Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yano, Naomine*; Yamada, Taro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Ohara, Takashi; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*
Acta Crystallographica Section D; Structural Biology (Internet), 74(11), p.1041 - 1052, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:74.07(Biochemical Research Methods)Tashiro, Koji*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Ohara, Takashi; Hanesaka, Makoto*; Yoshizawa, Yoshinori*; Yamamoto, Hiroko*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Kurihara, Kazuo*; et al.
Macromolecules, 51(11), p.3911 - 3922, 2018/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:18.18(Polymer Science)Yano, Naomine*; Yamada, Taro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Ohara, Takashi; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 6, p.36628_1 - 36628_9, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:61.6(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Unno, Masayoshi*; Ishikawa, Kumiko*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Tamada, Taro; Hagiwara, Yoshinori*; Sugishima, Masakazu*; Wada, Kei*; Yamada, Taro*; Tomoyori, Katsuaki; Hosoya, Takaaki*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 137(16), p.5452 - 5460, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:64.39(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Phycocyanobilin, a light-harvesting and photoreceptor pigment in higher plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, is synthesized from biliverdin IX (BV) by phycocyanobilin:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PcyA) via two steps of two-proton-coupled two-electron reduction. We determined the neutron structure of PcyA from cyanobacteria complexed with BV, revealing the exact location of the hydrogen atoms involved in catalysis. Notably, approximately half of the BV bound to PcyA was BVH
(BV) by phycocyanobilin:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PcyA) via two steps of two-proton-coupled two-electron reduction. We determined the neutron structure of PcyA from cyanobacteria complexed with BV, revealing the exact location of the hydrogen atoms involved in catalysis. Notably, approximately half of the BV bound to PcyA was BVH , a state in which all four pyrrole nitrogen atoms were protonated. The protonation states of BV complemented the protonation of adjacent Asp105. The "axial "water molecule that interacts with the neutral pyrrole nitrogen of the A-ring was identified. His88 N
, a state in which all four pyrrole nitrogen atoms were protonated. The protonation states of BV complemented the protonation of adjacent Asp105. The "axial "water molecule that interacts with the neutral pyrrole nitrogen of the A-ring was identified. His88 N was protonated to form a hydrogen bond with the lactam O atom of the BV A-ring. His88 and His74 were linked by hydrogen bonds via H
was protonated to form a hydrogen bond with the lactam O atom of the BV A-ring. His88 and His74 were linked by hydrogen bonds via H O
O . These results imply that Asp105, His88, and the axial water molecule contribute to proton transfer during PcyA catalysis.
. These results imply that Asp105, His88, and the axial water molecule contribute to proton transfer during PcyA catalysis.
Tashiro, Koji*; Hanesaka, Makoto*; Yamamoto, Hiroko*; Wasanasuk, K.*; Jayaratri, P.*; Yoshizawa, Yoshinori*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; et al.
Kobunshi Rombunshu, 71(11), p.508 - 526, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:22.37(Polymer Science)The crystal structure analysis of various polymer substances has been reviewed on the basis of wide-angle high-energy X-ray and neutron diffraction data. The progress in structural analytical techniques of polymer crystals have been reviewed at first. The structural models proposed so far were reinvestigated and new models have been proposed for various kinds of polymer crystals including polyethylene, poly(vinyl alcohol), poly(lactic acid) and its stereocomplex etc. The hydrogen atomic positions were also clarified by the quantitative analysis of wide-angle neutron diffraction data, from which the physical properties of polymer crystals have been evaluated theoretically. The bonded electron density distribution has been estimated for a polydiacetylene single crystal on the basis of the so-called X-N method or by the combination of structural information derived from X-ray and neutron diffraction data analysis. Some comments have been added about future developments in the field of structure-property relationship determination.
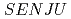 single-crystal time-of-flight neutron diffractometer at J-PARC/MLF
single-crystal time-of-flight neutron diffractometer at J-PARC/MLFKawasaki, Takuro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 735, p.444 - 451, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:80.14(Instruments & Instrumentation)Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Yamada, Taro*; Tomoyori, Katsuaki; Ohara, Takashi; Katagiri, Masaki*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 20(6), p.994 - 998, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:85.99(Instruments & Instrumentation)The IBARAKI biological crystal diffractometer, iBIX, is a high-performance time-of-flight neutron single-crystal diffractometer for elucidating mainly the hydrogen, protonation and hydration structures of biological macromolecules in various life processes. Since the end of 2008, iBIX has been available to user's experiments supported by Ibaraki University. Since August 2012, an upgrade of the 14-existing detectors has begun and 16 new detectors have been installed for iBIX. The total measurement efficiency of the present diffractometer has been impoved by one order of magnitude from the previous one with the increasing of accelerator power. In December 2012, commissioning of the new detectors was successful, and collection of the diffraction dataset of ribonucrease A as a standard protein was attempted in order to estimate the performance of the upgraded iBIX in comparison with previous results. The resolution of diffraction data, equivalence among intensities of symmetry-related reflections and reliability of the refined structure have been improved dramatically. iBIX is expected to be one of the highest-performance neutron single-crystal diffractometers for biological macromolecules in the world.
Yokoyama, Takeshi*; Mizuguchi, Mineyuki*; Nabeshima, Yuko*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Yamada, Taro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 20(6), p.834 - 837, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:33.62(Instruments & Instrumentation)Transthyretin (TTR) is a tetrameric protein. TTR misfolding and aggregation are associated with human amyloid diseases. Dissociation of the TTR tetramer is believed to be the rate-limiting step in the amyloid fibril formation cascade. Low pH is known to promote dissociation into monomer and the formation of amyloid fibrils. In order to reveal the molecular mechanisms underlying pH sensitivity and structural stabilities of TTR, neutron diffraction studies were conducted using the IBARAKI Biological Crystal Diffractometer with the time-of-flight method. Crystals for the neutron diffraction experiments were grown up to 2.5 mm for four months. The neutron crystal structure solved at 2.0
for four months. The neutron crystal structure solved at 2.0  revealed the protonation states of His88 and the detailed hydrogen-bond network depending on the protonation states of His88. This hydrogen-bond network is involved in monomer-monomer and dimer-dimer interactions, suggesting that the double protonation of His88 by acidification breaks the hydrogen-bond network and causes the destabilization of the TTR tetramer. Structural comparison with the X-ray crystal structure at acidic pH identified the three amino acid residues responsible for the pH sensitivity of TTR. Our neutron model provides insights into the molecular stability related to amyloidosis.
revealed the protonation states of His88 and the detailed hydrogen-bond network depending on the protonation states of His88. This hydrogen-bond network is involved in monomer-monomer and dimer-dimer interactions, suggesting that the double protonation of His88 by acidification breaks the hydrogen-bond network and causes the destabilization of the TTR tetramer. Structural comparison with the X-ray crystal structure at acidic pH identified the three amino acid residues responsible for the pH sensitivity of TTR. Our neutron model provides insights into the molecular stability related to amyloidosis.
 H
H ONH
ONH PbBr
PbBr studied using single-crystal neutron diffraction
studied using single-crystal neutron diffractionKawasaki, Takuro; Takahashi, Miwako*; Ohara, Takashi*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Yamada, Taro*; Kurihara, Kazuo
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(9), p.094602_1 - 094602_6, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.7(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nakamura, Tatsuya; Kawasaki, Takuro; Hosoya, Takaaki*; To, Kentaro; Oikawa, Kenichi; Sakasai, Kaoru; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Katagiri, Masaki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 686, p.64 - 70, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:90.36(Instruments & Instrumentation)A two-dimensional scintillator-based neutron detector that has a neutron-sensitive area of 256  256 mm
256 mm with a pixel size of 4 mm was developed. The detector was designed to be compact and modular with the smallest dead area for the SENJU time-of-flight Laue single-crystal diffractometer to be constructed in the Materials and Life Experimental Science Facility at the Japanese Proton Accelerator Research Complex. Two ZnS/
with a pixel size of 4 mm was developed. The detector was designed to be compact and modular with the smallest dead area for the SENJU time-of-flight Laue single-crystal diffractometer to be constructed in the Materials and Life Experimental Science Facility at the Japanese Proton Accelerator Research Complex. Two ZnS/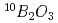 scintillator screens with an optimized scintillator thickness sandwiched the cross-arranged Wavelength-shifting fibre arrays to ensure a high detection efficiency for thermal neutrons. The prototype detector exhibited a detector efficiency of 40
scintillator screens with an optimized scintillator thickness sandwiched the cross-arranged Wavelength-shifting fibre arrays to ensure a high detection efficiency for thermal neutrons. The prototype detector exhibited a detector efficiency of 40  1 % for 1.6-
1 % for 1.6- neutrons and a
neutrons and a  Co
Co  -ray sensitivity of 6.0
-ray sensitivity of 6.0 0.1
0.1 
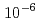 , which fulfilled the required detector specifications for SENJU.
, which fulfilled the required detector specifications for SENJU.
Yokoyama, Takeshi*; Mizuguchi, Mineyuki*; Nabeshima, Yuko*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Yamada, Taro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Ohara, Takashi*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Tomoyori, Katsuaki*; Tanaka, Ichiro*; et al.
Journal of Structural Biology, 177(2), p.283 - 290, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:83.41(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Tanaka, Ichiro*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Ohara, Takashi*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Yamada, Taro*; Onishi, Yuki*; Tomoyori, Katsuaki*; Yokoyama, Takeshi*
Acta Crystallographica Section D, 66(11), p.1194 - 1197, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:49 Percentile:94.6(Biochemical Research Methods)The IBARAKI Biological Crystal Diffractometer (iBIX), a new diffractometer for protein crystallography at the next-generation neutron source at J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex), has been constructed and has been operational since December 2008. Preliminary structure analyses of organic crystals showed that iBIX has high performance even at 120 kW operation and the first full data set is being collected from a protein crystal.
Tanaka, Ichiro*; Kusaka, Katsuhiro*; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Ohara, Takashi*; Kurihara, Kazuo; Niimura, Nobuo*
Yakugaku Zasshi, 130(5), p.665 - 670, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Pharmacology & Pharmacy)Ibaraki Prefectural Government together with Ibaraki University and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has almost finished constructing a time-of-flight (TOF) neutron diffractometer for biological macromolecules for industrial use at J-PARC, IBARAKI Biological Crystal Diffractometer (iBIX). Since 2009, Ibaraki University has been asked to operate this machine in order for users to do experiments by Ibaraki Prefecture. The diffractometer is designed to cover sample crystals which have their cell edges up to around 150  . It is expected to measure more than 100 samples per year if they have 2 mm
. It is expected to measure more than 100 samples per year if they have 2 mm in crystal volume, and to measure even around 0.1 mm
in crystal volume, and to measure even around 0.1 mm in crystal volume of biological samples. The efficiency of iBIX is also expected about 100 times larger than those of the present high performance diffractometers at JRR-3 in JAEA when 1MW power realizes in J-PARC. Since December 2008, iBIX has been open to users and several proteins and organic compounds were tested under 20 kW proton power of J-PARC. It was found that one of their proteins was diffracted up to 1.4
in crystal volume of biological samples. The efficiency of iBIX is also expected about 100 times larger than those of the present high performance diffractometers at JRR-3 in JAEA when 1MW power realizes in J-PARC. Since December 2008, iBIX has been open to users and several proteins and organic compounds were tested under 20 kW proton power of J-PARC. It was found that one of their proteins was diffracted up to 1.4  in d-spacing, which was nearly comparable resolution to that of BIX-3 in JRR-3 when used the same crystal as at iBIX for reasonable exposure time. In May 2009, 14 detector units were set up. By the end of fiscal year 2009, the basic part of data reduction software will be finished and an equipment blowing low temperature gas to the sample will be installed with the cooperation of JAEA.
in d-spacing, which was nearly comparable resolution to that of BIX-3 in JRR-3 when used the same crystal as at iBIX for reasonable exposure time. In May 2009, 14 detector units were set up. By the end of fiscal year 2009, the basic part of data reduction software will be finished and an equipment blowing low temperature gas to the sample will be installed with the cooperation of JAEA.
Hosoya, Takaaki*; Ohara, Takashi
Radioisotopes, 59(4), p.279 - 287, 2010/04
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Katagiri, Masaki; Hosoya, Takaaki*; Birumachi, Atsushi; Ebine, Masumi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Schooneveld, E.*; Rhodes, N.*
JAEA-Research 2008-115, 33 Pages, 2009/03
A compact two-dimensional neutron detector was developed for iBIX instrument in the J-PARC/MLF. The specifications required for the detector were a spatial resolution of less than 1 mm, a detector efficiency of more than 50% for thermal neutrons, a  sensitivity of less than 10
sensitivity of less than 10 , detector coverage of around 15
, detector coverage of around 15 15 cm
15 cm with least dead area, compactness, modularity, and a pulse pair resolution of less than 2
with least dead area, compactness, modularity, and a pulse pair resolution of less than 2  s. The detector components were studied in detail and optimized for the purpose. The compact prototype detector that has a neutron sensitive area of 13.3
s. The detector components were studied in detail and optimized for the purpose. The compact prototype detector that has a neutron sensitive area of 13.3 13.3 cm
13.3 cm was made and feasibility of the detector was demonstrated successfully in the experiments at the ISIS pulsed neutron source.
was made and feasibility of the detector was demonstrated successfully in the experiments at the ISIS pulsed neutron source.
Ohara, Takashi; Hosoya, Takaaki; Ohashi, Yuji*
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 50(1), p.98 - 102, 2008/02
The exchange of some hydrogen atoms with the other hydrogen atoms in the crystalline-state reactions, in which the reaction proceeds with retention of the single crystal form, can be directory observed by single crystal neutron diffraction technique if only the transferred hydrogen atoms were replaced with deuterium atoms before the photoirradiation. The method was successfully applied in the photoisomerization of three kinds of cobalt complex crystals and the mechanism in each reaction has been made clear.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; Sakasai, Kaoru; Katagiri, Masaki; Birumachi, Atsushi; Hosoya, Takaaki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Sato, Setsuo*; Shooneveld, E.*; Rhodes, N.*
JAEA-Research 2007-014, 14 Pages, 2007/03
The ENGIN-X type linear scintillation neutron detector was manufactured in Japan and the detector performances were evaluated. The ENGIN-X type linear scintillation neutron detector was originally developed by the detector group in Rutherford Appleton Laboratory and the Japanese prototype detector was identical to that which is one of the detector modules installed in the ENGIN-X diffractometer at ISIS pulsed neutron source. The prototype detector can install 240 elements of neutron-sensitive scintillator, where each element has 3 mm in width and 196 mm in length. The prototype detector exhibited a spatial resolution of 3 mm, detection efficiency of 64% for neutrons with wave-lengths of 1.8 , count uniformity of 6
, count uniformity of 6 7%,
7%,  Co
Co  sensitivity of
sensitivity of  5
5 10
10 . Technological transfer to the Japanese manufacturer was done successfully and the mass production of these detectors for the J-PARC project is feasible.
. Technological transfer to the Japanese manufacturer was done successfully and the mass production of these detectors for the J-PARC project is feasible.
Ohashi, Yuji*; Hosoya, Takaaki; Ohara, Takashi
Crystallography Reviews, 12(2), p.83 - 123, 2006/04
The crystal structure analysis with neutron diffraction can clearly make a distinction between the deuterium and hydrogen atoms although they cannot be distinguished by X-rays. Applying the neutron diffraction for the crystalline-state reaction, the mechanisms of the hydrogen transfer in several reactions have been made clear.
 -thiolactam formation in the crystalline state
-thiolactam formation in the crystalline stateHosoya, Takaaki*; Uekusa, Hidehiro*; Ohashi, Yuji*; Ohara, Takashi; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*
Acta Crystallographica Section B; Structural Science, Crystal Engineering and Materials (Internet), 62(1), p.153 - 160, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:48.75(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Since N,N-dibenzyl-1-cyclohexenecarbothioamide is photoisomerized to the optically active  -thiolactam with the retention of the single-crystal form, the mechanism of chirality induction was identified by X-ray crystal structure analyses during the process of the reaction. In order to clarify the mechanism of hydrogen transfer in the reaction, the H atomsof the benzyl groups were replaced with deuterium atoms. The crystal structure after photoisomerization was analyzed by neutron diffraction. One of four deuterium atoms of the two benzyl groups is transferred to the C atom of the cyclohexene ring. The absolute configuration of the -C
-thiolactam with the retention of the single-crystal form, the mechanism of chirality induction was identified by X-ray crystal structure analyses during the process of the reaction. In order to clarify the mechanism of hydrogen transfer in the reaction, the H atomsof the benzyl groups were replaced with deuterium atoms. The crystal structure after photoisomerization was analyzed by neutron diffraction. One of four deuterium atoms of the two benzyl groups is transferred to the C atom of the cyclohexene ring. The absolute configuration of the -C HD- group(chiral methylene) in the photoproduct r-thiolactam revealed that the deuterium atom occupies the equatorial position. This suggests that the deuterium atom is not transferred from the benzyl group of a neighbouring molecule, but from one of the benzyl groups within the molecule.
HD- group(chiral methylene) in the photoproduct r-thiolactam revealed that the deuterium atom occupies the equatorial position. This suggests that the deuterium atom is not transferred from the benzyl group of a neighbouring molecule, but from one of the benzyl groups within the molecule.
Ohara, Takashi; Kurihara, Kazuo; Kusaka, Katsuhiro; Hosoya, Takaaki; Tanaka, Ichiro*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Ozeki, Tomoji*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Morii, Yukio; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English