Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
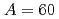
Tamii, Atsushi*; Pellegri, L.*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Allard, D.*; Goriely, S.*; Inakura, Tsunenori*; Khan, E.*; Kido, Eiji*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Litvinova, E.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 59(9), p.208_1 - 208_21, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.02(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Sr and
Sr and  Cs by AMS
Cs by AMSHonda, Maki; Martschini, M.*; Wieser, A.*; Marchhart, O.*; Lachner, J.*; Priller, A.*; Steier, P.*; Golser, R.*; Sakaguchi, Aya*
JAEA-Conf 2022-001, p.85 - 90, 2022/11
Accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) is an analytical method that combines mass spectrometry with a tandem accelerator, which has been used mainly in nuclear physics experiments. AMS is used to measure radionuclides with half-lives of 10 -10
-10 years. For radionuclides with half-lives of this order, the method of measuring their mass is 10
years. For radionuclides with half-lives of this order, the method of measuring their mass is 10 -10
-10 times more sensitive than measuring their activity. Because of this advantage, AMS has been widely applied in Earth and planetary sciences, atomic energy research, and other fields. Among the various studies, Wallner et al. (2021, 2016) have achieved excellent work in Earth and planetary sciences. For example, they have attained the ultra-sensitive analysis of
times more sensitive than measuring their activity. Because of this advantage, AMS has been widely applied in Earth and planetary sciences, atomic energy research, and other fields. Among the various studies, Wallner et al. (2021, 2016) have achieved excellent work in Earth and planetary sciences. For example, they have attained the ultra-sensitive analysis of  Fe and
Fe and  Pu in environmental samples. These are radionuclides produced by rapid-neutron-capture (r-process) nucleosynthesis. Our recent work shows that a new AMS system (VERA, University of Vienna), which combines laser isobaric separation and a typical AMS system, has been successfully applied to the ultra-sensitive determination of
Pu in environmental samples. These are radionuclides produced by rapid-neutron-capture (r-process) nucleosynthesis. Our recent work shows that a new AMS system (VERA, University of Vienna), which combines laser isobaric separation and a typical AMS system, has been successfully applied to the ultra-sensitive determination of  Sr and
Sr and  Cs in environment. For
Cs in environment. For  Sr in environmental samples, the
Sr in environmental samples, the  -ray measurement by the milking of the daughter nuclide
-ray measurement by the milking of the daughter nuclide  Y is still the principal method, which takes 3-6 weeks. The new AMS method has a detection limit of
Y is still the principal method, which takes 3-6 weeks. The new AMS method has a detection limit of  0.1 mBq, which is comparable to that of
0.1 mBq, which is comparable to that of  -ray measurement, with a more straightforward chemical treatment than
-ray measurement, with a more straightforward chemical treatment than  -measurement. Our achievement demonstrates that AMS can be a practical new method for determining
-measurement. Our achievement demonstrates that AMS can be a practical new method for determining  Sr in the environment.
Sr in the environment.
 Sr analysis of environmental samples by ion-laser interaction mass spectrometry
Sr analysis of environmental samples by ion-laser interaction mass spectrometryHonda, Maki; Martschini, M.*; Marchhart, O.*; Priller, A.*; Steier, P.*; Golser, R.*; Sato, Tetsuya; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Sakaguchi, Aya*
Analytical Methods, 14(28), p.2732 - 2738, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:45.92(Chemistry, Analytical)The sensitive  Sr analysis with accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) was developed for the advances of environmental radiology. One advantage of AMS is the ability to analyze various environmental samples with
Sr analysis with accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) was developed for the advances of environmental radiology. One advantage of AMS is the ability to analyze various environmental samples with  Sr/
Sr/ Sr atomic ratios of 10
Sr atomic ratios of 10 in a simple chemical separation. Three different IAEA samples with known
in a simple chemical separation. Three different IAEA samples with known  Sr concentrations (moss-soil, animal bone, Syrian soil: 1 g each) were analyzed to assess the validity of the chemical separation and the AMS measurement. The
Sr concentrations (moss-soil, animal bone, Syrian soil: 1 g each) were analyzed to assess the validity of the chemical separation and the AMS measurement. The  Sr measurements were conducted on the AMS system combined with the Ion Laser InterAction MasSpectrometry (ILIAMS) setup at the University of Vienna, which has excellent isobaric separation performance. The isobaric interference of
Sr measurements were conducted on the AMS system combined with the Ion Laser InterAction MasSpectrometry (ILIAMS) setup at the University of Vienna, which has excellent isobaric separation performance. The isobaric interference of  Zr in the
Zr in the  Sr AMS was first removed by chemical separation. The separation factor of Zr in two-step column chromatography with Sr resin and anion exchange resin was 10
Sr AMS was first removed by chemical separation. The separation factor of Zr in two-step column chromatography with Sr resin and anion exchange resin was 10 . The
. The  Zr remaining in the sample was removed by ILIAMS effectively. This simple chemical separation achieved a limit of detection
Zr remaining in the sample was removed by ILIAMS effectively. This simple chemical separation achieved a limit of detection  0.1 mBq in the
0.1 mBq in the  Sr AMS, which is lower than typical
Sr AMS, which is lower than typical  -ray detection. The agreement between AMS measurements and nominal values for the
-ray detection. The agreement between AMS measurements and nominal values for the  Sr concentrations of IAEA samples indicated that the new highly-sensitive
Sr concentrations of IAEA samples indicated that the new highly-sensitive  Sr analysis in the environmental samples with AMS is reliable even for high matrix samples of soil and bone.
Sr analysis in the environmental samples with AMS is reliable even for high matrix samples of soil and bone.
Hain, K.*; Martschini, M.*; G lce, F.*; Honda, Maki; Lachner, J.*; Kern, M.*; Pitters, J.*; Quinto, F.*; Sakaguchi, Aya*; Steier, P.*; et al.
lce, F.*; Honda, Maki; Lachner, J.*; Kern, M.*; Pitters, J.*; Quinto, F.*; Sakaguchi, Aya*; Steier, P.*; et al.
Frontiers in Marine Science (Internet), 9, p.837515_1 - 837515_17, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:96.12(Environmental Sciences)Recent major advances in accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) at the Vienna Environmental Research Accelerator (VERA) regarding detection efficiency and isobar suppression have opened possibilities for the analysis of additional long-lived radionuclides at ultra-low environmental concentrations. These radionuclides, including  U,
U,  Cs,
Cs,  Tc and
Tc and  Sr, will become important for oceanographic tracer application due to their generally conservative behavior in ocean water. In particular, the isotope ratios
Sr, will become important for oceanographic tracer application due to their generally conservative behavior in ocean water. In particular, the isotope ratios  U/
U/ U and
U and  Cs/
Cs/ Cs have proven to be powerful fingerprints for emission source identification as they are not affected by elemental fractionation. Improved detection efficiencies allowed us to analyze all major long-lived actinides, i.e.
Cs have proven to be powerful fingerprints for emission source identification as they are not affected by elemental fractionation. Improved detection efficiencies allowed us to analyze all major long-lived actinides, i.e.  U,
U,  Np,
Np, 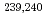 Pu,
Pu,  Am as well as the very rare
Am as well as the very rare  U, in the same 10 L water samples of an exemplary depth profile from the northwest Pacific Ocean. Especially for
U, in the same 10 L water samples of an exemplary depth profile from the northwest Pacific Ocean. Especially for  Sr analysis, our new approach has already been validated for selected reference materials (e.g. IAEA-A-12) and is ready for application in oceanographic studies. We estimate that a sample volume of only (1-3) L ocean water is sufficient for
Sr analysis, our new approach has already been validated for selected reference materials (e.g. IAEA-A-12) and is ready for application in oceanographic studies. We estimate that a sample volume of only (1-3) L ocean water is sufficient for  Sr as well as
Sr as well as  Cs analysis, respectively.
Cs analysis, respectively.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
Wu, P.*; Fan, F.-R.*; Hagihara, Masato*; Kofu, Maiko; Peng, K.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Lee, S.*; Honda, Takashi*; Yonemura, Masao*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 22(8), p.083083_1 - 083083_9, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:58.58(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Thermoelectric material SnSe has aroused world-wide interests in the past years, and its inherent strong lattice anharmonicity is regarded as a crucial factor for its outstanding thermoelectric performance. However, the understanding of lattice anharmonicity in SnSe system remains inadequate, especially regarding how phonon dynamics are affected by this behavior. In this work, we present a comprehensive study of lattice dynamics on Na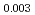 Sn
Sn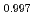 Se
Se S
S by means of neutron total scattering, inelastic neutron scattering, Raman spectroscopy as well as frozen-phonon calculations. Lattice anharmonicity is evidenced by pair distribution function, inelastic neutron scattering and Raman measurements. By separating the effects of thermal expansion and multi-phonon scattering, we found that the latter is very significant in high-energy optical phonon modes. The strong temperature-dependence of these phonon modes indicate the anharmonicity in this system. Moreover, our data reveals that the linewidths of high-energy optical phonons become broadened with mild doping of sulfur. Our studies suggest that the thermoelectric performance of SnSe could be further enhanced by reducing the contributions of high-energy optical phonon modes to the lattice thermal conductivity via phonon engineering.
by means of neutron total scattering, inelastic neutron scattering, Raman spectroscopy as well as frozen-phonon calculations. Lattice anharmonicity is evidenced by pair distribution function, inelastic neutron scattering and Raman measurements. By separating the effects of thermal expansion and multi-phonon scattering, we found that the latter is very significant in high-energy optical phonon modes. The strong temperature-dependence of these phonon modes indicate the anharmonicity in this system. Moreover, our data reveals that the linewidths of high-energy optical phonons become broadened with mild doping of sulfur. Our studies suggest that the thermoelectric performance of SnSe could be further enhanced by reducing the contributions of high-energy optical phonon modes to the lattice thermal conductivity via phonon engineering.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Arai, Takehiko*; Nakauchi, Yusuke*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Science, 364(6437), p.272 - 275, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:259 Percentile:99.73(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The near-Earth asteroid 162173 Ryugu, the target of Hayabusa2 sample return mission, is believed to be a primitive carbonaceous object. The Near Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on Hayabusa2 acquired reflectance spectra of Ryugu's surface to provide direct measurements of the surface composition and geological context for the returned samples. A weak, narrow absorption feature centered at 2.72 micron was detected across the entire observed surface, indicating that hydroxyl (OH)-bearing minerals are ubiquitous there. The intensity of the OH feature and low albedo are similar to thermally- and/or shock-metamorphosed carbonaceous chondrite meteorites. There are few variations in the OH-band position, consistent with Ryugu being a compositionally homogeneous rubble-pile object generated from impact fragments of an undifferentiated aqueously altered parent body.
Honda, Yuki; Fukaya, Yuji; Nakagawa, Shigeaki; Baker, R. I.*; Sato, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 8th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2016) (CD-ROM), p.704 - 713, 2016/11
A high-temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) has superior safety characteristics. A loss of forced cooling (LOFC) test using a high-temperature engineering test reactor (HTTR) has been carried out to verify the inherent safety of an HTGR when forced cooling is diminished without reactor scram. In the test, an all-gas circulator was tripped with an initial reactor power of 9 MW and re-criticality was shown. This study focuses on developing a point kinetics method with RELAP5-3D code for an LOFC accident. There is a large temperature difference between the inlet and outlet of the core in an HTGR, and the temperature fluctuation range has been large in several accidents. We analyze the temperature dependency of xenon-135 reactivity and show that the temperature dependency of xenon-135 microscopic absorption cross-section affected the re-criticality time of the LOFC test.
Buesseler, K. O.*; German, C. R.*; Honda, Makio*; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi; Black, E. E.*; Kawakami, Hajime*; Manganini, S. M.*; Pike, S.*
Environmental Science & Technology, 49(16), p.9807 - 9816, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:55.84(Engineering, Environmental)A three year time-series of particle fluxes is presented from sediment traps deployed at 500 and 1000 m at a site 115 km southeast of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP). Results show a high fraction of lithogenic material, suggesting a lateral source of sediments. The accident-derived radiocesium were enhanced in flux peaks that, given variations in trap  Cs/
Cs/ Pb ratios, are characteristic of material derived from shelf and slope sediments found from
Pb ratios, are characteristic of material derived from shelf and slope sediments found from  120 to
120 to  500 m. The fluxes of radiocesium are an order of magnitude higher than a previously reported for the trap located 100 km due east of FDNPP. We attribute the large difference due to the position of our trap under the southeasterly currents that carry contaminated waters and resuspended sediments in to the Pacific. These higher sedimentary fluxes of radiocesium to the offshore are still small relative to the inventory of radiocesium currently buried nearshore.
500 m. The fluxes of radiocesium are an order of magnitude higher than a previously reported for the trap located 100 km due east of FDNPP. We attribute the large difference due to the position of our trap under the southeasterly currents that carry contaminated waters and resuspended sediments in to the Pacific. These higher sedimentary fluxes of radiocesium to the offshore are still small relative to the inventory of radiocesium currently buried nearshore.
Koide, Yoshihiko; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Wanner, M.*; Barabaschi, P.*; Cucchiaro, A.*; Davis, S.*; Decool, P.*; Di Pietro, E.*; Disset, G.*; Genini, L.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 55(8), p.086001_1 - 086001_7, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:83.35(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The most distinctive feature of the superconducting magnet system for JT-60SA is the optimized coil structure in terms of the space utilization as well as the highly accurate coil manufacturing, thus meeting the requirements for the steady-state tokamak research: A conceptually new outer inter-coil structure separated from the casing is introduced to the toroidal field coils to realize their slender shape, allowing large-bore diagnostic ports for detailed plasma measurements. A method to minimize the manufacturing error of the equilibrium-field coils has been established, aiming at the precise plasma shape/position control. A compact butt-joint has been successfully developed for the Central Solenoid, which allows an optimized utilization of the limited space for the Central Solenoid to extend the duration of the plasma pulse.
 revealed by
revealed by  O-NMR
O-NMRTokunaga, Yo; Nishi, Tsuyoshi; Nakada, Masami; Ito, Akinori*; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Homma, Yoshiya*; Honda, Fuminori*; Aoki, Dai*; Walstedt, R. E.*
Physical Review B, 89(21), p.214416_1 - 214416_8, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:31.93(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The magnetic phase transition near 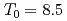 K in AmO
K in AmO has been investigated microscopically by means of
has been investigated microscopically by means of  O NMR. To avoid complexities arising from sample aging associated with the alpha decay of
O NMR. To avoid complexities arising from sample aging associated with the alpha decay of  Am, all measurements have been performed within 40 days after sample synthesis. Even during such a short period, however, a rapid change of NMR line shape has been observed at 1.5 K, suggesting that the ground state of AmO
Am, all measurements have been performed within 40 days after sample synthesis. Even during such a short period, however, a rapid change of NMR line shape has been observed at 1.5 K, suggesting that the ground state of AmO is very sensitive to disorder. We have also confirmed the loss of
is very sensitive to disorder. We have also confirmed the loss of  O NMR signal intensity over a wide temperature range below
O NMR signal intensity over a wide temperature range below 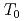 , and more than half of oxygen nuclei are undetectable at 1.5 K. This behavior reveals the persistence of slow and distributed spin fluctuations down to temperatures well below
, and more than half of oxygen nuclei are undetectable at 1.5 K. This behavior reveals the persistence of slow and distributed spin fluctuations down to temperatures well below 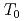 . In the paramagnetic state, strong NMR line broadening and spatially inhomogeneous spin fluctuations have been observed. The results are all indicative of short-range, spin-glass-like character for the magnetic transition in this system.
. In the paramagnetic state, strong NMR line broadening and spatially inhomogeneous spin fluctuations have been observed. The results are all indicative of short-range, spin-glass-like character for the magnetic transition in this system.
Sako, Hiroyuki; Ahn, J. K.*; Baek, K. H.*; Bassalleck, B.*; Fujioka, H.*; Guo, L.*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Hicks, K.*; Honda, R.*; Hwang, S. H.*; et al.
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 9(4), p.C04009_1 - C04009_10, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.04(Instruments & Instrumentation)A TPC has been developed for J-PARC E42 experiment to search for H-dibaryon in (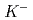 ,
, 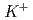 ) reaction. An event with 2
) reaction. An event with 2 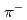 and 2 protons decaying from H-dibaryon is searched for inside the TPC. The TPC has octagonal prism shape drift volume with about 50 cm diameter with 55 cm drift length filled with Ar-CH
and 2 protons decaying from H-dibaryon is searched for inside the TPC. The TPC has octagonal prism shape drift volume with about 50 cm diameter with 55 cm drift length filled with Ar-CH (90:10) gas. At the end of the drift volume, 3-layer GEMs are equipped. In order to analyze momenta of produced particles, the TPC is applied with 1 T dipole magnetic field parallel to the drift electric field with a superconducting Helmholz magnet. In order to maximize the acceptance of H-dibaryon events, a diamond target is installed inside the TPC drift volume, in a cylindrical hole opened from the top to the middle of the drift volume. Since extremely high-rate
(90:10) gas. At the end of the drift volume, 3-layer GEMs are equipped. In order to analyze momenta of produced particles, the TPC is applied with 1 T dipole magnetic field parallel to the drift electric field with a superconducting Helmholz magnet. In order to maximize the acceptance of H-dibaryon events, a diamond target is installed inside the TPC drift volume, in a cylindrical hole opened from the top to the middle of the drift volume. Since extremely high-rate 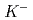 beam is directly injected into the TPC drift volume to the target, a gating grid and GEMs are adopted to suppress positive-ion feedback.
beam is directly injected into the TPC drift volume to the target, a gating grid and GEMs are adopted to suppress positive-ion feedback.
Imbeaux, F.*; Citrin, J.*; Hobirk, J.*; Hogeweij, G. M. D.*; K chl, F.*; Leonov, V. M.*; Miyamoto, Seiji; Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Parail, V.*; Pereverzev, G. V.*; et al.
chl, F.*; Leonov, V. M.*; Miyamoto, Seiji; Nakamura, Yukiharu*; Parail, V.*; Pereverzev, G. V.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(8), p.083026_1 - 083026_11, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:80.59(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Murakami, Masanori*; Park, J. M.*; Giruzzi, G.*; Garcia, J.*; Bonoli, P.*; Budny, R. V.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Imbeaux, F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Budny, R.*; Casper, T.*; Citrin, J.*; Fereira, J.*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Garcia, J.*; Gribov, Y. V.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Imbeaux, F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Budny, R.*; Casper, T.*; Citrin, J.*; Fereira, J.*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Garcia, J.*; Gribov, Y. V.*; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/10
In order to prepare adequate current ramp-up and ramp-down scenarios for ITER, present experiments from several tokamaks have been analyzed by means of integrated modeling in view of determining relevant heat transport models for these operation phases. The results of these studies are presented and projections to ITER current ramp-up and ramp-down scenarios are done, focusing on the baseline inductive scenario (main heating plateau current of 15 MA). Various transport models have been tested by means of integrated modeling against experimental data from ASDEX Upgrade, C-Mod, DIII-D, JET and Tore Supra, including both Ohmic plasmas and discharges with additional heating/current drive. With using the most successful models, projections to the ITER current ramp-up and ramp-down phases are carried out. Though significant differences between models appear on the electron temperature prediction, the final q-profiles reached in the simulation are rather close.
Giruzzi, G.*; Park, J. M.*; Murakami, M.*; Kessel, C. E.*; Polevoi, A.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Artaud, J. F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Bonoli, P.*; Budny, R. V.*; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
Ikeda, Yoshitaka; Hanada, Masaya; Kamada, Masaki; Kobayashi, Kaoru; Umeda, Naotaka; Akino, Noboru; Ebisawa, Noboru; Inoue, Takashi; Honda, Atsushi; Kawai, Mikito; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 36(4), p.1519 - 1529, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:41.25(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The JT-60SA N-NBI system is required to inject 10 MW for 100 s at 500 keV. Three key issues should be solved for the JT-60SA N-NBI ion source. One is to improve the voltage holding capability. Recent R&D tests suggested that the accelerator with a large area of grids may need a high margin in the design of electric field and a long time for conditioning. The second issue is to reduce the grid power loading. It was found that some beamlets were strongly deflected due to beamlet-beamlet interaction and strike on the grounded grid. The grids are to be designed by taking account of beamlet-beamlet interaction in three-dimensional simulation. Third is to maintain the D- production for 100 s. A simple cooling structure is proposed for the active cooled plasma grid, where a key is the temperature gradient on the plasma grid for uniform D- production. The modified N-NBI ion source will start on JT-60SA in 2015.
 ion beams in the JT-60 negative ion source
ion beams in the JT-60 negative ion sourceHanada, Masaya; Kamada, Masaki; Akino, Noboru; Ebisawa, Noboru; Honda, Atsushi; Kawai, Mikito; Kazawa, Minoru; Kikuchi, Katsumi; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 79(2), p.02A519_1 - 02A519_4, 2008/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:32.32(Instruments & Instrumentation)A long pulse production of high-current, high-energy D ion beams was studied in the JT-60U negative ion source that was designed to produce 22 A, 500 keV D
ion beams was studied in the JT-60U negative ion source that was designed to produce 22 A, 500 keV D ion beams. Prior to the long pulse production, the short pulse beams were produced to examine operational ranges for a stable voltage holding capability and an allowable grid power loading. From a correlation between the voltage holding capability and a light intensity of cathodoluminescence from the insulator made of Fiber Reinforced Plastic insulator, the voltage holding was found to be stable at
ion beams. Prior to the long pulse production, the short pulse beams were produced to examine operational ranges for a stable voltage holding capability and an allowable grid power loading. From a correlation between the voltage holding capability and a light intensity of cathodoluminescence from the insulator made of Fiber Reinforced Plastic insulator, the voltage holding was found to be stable at  340 kV where the light was sufficiently suppressed. The grid power loading for the long pulse operation was also decreased to the allowable level of
340 kV where the light was sufficiently suppressed. The grid power loading for the long pulse operation was also decreased to the allowable level of  1 MW without a significant reduction of the beam power by tuning the extraction voltage (Vext) and the arc power (Parc). These allow the production of 30 A D
1 MW without a significant reduction of the beam power by tuning the extraction voltage (Vext) and the arc power (Parc). These allow the production of 30 A D ion beams at 340 keV from two ion sources at Vacc = 340 kV. The pulse length was extended step by step, and finally reached up to 21 s, where the beam pulse length was limited by the surface temperature of the beam scraper without water cooling. The D
ion beams at 340 keV from two ion sources at Vacc = 340 kV. The pulse length was extended step by step, and finally reached up to 21 s, where the beam pulse length was limited by the surface temperature of the beam scraper without water cooling. The D ion beams were neutralized to via a gas cell, resulting in a long pulse injection of 3.2 MW D
ion beams were neutralized to via a gas cell, resulting in a long pulse injection of 3.2 MW D beams for 21 s. This is the first long injection of
beams for 21 s. This is the first long injection of  20 s in a power range of
20 s in a power range of  3 MW.
3 MW.
 and NpCoGa
and NpCoGa
Detlefs, B.*; Wilkins, S. B.*; Caciuffo, R.*; Paix o, J. A.*; Kaneko, Koji; Honda, Fuminori*; Metoki, Naoto; Bernhoeft, N.*; Rebizant, J.*; Lander, G. H.*
o, J. A.*; Kaneko, Koji; Honda, Fuminori*; Metoki, Naoto; Bernhoeft, N.*; Rebizant, J.*; Lander, G. H.*
Physical Review B, 77(2), p.024425_1 - 024425_10, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:58.3(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We report a resonant X-ray scattering study of the antiferromagnetic neptunium compounds NpCoGa and NpRhGa
and NpRhGa . Large resonant signals of magnetic dipole character are observed below the N
. Large resonant signals of magnetic dipole character are observed below the N el temperatures. The signals at the Np edges confirm the behavior determined previously from neutron diffraction. On application of a magnetic field of 9 T along the [010] direction in NpRhGa
el temperatures. The signals at the Np edges confirm the behavior determined previously from neutron diffraction. On application of a magnetic field of 9 T along the [010] direction in NpRhGa , we observe a change in the population of different [110]-type domains. We also observe a magnetic dipole signal at the Ga
, we observe a change in the population of different [110]-type domains. We also observe a magnetic dipole signal at the Ga  edge, similarly to the reported UGa
edge, similarly to the reported UGa case, that can be interpreted within a semilocalized model as an orbital polarization of the Ga 4
case, that can be interpreted within a semilocalized model as an orbital polarization of the Ga 4 states induced via strong hybridization with the Np 5
states induced via strong hybridization with the Np 5 valence band. Quantitative analysis of the signal shows that the Ga dipole on the two different Ga sites follows closely the Np magnetic moment reorientation in NpRhGa
valence band. Quantitative analysis of the signal shows that the Ga dipole on the two different Ga sites follows closely the Np magnetic moment reorientation in NpRhGa . The ratios of the signals on the two inequivalent Ga sites are not the same for the different compounds.
. The ratios of the signals on the two inequivalent Ga sites are not the same for the different compounds.