Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
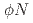 correlation function
correlation functionAbreu, L. M.*; Gubler, P.; Khemchandani, K. P.*; Mart nez Torres, A.*; Hosaka, Atsushi
nez Torres, A.*; Hosaka, Atsushi
Physics Letters B, 860, p.139175_1 - 139175_7, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:52.60(Astronomy & Astrophysics)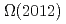 from QCD sum rules
from QCD sum rulesSu, N.*; Chen, H.-X.*; Gubler, P.; Hosaka, Atsushi
Nuclear and Particle Physics Proceedings, 347, p.2 - 5, 2024/12
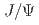 system
systemPan, Y.-W.*; Liu, Z.-W.*; Geng, L.-S.*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Liu, X.*
Physical Review D, 110(9), p.094004_1 - 094004_8, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Khemchandani, K. P.*; Mart nez Torres, A.*; Kim, S.-H.*; Nam, S.-I.*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Nagahiro, Hideko*
nez Torres, A.*; Kim, S.-H.*; Nam, S.-I.*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Nagahiro, Hideko*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 301, p.03001_1 - 03001_10, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
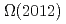 from QCD sum rules
from QCD sum rulesSu, N.*; Chen, H.-X.*; Gubler, P.; Hosaka, Atsushi
Physical Review D, 110(3), p.034007_1 - 034007_9, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)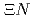 dibaryon as a weakly bound system in
dibaryon as a weakly bound system in 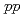 collisions
collisionsWu, T.-C.*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Geng, L.-S.*
Physical Review D, 109(11), p.114009_1 - 114009_8, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Song, Q.-F.*; L , Q.-F.*; Hosaka, Atsushi
, Q.-F.*; Hosaka, Atsushi
European Physical Journal C, 84(1), p.89_1 - 89_15, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:68.26(Physics, Particles & Fields)no abstracts in English
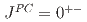 and
and 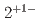
Xi, H.-Z.*; Jiang, Y.-W.*; Chen, H.-X.*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Su, N.*
Physical Review D, 108(9), p.094019_1 - 094019_13, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:49.66(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Meng, Q.*; Hiyama, Emiko*; Oka, Makoto*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Xu, C.*
Physics Letters B, 846, p.138221_1 - 138221_6, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:92.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Giachino, A.*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Santopinto, E.*; Takeuchi, Sachiko*; Takizawa, Makoto*; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro*
Physical Review D, 108(7), p.074012_1 - 074012_6, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:79.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Takada, Hiroto*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Harada, Masayasu*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Oka, Makoto*
Physical Review D, 108(5), p.054033_1 - 054033_15, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:49.66(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
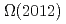 in a coupled-channel approach
in a coupled-channel approachL , Q.-F.*; Nagahiro, Hideko*; Hosaka, Atsushi
, Q.-F.*; Nagahiro, Hideko*; Hosaka, Atsushi
Physical Review D, 107(1), p.014025_1 - 014025_10, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:72.68(Astronomy & Astrophysics)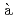 la the nuclear force
la the nuclear forceYamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Yasui, Shigehiro*; Hosaka, Atsushi
Physical Review D, 106(9), p.094001_1 - 094001_16, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.47(Astronomy & Astrophysics)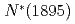 and its impact on photoproduction of light hyperons
and its impact on photoproduction of light hyperonsKhemchandani, K. P.*; Mart nez Torres, A.*; Kim, S.-H.*; Nam, S.-I.*; Hosaka, Atsushi
nez Torres, A.*; Kim, S.-H.*; Nam, S.-I.*; Hosaka, Atsushi
Acta Physica Polonica A, 142(3), p.329 - 336, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:27.99(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Fujii, Daisuke; Iwanaka, Akihiro*; Hosaka, Atsushi*
Physical Review D, 106(1), p.014010_1 - 014010_6, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.52(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The Roper resonance, the first excited state of the nucleon, is one of the best established baryon resonates. Yet, its properties have not been consistently explained by effective models of QCD, such as the non-relativistic quark model. In this paper, we propose an alternative approach in the Sakai-Sugimoto model that is one of the holographic models of QCD. In particular, we analyze the helicity amplitude of the electromagnetic transitions at the leading of 't Hooft coupling 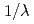 . The model incorporates baryon structure at short distance by nonlinear mesons surrounded by meson clouds at long distance. We demonstrate that the recently observed data by CLAS are explained in the present approach.
. The model incorporates baryon structure at short distance by nonlinear mesons surrounded by meson clouds at long distance. We demonstrate that the recently observed data by CLAS are explained in the present approach.
 (1535) in the holographic QCD
(1535) in the holographic QCDIwanaka, Akihiro*; Fujii, Daisuke*; Hosaka, Atsushi
Physical Review D, 105(11), p.114057_1 - 114057_6, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.52(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Arifi, A. J.*; Suenaga, Daiki*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Oh, Y. S.*
Physical Review D, 105(9), p.094006_1 - 094006_17, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:82.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Suenaga, Daiki*; Hosaka, Atsushi
Physical Review D, 105(7), p.074036_1 - 074036_13, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:66.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Sangkhakrit, T.*; Shim, S.-I.*; Yan, Y.*; Hosaka, Atsushi
European Physical Journal A, 58(2), p.32_1 - 32_11, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:43.00(Physics, Nuclear)Meng, Q.*; Harada, Masayasu*; Hiyama, Emiko; Hosaka, Atsushi; Oka, Makoto
Physics Letters B, 824, p.136800_1 - 136800_5, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:97.52(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Spectrum of the doubly heavy tetraquarks, 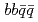 , is studied in a constituent quark model. Four-body problem is solved in a variational method where the real scaling technique is used to identify resonant states above the fall-apart decay thresholds. In addition to the two bound states that were reported in the previous study we have found several narrow resonant states above the
, is studied in a constituent quark model. Four-body problem is solved in a variational method where the real scaling technique is used to identify resonant states above the fall-apart decay thresholds. In addition to the two bound states that were reported in the previous study we have found several narrow resonant states above the 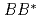 and
and 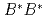 thresholds. Their structures are studied and are interpreted by the quark dynamics. A narrow resonance with spin-parity
thresholds. Their structures are studied and are interpreted by the quark dynamics. A narrow resonance with spin-parity 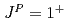 is found to be a mixed state of a compact tetraquark and a
is found to be a mixed state of a compact tetraquark and a 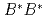 scattering state. This is driven by a strong color Coulombic attraction between the
scattering state. This is driven by a strong color Coulombic attraction between the 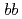 quarks. Negative-parity excited resonances with
quarks. Negative-parity excited resonances with 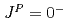 ,
, 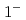 and
and 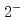 form a triplet under the heavy-quark spin symmetry. It turns out that they share a similar structure to the
form a triplet under the heavy-quark spin symmetry. It turns out that they share a similar structure to the  -mode of a singly heavy baryon as a result of the strongly attractive correlation for the doubly heavy diquark.
-mode of a singly heavy baryon as a result of the strongly attractive correlation for the doubly heavy diquark.