Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Rajeev, H. S.*; Hu, X.*; Chen, W.-L.*; Zhang, D.*; Chen, T.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Chen, A. Z.*; Johnson, G. C.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(3), p.034602_1 - 034602_14, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Liu, P.-F.*; Li, X.*; Li, J.*; Zhu, J.*; Tong, Z.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Nirei, Masami; Xu, J.*; Yin, W.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
National Science Review, 11(12), p.nwae216_1 - nwae216_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:94.32(Multidisciplinary Sciences) SR study on the noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe
SR study on the noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe
Jiao, J. C.*; Chen, K. W.*; Hillier, A. D.*; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Li, Z.*; Lv, B.*; Xu, Z.-A.*; Shu, L.*
Physical Review B, 110(21), p.214516_1 - 214516_9, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Li, X.*; Zhu, R.*; Xin, J.*; Luo, M.*; Shang, S.-L.*; Liu, Z.-K.*; Yin, C.*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Dippenaar, R. J.*; Higo, Yuji*; et al.
CALPHAD; Computer Coupling of Phase Diagrams and Thermochemistry, 84, p.102641_1 - 102641_6, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Thermodynamics)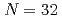
Linh, B. D.*; Corsi, A.*; Gillibert, A.*; Obertelli, A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; G mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
mez-Ramos, M.*; Holt, J. D.*; Hu, B. S.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(3), p.034312_1 - 034312_15, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Fe
Fe intermetallic compound
intermetallic compoundCao, Y.*; Zhou, H.*; Khmelevskyi, S.*; Lin, K.*; Avdeev, M.*; Wang, C.-W.*; Wang, B.*; Hu, F.*; Kato, Kenichi*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Chemistry of Materials, 35(8), p.3249 - 3255, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.33(Chemistry, Physical)Hydrostatic and chemical pressure are efficient stimuli to alter the crystal structure and are commonly used for tuning electronic and magnetic properties in materials science. However, chemical pressure is difficult to quantify and a clear correspondence between these two types of pressure is still lacking. Here, we study intermetallic candidates for a permanent magnet with a negative thermal expansion (NTE). Based on in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction, negative chemical pressure is revealed in Ho Fe
Fe on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
on Al doping and quantitatively evaluated by using temperature and pressure dependence of unit cell volume. A combination of magnetization and neutron diffraction measurements also allowed one to compare the effect of chemical pressure on magnetic ordering with that of hydrostatic pressure. Intriguingly, pressure can be used to control suppression and enhancement of NTE. Electronic structure calculations indicate that pressure affected the top of the majority band with respect to the Fermi level, which has implications for the magnetic stability, which in turn plays a critical role in modulating magnetism and NTE. This work presents a good example of understanding the effect of pressure and utilizing it to control properties of functional materials.
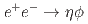 via initial state radiation at Belle
via initial state radiation at BelleZhu, W. J.*; Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*; 174 of others*
Physical Review D, 107(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_10, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.46(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Zhang, W. Q.*; Yamaguchi, Toshio*; Fang, C. H.*; Yoshida, Koji*; Zhou, Y. Q.*; Zhu, F. Y.*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Li, W.*
Journal of Molecular Liquids, 348, p.118080_1 - 118080_11, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:24.49(Chemistry, Physical)The ion hydration and association and hydrogen-bonded water structure in an aqueous 3 mol/kg RbCl solution were investigated at 298 K/0.1 MPa, 298 K/1 GPa, 523 K/1 GPa, and 523 K/4 GPa by neutron diffraction combined with EPSR methods. The second hydration layer of Rb and Cl
and Cl becomes evident under elevated pressure and temperature conditions. The average oxygen coordination number of Rb
becomes evident under elevated pressure and temperature conditions. The average oxygen coordination number of Rb (Cl
(Cl ) in the first hydration layer increases from 6.3 (5.9) ambient pressure to 8.9 (9.1) at 4 GPa, while decreasing coordination distance from 0.290 nm (0.322 nm) to 0.288 nm (0.314 nm). The orientation of the water dipole in the first solvation shell of Rb
) in the first hydration layer increases from 6.3 (5.9) ambient pressure to 8.9 (9.1) at 4 GPa, while decreasing coordination distance from 0.290 nm (0.322 nm) to 0.288 nm (0.314 nm). The orientation of the water dipole in the first solvation shell of Rb and a central water molecule is sensitive to pressure, but that in the first solvation shell of Cl
and a central water molecule is sensitive to pressure, but that in the first solvation shell of Cl does not change very much. The number of contact-ion pairs Rb
does not change very much. The number of contact-ion pairs Rb -Cl
-Cl decreases with elevated temperature and increases with elevated pressure. Water molecules are closely packed, and the tetrahedral hydrogen-bonded network of water molecules no longer exists in extreme conditions.
decreases with elevated temperature and increases with elevated pressure. Water molecules are closely packed, and the tetrahedral hydrogen-bonded network of water molecules no longer exists in extreme conditions.
 Bi
BiDoherty, D. T.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Seweryniak, D.*; Woods, P. J.*; Carpenter, M. P.*; Auranen, K.*; Ayangeakaa, A. D.*; Back, B. B.*; Bottoni, S.*; Canete, L.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(20), p.202501_1 - 202501_6, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:64.24(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the
Fe cross section from the surrogate ratio method and its effect on the  Fe nucleosynthesis
Fe nucleosynthesisYan, S. Q.*; Li, X. Y.*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Lugaro, M.*; Li, Z. H.*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Pignatari, M.*; Wang, Y. B.*; Orlandi, R.; Hirose, Kentaro; et al.
Astrophysical Journal, 919(2), p.84_1 - 84_7, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.27(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Kong, L.*; Gong, J.*; Hu, Q.*; Capitani, F.*; Celeste, A.*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Li, N.*; Yang, W.*; Liu, G.*; et al.
Advanced Functional Materials, 31(9), p.2009131_1 - 2009131_12, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:82.86(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The soft nature of organic-inorganic halide perovskites renders their lattice particularly tunable to external stimuli such as pressure, undoubtedly offering an effective way to modify their structure for extraordinary optoelectronic properties. However, these soft materials meanwhile feature a general characteristic that even a very mild pressure will lead to detrimental lattice distortion and weaken the critical light-matter interaction, thereby triggering the performance degradation. Here, using the methylammonium lead iodide as a representative exploratory platform, we observed the pressure-driven lattice disorder can be significantly suppressed via hydrogen isotope effect, which is crucial for better optical and mechanical properties previously unattainable.
 particles triggered strong interaction with LaFeO
particles triggered strong interaction with LaFeO framework for total and preferential CO oxidation
framework for total and preferential CO oxidationZheng, Y.*; Xiao, H.*; Li, K.*; Wang, Y.*; Li, Y.*; Wei, Y.*; Zhu, X.*; Li, H.-W.*; Matsumura, Daiju; Guo, B.*; et al.
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 12(37), p.42274 - 42284, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:70.49(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) Ir
Ir Sn
Sn
Kaneko, Koji; Cheung, Y. W.*; Hu, Y.*; Imai, Masaki*; Tanioku, Yasuaki*; Kanagawa, Hibiki*; Murakawa, Joichi*; Moriyama, Kodai*; Zhang, W.*; Lai, K. T.*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 30, p.011032_1 - 011032_6, 2020/03
 -decay properties of
-decay properties of 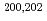 Fr
FrGhys, L.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Huyse, M.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Antalic, S.*; Barzakh, A.*; Capponi, L.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; Cubiss, J.*; Derkx, X.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 100(5), p.054310_1 - 054310_13, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:75.29(Physics, Nuclear)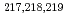 At revealed by in-source laser spectroscopy
At revealed by in-source laser spectroscopyBarzakh, A. E.*; Cubiss, J. G.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Seliverstov, M. D.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Ascher, P.*; Atanasov, D.*; Beck, D.*; Biero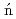 , J.*; et al.
, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(5), p.054317_1 - 054317_9, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:73.32(Physics, Nuclear) Sr
Sr )
) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn from a lattice dynamics study
from a lattice dynamics studyCheung, Y. W.*; Hu, Y. J.*; Imai, Masaki*; Tanioku, Yasuaki*; Kanagawa, Hibiki*; Murakawa, Joichi*; Moriyama, Kodai*; Zhang, W.*; Lai, K. T.*; Yoshimura, Kazuyoshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(16), p.161103_1 - 161103_5, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:63.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Sr
Sr )
) Rh
Rh Sn
Sn
Cheung, Y. W.*; Hu, Y. J.*; Goh, S. K.*; Kaneko, Koji; Tsutsui, Satoshi; Logg, P. W.*; Grosche, F. M.*; Kanagawa, Hibiki*; Tanioku, Yasuaki*; Imai, Masaki*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 807(3), p.032002_1 - 032002_4, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:80.71(Physics, Condensed Matter) (As
(As P
P )
) superconductor
superconductorHu, D.*; Yin, Z.*; Zhang, W.*; Ewings, R. A.*; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Roessli, B.*; Wei, Y.*; Zhao, L.*; Chen, G.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 94(9), p.094504_1 - 094504_7, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:62.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The temperature and energy dependence of spin excitations in an optimally P-doped BaFe (As
(As P
P )
) superconductor (T
superconductor (T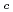 = 30 K) were studied by using inelastic neutron scattering. Experimental results are consistent with calculations from a combined density functional theory and dynamical mean field theory, and suggest that the decreased average pnictogen height in BaFe
= 30 K) were studied by using inelastic neutron scattering. Experimental results are consistent with calculations from a combined density functional theory and dynamical mean field theory, and suggest that the decreased average pnictogen height in BaFe (As
(As P
P )
) reduces the strength of electron correlations and increases the effective bandwidth of magnetic excitation.
reduces the strength of electron correlations and increases the effective bandwidth of magnetic excitation.
 -delayed fission and
-delayed fission and  decay of
decay of 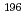 At
AtTruesdale, V. L.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ghys, L.*; Huyse, M.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Sels, S.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Barzakh, A.*; Capponi, L.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 94(3), p.034308_1 - 034308_11, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:60.04(Physics, Nuclear) Co
Co Sn
Sn
Cheung, Y. W.*; Zhang, J. Z.*; Zhu, J. Y.*; Yu, W. C.*; Hu, Y. J.*; Wang, D. G.*; Otomo, Yuka*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Kaneko, Koji; Imai, Masaki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 93(24), p.241112_1 - 241112_5, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:57.50(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)