; et al.
Proceedings of ASME 2021 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2021) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2021/07
Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Hirota, Katsuya*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011116_1 - 011116_6, 2021/03
In neutron fundamental physics, study of correlation term  of a neutron spin
of a neutron spin 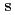 and a target nuclear spin
and a target nuclear spin 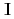 is important because
is important because  term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to
term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to 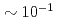 by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study
by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study  term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by
term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by  term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of
term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of  Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change
Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change  of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (
of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (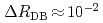 ) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of
) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of  has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained
has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained  in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
 He neutron spin filter at J-PARC
He neutron spin filter at J-PARCOkudaira, Takuya; Oku, Takayuki; Ino, Takashi*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakai, Kenji; Hiroi, Kosuke; Takahashi, Shingo*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Endo, Hitoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 977, p.164301_1 - 164301_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:89.09(Instruments & Instrumentation) rays from neutron-induced compound states of
rays from neutron-induced compound states of  La
LaYamamoto, Tomoki*; Okudaira, Takuya; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; et al.
Physical Review C, 101(6), p.064624_1 - 064624_8, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:84.76(Physics, Nuclear) -rays after neutron capture by
-rays after neutron capture by  La for a T-violation search
La for a T-violation searchOkudaira, Takuya; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Haddock, C. C.*; Ito, Ikuya*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Endo, Shunsuke*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Sato, Takumi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 219, p.09001_1 - 09001_6, 2019/12
Parity violating effects enhanced by up to 10 times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n,
times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n, ) reaction was measured with
) reaction was measured with  La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized
La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized  La target and a 70% polarized
La target and a 70% polarized  He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm
He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm cm are needed. Therefore high quality
cm are needed. Therefore high quality  He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n,
He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n, ) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the
) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the  He spin filter will be presented.
He spin filter will be presented.
 rays from neutron-induced compound states of
rays from neutron-induced compound states of  La
LaOkudaira, Takuya*; Takada, Shusuke*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; Nagamoto, Kosuke*; Nakao, Taro*; Okada, Anju*; Sakai, Kenji; et al.
Physical Review C, 97(3), p.034622_1 - 034622_15, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:78.26(Physics, Nuclear) -rays at the ANNRI in the MLF of the J-PARC
-rays at the ANNRI in the MLF of the J-PARCTakada, Shusuke*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Goto, Fumiya*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; Nakao, Taro*; Sakai, Kenji; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; et al.
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 13(2), p.P02018_1 - P02018_21, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:34.64(Instruments & Instrumentation) Na
Na )TiO
)TiO
Matsuura, Masato*; Iida, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Kazuma*; Owada, Kenji; Noguchi, Yuji*; Miyayama, Masaru*
Physical Review B, 87(6), p.064109_1 - 064109_10, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:73.50(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Neutron-scattering studies of (Bi Na
Na )TiO
)TiO (BNT) have been performed to elucidate the microscopic mechanism of the broad maximum in the temperature dependence of the dielectric constant at Tm
(BNT) have been performed to elucidate the microscopic mechanism of the broad maximum in the temperature dependence of the dielectric constant at Tm  600 K and the reduction in the piezoelectric properties above the depolarization temperature, 460
600 K and the reduction in the piezoelectric properties above the depolarization temperature, 460  480 K. We observed diffuse scattering near the
480 K. We observed diffuse scattering near the  point below 700 K, which competes with the superlattice peak at the M point of the tetragonal phase but coexists with the superlattice peak at the R point of the rhombohedral phase. The diffuse scattering shows an anisotropic Q shape extending along the
point below 700 K, which competes with the superlattice peak at the M point of the tetragonal phase but coexists with the superlattice peak at the R point of the rhombohedral phase. The diffuse scattering shows an anisotropic Q shape extending along the  100
100 direction transverse to the scattering vector Q, which is explained by atomic shifts bridging the tetragonal and rhombohedral structures. We propose that the broad maximum in the dielectric constant is associated with a diffusive first-order transition between the competing tetragonal and rhombohedral phases. In addition, we found that the diffuse scattering is reduced for single crystals grown under high oxygen pressure, which suggests an analogy with the central peak in hydrogen-reduced SrTiO
direction transverse to the scattering vector Q, which is explained by atomic shifts bridging the tetragonal and rhombohedral structures. We propose that the broad maximum in the dielectric constant is associated with a diffusive first-order transition between the competing tetragonal and rhombohedral phases. In addition, we found that the diffuse scattering is reduced for single crystals grown under high oxygen pressure, which suggests an analogy with the central peak in hydrogen-reduced SrTiO . Inelastic neutron scattering near the
. Inelastic neutron scattering near the  point reveals a heavily overdamped soft mode similar to those reported in lead-based relaxors, the "waterfall" feature. Moreover, a damped soft transverse acoustic mode is observed for the
point reveals a heavily overdamped soft mode similar to those reported in lead-based relaxors, the "waterfall" feature. Moreover, a damped soft transverse acoustic mode is observed for the  100
100 direction as the anisotropic diffuse scattering, indicating phase instabilities with the same origin as that of the diffuse scattering. The recovery of the soft mode is observed near the depolarization temperature, which coincides with the disappearance of the superlattice peak at the M point. These results indicate that the depolarization and the waterfall feature originate in the dynamic nature of ferroelectric clusters in the coexisting tetragonal/rhombohedral phase.
direction as the anisotropic diffuse scattering, indicating phase instabilities with the same origin as that of the diffuse scattering. The recovery of the soft mode is observed near the depolarization temperature, which coincides with the disappearance of the superlattice peak at the M point. These results indicate that the depolarization and the waterfall feature originate in the dynamic nature of ferroelectric clusters in the coexisting tetragonal/rhombohedral phase.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O
Owada, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Mizuki, Junichiro; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(3), p.2509 - 2514, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.52(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. Orderd PIN (O-PIN, without B-site randomness) is supposed to be an ideal system of lead-based complex perovskite Pb(B'B'')O
(PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. Orderd PIN (O-PIN, without B-site randomness) is supposed to be an ideal system of lead-based complex perovskite Pb(B'B'')O and expected to give us a clear picture of the AFE/relaxor nature of the ground state by the B-site randomness. We studied the dynamics of O-PIN by inelastic X-ray scattering. The quasielastic (QE) scattering shows the critical slowing down and the transverse acoustic (TA) mode shows the softening towards
and expected to give us a clear picture of the AFE/relaxor nature of the ground state by the B-site randomness. We studied the dynamics of O-PIN by inelastic X-ray scattering. The quasielastic (QE) scattering shows the critical slowing down and the transverse acoustic (TA) mode shows the softening towards  . On the other hand, the transverse optic (TO) mode shows the softening toward low temperature with no clear anomaly at
. On the other hand, the transverse optic (TO) mode shows the softening toward low temperature with no clear anomaly at  . These results represent that the antiferroelectric (AFE) phase transition is associated with the TA and the origin of the QE scattering, while ferroelectric correlation does exist behind the AFE ordering. The effect of B-site randomness is finally discussed on the basis of the results.
. These results represent that the antiferroelectric (AFE) phase transition is associated with the TA and the origin of the QE scattering, while ferroelectric correlation does exist behind the AFE ordering. The effect of B-site randomness is finally discussed on the basis of the results.

 in Pb(Zn
in Pb(Zn Nb
Nb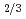 )O
)O -9%PbTiO
-9%PbTiO PbTiO
PbTiO
Owada, Kenji; Mizuki, Junichiro; Namikawa, Kazumichi*; Matsushita, Mitsuyoshi*; Shimomura, Susumu*; Nakao, Hironori*; Hirota, Kazuma*
Physical Review B, 83(22), p.224115_1 - 224115_7, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:37.64(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Complementary use of coherent X-ray diffraction (CXD), X-ray diffuse scattering, conventional X-ray diffraction techniques and dielectric measurements has enabled us to investigate Pb(Zn Nb
Nb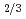 )O
)O -9%PbTiO
-9%PbTiO with a multiple-length-scale approach from the macroscale (lattice constants, bulk averaged) and microscale to the nanoscale (polar nanoregions (PNRs)) and discuss the contribution of each scale to the dielectric permittivity.
with a multiple-length-scale approach from the macroscale (lattice constants, bulk averaged) and microscale to the nanoscale (polar nanoregions (PNRs)) and discuss the contribution of each scale to the dielectric permittivity.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O and ferroelectric correlation in antiferroelectric Pb(In
and ferroelectric correlation in antiferroelectric Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O
Owada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 34(1), p.19 - 22, 2009/03
Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. This is characterized by measurements of dielectric response, which shows behavior that is usually clearly in one of those three classes. In contrast, X-ray scattering studies suggest the presence of AFE correlation in the relaxor state and FE in AFE state. Weak phonon softening at zone boundary in relaxor state shows that the AFE correlation intrinsically exists in PIN, as does the corresponding elastic scattering at (
(PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. This is characterized by measurements of dielectric response, which shows behavior that is usually clearly in one of those three classes. In contrast, X-ray scattering studies suggest the presence of AFE correlation in the relaxor state and FE in AFE state. Weak phonon softening at zone boundary in relaxor state shows that the AFE correlation intrinsically exists in PIN, as does the corresponding elastic scattering at (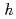 /2
/2  /2 0), while weak diffuse scattering around 333 Bragg reflection appears in AFE state suggesting FE correlation. These results will support our previous speculation that the AFE and FE correlations coexist in PIN (K. Owada
/2 0), while weak diffuse scattering around 333 Bragg reflection appears in AFE state suggesting FE correlation. These results will support our previous speculation that the AFE and FE correlations coexist in PIN (K. Owada 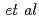 ., Phys, Rev. B
., Phys, Rev. B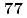 094136 (2008)). Such a coexistence or competition is widely seen in the perovskite relaxor and the coexistence of FE and AFE correlations is essential for generating relaxor state.
094136 (2008)). Such a coexistence or competition is widely seen in the perovskite relaxor and the coexistence of FE and AFE correlations is essential for generating relaxor state.
Mishima, Kenji*; Ino, Takashi*; Sakai, Kenji; Shinohara, Takenao; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ikeda, Kazuaki*; Sato, Hiromi*; Otake, Yoshie*; Omori, Hitoshi*; Muto, Suguru*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 600, p.342 - 345, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:87.48(Instruments & Instrumentation)A new beamline for a fundamental physics experiment is under construction at BL05 port in the Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF) at Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), this beamline is designed using novel techniques of neutron optics and it is termed "Neutron Optics and Physics". The beam from the moderator is deflected by multi-channel supermirrors and split into three branches for individual experiments. In this study, we have optimized the design of the beam optics and shields using the Monte Carlo simulation package PHITS. The neutron fluxes of beams are expected to be 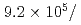 cm
cm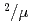 str
str s
s MW,
MW, 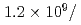 cm
cm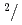 s
s MW,
MW, 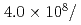 cm
cm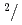 s
s MW, with polarization of 99.8%.
MW, with polarization of 99.8%.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O revealed by changing B-site randomness; Inelastic X-ray scattering study
revealed by changing B-site randomness; Inelastic X-ray scattering studyOwada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Physical Review B, 77(9), p.094136_1 - 094136_8, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:60.13(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or relaxor states can appear in Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. We studied the effects of this randomness on the dynamics of PIN by high resolution inelastic X-ray scattering using ordered PIN (AFE) and disordered PIN (relaxor) single crystals. We have found a clear softening of a transverse optic mode at the
(PIN) depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. We studied the effects of this randomness on the dynamics of PIN by high resolution inelastic X-ray scattering using ordered PIN (AFE) and disordered PIN (relaxor) single crystals. We have found a clear softening of a transverse optic mode at the  point in both the samples, indicating a robust and intrinsic ferroelectric instability regardless of the actual ground state. We interpret that AFE is stabilized only when In and Nb ions are spatially ordered enough to overwhelm the FE instability. As the B-site randomness becomes larger, AFE is suppressed and the hidden FE state starts appearing. Ultimately, the randomness begins to predominate over the development of FE regions and blocks a long range FE order, which we believe yields polar nanoregions resulting in relaxor behaviors.
point in both the samples, indicating a robust and intrinsic ferroelectric instability regardless of the actual ground state. We interpret that AFE is stabilized only when In and Nb ions are spatially ordered enough to overwhelm the FE instability. As the B-site randomness becomes larger, AFE is suppressed and the hidden FE state starts appearing. Ultimately, the randomness begins to predominate over the development of FE regions and blocks a long range FE order, which we believe yields polar nanoregions resulting in relaxor behaviors.