Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sn
Sn
Huang, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Ye, H.*; Bao, S.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Liao, J.*; Cao, S.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Deng, G.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 109(1), p.014434_1 - 014434_9, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0Bao, S.*; Gu, Z.-L.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Zhang, B.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Wang, W.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 14, p.6093_1 - 6093_9, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:61.99(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Visuri, A.-M.*; Mohan, J.*; Uchino, Shun; Huang, M.-Z.*; Esslinger, T.*; Giamarchi, T.*
Physical Review Research (Internet), 5(3), p.033095_1 - 033095_11, 2023/08
We study the current-voltage characteristics of a superconducting junction with particle losses at the contacts. We adopt the Keldysh formalism to compute the steady-state current for varying transmission of the contact. In the low transmission regime, the dissipation leads to an enhancement of the current at low bias, a nonmonotonic dependence of current on dissipation, and the emergence of new structures in the current-voltage curves. The effect of dissipation by particle loss is found to be qualitatively different from that of a finite temperature and a finite inelastic scattering rate in the reservoirs.
 ; Bandgap narrowing, metallization, and remarkable enhancement of photoelectric activity
; Bandgap narrowing, metallization, and remarkable enhancement of photoelectric activityFang, Y.*; Kong, L.*; Wang, R.*; Zhang, Z.*; Li, Z.*; Wu, Y.*; Bu, K.*; Liu, X.*; Yan, S.*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Materials Today Physics (Internet), 34, p.101083_1 - 101083_7, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The layered van der Waals halides are particularly sensitive to external pressure, suggesting a feasible route to pinpoint their structure with extraordinary behavior. However, a very sensitive pressure response usually lead to a detrimental phase transition and/or lattice distortion, making the approach of materials manipulation in a continuous manner remain challenging. Here, the extremely weak interlayer coupling and high tunability of layered RhI crystals are observed. A pressure-driven phase transition occurs at a moderate pressure of 5 GPa, interlinking to a change of layer stack mode. Strikingly, such a phase transition does not affect the tendency of quasi-linear bandgap narrowing, and a metallization with an ultra-broad tunability of 1.3 eV redshift is observed at higher pressures. Moreover, the carrier concentration increases by 4 orders of magnitude at 30 GPa, and the photocurrent enhances by 5 orders of magnitude at 7.8 GPa. These findings create new opportunities for exploring, tuning, and understanding the van der Waals halides by harnessing their unusual feature of a layered structure, which is promising for future devices based on materials-by-design that are atomically thin.
crystals are observed. A pressure-driven phase transition occurs at a moderate pressure of 5 GPa, interlinking to a change of layer stack mode. Strikingly, such a phase transition does not affect the tendency of quasi-linear bandgap narrowing, and a metallization with an ultra-broad tunability of 1.3 eV redshift is observed at higher pressures. Moreover, the carrier concentration increases by 4 orders of magnitude at 30 GPa, and the photocurrent enhances by 5 orders of magnitude at 7.8 GPa. These findings create new opportunities for exploring, tuning, and understanding the van der Waals halides by harnessing their unusual feature of a layered structure, which is promising for future devices based on materials-by-design that are atomically thin.
Huang, M.-Z.*; Mohan, J.*; Visuri, A.-M.*; Fabritius, P.*; Talebi, M.*; Wili, S.*; Uchino, Shun; Giamarchi, T.*; Esslinger, T.*
Physical Review Letters, 130(20), p.200404_1 - 200404_8, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:88.42(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We measure superfluid transport of strongly-interacting fermionic lithium atoms through a quantum point contact with local, spin-dependent particle loss. We observe that the characteristic non-Ohmic superfluid transport enabled by high-order multiple Andreev reflections transitions into an excess Ohmic current as the dissipation strength exceeds the superfluid gap. We develop a model with mean-field reservoirs connected via tunneling to a dissipative site. Our calculations in the Keldysh formalism reproduce the observed non-equilibrium particle current, yet do not fully explain the observed loss rate or spin current.
 isomer in
isomer in 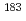 Hg and
Hg and  (
(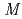 2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chart
2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chartHuang, H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Li, Z. H.*; Guo, C. Y.*; Barzakh, A. E.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Andel, B.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 833, p.137345_1 - 137345_8, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Yoshida, Shuhei*; Fu, R.*; Gong, W.; Ikeuchi, Takuto*; Bai, Y.*; Feng, Z.*; Wu, G.*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Hansen, N.*; Huang, X.*; et al.
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 1249, p.012027_1 - 012027_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.83(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering) Bi and
Bi and  Po
PoZhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Huang, H.*; 37 of others*
Physical Review C, 106(2), p.024317_1 - 024317_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:33.4(Physics, Nuclear) decay of the 8
decay of the 8 isomer in
isomer in 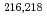 U
UZhang, M. M.*; Tian, Y. L.*; Wang, Y. S.*; Zhang, Z. Y.*; Gan, Z. G.*; Yang, H. B.*; Huang, M. H.*; Ma, L.*; Yang, C. L.*; Wang, J. G.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(2), p.024305_1 - 024305_6, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:52.69(Physics, Nuclear) K
K (Zn
(Zn Mn
Mn )
) As
As studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scattering
studied by X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and resonant inelastic X-ray scatteringSuzuki, Hakuto*; Zhao, G.*; Okamoto, Jun*; Sakamoto, Shoya*; Chen, Z.-Y.*; Nonaka, Yosuke*; Shibata, Goro; Zhao, K.*; Chen, B.*; Wu, W.-B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(6), p.064710_1 - 064710_5, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Pb
PbZhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Huang, H.*; Li, Z. H.*; Li, J. G.*; Guo, C. Y.*; 34 of others*
Physics Letters B, 829, p.137129_1 - 137129_7, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:76.34(Astronomy & Astrophysics)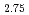 GeTe
GeTe
Bao, S.*; Wang, W.*; Shangguan, Y.*; Cai, Z.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Huang, Z.*; Si, W.*; Ma, Z.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; et al.
Physical Review X, 12(1), p.011022_1 - 011022_15, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:78.27(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Cu
Cu TeO
TeO
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Cai, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Huang, Z.*; Ma, Z.*; Liao, J.*; Zhao, X.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(22), p.224430_1 - 224430_8, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Sn and Mg
Sn and Mg Si single crystals
Si single crystalsSaito, Wataru*; Hayashi, Kei*; Huang, Z.*; Sugimoto, Kazuya*; Oyama, Kenji*; Happo, Naohisa*; Harada, Masahide; Oikawa, Kenichi; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Hayashi, Koichi*; et al.
ACS Applied Energy Materials (Internet), 4(5), p.5123 - 5131, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:64.95(Chemistry, Physical)Miao, P.*; Tan, Z.*; Lee, S. H.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Torii, Shuki*; Yonemura, Masao*; Koda, Akihiro*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sano, Asami; et al.
Physical Review B, 103(9), p.094302_1 - 094302_18, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The layered perovskite PrBaCo O
O demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo
demonstrates a strong negative thermal expansion (NTE) which holds potential for being fabricated into composites with zero thermal expansion. The NTE was found to be intimately associated with the spontaneous magnetic ordering, known as magneto-volume effect (MVE). Here we report with compelling evidences that the continuous-like MVE in PrBaCo O
O is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
is intrinsically of discontinuous character, originating from an magnetoelectric transition from an antiferromagnetic insulating large-volume (AFILV) phase to a ferromagnetic less-insulating small-volume (FLISV) phase. Furthermore, the magnetoelectric effect (ME) shows high sensitivity to multiple external stimuli such as temperature, carrier doping, hydrostatic pressure, magnetic field etc. In contrast to the well-known ME such as colossal magnetoresistance and multi-ferroic effect which involve symmetry breaking of crystal structure, the ME in the cobaltite is purely isostructural. Our discovery provides a new path way to realizing the ME as well as the NTE, which may find applications in new techniques.
 clusters in dilute neutron-rich matter
clusters in dilute neutron-rich matterTanaka, Junki*; Yang, Z.*; Typel, S.*; Adachi, Satoshi*; Bai, S.*; van Beek, P.*; Beaumel, D.*; Fujikawa, Yuki*; Han, J.*; Heil, S.*; et al.
Science, 371(6526), p.260 - 264, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:99.12(Multidisciplinary Sciences)By employing quasi-free  -cluster-knockout reactions, we obtained direct experimental evidence for the formation of
-cluster-knockout reactions, we obtained direct experimental evidence for the formation of  clusters at the surface of neutron-rich tin isotopes. The observed monotonous decrease of the reaction cross sections with increasing mass number, in excellent agreement with the theoretical prediction, implies a tight interplay between
clusters at the surface of neutron-rich tin isotopes. The observed monotonous decrease of the reaction cross sections with increasing mass number, in excellent agreement with the theoretical prediction, implies a tight interplay between  -cluster formation and the neutron skin.
-cluster formation and the neutron skin.
Dimitriou, P.*; Basunia, S*; Bernstein, L.*; Chen, J.*; Elekes, Z.*; Huang, X.*; Hurst, A.*; Iimura, Hideki; Jain, A. K.*; Kelley, J.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 239, p.15004_1 - 15004_4, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.1(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Evaluated Nuclear Structure Data File (ENSDF) includes the most extensive and comprehensive set of nuclear structure and decay data evaluations performed by the international network of Nuclear Structure and Decay Data evaluators (NSDD) under the auspices of the IAEA. In this report we describe some of the recent NSDD activities and provide future perspectives.
Naeem, M.*; He, H.*; Zhang, F.*; Huang, H.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Wang, B.*; Lan, S.*; Wu, Z.*; Wang, F.*; et al.
Science Advances (Internet), 6(13), p.eaax4002_1 - eaax4002_8, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:145 Percentile:99.09(Multidisciplinary Sciences) decay of
decay of 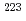 U
USun, M. D.*; Liu, Z.*; Huang, T. H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ding, B.*; Wang, J. G.*; Liu, X. Y.*; Lu, H. Y.*; Hou, D. S.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 800, p.135096_1 - 135096_5, 2020/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:79.42(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Tanaka, Taiki*; Narikiyo, Yoshihiro*; Morita, Kosuke*; Fujita, Kunihiro*; Kaji, Daiya*; Morimoto, Koji*; Yamaki, Sayaka*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Tanaka, Kengo*; Takeyama, Mirei*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 87(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_9, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:74.47(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Excitation functions of quasielastic scattering cross sections for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb,
Pb,  Ti +
Ti +  Pb, and
Pb, and  Ca +
Ca +  Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the
Cm reactions were successfully measured by using the gas-filled recoil-ion separator GARIS. Fusion barrier distributions were extracted from these data, and compared with the coupled-channels calculations. It was found that the peak energies of the barrier distributions for the  Ca +
Ca +  Pb and
Pb and  Ti +
Ti +  Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the
Pb systems coincide with those of the 2n evaporation channel cross sections for the systems, while that of the  Ca +
Ca +  Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.
Cm is located slightly below the 4n evaporation ones. This results provide us helpful information to predict the optimum beam energy to synthesize superheavy nuclei.