Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 for brittle fracture in ductile-brittle transition temperature region
for brittle fracture in ductile-brittle transition temperature regionHojo, Kiminobu*; Hirota, Takatoshi*; Nagoshi, Yasuto*; Fukahori, Takuya*; Shimizu, Kazuma*; Shimodaira, Masaki; Ogawa, Takuya*; Yashirodai, Kenji*; Ohata, Mitsuru*; Minami, Fumiyoshi*
Proceedings of ASME 2024 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference (PVP 2024) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2024/07
no abstracts in English
Yasuoka, Yumi*; Fujita, Hiroki; Tsuji, Tomoya; Tsujiguchi, Takakiyo*; Sasaki, Michiya*; Miyazaki, Tomoyuki*; Hashima, Shun*; Yasuda, Hiroshi*; Shimada, Kazumasa; Hirota, Seiko*
Hoken Butsuri (Internet), 57(3), p.146 - 155, 2022/12
no abstracts in English
 O(
O( He,
He, )
) F reaction; Identification of the low-energy "super" -Gamow-Teller state
F reaction; Identification of the low-energy "super" -Gamow-Teller stateFujita, Hirohiko*; Fujita, Yoshitaka*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Yoshida, Kenichi*; Adachi, Tatsuya*; Algora, A.*; Csatl s, M.*; Deaven, J. M.*; Estevez-Aguado, E.*; Guess, C. J.*; et al.
s, M.*; Deaven, J. M.*; Estevez-Aguado, E.*; Guess, C. J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 100(3), p.034618_1 - 034618_13, 2019/09
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.80(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Ino, Kohei*; Hernsdorf, A. W.*; Konno, Yuta*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Yanagawa, Katsunori*; Kato, Shingo*; Sunamura, Michinari*; Hirota, Akinari*; Togo, Yoko*; Ito, Kazumasa*; et al.
ISME Journal, 12(1), p.31 - 47, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:54 Percentile:90.03(Ecology)In this study, we found the dominance ofanaerobic methane-oxidizing archaea in groundwater enriched in sulfate and methane from a 300-m deep underground borehole in granitic rock.
Ino, Kohei*; Konno, Yuta*; Kozuka, Mariko*; Hirota, Akinari*; Togo, Yoko*; Fukuda, Akari*; Komatsu, Daisuke*; Tsunogai, Urumu*; Tanabe, Akifumi*; Yamamoto, Satoshi*; et al.
Environmental Microbiology Reports (Internet), 8(2), p.285 - 294, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:70.41(Environmental Sciences)To understand the subsurface biosphere, borehole investigation was conducted for 300-m deep granitic rocks at the Mizunami underground research laboratory, Japan. The initial biomass was the highest with the flourish of aerobic H -oxidizing Hydrogenophaga spp., whereas an uncultivated lineage of the phylum Nitrospirae became predominant after three years with decreasing biomass. The common occurrence of many species of Nitrospirae and Chlorobi phyla at the geographically distinct sites and the exclusive detection of their phylogenetically related environmental sequences from deep groundwaters and terrestrial hot springs, suggest that these bacteria are indigenous and potentially adapted to the deep terrestrial subsurface.
-oxidizing Hydrogenophaga spp., whereas an uncultivated lineage of the phylum Nitrospirae became predominant after three years with decreasing biomass. The common occurrence of many species of Nitrospirae and Chlorobi phyla at the geographically distinct sites and the exclusive detection of their phylogenetically related environmental sequences from deep groundwaters and terrestrial hot springs, suggest that these bacteria are indigenous and potentially adapted to the deep terrestrial subsurface.
Suzuki, Yohei*; Konno, Yuta*; Fukuda, Akari*; Komatsu, Daisuke*; Hirota, Akinari*; Watanabe, Katsuaki*; Togo, Yoko*; Morikawa, Noritoshi*; Hagiwara, Hiroki; Aosai, Daisuke*; et al.
PLOS ONE (Internet), 9(12), p.e113063_1 - e113063_20, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:38.53(Multidisciplinary Sciences)We present multi-isotopic evidence of microbially mediated sulfate reduction in a granitic aquifer, a representative of the terrestrial crust habitat. Deep groundwater of meteoric origin was collected from underground boreholes drilled into the Cretaceous Toki granite, central Japan. A large sulfur isotopic fractionation of 20-60 permil diagnostic to microbial sulfate reduction is associated with the investigated groundwater containing sulfate below 0.2 mM. In contrast, a small carbon isotopic fractionation ( 30 permil) is not indicative of methanogenesis. Our results demonstrate that the deep biosphere in the terrestrial crust is metabolically active and playing a crucial role in the formation of reducing groundwater even under low energy fluxes.
30 permil) is not indicative of methanogenesis. Our results demonstrate that the deep biosphere in the terrestrial crust is metabolically active and playing a crucial role in the formation of reducing groundwater even under low energy fluxes.
 Na
Na )TiO
)TiO
Matsuura, Masato*; Iida, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Kazuma*; Owada, Kenji; Noguchi, Yuji*; Miyayama, Masaru*
Physical Review B, 87(6), p.064109_1 - 064109_10, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:73.50(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Neutron-scattering studies of (Bi Na
Na )TiO
)TiO (BNT) have been performed to elucidate the microscopic mechanism of the broad maximum in the temperature dependence of the dielectric constant at Tm
(BNT) have been performed to elucidate the microscopic mechanism of the broad maximum in the temperature dependence of the dielectric constant at Tm  600 K and the reduction in the piezoelectric properties above the depolarization temperature, 460
600 K and the reduction in the piezoelectric properties above the depolarization temperature, 460  480 K. We observed diffuse scattering near the
480 K. We observed diffuse scattering near the  point below 700 K, which competes with the superlattice peak at the M point of the tetragonal phase but coexists with the superlattice peak at the R point of the rhombohedral phase. The diffuse scattering shows an anisotropic Q shape extending along the
point below 700 K, which competes with the superlattice peak at the M point of the tetragonal phase but coexists with the superlattice peak at the R point of the rhombohedral phase. The diffuse scattering shows an anisotropic Q shape extending along the  100
100 direction transverse to the scattering vector Q, which is explained by atomic shifts bridging the tetragonal and rhombohedral structures. We propose that the broad maximum in the dielectric constant is associated with a diffusive first-order transition between the competing tetragonal and rhombohedral phases. In addition, we found that the diffuse scattering is reduced for single crystals grown under high oxygen pressure, which suggests an analogy with the central peak in hydrogen-reduced SrTiO
direction transverse to the scattering vector Q, which is explained by atomic shifts bridging the tetragonal and rhombohedral structures. We propose that the broad maximum in the dielectric constant is associated with a diffusive first-order transition between the competing tetragonal and rhombohedral phases. In addition, we found that the diffuse scattering is reduced for single crystals grown under high oxygen pressure, which suggests an analogy with the central peak in hydrogen-reduced SrTiO . Inelastic neutron scattering near the
. Inelastic neutron scattering near the  point reveals a heavily overdamped soft mode similar to those reported in lead-based relaxors, the "waterfall" feature. Moreover, a damped soft transverse acoustic mode is observed for the
point reveals a heavily overdamped soft mode similar to those reported in lead-based relaxors, the "waterfall" feature. Moreover, a damped soft transverse acoustic mode is observed for the  100
100 direction as the anisotropic diffuse scattering, indicating phase instabilities with the same origin as that of the diffuse scattering. The recovery of the soft mode is observed near the depolarization temperature, which coincides with the disappearance of the superlattice peak at the M point. These results indicate that the depolarization and the waterfall feature originate in the dynamic nature of ferroelectric clusters in the coexisting tetragonal/rhombohedral phase.
direction as the anisotropic diffuse scattering, indicating phase instabilities with the same origin as that of the diffuse scattering. The recovery of the soft mode is observed near the depolarization temperature, which coincides with the disappearance of the superlattice peak at the M point. These results indicate that the depolarization and the waterfall feature originate in the dynamic nature of ferroelectric clusters in the coexisting tetragonal/rhombohedral phase.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O
Owada, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Mizuki, Junichiro; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, 59(3), p.2509 - 2514, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.52(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. Orderd PIN (O-PIN, without B-site randomness) is supposed to be an ideal system of lead-based complex perovskite Pb(B'B'')O
(PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. Orderd PIN (O-PIN, without B-site randomness) is supposed to be an ideal system of lead-based complex perovskite Pb(B'B'')O and expected to give us a clear picture of the AFE/relaxor nature of the ground state by the B-site randomness. We studied the dynamics of O-PIN by inelastic X-ray scattering. The quasielastic (QE) scattering shows the critical slowing down and the transverse acoustic (TA) mode shows the softening towards
and expected to give us a clear picture of the AFE/relaxor nature of the ground state by the B-site randomness. We studied the dynamics of O-PIN by inelastic X-ray scattering. The quasielastic (QE) scattering shows the critical slowing down and the transverse acoustic (TA) mode shows the softening towards  . On the other hand, the transverse optic (TO) mode shows the softening toward low temperature with no clear anomaly at
. On the other hand, the transverse optic (TO) mode shows the softening toward low temperature with no clear anomaly at  . These results represent that the antiferroelectric (AFE) phase transition is associated with the TA and the origin of the QE scattering, while ferroelectric correlation does exist behind the AFE ordering. The effect of B-site randomness is finally discussed on the basis of the results.
. These results represent that the antiferroelectric (AFE) phase transition is associated with the TA and the origin of the QE scattering, while ferroelectric correlation does exist behind the AFE ordering. The effect of B-site randomness is finally discussed on the basis of the results.

 in Pb(Zn
in Pb(Zn Nb
Nb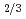 )O
)O -9%PbTiO
-9%PbTiO PbTiO
PbTiO
Owada, Kenji; Mizuki, Junichiro; Namikawa, Kazumichi*; Matsushita, Mitsuyoshi*; Shimomura, Susumu*; Nakao, Hironori*; Hirota, Kazuma*
Physical Review B, 83(22), p.224115_1 - 224115_7, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:37.64(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Complementary use of coherent X-ray diffraction (CXD), X-ray diffuse scattering, conventional X-ray diffraction techniques and dielectric measurements has enabled us to investigate Pb(Zn Nb
Nb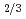 )O
)O -9%PbTiO
-9%PbTiO with a multiple-length-scale approach from the macroscale (lattice constants, bulk averaged) and microscale to the nanoscale (polar nanoregions (PNRs)) and discuss the contribution of each scale to the dielectric permittivity.
with a multiple-length-scale approach from the macroscale (lattice constants, bulk averaged) and microscale to the nanoscale (polar nanoregions (PNRs)) and discuss the contribution of each scale to the dielectric permittivity.
 and CePtSi
and CePtSi
Hirose, Yusuke*; Nishimura, Naoto*; Honda, Fuminori*; Sugiyama, Kiyohiro*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kindo, Koichi*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuura, Masato*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(2), p.024711_1 - 024711_12, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:57.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary) revealed by the absence of an anomaly in
revealed by the absence of an anomaly in  -polarized phonon dispersion
-polarized phonon dispersionKajimoto, Ryoichi; Sagayama, Hajime*; Sasai, Kenzo*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Arima, Takahisa*; Hirota, Kazuma*; Mitsui, Yukari*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 102(24), p.247602_1 - 247602_4, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:57.99(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Nb
Nb )O
)O and ferroelectric correlation in antiferroelectric Pb(In
and ferroelectric correlation in antiferroelectric Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O
Owada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 34(1), p.19 - 22, 2009/03
Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. This is characterized by measurements of dielectric response, which shows behavior that is usually clearly in one of those three classes. In contrast, X-ray scattering studies suggest the presence of AFE correlation in the relaxor state and FE in AFE state. Weak phonon softening at zone boundary in relaxor state shows that the AFE correlation intrinsically exists in PIN, as does the corresponding elastic scattering at (
(PIN) can be antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or a relaxor depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. This is characterized by measurements of dielectric response, which shows behavior that is usually clearly in one of those three classes. In contrast, X-ray scattering studies suggest the presence of AFE correlation in the relaxor state and FE in AFE state. Weak phonon softening at zone boundary in relaxor state shows that the AFE correlation intrinsically exists in PIN, as does the corresponding elastic scattering at (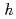 /2
/2  /2 0), while weak diffuse scattering around 333 Bragg reflection appears in AFE state suggesting FE correlation. These results will support our previous speculation that the AFE and FE correlations coexist in PIN (K. Owada
/2 0), while weak diffuse scattering around 333 Bragg reflection appears in AFE state suggesting FE correlation. These results will support our previous speculation that the AFE and FE correlations coexist in PIN (K. Owada  ., Phys, Rev. B
., Phys, Rev. B 094136 (2008)). Such a coexistence or competition is widely seen in the perovskite relaxor and the coexistence of FE and AFE correlations is essential for generating relaxor state.
094136 (2008)). Such a coexistence or competition is widely seen in the perovskite relaxor and the coexistence of FE and AFE correlations is essential for generating relaxor state.
 Nb
Nb )O
)O revealed by changing B-site randomness; Inelastic X-ray scattering study
revealed by changing B-site randomness; Inelastic X-ray scattering studyOwada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tsutsui, Satoshi*; Baron, A. Q. R.*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Physical Review B, 77(9), p.094136_1 - 094136_8, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:60.13(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Antiferroelectric (AFE), ferroelectric (FE) or relaxor states can appear in Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. We studied the effects of this randomness on the dynamics of PIN by high resolution inelastic X-ray scattering using ordered PIN (AFE) and disordered PIN (relaxor) single crystals. We have found a clear softening of a transverse optic mode at the
(PIN) depending upon the perovskite B-site randomness. We studied the effects of this randomness on the dynamics of PIN by high resolution inelastic X-ray scattering using ordered PIN (AFE) and disordered PIN (relaxor) single crystals. We have found a clear softening of a transverse optic mode at the  point in both the samples, indicating a robust and intrinsic ferroelectric instability regardless of the actual ground state. We interpret that AFE is stabilized only when In and Nb ions are spatially ordered enough to overwhelm the FE instability. As the B-site randomness becomes larger, AFE is suppressed and the hidden FE state starts appearing. Ultimately, the randomness begins to predominate over the development of FE regions and blocks a long range FE order, which we believe yields polar nanoregions resulting in relaxor behaviors.
point in both the samples, indicating a robust and intrinsic ferroelectric instability regardless of the actual ground state. We interpret that AFE is stabilized only when In and Nb ions are spatially ordered enough to overwhelm the FE instability. As the B-site randomness becomes larger, AFE is suppressed and the hidden FE state starts appearing. Ultimately, the randomness begins to predominate over the development of FE regions and blocks a long range FE order, which we believe yields polar nanoregions resulting in relaxor behaviors.
Owada, Kenji; Namikawa, Kazumichi; Mizuki, Junichiro; Shimomura, Susumu*; Nakao, Hironori*; Ito, Kazuki*; Matsushita, Mitsuyoshi*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Murakami, Yoichi*; Hirota, Kazuma*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 32(1), p.7 - 10, 2007/03
An X-ray speckle pattern well reflects a particle or domain alignment on the inside of materials. Detecting the alignment is important for understanding a function of the materials such as ferroelectric, piezoelectric materials, photonic crystals and so on. We have thus constructed the apparatus for coherent X-ray diffraction at BL22XU@SPring-8, high quality slits for obtaining the full coherent X-ray beam, high resolution X-ray CCD camera for obtaining the well-resolved speckle pattern, and so on. By using the devices, we have successfully observed the speckle pattern from Cu Au, the ferroelectric material PZN-9%PT (91%Pb(Zn
Au, the ferroelectric material PZN-9%PT (91%Pb(Zn Nb
Nb )O
)O -9%PbTiO
-9%PbTiO ) and Sr-doped BaTiO
) and Sr-doped BaTiO . The 2DFFT image gives us a spatial autocorrelation function which includes the information of the arrangement of the domains in the crystal within micrometers scale.
. The 2DFFT image gives us a spatial autocorrelation function which includes the information of the arrangement of the domains in the crystal within micrometers scale.
 Pb(In
Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O single crystal studied by a complementary use of X-ray and neutron scatterings
single crystal studied by a complementary use of X-ray and neutron scatteringsOwada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Terauchi, Hikaru*; Owa, Hidehiro*; Yasuda, Naohiko*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 75(2), p.024606_1 - 024606_6, 2006/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.24(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Structural properties of  Pb(In
Pb(In Nb
Nb )O
)O (PIN) single crystals at room temperature (RT) were investigated by X-ray and neutron scattering techniques, taking much account of the difference in the penetration depth and spatial resolution of X-rays and those of neutrons. A strong diffuse scattering was observed by X-ray while h/4, k/4, 0 superlattice reflections were found by neutron, indicating a relaxor state in the outer-layer of the crystal and an antiferroelectric (AFE) state in the bulk. The phonon dispersion was measured for the first time for the PIN series. Two transverse optic (TO1 and TO2) modes were clarified near the zone center though neither water-fall behavior nor folding of phonon branches was confirmed. We have thus concluded that a major part of the
(PIN) single crystals at room temperature (RT) were investigated by X-ray and neutron scattering techniques, taking much account of the difference in the penetration depth and spatial resolution of X-rays and those of neutrons. A strong diffuse scattering was observed by X-ray while h/4, k/4, 0 superlattice reflections were found by neutron, indicating a relaxor state in the outer-layer of the crystal and an antiferroelectric (AFE) state in the bulk. The phonon dispersion was measured for the first time for the PIN series. Two transverse optic (TO1 and TO2) modes were clarified near the zone center though neither water-fall behavior nor folding of phonon branches was confirmed. We have thus concluded that a major part of the 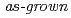 PIN crystal at RT is ferroelectric (FE). These results imply that the
PIN crystal at RT is ferroelectric (FE). These results imply that the  -site chemical ordering, i.e. inhomogeneity, which controls the structural properties of PIN, is unevenly distributed throughout the crystal. We speculate that small AFE grains coexist with the FE matrix while the outer-layer is in a relaxor state in the
-site chemical ordering, i.e. inhomogeneity, which controls the structural properties of PIN, is unevenly distributed throughout the crystal. We speculate that small AFE grains coexist with the FE matrix while the outer-layer is in a relaxor state in the 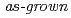 PIN.
PIN.
Hirota, Kazuma*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Cox, D. E.*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 75(11), p.111006_1 - 111006_13, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:73 Percentile:59.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The extensive and wide-ranging neutron and X-ray scattering studies of relaxors carried out by Gen Shirane and his collaborators are reviewed. Among the many results they have reported in some 50 scientific papers published since 1999, there are three especially notable accomplishments; namely, the discovery of a monoclinic phase near the morphotropic phase boundary, the clarification of the existence and roles of transverse optic soft-mode phonons, and detailed studies of polar nanoregions particularly by diffuse scattering techniques. We will focus mostly on the above topics, and discuss the impact of these on the research and understanding of relaxors.

Aso, Naofumi*; Owada, Kenji; Watanuki, Tetsu; Machida, Akihiko; Omura, Ayako; Inami, Toshiya; Homma, Yoshiya*; Shiokawa, Yoshinobu*; Hirota, Kazuma*; Sato, Noriaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 75(Suppl.), p.88 - 90, 2006/08
no abstracts in English
 Sr
Sr MnO
MnO studied by resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
studied by resonant inelastic X-ray scatteringIshii, Kenji; Inami, Toshiya; Owada, Kenji; Kuzushita, Kaori; Mizuki, Junichiro; Murakami, Yoichi; Ishihara, Sumio*; Endo, Yasuo*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Hirota, Kazuma*; et al.
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 66(12), p.2157 - 2162, 2005/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We have studied electronic excitations of hole-doped manganese oxides La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO (
(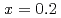 and
and 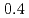 ) by resonant inelastic X-ray scattering at Mn K absorption edge. We observed in the excitation spectra that the Mott gap of La
) by resonant inelastic X-ray scattering at Mn K absorption edge. We observed in the excitation spectra that the Mott gap of La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO was filled by hole-doping. In La
was filled by hole-doping. In La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO , which shows a metal-insulator transition, we found that temperature dependence of scattering intensity is different between two scattering vectors. It may reflects a anisotropic electronic structure which originates from the orbital degrees of freedom in manganese oxides.
, which shows a metal-insulator transition, we found that temperature dependence of scattering intensity is different between two scattering vectors. It may reflects a anisotropic electronic structure which originates from the orbital degrees of freedom in manganese oxides.
 Sr
Sr MnO
MnO (
(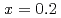 ,
, 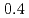 )
)Ishii, Kenji; Inami, Toshiya; Owada, Kenji; Kuzushita, Kaori; Mizuki, Junichiro; Murakami, Yoichi; Ishihara, Sumio*; Endo, Yasuo*; Maekawa, Sadamichi*; Hirota, Kazuma*; et al.
Physical Review B, 70(22), p.224437_1 - 224437_6, 2004/12
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:67.48(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Electronic excitations in the hole doped manganese oxides (La Sr
Sr MnO
MnO ,
, 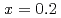 and
and 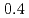 ) have been elucidated by using the resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) method. A doping effect in the strongly correlated electron systems has been observed for the first time. The scattering spectra show that a salient peak appears in low energies indicating the persistence of the Mott gap. At the same time, the energy gap is partly filled by doping holes and the spectral weight energy shifts toward lower energies. The excitation spectra show little change in the momentum space as is in undoped LaMnO
) have been elucidated by using the resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS) method. A doping effect in the strongly correlated electron systems has been observed for the first time. The scattering spectra show that a salient peak appears in low energies indicating the persistence of the Mott gap. At the same time, the energy gap is partly filled by doping holes and the spectral weight energy shifts toward lower energies. The excitation spectra show little change in the momentum space as is in undoped LaMnO . On the other hand, the scattering intensities in the low energy excitations of
. On the other hand, the scattering intensities in the low energy excitations of 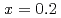 are anisotropic in temperature dependence, which indicates an anisotropy of magnetic interaction and underlying effect of the orbital.
are anisotropic in temperature dependence, which indicates an anisotropy of magnetic interaction and underlying effect of the orbital.
 Nb
Nb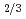 )
)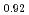 Ti
Ti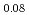 ]O
]O
Owada, Kenji; Hirota, Kazuma*; Rehrig, P. W.*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*; Shirane, Gen*
Physical Review B, 67(9), p.094111_1 - 094111_8, 2003/03
Times Cited Count:105 Percentile:94.48(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)High-temperature ( ) and high-electric-field (
) and high-electric-field ( ) effects on Pb[(Zn
) effects on Pb[(Zn Nb
Nb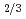 )
)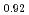 Ti
Ti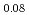 ]O
]O (PZN-8%PT) were studied comprehensively by neutron diffraction in the ranges
(PZN-8%PT) were studied comprehensively by neutron diffraction in the ranges 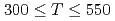 ~K and
~K and 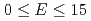 ~kV/cm. We have focused on how phase transitions depend on preceding thermal and electrical sequences. In the field cooling process (FC,
~kV/cm. We have focused on how phase transitions depend on preceding thermal and electrical sequences. In the field cooling process (FC, ![$$E parallel [001] ge 0.5$$](/search/images/ERCSAXDQMFZGC1DMMVWCAWZQGAYV0IC2M3SSAMBOGUSA.gif) ~kV/cm), a successive cubic (C)
~kV/cm), a successive cubic (C)  tetragonal (T)
tetragonal (T)  monoclinic (M
monoclinic (M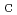 ) transition was observed. In the zero field cooling process (ZFC), however, we have found that the system does
) transition was observed. In the zero field cooling process (ZFC), however, we have found that the system does 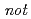 transform to the rhombohedral (R) phase as widely believed, but to a new, unidentified phase, which we call X. X gives a Bragg peak profile similar to that expected for R, but the
transform to the rhombohedral (R) phase as widely believed, but to a new, unidentified phase, which we call X. X gives a Bragg peak profile similar to that expected for R, but the  -axis is always slightly shorter than the
-axis is always slightly shorter than the  -axis. As for field effects on the X phase, it transforms into the M
-axis. As for field effects on the X phase, it transforms into the M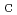 phase via another monoclinic phase (M
phase via another monoclinic phase (M ) as expected from a previous report [Noheda
) as expected from a previous report [Noheda 
 , 224101 (2002)].
, 224101 (2002)].