Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Aizawa, Kosuke; Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Kobayashi, Jun; Kurihara, Akikazu
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2023/05
Self-actuated shutdown system (SASS) is a passive reactor-shutdown system that utilizes a Curie-point electromagnet (CPEM), which features the characteristic of loss in magnetism when the magnet temperature reaches the Curie point. A control rod with SASS is inserted into the core by gravity without recourse to any active shutdown system. To allow the SASS to effectively function, efficiently guiding high-temperature fluid from the fuel assembly to CPEM is important. Therefore, CPEM features a complicated shape such as having 45 fins, and a flow collector is installed upstream of CPEM to direct the flow from the fuel subassembly outlet to CPEM. In this report, the water experiment was performed on the full-scale model that simulates from the outlets of the fuel assemblies to the SASS flow collector, and flow phenomena around the temperature sensing part was analyzed from the data obtained by PIV measurement.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Aizawa, Kosuke; Nishimura, Masahiro; Kurihara, Akikazu
JAEA-Research 2021-009, 29 Pages, 2021/11
In sodium-cooled fast reactors, high burnup of fuel is required for practical use. It is important to predict and evaluate the flow behavior in a fuel assembly because there is a concern that the heat removal capacity of the fuel assembly with high burnup will be locally reduced due to swirling and thermal deformation of the fuel rods. In this study, flow field measurement tests were conducted using a 3-pin bundle system test specimen for the purpose of elucidating the phenomenon and constructing a verification database for thermal hydraulics analysis code. The viewpoints of the experiment for elucidating the phenomenon are as follows; (1) Overall flow behavior in the subchannel including near the wrapping wire, (2) Relationship between Reynolds number including laminar flow region and flow field, and (3) Evaluation of the effect of the presence or absence of wrapping wire on the flow field. As a result, detailed flow field data in the subchannel was obtained by PIV measurement. It was found that when the wrapping wire crossed the subchannel, the flow occurred toward adjacent subchannel and the flow occurred that follows the winding direction of the wrapping wire. It was confirmed that the tendency of the flow velocity distribution of the Reynolds number in the laminar flow region is significantly different from that of the transition region and the turbulent region under the condition. The test was conducted using a same 3-pin bundle system without the wrapping wire, and it was confirmed that mixing by the wrapping wire occurred even in the laminar flow region.
Aizawa, Kosuke; Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Nishimura, Masahiro; Kurihara, Akikazu; Ishida, Katsuji*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 8(4), p.20-00547_1 - 20-00547_11, 2021/08
A sodium-cooled fast reactor has been designed to attain a high burn-up core in commercialized fast reactor cycle systems. The sodium-cooled fast reactor adopts a wire spacer between fuel pins. The wire spacer performs functions of securing the coolant channel and the mixing between subchannels. In high burn-up fuel subassemblies, the fuel pin deformation due to swelling and thermal bowing may decrease the local flow velocity in the subassembly and influence the heat removal capability. Therefore, understanding the flow field in a wire-wrapped pin bundle is important. This study performed particle image velocimetry (PIV) measurements using a wire-wrapped three-pin bundle water model to grasp the flow field in the subchannel under conditions, including the laminar to turbulent regions. In the region away from the wrapping wire, the maximum flow velocity was increased by decreasing the Re number. Accordingly, the PIV measurements using the three-pin bundle geometry without the wrapping wire were also conducted to understand the effect of the wrapping wires on the flow field in the subchannel. The results confirmed that the mixing due to the wrapping wire occurred, even in the laminar condition. These experimental results are useful not only for understanding the pin bundle thermal hydraulics, but also for the code validation.
Aizawa, Kosuke; Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Nishimura, Masahiro; Kurihara, Akikazu; Ishida, Katsuji*
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2020/08
A sodium-cooled fast reactor is designed to attain a high burn-up core in commercialized fast reactor cycle systems. In high burn-up fuel subassemblies, the deformation of fuel pin due to the swelling and thermal bowing may decrease local flow velocity in the subassembly and influence the heat removal capability. Therefore, it is important to obtain the flow velocity distribution in a wire wrapped pin bundle. In this study, the detailed flow velocity distribution in the subchannel has been obtained by PIV (Particle Image Velocimetry) measurement using a wire-wrapped 3-pin bundle water model. Flow velocity conditions in the pin bundle were set from 0.036 m/s (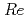 = 270) to 1.6m/s (
= 270) to 1.6m/s (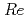 = 13,500). From the PIV results, the maximum flow velocity was increased by decreasing the
= 13,500). From the PIV results, the maximum flow velocity was increased by decreasing the 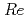 number in the region away from the wrapping wire. Moreover, the PIV measurements by using the 3-pin bundle geometry without the wrapping wire were conducted. From the results, the effect of the wrapping wire on the flow field in the subchannel was understood. There experimental results useful not only for understanding of pin bundle thermal hydraulics but also code validation.
number in the region away from the wrapping wire. Moreover, the PIV measurements by using the 3-pin bundle geometry without the wrapping wire were conducted. From the results, the effect of the wrapping wire on the flow field in the subchannel was understood. There experimental results useful not only for understanding of pin bundle thermal hydraulics but also code validation.
Doda, Norihiro; Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Tanaka, Masaaki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Thomas, J.*; Vilim, R. B.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Next Generation Nuclear Systems for Sustainable Development (FR-17) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2017/06
In sodium-cooled fast reactors, a natural circulation is expected to remove the core decay heat when the plant gets into a station blackout. From a perspective of reactor safety, the core hot spot temperature arising in the natural circulation should be evaluated accurately. To this end, Japan Atomic Energy Agency is trying to couple a 1-D plant dynamics analysis code Super-COPD and a 3-D CFD code AQUA to solve the thermal-hydraulic field in the whole plant under natural circulation condition. As a validation study, the coupled code was applied to an analysis of EBR-II shutdown heat removal test. The obtained numerical results reasonably agreed with the measured data, which demonstrated the validity of the coupled code.
Kikuchi, Norihiro; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Imai, Yasutomo*; Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Nishimura, Masahiro; Tanaka, Masaaki
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Kanto Shibu Ibaraki Koenkai 2015 Koen Rombunshu, p.179 - 180, 2015/08
In an economically improved sodium-cooled fast reactor, a narrower gap is considered among the fuel pins so as to achieve a high burn-up. Therefore, it is needed to evaluate thermal-hydraulic characteristics in case of a change of the gap geometry due to deformation of fuel pin caused by such as a swelling and a thermal bowing. For this purpose, a FEM analysis code, SPIRAL has been being developed in JAEA and the code validations using water or sodium experimental results have also being performed. In this study, a numerical analysis of a flow field around wire-wrapped fuel pins based on a 3-pin bundle water experiment was carried out as a validation study of SPIRAL. As a result, it was demonstrated that the hybrid-type turbulent model incorporated in SPIRAL has a high applicability to investigate the flow structure of the narrow gap in the fuel assembly.
Nishimura, Masahiro; Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Kamide, Hideki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Nagasawa, Kazuyoshi*; Imai, Yasutomo*
Proceedings of 9th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-9) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2014/11
Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Doda, Norihiro; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Iwasaki, Takashi*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 78(787), p.468 - 470, 2012/03
An analysis of JOYO MK-II natural circulation test has been performed to evaluate the applicability of the fast reactor plant dynamics code super-COPD to natural circulation decay heat removal phenomena. The analysis domain is set from the reactor core to the intermediate heat exchanger (IHX) so as to focus on the simulation accuracy of natural circulation behavior in the primary system and we compared the numerical results with experimental measurement. As a result, it was found that natural circulation behavior is much influenced by the coolant mixing regime in the upper plenum of the reactor vessel. The predicted transient changes of the core outlet coolant temperature and the primary flow rate showed good agreement with the test results by using a variable mesh partitioning method and by setting appropriate mixing volume in the upper plenum region which can include the effect of thermal stratification phenomena on the natural circulation behavior.
Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Doda, Norihiro; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Iwasaki, Takashi*
Dai-16-Kai Doryoku, Enerugi Gijutsu Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu, p.217 - 218, 2011/06
An analysis of JOYO MK-II natural circulation tests has been performed to evaluate the applicability of the fast reactor plant dynamic analysis code, Super-COPD, to natural circulation decay heat removal phenomena. In this analysis, the predicted transient behaviors of the core outlet coolant temperature and the primary flow rate showed good agreement with the test results by using a variable mesh partitioning method for the upper plenum region which can include the effect of thermal stratification phenomena.
Ebisawa, Hiroyuki; Hanakawa, Hiroki; Asano, Norikazu; Kusunoki, Hidehiko; Yanai, Tomohiro; Sato, Shinichi; Miyauchi, Masaru; Oto, Tsutomu; Kimura, Tadashi; Kawamata, Takanori; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-030, 165 Pages, 2009/07
The condition of facilities and machinery used continuously were investigated before the renewal work of JMTR on FY 2007. The subjects of investigation were reactor building, primary cooling system tanks, secondary cooling system piping and tower, emergency generator and so on. As the result, it was confirmed that some facilities and machinery were necessary to repair and others were used continuously for long term by maintaining on the long-term maintenance plan. JMTR is planed to renew by the result of this investigation.
Okuno, Hiroshi; Takada, Tomoyuki; Yoshiyama, Hiroshi; Miyoshi, Yoshinori
JAEA-Data/Code 2005-001, 117 Pages, 2005/11
Criticality calculation codes/code systems MCNP, MVP, SCALE and JACS, which are currently typically used in Japan for nuclear criticality safety evaluation, were benchmarked for so called dissolver-typed systems, i.e., fuel rod arrays immersed in fuel solution. The benchmark analyses were made for the evaluated critical experiments published in the International Criticality Safety Benchmark Evaluation Project (ICSBEP) Handbook: one evaluation representing five critical configurations from heterogeneous core of low-enriched uranium dioxides at the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute and two evaluations representing 16 critical configurations from heterogeneous core of mixed uranium and plutonium dioxides (MOXs) at the Battelle Pacific Northwest Laboratories of the U.S.A.. The results of the analyses showed that the minimum values of the neutron multiplication factor obtained with MCNP, MVP, SCALE and JACS were 0.993, 0.990, 0.993, 0.972, respectively, which values are from 2% to 4% larger than the maximum permissible multiplication factor of 0.95.
Nabeshima, Kunihiko; Doda, Norihiro; Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Mori, Takero; Ohira, Hiroaki
no journal, ,
Fast reactor plant dynamics simulation code Super-COPD has been validated through the application to the analysis of natural circulation tests in the experimental fast reactor JOYO. The analysis domain is set from the reactor core to the air cooler so as to focus on the simulation accuracy of natural circulation behavior with the full scale of core assembly modeling.
Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Nishimura, Masahiro; Kamide, Hideki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Nagasawa, Kazuyoshi*; Imai, Yasutomo*
no journal, ,
In high burn-up fuel subassemblies of sodium cooled fast reactor, deformation of fuel pin due to the swelling and thermal bowing may decrease local flow velocity via change of flow area in the subassembly. Therefore, it is important to developed detailed evaluation method of flow field in a wire wrapped pin bundle. In this study, water experiments were carried out to investigate the detailed velocity distribution in the wire wrapped pin bundle. The test section consists of an acrylic duct tube and fluorinated resin 3 pins which have nearly the same refractive index with that of water. The velocity distribution in the inner subchannel with the wrapping wire was measured by PIV. Furthermore, a detailed simulation code was applied to the experimental analysis and the calculated results were consistent with the experimental data. These data can contribute to construct the database to validate simulation codes.
Nishimura, Masahiro; Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Kamide, Hideki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Nagasawa, Kazuyoshi*; Imai, Yasutomo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Doda, Norihiro; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Iwasaki, Takashi*
no journal, ,
An analysis of JOYO MK-II natural circulation tests has been performed to evaluate the applicability of the fast reactor plant dynamics code Super-COPD to natural circulation decay heat removal phenomena. In this analysis, it was clarified that the natural circulation behavior is greatly influenced by the coolant mixing in the upper plenum. The predicted core outlet coolant temperature and primary flow rate showed good agreement with the test results during transients by setting appropriate mixing volume in the plenum model.
Aizawa, Kosuke; Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Kobayashi, Jun; Kurihara, Akikazu
no journal, ,
The self-actuated shutdown system (SASS) is a device that passively detach the control rod in response to a temperature rise at the reactor core outlet by utilizing the property that the magnetism of a temperature sensing part disappears as the temperature rises. In order to function the SASS effectively, it is important to efficiently guide high temperature fluid from the fuel assembly to the temperature sensing part, so the circumstance of temperature sensing alloy has a complicated shape such as 45 fins. In order to develop the SASS performance evaluation method, we plan to carry out the full-scale experiment to understand phenomena and acquire data for code validation. In this report, the water experiment was performed on the full-scale model that simulates from the outlets of the fuel assemblies to the SASS flow collector, and flow phenomena around the temperature sensing part was analyzed from the data obtained by PIV measurement.
Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Doda, Norihiro; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Iwasaki, Takashi*
no journal, ,
As the upgrade of the Super-COPD code for plant dynamics, the analysis for natural circulation tests during JOYO MK-II core is being carried out to verify the natural circulation applicability of the code. In this study, focused on the heat exchange characteristic of the intermediate heat exchanger (IHX), the analysis has been performed to estimate the sensibility of the IHX modeling for natural circulation characteristics. We tried to analysis the momentum and the energy transport in JOYO MK-II by the IHX model with or without additional bypass channel. As a result, it is found that the reverse flow in the IHX bypass is able to simulate by the modeling of the bypass flow and this reverse flow gives effects on the natural circulation characteristics in the primary cooling system.
Nishimura, Masahiro; Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Kamide, Hideki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Nagasawa, Kazuyoshi*; Imai, Yasutomo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hiyama, Tomoyuki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Takata, Takashi*
no journal, ,
In the piping system of fast breeder reactor, mixture of hot and cold liquid sodium causes thermal striping phenomena in which fluid temperature fluctuation is transmitted to the structure of the piping. The thermal striping causes the thermal stress in the piping structure and may damage it. It is thought that the liquid sodium can be controlled to reduce temperature fluctuation by applying magnetic field from the outside of the piping. In this study a numerical simulation code has been developed using a Finite Element Method to simulate electromagnetic flow fields controlled by applying the magnetic field. Numerical analyses of T-junction piping flow mixing have been carried out in condition of, "no magnetic field", "ladder type magnetic field", and "surround type magnetic field". The results have been compared for evaluating mitigation effects on the temperature fluctuation from the viewpoints of intensity and power spectrum.