Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ichikawa, Kenta*; Kanda, Hironori; Yoshioka, Naoki*; Ara, Kuniaki; Saito, Junichi; Nagai, Keiichi
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2018/07
Studies on the suppression of the reactivity of sodium itself have been performed on the basis of the concept of suspended nanoparticles in liquid sodium (sodium nanofluid). According to the experimental and theoretical results of studies for sodium nanofluid, velocity and heat of sodium nanofluid-water reaction are lower than those of the pure sodium-water reaction. The analytical model for the peak temperature of a sodium nanofluid-water reaction jet has been developed in consideration of these suppression effects by the authors. In this paper, the prediction method for mitigation effects for a damage of adjacent tubes in a steam generator tube rupture (SGTR) accidents is arranged by applying this analytical model for the peak temperature of the reaction jet. On the assumption that the sodium nanofluid is used for the secondary coolant of sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), mitigation effects under the design-base accident (DBA) condition and the design-extension condition (DEC) of SGTR are estimated by using this method. As a result, there is a possibility to reduce the number of damaged tubes and to suppress the pressure generated by SGTR accidents by using sodium nanofluid in the secondary coolant.
Takei, Satoshi*; Oshima, Akihiro*; Ichikawa, Takumi*; Sekiguchi, Atsushi*; Kashiwakura, Miki*; Kozawa, Takahiro*; Tagawa, Seiichi*; Oyama, Tomoko; Ito, Shoji*; Miyasaka, Hiroshi*
Microelectronic Engineering, 122, p.70 - 76, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:76.82(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Biomass-derived branched sugar resist material was developed for environmentally-friendly electron beam lithography (EBL). The developed resist enables organic solvent-free water-developable process. The resist performance was evaluated using 75 keV EBL system. Lines of 50-200 nm were fabricated with high sensitivity of 7  C/cm
C/cm . The resist is developable in pure water at 23
. The resist is developable in pure water at 23  C for 60 s, and it has acceptable CF
C for 60 s, and it has acceptable CF etch selectivity.
etch selectivity.
 =20 shell in
=20 shell in 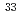 Al investigated through the ground-state electric quadrupole moment
Al investigated through the ground-state electric quadrupole momentShimada, Kenji*; Ueno, Hideki*; Neyens, G.*; Asahi, Koichiro*; Balabanski, D. L.*; Daugas, J. M.*; Depuydt, M.*; De Rydt, M.*; Gaudefroy, L.*; Gr vy, S.*; et al.
vy, S.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 714(2-5), p.246 - 250, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:41.35(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Takaya, Shigeru; Yamagata, Ichiro; Ichikawa, Shoichi; Nagae, Yuji; Wakai, Eiichi; Aoto, Kazumi
Hozengaku, 9(1), p.51 - 56, 2010/04
The remote operated vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) for neutron irradiated samples has been developed. The maximum range of applied magnetic field is more than  0.5/
0.5/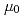 A/m, and the resolution of magnetization is higher than 5
A/m, and the resolution of magnetization is higher than 5 10
10 A
A m
m . The hysteresis loops of neutron irradiated samples were measured by this VSM, and the relationships between dose, which is one of representative irradiation parameter, and magnetic properties such as magnetic coercive force were examined. As result, it was revealed that there are good correlations between them. This fact shows the possibility of nondestructive evaluation of irradiation damage by using VSM.
. The hysteresis loops of neutron irradiated samples were measured by this VSM, and the relationships between dose, which is one of representative irradiation parameter, and magnetic properties such as magnetic coercive force were examined. As result, it was revealed that there are good correlations between them. This fact shows the possibility of nondestructive evaluation of irradiation damage by using VSM.
Matsui, Yoshinori; Takahashi, Hiroyuki; Yamamoto, Masaya; Nakata, Masahito; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Abe, Kazuyuki; Yoshikawa, Katsunori; Iwamatsu, Shigemi; Ishikawa, Kazuyoshi; Kikuchi, Taiji; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2009-072, 144 Pages, 2010/03
"R&D Project on Irradiation Damage Management Technology for Structural Materials of Long-life Nuclear Plant" was carried out from FY2006 in a fund of a trust enterprise of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology. The coupled irradiations or single irradiation by JOYO fast reactor and JRR-3 thermal reactor were performed for about two years. The irradiation specimens are very important materials to establish of "Evaluation of Irradiation Damage Indicator" in this research. For the acquisition of the examination specimens irradiated by the JOYO and JRR-3, we summarized about the overall plan, the work process and the results for the study to utilize these reactors and some facilities of hot laboratory (WASTEF, JMTR-HL, MMF and FMF) of the Oarai Research-and-Development Center and the Nuclear Science Research Institute in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency.
Kasai, Noboru; Seko, Noriaki; Tamada, Masao; Ichikawa, Eiichi*
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 46, 2007/02
no abstracts in English
Seko, Noriaki; Kasai, Noboru; Tamada, Masao; Ichikawa, Eiichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Seko, Noriaki; Kasai, Noboru; Hoshina, Hiroyuki*; Tamada, Masao; Ichikawa, Eiichi*
no journal, ,
Adsorption method is attractive to collect the metal from the seawater and the ground water without any slag from the viewpoint of security of metal resources and environmental preservation. In this method, the adsorbent needs the high selectivity and capacity for metal adsorption from the solution. We found that the rare metals such as a scandium were solved in the hot spring water. The temperature of hot spring water is feasible for metal adsorption by means of the graft adsorbent. Noble adsorbent is necessary for collecting the scandium from hot spring water since pH of the hot spring water is less than 2. We have synthesized a fibrous phosphoric adsorbent for recovery of scandium by using graft technique. The phosphoric adsorbent has high performance for scandium even in highly acidic condition when the phosphoric adsorbent was dipped into the 100ppb scandium solution it was found that 99% of scandium ions could be adsorbed within 2 hours. Removal of toxic metals from streaming water and the groundwater is also important task to preserve environment. Hot spring water contains toxic metals such as arsenic. The arsenic adsorbent was synthesized by loading zirconium on the phosphoric adsorbent. The resulting adsorbent had 100 times faster rate of arsenic adsorption than that of commercial resin. Furthermore, the zirconium loading phosphoric adsorbent could be adapted to the removal of arsenic from the hot spring water. This adsorbent adsorbed 1g-arsenic/kg-adsorbent for 1 week soaking in hot spring.
Takaya, Shigeru; Ichikawa, Shoichi; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Kato, Shoichi; Wakai, Eiichi; Aoto, Kazumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takaya, Shigeru; Nagae, Yuji; Aoto, Kazumi; Yamagata, Ichiro; Ichikawa, Shoichi; Konno, Shotaro; Ogawa, Ryuichiro; Wakai, Eiichi
no journal, ,
Magnetic flux densities for neutron irradiated specimens of austenitic stainless steels were measured by using a flux gate (FG) sensor to investigate the nondestructive evaluation method of irradiation damage parameters, dose and He content. The range of dose, He content and irradiation temperature of the neutron irradiated samples studied in this paper were 0.01-30 displacement per atom (dpa), 1.0-17 appm and 470-560  C, respectively. Magnetic flux density increased with dose although there may be a threshold dose for magnetic property to change between 2 and 5 dpa for 316FR. This result shows the possibility of nondestructive evaluation of dose by measuring magnetic flux density by an FG sensor. On the other hand, magnetic flux density did not depend on He content.
C, respectively. Magnetic flux density increased with dose although there may be a threshold dose for magnetic property to change between 2 and 5 dpa for 316FR. This result shows the possibility of nondestructive evaluation of dose by measuring magnetic flux density by an FG sensor. On the other hand, magnetic flux density did not depend on He content.
Takaya, Shigeru; Yamagata, Ichiro; Ichikawa, Shoichi; Nagae, Yuji; Wakai, Eiichi; Aoto, Kazumi
no journal, ,
The remote operated vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) for neutron irradiated samples has been developed. The maximum range of applied magnetic field is more than  0.5/
0.5/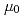 A/m, and the resolution of magnetization is higher than 5
A/m, and the resolution of magnetization is higher than 5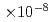 A
A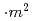 . The magnetization curves of neutron irradiated samples were measured by this VSM, and the relationships between dose, which is one of representative irradiation parameter, and magnetic properties such as magnetic coercive force. As result, it was revealed that there are good correlations between them. This fact leads the possibility of nondestructive evaluation of irradiation damage by using VSM.
. The magnetization curves of neutron irradiated samples were measured by this VSM, and the relationships between dose, which is one of representative irradiation parameter, and magnetic properties such as magnetic coercive force. As result, it was revealed that there are good correlations between them. This fact leads the possibility of nondestructive evaluation of irradiation damage by using VSM.