Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Morishita, Yuki; Takasaki, Koji; Kitayama, Yoshiharu; Tagawa, Akihiro; Shibata, Takuya; Hoshi, Katsuya; Kaneko, Junichi*; Higuchi, Mikio*; Oura, Masatoshi*
Radiation Measurements, 160, p.106896_1 - 106896_10, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:91.24(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study proposes a newly developed phoswich alpha/beta detector that can discriminate alpha and beta particles emitted from the alpha and beta contaminations in the FDNPS site. The phoswich alpha/beta detector is made up of two layers of scintillators that detect alpha and beta particles. The pulse shape discrimination (PSD) method was used to detect alpha particles in high beta particle and high gamma-ray (comparable to gamma-ray dose rate near the FDNPS reactor building) environments. Due to a 23.3% full width at half maximum (FWHM) energy resolution for alpha particles, the detector can be used to distinguish between nuclear fuel materials such as plutonium and its radon progeny (Po-214). Moreover, the detector could distinguish alpha particles from  Cs gamma rays with a dose rate background up to 9.0 mSv/h. It is the first to demonstrate that the developed phoswich detector can be used to discriminate and measure alpha and beta particles of the actual contaminated FDNPS samples.
Cs gamma rays with a dose rate background up to 9.0 mSv/h. It is the first to demonstrate that the developed phoswich detector can be used to discriminate and measure alpha and beta particles of the actual contaminated FDNPS samples.
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Hirao, Shigekazu*; Aoki, Katsunori; Tachiki, Shuichi*; Ezaki, Iwao*; Hoshi, Katsuya; Tsujimura, Norio
Journal of Radiological Protection, 42(3), p.031504_1 - 031504_17, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.39(Environmental Sciences)In Japan, the radiation-dose limit for the lens of the eye was revised in April 2021. Consequently, for workers, the numerical values of the equivalent dose to the lens of the eye are equal to those of the effective dose. Radiation workers, radiation safety officers and licensees must comply with regulations related to radiation protection and optimize protection. The new guidelines on dose monitoring of the lens of the eye developed by the Japan Health Physics Society recommend for the dose to be estimated near the eye for accurate estimation, when the dose to the lens approaches or exceeds the management criteria. However, there is limited information regarding the non-uniform exposure of nuclear power plant workers. In this study, the dose equivalents of high-dose-rate workplaces and the personal doses of 88 workers were estimated at four Japanese commercial nuclear power plant sites (RWR: 3 units and BWR: 3 units) and the dose to the lens of the eye and the exposure situations of the workers were analyzed.
 Sr+
Sr+ Y beta field; Full-face mask respirator shielding and dosemeter positioning
Y beta field; Full-face mask respirator shielding and dosemeter positioningTsujimura, Norio; Hoshi, Katsuya; Yamazaki, Takumi; Momose, Takumaro; Aoki, Katsunori; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Yokoyama, Sumi*
KEK Proceedings 2020-5, p.21 - 28, 2020/11
Yokoyama, Sumi*; Ezaki, Iwao*; Tatsuzaki, Hideo*; Tachiki, Shuichi*; Hirao, Shigekazu*; Aoki, Katsunori; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Hoshi, Katsuya; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tsujimura, Norio
Radiation Measurements, 138, p.106399_1 - 106399_5, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)Morishita, Yuki; Hoshi, Katsuya; Torii, Tatsuo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 966, p.163795_1 - 163795_8, 2020/06
To date, alpha and high beta particle emitters have been detected in the reactor buildings of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS). Since the beta radiation levels in the FDNPS buildings are extremely high, a commercial beta survey meter, such as a Geiger-Muller (GM) counter, would no longer have the ability to measure the beta contamination levels. In order to solve this issue, we utilized ultra-thin plastic scintillators to increase the detection rate of alpha and beta contamination. In this study, ultra-thin plastic scintillators with varied thicknesses of 7, 22, 24, 31, 39, and 55 um were prepared. To test their sensitivity, each scintillator was optically coupled to a glass plate and a 2-in square position-sensitive photomultiplier tube, and exposed to either an alpha, beta, or gamma source. Results from alpha spectrometry show that only the 55 um-thick plastic scintillator fully absorbed the alpha particles (5.5 MeV) with a 16.7% Full Width at Half Maximum. For alpha imaging under a high beta background, the 7 um-thick plastic scintillator was found to be the best choice, with an alpha to beta ratio of 652. This plastic scintillator also had the lowest sensitivity to beta particles, measuring only 41.74 cps when exposed to a 1 MBq  Sr/
Sr/ Y source in contact. It would therefore be possible to use the 7 um-thick plastic scintillator, to directly measure the surface contamination levels at the FDNPS site in real-time, where previous methods have fallen short. Thus, the developed detector would be a useful tool for the detection of alpha and beta contamination in the FDNPS.
Y source in contact. It would therefore be possible to use the 7 um-thick plastic scintillator, to directly measure the surface contamination levels at the FDNPS site in real-time, where previous methods have fallen short. Thus, the developed detector would be a useful tool for the detection of alpha and beta contamination in the FDNPS.
Tsujimura, Norio; Hoshi, Katsuya; Aoki, Katsunori; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Yokoyama, Sumi*
Radiation Measurements, 134, p.106305_1 - 106305_5, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)Hoshi, Katsuya; Yoshitomi, Hiroshi; Aoki, Katsunori; Tanimura, Yoshihiko; Tsujimura, Norio; Yokoyama, Sumi*
Radiation Measurements, 134, p.106304_1 - 106304_5, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:34.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)In FY 2017, the Japanese Nuclear Regulatory Agency (NRA) established the Radiation Safety Research Promotion Fund for funding projects on nuclear safety regulation, and adopted the two-year research project entitled "Study on standard eye lens monitoring, suitable dose management and radiation protection for nuclear and medical workers". The study is a two-phase study: a laboratory study on the eye lens dosemeter's characteristics to photons, and a field study executed at actual workplaces at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. This paper summarizes the results of the first-phase study, which was designed to clarify the eye lens dosemeter positioning and the shielding effect of full face mask respirators used at the station. No marked difference was observed in readings of the dosemeters attached on the different positions on the head phantom. Two types of full face mask respirators provided insignificant shielding effect for photons of 83 keV to 662 keV.
Morishita, Yuki; Usami, Hiroshi; Furuta, Yoshihiro; Aoki, Katsunori; Tsurudome, Koji; Hoshi, Katsuya; Torii, Tatsuo
Radiation Protection Dosimetry, 189(2), p.172 - 181, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Environmental Sciences)We developed a remote continuous air monitoring (RCAM) system. The RCAM system consisted of a personal air monitor and a robot. The personal air monitor (poCAMon, SARAD, Germany) had a 400 mm ion-injected silicon detector and a membrane air filter with 25 mm-diameter. The personal air monitor provides the alpha energy spectra for any measurement time interval. Demonstration measurements were taken underground at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) and at a poorly ventilated concrete building. The RCAM system was remotely operated and successfully measured the
ion-injected silicon detector and a membrane air filter with 25 mm-diameter. The personal air monitor provides the alpha energy spectra for any measurement time interval. Demonstration measurements were taken underground at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) and at a poorly ventilated concrete building. The RCAM system was remotely operated and successfully measured the  Rn progeny even though the relative humidity (RH) was almost 100%. In the measured alpha spectra, the peaks of
Rn progeny even though the relative humidity (RH) was almost 100%. In the measured alpha spectra, the peaks of 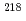 Po (6.0 MeV alpha) and
Po (6.0 MeV alpha) and  Po (7.7 MeV alpha) were clearly identified. Our developed monitor is promising for alpha dust monitoring in a high gamma-ray environment or contaminated areas where a worker cannot safely physically enter.
Po (7.7 MeV alpha) were clearly identified. Our developed monitor is promising for alpha dust monitoring in a high gamma-ray environment or contaminated areas where a worker cannot safely physically enter.
 Am-Li sources
Am-Li sourcesHoshi, Katsuya; Nishino, Sho; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Tsujimura, Norio
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 24, p.011020_1 - 011020_6, 2019/01
We studied the application of AmLi interrogation neutron sources, which originally deployed in non-destructive assay apparatus for nuclear safeguard, to calibration work. To determine the emission rate, the angular distribution of neutron fluence was measured by a potable long counter. The emission rate at the date of measurement (October 23rd, 2015) was determined to be 1.00 10
10 n/s (
n/s ( 4.1% (
4.1% ( = 2)).
= 2)).
Hoshi, Katsuya; Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Kurihara, Osamu*; Kim, E.*; Yajima, Kazuaki*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 6, p.152 - 155, 2019/01
Morishita, Yuki; Yamamoto, Seiichi*; Izaki, Kenji; Kaneko, Junichi*; Hoshi, Katsuya; Torii, Tatsuo
Radiation Measurements, 112, p.1 - 5, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:87.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)To detect plutonium isotopes ( Pu,
Pu,  Pu, and
Pu, and  Pu) in a field of high beta and
Pu) in a field of high beta and  background, an alpha particle detector with low beta and
background, an alpha particle detector with low beta and  -ray sensitivity is required. Therefore, we optimized the thickness of the GAGG scintillator for alpha particle detection in a field of high beta and
-ray sensitivity is required. Therefore, we optimized the thickness of the GAGG scintillator for alpha particle detection in a field of high beta and  background. We prepared three GAGG scintillators with thicknesses of 0.05 mm, 0.07 mm, and 0.1 mm. Each of the GAGG scintillators was coupled optically to the SiPM array, which was used as the photodetector. Alpha, beta, and
background. We prepared three GAGG scintillators with thicknesses of 0.05 mm, 0.07 mm, and 0.1 mm. Each of the GAGG scintillators was coupled optically to the SiPM array, which was used as the photodetector. Alpha, beta, and  rays were irradiated onto the developed alpha particle detector, and their spectra were obtained. All GAGG scintillators used in this study were not sensitive to
rays were irradiated onto the developed alpha particle detector, and their spectra were obtained. All GAGG scintillators used in this study were not sensitive to  rays with a dose rate of 1 mSv/h. The beta count of the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG was only 1/100 that of the 0.1-mm-thick GAGG. Therefore, the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG scintillator is promising from the viewpoint of detecting plutonium contamination in a field with high beta and
rays with a dose rate of 1 mSv/h. The beta count of the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG was only 1/100 that of the 0.1-mm-thick GAGG. Therefore, the 0.05-mm-thick GAGG scintillator is promising from the viewpoint of detecting plutonium contamination in a field with high beta and  background.
background.
Nishino, Sho; Hoshi, Katsuya; Tsujimura, Norio; Kowatari, Munehiko; Yoshida, Tadayoshi
Proceedings of 14th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-14), Vol.3 (Internet), p.1258 - 1263, 2017/11
In order to investigate how neutron dosimeters respond in the continuous neutron fields in workplaces, we performed performance tests of four widely-used neutron survey meters in various simulated workplace neutron calibration fields established in two calibration facilities (FRS and ICF) in JAEA. As a result, we found that survey meters significantly over or underestimate neutron dose in the fields which have spectral components only in the energy range below 1 MeV, while those show good performance in the fields which have spectral components in the energy range above 1 MeV.
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Hoshi, Katsuya
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 11, p.070003_1 - 070003_7, 2016/11
Hoshi, Katsuya; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Tsujimura, Norio; Okada, Kazuhiko
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 11, p.070009_1 - 070009_6, 2016/11
Beta spectra of various nuclide species were measured by commercially available compact spectrometer. The shape of spectra obtained from the spectrometer approximately agreed with that of theoretical spectra. The beta dose equivalent at any depths has been able to be obtained as a product of measured pulse height spectra and appropriate conversion coefficients of ICRP Publ. 74. The dose rates evaluated from the spectra were comparable to the reference dose rates of standard beta calibration sources. And, we were able to determine the dose equivalent with relative error of indication of 10% without the complicated correction.
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Hoshi, Katsuya; Momose, Takumaro
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 11, p.070008_1 - 070008_6, 2016/11
Hoshi, Katsuya; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Tsujimura, Norio; Tsuchiko, Yasuhiro*; Suto, Yudai*; Okada, Kazuhiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Hoshi, Katsuya
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 -ray 3mm dose equivalent and protection measures of the lens of eyes, 1; Ionization chamber
-ray 3mm dose equivalent and protection measures of the lens of eyes, 1; Ionization chamberTakimoto, Misaki; Yamazaki, Takumi; Imahashi, Atsushi; Hoshi, Katsuya; Kawasaki, Takashi; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Takada, Chie; Tsujimura, Norio; Okada, Kazuhiko; Ishikawa, Hisashi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 rays
raysYamazaki, Takumi; Takada, Chie; Nakamura, Keisuke; Sagawa, Naoki; Hoshi, Katsuya; Nakagawa, Takahiro; Takimoto, Misaki; Tanimura, Yoshihiko*; Takahashi, Fumiaki; Momose, Takumaro; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kojima, Naomi; Hoshi, Katsuya; Yamazaki, Takumi; Takada, Chie; Takada, Masashi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English