Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -rays after neutron capture by
-rays after neutron capture by  La for a T-violation search
La for a T-violation searchOkudaira, Takuya; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Haddock, C. C.*; Ito, Ikuya*; Yamamoto, Tomoki*; Endo, Shunsuke*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Sato, Takumi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 219, p.09001_1 - 09001_6, 2019/12
Parity violating effects enhanced by up to 10 times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n,
times have been observed in several neutron induced compound nuclei. There is a theoretical prediction that time reversal (T) violating effects can also be enhanced in these nuclei implying that T-violation can be searched for by making very sensitive measurements. However, the enhancement factor has not yet been measured in all nuclei. The angular distribution of the (n, ) reaction was measured with
) reaction was measured with  La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized
La by using a germanium detector assembly at J-PARC, and the enhancement factor was obtained. From the result, the measurement time to achieve the most sensitive T-violation search was estimated as 1.4 days, and a 40% polarized  La target and a 70% polarized
La target and a 70% polarized  He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm
He spin filter whose thickness is 70 atm cm are needed. Therefore high quality
cm are needed. Therefore high quality  He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n,
He spin filter is developed in JAEA. The measurement result of the (n, ) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the
) reaction at J-PARC and the development status of the  He spin filter will be presented.
He spin filter will be presented.
Hirota, Koichi
Hoshasen To Sangyo, (139), p.33 - 36, 2015/12
The article describes utilization programs for irradiation facilities for ion beam,  -ray and electron beam in Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute under the MEXT (Ministry of Education, Sports, Culture, Science and Technology) grants. The feature of the facilities and technical support of assistants in the fields of creation of genetic resources, analytical technology, and material development under the grants are introduced. The article also includes recent research activities of development of new flowers, visualization of Li in lithium-ion battery, and development of distortion resistance of fluoro-rubber etc.
-ray and electron beam in Takasaki Advanced Radiation Research Institute under the MEXT (Ministry of Education, Sports, Culture, Science and Technology) grants. The feature of the facilities and technical support of assistants in the fields of creation of genetic resources, analytical technology, and material development under the grants are introduced. The article also includes recent research activities of development of new flowers, visualization of Li in lithium-ion battery, and development of distortion resistance of fluoro-rubber etc.
Hirota, Koichi
Genshiryoku, Ryoshi, Kakuyugo Jiten, 4, p.126 - 127, 2014/12
Treatment of volatile organic compounds and dioxin by electron beams are presented in the specialized book. The book reviews experimental apparatus, decomposition, intermediates produced by oxidation of target substance from radiation chemistry point of view. For example, volatile organic compounds can be oxidized by radicals like OH produced by the irradiation of water existing in air by electron beams. Aromatic compounds are decomposed to be organic acids of formic, acetic, and propionic acids. These intermediates can be oxidized to carbon dioxides with a help of catalyst of manganese oxide. In the case of dioxin treatment, more than 90% decomposition of dioxin and furan was obtained by electron beam irradiation using actual fuel gases from Takahama Clean Center at Takasaki city. Dechlorination of higher chlorinated furan homologues during irradiation caused its lower decomposition compared to that of dioxins.
Hirota, Koichi
Isotope News, (698), p.24 - 25, 2012/06
no abstracts in English
Hirota, Koichi
Hoshasen To Sangyo, (131), p.64 - 65, 2011/12
no abstracts in English
Parajuli, D.; Hirota, Koichi; Seko, Noriaki; Oto, Keisuke*
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology (CEST 2011), p.B835 - B842, 2011/09
Cotton consisting of nearly 100% cellulose is one of the widely available natural polymers with versatile applications. In order to know the possibility of using cellulosic materials for the development of functional adsorbents by radiation induced vinyl graft modification method, cotton was studied as a representative natural material. In the present study, cotton was pre-irradiated with electron beam and glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) was grafted onto it. Various parameters like irradiation dose, solvent system, monomer concentration, grafting time, etc were studied to achieve the optimum graft yield. Once GMA containing reactive epoxy group was grafted onto the cotton matrix, various functional groups possessing different selectivity behavior for different metals were introduced by simple chemical reaction. The newly developed functional-cotton derivatives were studied for their ion exchange performances and selectivity patterns mainly for palladium in HCl and HCl-HNO systems.
systems.
Hirota, Koichi; Parajuli, D.; Seko, Noriaki
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Radiation Curing in Asia (RadTech Asia 2011) (Internet), p.136 - 137, 2011/06
Conventional methods for the recovery of precious metals are solvent extraction, chemical precipitation, and use of ion exchange resins. However these methods are facing to significant disadvantages like high capital costs, large chemical and energy requirements, and generation of toxic sludge or other waste products creating additional burden. Development of biomass based sorbents is a better, probably the best, option with lower capital cost and higher efficiency. Although the biomass-sorbents are better than the existing methods, the methods of preparing sorbents from them usually use several kinds of chemicals. In the present work, biomass has been modified with functional groups after electron beam irradiation and its performance for the recovery of precious metals has been studied. The obtained results are compared with that of chemically modified derivative.
Hirota, Koichi; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kimura, Atsushi; Kojima, Takuji
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Radiation Curing in Asia (RadTech Asia 2011) (Internet), p.108 - 109, 2011/06
We have focused on using MnO for the oxidation of intermediates produced from electron beam irradiation of VOC. Manganese dioxide can decompose ozone, produced by the irradiation of air containing VOCs, into activated oxygen, which can ultimately oxide the intermediates. Hybrid system equipped with electron accelerator and MnO
for the oxidation of intermediates produced from electron beam irradiation of VOC. Manganese dioxide can decompose ozone, produced by the irradiation of air containing VOCs, into activated oxygen, which can ultimately oxide the intermediates. Hybrid system equipped with electron accelerator and MnO has demonstrated the complete oxidation of the intermediates produced during the irradiation of xylene and toluene. The electron-beam treatment of dioxin from municipal solid waste incinerator was carried out at Takahama Clean Center in Japan. An incinerator gas of 1000 m
has demonstrated the complete oxidation of the intermediates produced during the irradiation of xylene and toluene. The electron-beam treatment of dioxin from municipal solid waste incinerator was carried out at Takahama Clean Center in Japan. An incinerator gas of 1000 m N/h was diverted downstream of a dry electric precipitator and was irradiated with electron beams using an electron accelerator that supplied 300 kV with a maximum energy of 12 kW. The results showed electron-beam is a promising technology for destroying dioxin in exhaust gases.
N/h was diverted downstream of a dry electric precipitator and was irradiated with electron beams using an electron accelerator that supplied 300 kV with a maximum energy of 12 kW. The results showed electron-beam is a promising technology for destroying dioxin in exhaust gases.
Parajuli, D.; Hirota, Koichi; Seko, Noriaki
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 288(1), p.53 - 58, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:81.98(Chemistry, Analytical) and CePtSi
and CePtSi
Hirose, Yusuke*; Nishimura, Naoto*; Honda, Fuminori*; Sugiyama, Kiyohiro*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kindo, Koichi*; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuura, Masato*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 80(2), p.024711_1 - 024711_12, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:57.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sugo, Yumi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Sasaki, Yuji; Hirota, Koichi; Morita, Yasuji
JAEA-Review 2010-065, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2009, P. 17, 2011/01
Hirota, Koichi
Charged Particle and Photon Interactions with Matter; Recent Advances, Applications, and Interfaces, p.923 - 941, 2010/12
Ionizing radiation is one of the advanced technologies for treating environmental pollutants. The technology is based on oxidation reactions with active species produced by the irradiation to media. When air is irradiated, many active species such as OH, O, and N
 are produced. Among them, OH is the most important radical that can effectively oxidize harmful chemicals. On the other hand, OH and hydrated electron play roles in oxidation and reduction while treating organic compounds in water. Although
are produced. Among them, OH is the most important radical that can effectively oxidize harmful chemicals. On the other hand, OH and hydrated electron play roles in oxidation and reduction while treating organic compounds in water. Although  ray irradiation is also an option for the treatment of various kinds of environmental pollutants, electron beam is preferable because maintaining an electron accelerator is easier and has better radiation security. On the basis of basic experiments, the pilot-scale and full-scale plants have been constructed around the world for the treatment of environmental pollutants such as NO
ray irradiation is also an option for the treatment of various kinds of environmental pollutants, electron beam is preferable because maintaining an electron accelerator is easier and has better radiation security. On the basis of basic experiments, the pilot-scale and full-scale plants have been constructed around the world for the treatment of environmental pollutants such as NO and SO
and SO , dioxin, VOC, and pollutants in wastewater.
, dioxin, VOC, and pollutants in wastewater.
Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kondo, Takafumi*; Yang, J.*; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Hirota, Koichi
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 79(11), p.1159 - 1164, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.14(Chemistry, Physical)Much of this past research has focused on finding more effective reactions between charged reactive species in room temperature ionic liquid (RTILs), which have a coulombic field. Reactions in RTILs involving the charged reactive species, particularly solvated electrons, have been studied by the techniques of radiation chemistry. The reaction behavior of halophenols in RTILs were investigated by  ray and pulsed electron radiolysis. The yield of CP decomposition in the RTILs was almost the same as that of solvated electrons formation. The yield of CP decomposition and phenol formation in the RTILs was low in the presence of electron scavengers such as nitrous oxide, indicating that solvated electrons primarily contributed to the decomposition of CP. The type of halogen group with the exception of fluorine had a negligible effect on the decomposition of halophenols in the RTILs. Therefore, RTILs could be applied as an reaction media for the reduction by ionizing radiation.
ray and pulsed electron radiolysis. The yield of CP decomposition in the RTILs was almost the same as that of solvated electrons formation. The yield of CP decomposition and phenol formation in the RTILs was low in the presence of electron scavengers such as nitrous oxide, indicating that solvated electrons primarily contributed to the decomposition of CP. The type of halogen group with the exception of fluorine had a negligible effect on the decomposition of halophenols in the RTILs. Therefore, RTILs could be applied as an reaction media for the reduction by ionizing radiation.
 -saturated system
-saturated systemNakagawa, Seiko*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Hirota, Koichi; Murakami, Takeshi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 79(8), p.890 - 893, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:23.14(Chemistry, Physical)Hydroxymaleimide was irradiated in N -saturated 2-propanol solutions by high-energy heavy ions over a wide range of LET values. The differential G-values of the degradation of hydroxymaleimide by irradiation with the heavier ions were lower than those of the lighter ions for the same LET value. It was opposite result obtained in the air-saturated system. The degradation efficiency was 1.5 times higher, when the dose rate was 1/10 times lower. When irradiated at an LET value lower than 8 eV/nm, the G-values converged to a value less than that obtained by
-saturated 2-propanol solutions by high-energy heavy ions over a wide range of LET values. The differential G-values of the degradation of hydroxymaleimide by irradiation with the heavier ions were lower than those of the lighter ions for the same LET value. It was opposite result obtained in the air-saturated system. The degradation efficiency was 1.5 times higher, when the dose rate was 1/10 times lower. When irradiated at an LET value lower than 8 eV/nm, the G-values converged to a value less than that obtained by  -irradiation.
-irradiation.
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Sugo, Yumi; Araki, Koshi*; Dally, E. B.*; Hirota, Koichi
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 49(12), p.5517 - 5522, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:37.55(Engineering, Chemical)An electron-beam (EB) irradiation/catalytic oxidation system was developed for the purification of a volatile organic compounds (VOC) gas stream under a practical gas flow condition. This system consists of a compact-sized electron accelerator and an ozone decomposition catalyst, which is MnO . The decomposition of toluene and/or xylene and their mineralization were examined with and without catalytic oxidation for a gas stream at a flow rate of 500 Nm
. The decomposition of toluene and/or xylene and their mineralization were examined with and without catalytic oxidation for a gas stream at a flow rate of 500 Nm /h. A combined catalyst bed enhanced the decomposition of VOCs and the mineralization of VOC and its irradiation organic byproducts. For example, the mineralization ratio for a 5-ppmv toluene/xylene/air mixture increased from 42% by EB irradiation to 100% by the combination treatment at 9.3 kGy. Furthermore, the yield of CO
/h. A combined catalyst bed enhanced the decomposition of VOCs and the mineralization of VOC and its irradiation organic byproducts. For example, the mineralization ratio for a 5-ppmv toluene/xylene/air mixture increased from 42% by EB irradiation to 100% by the combination treatment at 9.3 kGy. Furthermore, the yield of CO relative to CO
relative to CO increased from 59% to 85% by this catalytic treatment.
increased from 59% to 85% by this catalytic treatment.
 -Al
-Al O
O on the oxidation of xylene in air at low temperature under electron-beam irradiation
on the oxidation of xylene in air at low temperature under electron-beam irradiationHakoda, Teruyuki; Matsumoto, Kanae*; Mizuno, Akira*; Hirota, Koichi
International Journal of Plasma Environmental Science & Technology, 4(1), p.65 - 70, 2010/03
The catalytic effect of Pt/Al O
O and Ag/Al
and Ag/Al O
O on the oxidation of xylene in air was studied at a constant temperature of 373 K, when they were combined with electron-beam (EB)-induced non-thermal plasmas (NTPs). The presence of a catalyst bed was found to enhance the oxidation of the irradiation products of xylene. However, the degree of catalytic oxidation was different depending on the type of loaded metal and the position of the catalyst bed. Compared with a Al
on the oxidation of xylene in air was studied at a constant temperature of 373 K, when they were combined with electron-beam (EB)-induced non-thermal plasmas (NTPs). The presence of a catalyst bed was found to enhance the oxidation of the irradiation products of xylene. However, the degree of catalytic oxidation was different depending on the type of loaded metal and the position of the catalyst bed. Compared with a Al O
O bed, a Pt/Al
bed, a Pt/Al O
O bed in the NTP space suppressed oxidation, while an Ag/Al
bed in the NTP space suppressed oxidation, while an Ag/Al O
O bed downstream of the NTP space enhanced it. Under low temperature conditions, Pt/Al
bed downstream of the NTP space enhanced it. Under low temperature conditions, Pt/Al O
O was not a suitable catalyst for the oxidation of organics in combination with the NTP process. On the other hand, the Ag/Al
was not a suitable catalyst for the oxidation of organics in combination with the NTP process. On the other hand, the Ag/Al O
O catalyst was a preferable catalyst for the NTP-induced oxidation of organics under such low temperature conditions.
catalyst was a preferable catalyst for the NTP-induced oxidation of organics under such low temperature conditions.
Sugo, Yumi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Sasaki, Yuji; Hirota, Koichi; Morita, Yasuji
JAEA-Review 2009-041, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2008, P. 26, 2009/12
The radiolytic stabilities of the organic extractants for the separation of actinides have been commonly evaluated by the irradiation with  -rays as the most convenient method. However in the actual partitioning process of HLW, the extractants will be exposed to alpha-particles emitted from actinides, as well as beta- and
-rays as the most convenient method. However in the actual partitioning process of HLW, the extractants will be exposed to alpha-particles emitted from actinides, as well as beta- and  -rays from various fission products. In this study, alpha-radiolysis of
-rays from various fission products. In this study, alpha-radiolysis of 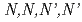 -tetraoctyldiglycolamide (TODGA) in
-tetraoctyldiglycolamide (TODGA) in  -dodecane was investigated by the irradiation with helium ion beam accelerated by a tandem accelerator using the TC1 irradiation apparatus in the TIARA facility. The sample was also irradiated with
-dodecane was investigated by the irradiation with helium ion beam accelerated by a tandem accelerator using the TC1 irradiation apparatus in the TIARA facility. The sample was also irradiated with  Co
Co  -rays for comparison of the radiation chemical yields between
-rays for comparison of the radiation chemical yields between  - and
- and  -rays. It was found that TODGA had almost fourfold resistance to
-rays. It was found that TODGA had almost fourfold resistance to  -rays, as compared with
-rays, as compared with  -rays. This result suggests that the radiolytic degradation of TODGA has been hitherto overestimated only by the irradiation with
-rays. This result suggests that the radiolytic degradation of TODGA has been hitherto overestimated only by the irradiation with  -rays.
-rays.
 catalyst
catalystHakoda, Teruyuki; Chowdhury, M. A. Z.*; Shimada, Akihiko; Hirota, Koichi
Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing, 29(6), p.549 - 557, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:26.08(Engineering, Chemical)The decomposition of dimethyl sulfide (DMS) at initial concentrations of 4.5-18.0 ppmv in air was studied under electron-beam (EB) irradiation. Doses to decompose 90% of input DMS were 2.5 kGy for 4.5 ppmv, 3.4 kGy for 10.6 ppmv, and 3.9 kGy for 18.0 ppmv. HCOOH, (CH )
) SO, and trace CH
SO, and trace CH OH and (CH
OH and (CH )
) SO
SO were produced as irradiation products in addition to CO
were produced as irradiation products in addition to CO and CO. Application of an O
and CO. Application of an O decomposition catalyst to an irradiated sample gas led to an enhancement in the oxidation of DMS and its products into CO
decomposition catalyst to an irradiated sample gas led to an enhancement in the oxidation of DMS and its products into CO and the decomposition of O
and the decomposition of O . For 10.6 ppmv DMS/air, the mineralization ratio increased from 41% via only EB irradiation to 100% via the combination treatment at 6.3 kGy. The yield of CO
. For 10.6 ppmv DMS/air, the mineralization ratio increased from 41% via only EB irradiation to 100% via the combination treatment at 6.3 kGy. The yield of CO to CO
to CO increased from 5.3% to 87.6% by combination with catalytic oxidation. This combination treatment enables the irradiation energy used to deodorize gas streams containing DMS to be reduced.
increased from 5.3% to 87.6% by combination with catalytic oxidation. This combination treatment enables the irradiation energy used to deodorize gas streams containing DMS to be reduced.
Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Baldacchino, G.*; Kurashima, Satoshi; Kimura, Atsushi; Sugo, Yumi; Katsumura, Yosuke*; Hirota, Koichi
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 78(12), p.1169 - 1174, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.45(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Sugo, Yumi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Sasaki, Yuji; Hirota, Koichi; Kimura, Takaumi
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 78(12), p.1140 - 1144, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:88.11(Chemistry, Physical)In the actual partitioning process of HLW, the organic complexing agent will be exposed to  -particles emitted by
-particles emitted by  -decay of the actinides. In this study,
-decay of the actinides. In this study,  -radiolysis of TODGA in
-radiolysis of TODGA in  -dodecane was investigated by the irradiation with helium ion beam accelerated by the AVF cyclotron or the tandem accelerator in the TIARA facility at JAEA Takasaki. It was found that the radiation chemical yield for the degradation of TODGA by helium ion beam irradiation was less than that by
-dodecane was investigated by the irradiation with helium ion beam accelerated by the AVF cyclotron or the tandem accelerator in the TIARA facility at JAEA Takasaki. It was found that the radiation chemical yield for the degradation of TODGA by helium ion beam irradiation was less than that by  -rays irradiation. It was also observed the radiation chemical yield gradually increased with the incident energy of helium ions. These results indicate that the radiolytic degradation of TODGA is reduced by high LET radiations such as
-rays irradiation. It was also observed the radiation chemical yield gradually increased with the incident energy of helium ions. These results indicate that the radiolytic degradation of TODGA is reduced by high LET radiations such as  -particles. Because the radical cations of
-particles. Because the radical cations of  -dodecane, which contribute to the charge transfer reaction described above, decrease by recombination in track.
-dodecane, which contribute to the charge transfer reaction described above, decrease by recombination in track.