Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hirota, Koichi; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kimura, Atsushi; Kojima, Takuji
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Radiation Curing in Asia (RadTech Asia 2011) (Internet), p.108 - 109, 2011/06
We have focused on using MnO for the oxidation of intermediates produced from electron beam irradiation of VOC. Manganese dioxide can decompose ozone, produced by the irradiation of air containing VOCs, into activated oxygen, which can ultimately oxide the intermediates. Hybrid system equipped with electron accelerator and MnO
for the oxidation of intermediates produced from electron beam irradiation of VOC. Manganese dioxide can decompose ozone, produced by the irradiation of air containing VOCs, into activated oxygen, which can ultimately oxide the intermediates. Hybrid system equipped with electron accelerator and MnO has demonstrated the complete oxidation of the intermediates produced during the irradiation of xylene and toluene. The electron-beam treatment of dioxin from municipal solid waste incinerator was carried out at Takahama Clean Center in Japan. An incinerator gas of 1000 m
has demonstrated the complete oxidation of the intermediates produced during the irradiation of xylene and toluene. The electron-beam treatment of dioxin from municipal solid waste incinerator was carried out at Takahama Clean Center in Japan. An incinerator gas of 1000 m N/h was diverted downstream of a dry electric precipitator and was irradiated with electron beams using an electron accelerator that supplied 300 kV with a maximum energy of 12 kW. The results showed electron-beam is a promising technology for destroying dioxin in exhaust gases.
N/h was diverted downstream of a dry electric precipitator and was irradiated with electron beams using an electron accelerator that supplied 300 kV with a maximum energy of 12 kW. The results showed electron-beam is a promising technology for destroying dioxin in exhaust gases.
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Sugo, Yumi; Araki, Koshi*; Dally, E. B.*; Hirota, Koichi
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 49(12), p.5517 - 5522, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:38.85(Engineering, Chemical)An electron-beam (EB) irradiation/catalytic oxidation system was developed for the purification of a volatile organic compounds (VOC) gas stream under a practical gas flow condition. This system consists of a compact-sized electron accelerator and an ozone decomposition catalyst, which is MnO . The decomposition of toluene and/or xylene and their mineralization were examined with and without catalytic oxidation for a gas stream at a flow rate of 500 Nm
. The decomposition of toluene and/or xylene and their mineralization were examined with and without catalytic oxidation for a gas stream at a flow rate of 500 Nm /h. A combined catalyst bed enhanced the decomposition of VOCs and the mineralization of VOC and its irradiation organic byproducts. For example, the mineralization ratio for a 5-ppmv toluene/xylene/air mixture increased from 42% by EB irradiation to 100% by the combination treatment at 9.3 kGy. Furthermore, the yield of CO
/h. A combined catalyst bed enhanced the decomposition of VOCs and the mineralization of VOC and its irradiation organic byproducts. For example, the mineralization ratio for a 5-ppmv toluene/xylene/air mixture increased from 42% by EB irradiation to 100% by the combination treatment at 9.3 kGy. Furthermore, the yield of CO relative to CO
relative to CO increased from 59% to 85% by this catalytic treatment.
increased from 59% to 85% by this catalytic treatment.
 catalyst
catalystHakoda, Teruyuki; Chowdhury, M. A. Z.*; Shimada, Akihiko; Hirota, Koichi
Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 29(6), p.549 - 557, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.87(Engineering, Chemical)The decomposition of dimethyl sulfide (DMS) at initial concentrations of 4.5-18.0 ppmv in air was studied under electron-beam (EB) irradiation. Doses to decompose 90% of input DMS were 2.5 kGy for 4.5 ppmv, 3.4 kGy for 10.6 ppmv, and 3.9 kGy for 18.0 ppmv. HCOOH, (CH )
) SO, and trace CH
SO, and trace CH OH and (CH
OH and (CH )
) SO
SO were produced as irradiation products in addition to CO
were produced as irradiation products in addition to CO and CO. Application of an O
and CO. Application of an O decomposition catalyst to an irradiated sample gas led to an enhancement in the oxidation of DMS and its products into CO
decomposition catalyst to an irradiated sample gas led to an enhancement in the oxidation of DMS and its products into CO and the decomposition of O
and the decomposition of O . For 10.6 ppmv DMS/air, the mineralization ratio increased from 41% via only EB irradiation to 100% via the combination treatment at 6.3 kGy. The yield of CO
. For 10.6 ppmv DMS/air, the mineralization ratio increased from 41% via only EB irradiation to 100% via the combination treatment at 6.3 kGy. The yield of CO to CO
to CO increased from 5.3% to 87.6% by combination with catalytic oxidation. This combination treatment enables the irradiation energy used to deodorize gas streams containing DMS to be reduced.
increased from 5.3% to 87.6% by combination with catalytic oxidation. This combination treatment enables the irradiation energy used to deodorize gas streams containing DMS to be reduced.
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Matsumoto, Kanae*; Hirota, Koichi
Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 29(1), p.69 - 78, 2009/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:26.84(Engineering, Chemical)Electron beam (EB) technology has an advantage for treating dilute environmental pollutants in gases due to high-density population of active species such as radicals and atoms. In general, OH radicals play an important role of initiating the decomposition and removal of such pollutants. It is quite important to understand the behavior of OH radical production for the development of efficient decomposition/removal processes and the comparison with other purification methods. The number of OH radicals produced in humid N at doses of 2.0-10.0 kGy with dose rates of 0.17-2.55 kGy/s under 1-MeV EB irradiation was indirectly determined using an index of oxidation of CO to CO
at doses of 2.0-10.0 kGy with dose rates of 0.17-2.55 kGy/s under 1-MeV EB irradiation was indirectly determined using an index of oxidation of CO to CO , which has been used in atmospheric chemistry. An experiment under conditions where all OH radicals produced react with CO demonstrated that the concentration of CO
, which has been used in atmospheric chemistry. An experiment under conditions where all OH radicals produced react with CO demonstrated that the concentration of CO increased linearly with doses of 0-10 kGy, and the
increased linearly with doses of 0-10 kGy, and the 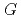 (OH) was estimated as 4.90.
(OH) was estimated as 4.90.
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Matsumoto, Kanae; Shimada, Akihiko; Narita, Tadashi*; Kojima, Takuji; Hirota, Koichi
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(5), p.585 - 590, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:48.87(Chemistry, Physical)The electron beam (EB) oxidation of gaseous xylene in air, appearing as ventilation gases emitted from painting factories, was investigated under various experimental conditions. Thereby the implementation of an ozone decomposition catalyst, MnO , into EB-induced oxidation of xylene/air mixtures strongly contributed in the achievement of a better purification degree.
, into EB-induced oxidation of xylene/air mixtures strongly contributed in the achievement of a better purification degree.
Shimada, Akihiko; Hirota, Koichi
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 55, 2008/03
no abstracts in English

Aso, Naofumi*; Owada, Kenji; Watanuki, Tetsu; Machida, Akihiko; Omura, Ayako; Inami, Toshiya; Homma, Yoshiya*; Shiokawa, Yoshinobu*; Hirota, Kazuma*; Sato, Noriaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 75(Suppl.), p.88 - 90, 2006/08
no abstracts in English
Shimada, Akihiko; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Matsumoto, Kanae*; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
The quantity of OH radicals, produced in humid N under 1-MeV EB irradiation, was indirectly determined using an index of oxidation of CO to CO
under 1-MeV EB irradiation, was indirectly determined using an index of oxidation of CO to CO , which has been used in atmospheric chemistry. The concentration of water vapor to fully react with the positive ions/excited species was examined under different initial concentrations of water vapor. The concentration of CO to scavenge completely the produced OH radicals was also measured under different initial CO concentrations. As a result, such concentrations of water vapor and CO were higher than 6,000 and 2,000 ppmv, respectively. The experiment using this condition of CO and water vapor demonstrated that the concentration of CO
, which has been used in atmospheric chemistry. The concentration of water vapor to fully react with the positive ions/excited species was examined under different initial concentrations of water vapor. The concentration of CO to scavenge completely the produced OH radicals was also measured under different initial CO concentrations. As a result, such concentrations of water vapor and CO were higher than 6,000 and 2,000 ppmv, respectively. The experiment using this condition of CO and water vapor demonstrated that the concentration of CO , produced from reaction of CO with OH radicals, lineally increased with doses of 0-10 kGy and the G(OH) was estimated as 4.90.
, produced from reaction of CO with OH radicals, lineally increased with doses of 0-10 kGy and the G(OH) was estimated as 4.90.
Hirota, Koichi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Kimura, Atsushi
no journal, ,
Shimada, Akihiko; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Hirota, Koichi; Araki, Koshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 plasmas
plasmasMatsunaga, Go; Shinohara, Koji; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Takechi, Manabu; Suzuki, Takahiro; Isayama, Akihiko; Hirota, Makoto; Oyama, Naoyuki; Asakura, Nobuyuki; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hirota, Koichi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Kimura, Atsushi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Araki, Koshi*; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
An electron-beam treatment system was developed for the purification of VOC gas stream under a practical gas flow condition. This system consists of a compact-sized electron accelerator and a MnO catalyst bed. The decomposition and mineralization of toluene and/or xylene were examined with and without a catalytic treatment for gas stream at a flow rate of 500 m
catalyst bed. The decomposition and mineralization of toluene and/or xylene were examined with and without a catalytic treatment for gas stream at a flow rate of 500 m /h. The EB/catalyst system accelerated the decomposition and the mineralization. For example, the mineralization ratio increased from 42% by EB irradiation to 100% by the combination treatment at 9.3 kGy. Furthermore, the yield of CO
/h. The EB/catalyst system accelerated the decomposition and the mineralization. For example, the mineralization ratio increased from 42% by EB irradiation to 100% by the combination treatment at 9.3 kGy. Furthermore, the yield of CO relative to CO
relative to CO increased from 59% to 85% by this catalytic treatment.
increased from 59% to 85% by this catalytic treatment.
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Matsumoto, Kanae*; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Araki, Koshi*; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
An electron-beam irradiation/catalytic oxidation system was developed for the purification of a volatile organic compound (VOC) gas stream under a practical gas flow condition. The removal of toluene and/or xylene and their mineralization were examined with and without catalytic oxidation for a gas stream at a flow rate of 500 m /h. A combined catalyst bed enhanced the removal of VOCs and the mineralization of VOC and its irradiation organic byproducts.
/h. A combined catalyst bed enhanced the removal of VOCs and the mineralization of VOC and its irradiation organic byproducts.
Fukasawa, Tsuyoshi*; Hirayama, Tomoyuki*; Hirota, Akihiko*; Somaki, Takahiro*; Miyagawa, Takayuki*; Uchita, Masato*; Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Miyazaki, Masashi; Okamura, Shigeki*; Fujita, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fukasawa, Tsuyoshi*; Hirayama, Tomoyuki*; Yokoi, Shinobu*; Hirota, Akihiko*; Somaki, Takahiro*; Yukawa, Masaki*; Miyagawa, Takayuki*; Uchita, Masato*; Yamamoto, Tomohiko; Miyazaki, Masashi; et al.
no journal, ,
The seismic integrity of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR) designs in nuclear power plants is of paramount importance. Based on the static loading test, this study investigates the force-displacement relationship and load transference in a three-dimensional seismic isolation system that is envisaged for use in reactor buildings. In SFR designs, the necessity for thin-walled structures to maintain high-temperature structure integrity can unintentionally compromise the seismic design. Consequently, addressing horizontal and vertical seismic forces become vital for ensuring seismic resilience. Currently, there are no specific codes or standards governing the integration of Three-dimensional seismic isolation systems into nuclear reactor buildings. However, current guidelines for the design of horizontal seismic isolation systems emphasize the necessity to clarify the force-displacement relationship and load transfer under conditions of superimposed horizontal and vertical loads. This study involves static loading tests performed on a half-scale specimen, which is subjected to horizontal and vertical loads exceeding the design basis ground motions for the SFR. The findings affirm that the system's horizontal supporting function maintains the segregation of horizontal and vertical load transference, even under seismic loads that exceed the design basis ground motions.