Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 titanium alloys strong and ductile
titanium alloys strong and ductileChong, Y.*; Gholizadeh, R.*; Guo, B.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Zhao, G.*; Yoshida, Shuhei*; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Godfrey, A.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 257, p.119165_1 - 119165_14, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:98.38(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Metastable  titanium alloys possess excellent strain-hardening capability, but suffer from a low yield strength. As a result, numerous attempts have been made to strengthen this important structural material in the last decade. Here, we explore the contributions of grain refinement and interstitial additions in raising the yield strength of a Ti-12Mo (wt.%) metastable
titanium alloys possess excellent strain-hardening capability, but suffer from a low yield strength. As a result, numerous attempts have been made to strengthen this important structural material in the last decade. Here, we explore the contributions of grain refinement and interstitial additions in raising the yield strength of a Ti-12Mo (wt.%) metastable  titanium alloy. Surprisingly, rather than strengthening the material, grain refinement actually lowers the ultimate tensile strength in this alloy. This unexpected and anomalous behavior is attributed to a significant enhancement in strain-induced
titanium alloy. Surprisingly, rather than strengthening the material, grain refinement actually lowers the ultimate tensile strength in this alloy. This unexpected and anomalous behavior is attributed to a significant enhancement in strain-induced  martensite phase transformation, where in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction analysis reveals, for the first time, that this phase is much softer than the parent
martensite phase transformation, where in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction analysis reveals, for the first time, that this phase is much softer than the parent  phase. Instead, a combination of both oxygen addition and grain refinement is found to realize an unprecedented strength-ductility synergy in a Ti-12Mo-0.3O (wt.%) alloy. The advantageous effect of oxygen solutes in this ternary alloy is twofold. Firstly, solute oxygen largely suppresses strain-induced transformation to the
phase. Instead, a combination of both oxygen addition and grain refinement is found to realize an unprecedented strength-ductility synergy in a Ti-12Mo-0.3O (wt.%) alloy. The advantageous effect of oxygen solutes in this ternary alloy is twofold. Firstly, solute oxygen largely suppresses strain-induced transformation to the  martensite phase, even in a fine-grained microstructure, thus avoiding the softening effect of excessive amounts of
martensite phase, even in a fine-grained microstructure, thus avoiding the softening effect of excessive amounts of  martensite. Secondly, oxygen solutes readily segregate to twin boundaries, as revealed by atom probe tomography. This restricts the growth of
martensite. Secondly, oxygen solutes readily segregate to twin boundaries, as revealed by atom probe tomography. This restricts the growth of 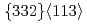 deformation twins, thereby promoting more extensive twin nucleation, leading to enhanced microstructural refinement. The insights from our work provide a cost-effective rationale for the design of strong yet tough metastable
deformation twins, thereby promoting more extensive twin nucleation, leading to enhanced microstructural refinement. The insights from our work provide a cost-effective rationale for the design of strong yet tough metastable  titanium alloys, with significant implications for more widespread use of this high strength-to-weight structural material.
titanium alloys, with significant implications for more widespread use of this high strength-to-weight structural material.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:75.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 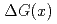 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:193 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.53(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:181 Percentile:98.32(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of 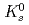 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
Yang, H. L.*; Kim, Y. S.*; Park, Y. M.*; Bae, Y. S.*; Kim, H. K.*; Kim, K. M.*; Lee, K. S.*; Kim, H. T.*; Bang, E. N.*; Joung, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Because the 2010 operation of Korea Superconducting Tokamak Advanced Research (KSTAR) mainly aims to achieve strongly elongated and diverted plasma, all the necessary hardware systems to provide an essential circumstance for the plasma shaping were newly installed and upgraded in 2010. In this paper, general configuration of the upgraded systems described earlier will be outlined. Moreover, several key performances and test results of the systems will be also reported in summary.
Ioki, Kimihiro; Elio, F.*; Barabash, V.*; Chuyanov, V.*; Rozov, V.*; Wang, X.*; Chen, J.*; Wang, L.*; Lorenzetto, P.*; Peacock, A.*; et al.
Fusion Engineering and Design, 82(15-24), p.1774 - 1780, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:66.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)In December 2005, the new procurement allocation plan of the ITER components among the seven Parties was prepared. The need to qualify for procurement of the specific components was especially introduced in the document. The main features and milestones of the qualification program are described in "Procurement Plan" for each specific component. Due to the complicated features of FW procurement, the procurement document has to be developed precisely. To guarantee high quality of 1700 FW panels produced by 6 different Parties, a qualification program is essential. The qualification mock-up is 80 mm wide, 240 mm long and 81 mm thick with 3 beryllium tiles 10 mm thick. Heat load tests will be performed on the qualification mock-ups in 2007 in EU and USA facilities. The maximum design heat load on the ITER FW is 0.5 MW/m  (steady state)
(steady state)  30,000 shots. Mechanical tests of joints are also required using standardized methods. Only Parties which have satisfied the acceptance criteria of the qualification tests can proceed to the procurement stage of the ITER FW. Semi-prototypes (roughly 1000 mm
30,000 shots. Mechanical tests of joints are also required using standardized methods. Only Parties which have satisfied the acceptance criteria of the qualification tests can proceed to the procurement stage of the ITER FW. Semi-prototypes (roughly 1000 mm  200 mm) are also requested before the ITER FW manufacturing.
200 mm) are also requested before the ITER FW manufacturing.
Akiba, Masato; Boccaccini, L. V.*; Cho, S. Y.*; Devidov, V.*; Enoeda, Mikio; Feng, K. M.*; Hong, B. G.*; Kovalenko, V.*; Ying, A.*
no journal, ,
A recent study in the frame of the Test Blanket Working Group aimed to identify general issues connected to solid breeder blanket concept and to assess particular needs related to the development of its different variants. The present paper overviews the results of this study, outlining its outcomes for the implementation of an international co-operation programme and giving guidelines for the identification of a limited number of basic TBM configurations suitable for being tested in ITER.